Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Connective and Epithelial MSHB
Connective and Epithelial MSHB
Uploaded by
P0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
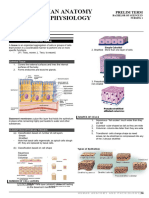
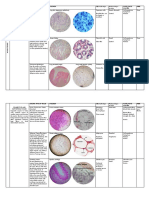
46 views6 pagesEpithelial tissue forms a continuous sheet of closely packed cells that lines body surfaces and cavities. There are two main types of epithelial tissue: membrane epithelium and glandular epithelium. Membrane epithelium covers surfaces and internal linings. Glandular epithelium is specialized to synthesize and secrete products and can be classified by cell type, number of cells, secretory products, and structure. Epithelial cells form strong intercellular junctions and polarize their functions towards the apical or basal surfaces.
Original Description:
Micro Anatomy Connective and Epithelial Tissues
Original Title
Connective and Epithelial Mshb
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEpithelial tissue forms a continuous sheet of closely packed cells that lines body surfaces and cavities. There are two main types of epithelial tissue: membrane epithelium and glandular epithelium. Membrane epithelium covers surfaces and internal linings. Glandular epithelium is specialized to synthesize and secrete products and can be classified by cell type, number of cells, secretory products, and structure. Epithelial cells form strong intercellular junctions and polarize their functions towards the apical or basal surfaces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views6 pagesConnective and Epithelial MSHB
Connective and Epithelial MSHB
Uploaded by
PEpithelial tissue forms a continuous sheet of closely packed cells that lines body surfaces and cavities. There are two main types of epithelial tissue: membrane epithelium and glandular epithelium. Membrane epithelium covers surfaces and internal linings. Glandular epithelium is specialized to synthesize and secrete products and can be classified by cell type, number of cells, secretory products, and structure. Epithelial cells form strong intercellular junctions and polarize their functions towards the apical or basal surfaces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Fundamental Types of CLASSIFICATION
Tissues FUNDAMENTAL TYPE – EPITHELIAL
Forms of Epithelial Tissues
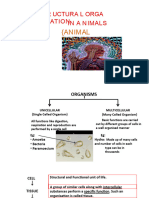
1. Epithelial Tissue
2. Connective Tissue
I. Membrane Epithelium
3. Muscular Tissue
- those lining the body surface cavities or
4. Nervous Tissue
coverings.
Acdg to Shape
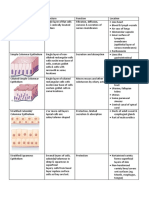
EPITHELIAL TISSUES Squamous
Cuboidal
COMPOSITION:
Columnar
A. EPITHELIAL CELLS
Acdg to Layer
B. EXTRA/INTERCELLULAR
Simple
SUBSTANCE Pseudostratified
Stratified
CHARACTERISTICS & Fx
Transitional
Consists of continuous sheet of closely
Acdg to Cell Surfae Specialization
adherent cells covering a large portion
of their surface. Cilia
Forms boundary layer that control Microvillus
movement o Brush Border
For absorption, secretion and ion o Straited Border
transport o Stereocilia
Lower most cells rest on continuous Keratin
thin supporting layer- BASAL LAMINA
Closely adherent
Arranged in layer/sheets Examples
AVASCULAR
CONTINUOUSLY RENEWED/REPLACED Simple Squamous- Mesothelium, Endothelium,
Parietal Layer of Bowman’s Capsule (MEP)
LITTLE INTERCELLULAR SPACE
Simple Cuboidal- Thyroid gland, DCT of
kidney,Rete Testis
Simple Cuboidal with Brush border- PCT
Simple Columnar- Gallbladder
Simple Columnar Striated Border- Ileum (SI)
Simple Columnar Ciliated- Fallopian tube,
Uterus
Pseudostratified columnar- vas deferens
Pseudostratified columnar with stereocilia- o Eccrine Sweat glands,Pancreatic
Epididymis Acinus
Apocrine- partial desctuction of the cell
Pseudostratified columnar with goblet cells-
o Mammary Gland/ apocrine of
trache and most of resp tract
axilla areas
Pseudostratified columnar without goblet cell- Holocrine- lysis of the cell
olfactory mucosa o Skin sebaceous glands
Stratified Squamous non keratinized- Oral Acdg to Structure of Multicellular Exocrine
cavity, Esophagus, Vagina Gland
Stratified Squamous Keratinized- Epidermis Tubular
o Simple Tubuluar- intestinal
Stratified Cuboidal- Pars Cavernosa
crypts of Lieberkuhn
Stratified Columnar- Penile Urethra Mammary o Simple Coiled Tubular- Eccrine
Gland sweat glands of skin
o Simple Branched Tubular-fundic
glands stomach
II. Glandular Epithelium o Compound Tubular- Liver testis
=- specialized to synthesize specific products.
Alveolar/Acine/Saccular
- contains extensive rough endoplasmic
o Simple Alveolar-Sebaceous
reticulum.
Gland
Classification o Simple Branched alveolar-
Sebaceous Gland
Acdg to # of Cells o Compound Alveolar- Mammary
Unicellular- single cell Goblet Cell Gland
Multicellular- many cell Salivary Gland Tubulo-alveolar/Mixed/Racemose
o Compound tubule-
Acdg to type of secretios alveolar/acinar- Salivary Glands
Purely Serous-parotid gland, von ebners EPITHELIAL POLARITY- cells polarized if its
Purely Mucous- goblet cells fuctions are preferentialy directed towards the
Mucoserous- submandibular-serous end
Sublingual mucous
-apical specializations that amplify the
Cytogenic- produce cells in testis
area of their free surface
Acdg to how they pour secretions Supranuclear position of the golgi
complex
Exocrine- has duct (Exocrine Pancreas)
Accumulation of secretory products on
Endocrine – ductless (Secretion in the
apical cytoplasm
blood) Insulin/Beta Cells and
Glucagon/A cells Cell Adhesions due to CADHERINS
Acdg to mode of secretions And by local specializations called Junctional
Complexes
Merocrine- exit glands by exocytosis
without loss of membrance
FORMS OF JUNCTIONAL COMPLEXES o Withstand blows exclusive for
stratified epithelium
ZONULA OCCLUDENS/TIGHT
JUNCTIONS- BASAL LAMINA- outer layer found beneath the
o Tight junction epithelia, formerly called basement membrane
o Occluding junctions
Made of 2 layers:
o Belt like specialization encircle
columnar cells Lamina Lucida (CIV)
o Selective permeable Barrier o Transparent and adjacent layer
between apical and basolateral o Made of large proteoglycan
Plasma membrance Lamina Densa(CVII)
o Occludin- protein at sites of o Meshwork of fine filaments
apparent fusion of opposing o Anchoring fibers of CVII loop
membranes around CI
ZONULA ADHERENS/INTERMEDIATE
JUNCTIONS CONNECTIVE TISSUE- mesodermal origin
o Intermediate Junction o Provides structural support
o Fascia Adherens o Metabolic support by creating a
o Encircle apical Portion below hydrophilic environment that
occludens mediates exchange of
o Crosslinks by Myosin,,Actin & substance and tissue
Vinculin
o Stabilize by connecting terminal Components
webs of adjoining cells o CT CELLS
o Cell to cell adhernce o CT Fibers (CER) – extracellular
MACULA ADHERENS/DESMOSOMES matrix
o Small,round on sides of o Ground Substance- extracellular
adjoining cells matrix
o Linkers bind membranes and
dense plaques Ground Substance
o Stabilize by linking cytoskeleton
a mixture of glycoproteins and complex
of adjoining cells
carbohydrates with profound water-
o Cell to cell attachment binding ability.
NEXUS/GAP JUNCTIONS Transparent and semi solid
o Low resistance ensuring Amorphous when stained with dyes
contractions Clear space when stained with H&E
o Has patch called CONNEXONS MAJOR COMPONENT IS GAGS
on each sides
o Cell to cell communication Other component is Proteoglycan (large) and
Glycoproteins – Hydrophillic
HEMIDESMOSOMES-
So allows diffusion of water soluble molecules
o anchor basal cells to basal but inhibits large macromolecules and bacteria
lamina.
Examples of GAGS o FIbrocyte- if quiescent
condensed
Hyaluronate – not bounded by core
o Synthesis of all components of
protein
extracellular matrix (CER
Chondroitin &GAG)
Keratin Adipose- arise from mesenchymal
Heparin o SIGNET RING IN APPEARANCE
Proteoglycan – adhesion proteins o Take up and store TG
Mesenchymal – round stellate
Types o PLURIPOTENT-MULTIPOTENT
Fibronectin- interconnect 3 components Reticular- produce reticular fibers
of CT o Stellate with thin cytoplasmic
Integrins- binds collagen fibers directly process
Laminins- binding site for cell o Phagocytose antigenic materials
membrane (copolymerize with type IV FREE/WANDERING
collagen and entactin to form Basal
Lamina) 1 .Macrophage- aka Tissue Histocyte
Collagen are 28 types o Derived from blood monocyte
o ANTIGEN Presentor part of MPS
5 common:
Different names
Collagen I: skin, tendon, vascular
ligature, organs, bone (main o Monocyte- Blood
component of the organic part bone) o Macrophage- Connective Tissue
Collagen II: CARTILAGE (main o Kupffer Cells- Liver
component of cartilage) o Microglia- Nerve Tissue
o Langerhan- Skin
Collagen III: reticulate (main component
o Dendritic- Lymph node
of reticular fibers), commonly found
o Osteoclast- Bones
alongside type I
Collagen IV: forms basal lamina, the
epithelium-secreted layer of the 2. Leukocyte (WBC) the transient cells of CT
basement membrane.
Collagen V: cell surfaces, hair and -migrate thru diapedesis
placenta NON GRANULAR
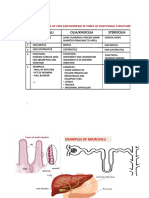
CONNECTIVE TISSUE CELLS o LYMPHOCYTE- bean shaped associated
with immunosurveillane
Acdg origin and function
o MONOCYTE- part of MPS transform to
FIXED CELLS Macrophages once in the tissue
Fibroblast- principal cells CT GRANULAR
o Fusiform on both ends
o NEUTROPHIL(POLYMORPHS) 3-5 lobes
o flat stellate. Nuclei is ovoid
o Most abundant in infection
o Fibroblast- if active fine
chromatin
o
Receptor for endothelial o 5-10 have restricted distributions
adhesion molecule 1
Elastic Fibers
o EOSINOPHIL- bilobed
o Antiparasitic o They are composed of two proteins,
o Allergic rxn fx elastin and fibrillin,
o Contain peroxidase, acid o do not have a banding pattern.
phosphatase, o Desmosine and isodesmosine are A.A of
cathepsin,ribonuclease and these fibers
arginine rich which is o These fibers are primarily produced by
antiparasitic the fibroblasts but can also be
produced by smooth muscle cells and
o Releases aryl sulfatases and
chondrocytes of large arteries
histaminase
o Seen as internal elastic lamina
o BASOPHILS- 3 lobed S shape
o Similar to mast cells Reticular Fibers- support parenchyma of many
inflammatory rxn organs
o Limited amoeboid movement o Argyrophilic
o Most abundant in
3.Plasma Cell- derived from B lymphocyte
hemopoetic,lymphoid and
o Oval shape, Cart-wheel appearance hollow organs
o Secretes antibodies that are antigen o Produced by TYPE 3 collagen
specific
CONNECTIVE TISSUE SUBTYPES
4.Mast Cell
1.EMBRYONIC
o Intensely Basophillic
MESENCHYMAL TISSUE- pluripotent
o Associated with IGE
found in developing embryo.
hypersensitivity reactions
o Contains In adults found in bone marrow
heparin,histamine,tryptase,chy (adventitial cells)
mase
MUCOUS TISSUE- protects stuctures
Connective Tissue Fibers from pressure. Wharton’s Jelly (umbilical cord)
1. Collagenous fibers – pink and wavy H&E 2. Connective tissue proper
2. Elastic glassy- red H&E Collagenous
Loose Collagenous
3. Reticular
Areolar tissue
Collagen Fibers Areas in less resistance
is required
o are the most common and abundant
Small moderately
fibers in connective tissue
o composed primarily of type I collagen. abundant and loosely
o Made of tropocollagen which is a interwoven
product of the fibroblast. Found in:
o Type I II III collagens are most common Lamina Propia stomach
o 1-3 are interstitial collagen Pia mater
EndonEndomy
Caps of Thymus 6. Adipose
Papillary dermis
Dense Irregular- coarse and o Adipose Tissue
very abundant with random White Adipose Tissue-white to
orientation yellow depending on the amount
Found in: ofcarotenoids; insulators
Epimysium unilocular
Epineurium Leptin-controls appetite
All caps exc thymus center in the brain
Reticular Dermis o Influence carb and
Dense Regular-fibers are closely lipid metabolism
packed o Promote growth of
Found in: cappilaries and
F.L.A.T stimulate immune
system for
THERMOGENIN-protein malnourished animals
that converts chemical Resistin- cause increase
energy to heat energy resistance in insulin
3. Specialize Connective tissue Brown Adipose Tissue
1. Bones multilocular
2. Cartilages Colors is rich due to
3. Blood and Lymph cytochrome
4. Lymphatics Energy reserce but no
insulating factor
5. Reticular Tissue- made of Type 3 Babies rely on this for
collagen (bone marrow)(liver) heat generation
(endorcrine) Abundant in animas that
hibernate
is a specialized loose connective tissue that
contains a network of branched reticular fibers,
reticulocytes (specialized fibroblasts), 7. Elastic tissue- found in
macrophages, and parenchymal cells, such as Elastic membrance medium
pancreatic cells and hepatocytes. sized artery
provides the architectural framework for Tunica media of aorta
parenchymal organs, such as lymphoid nodes,
spleen, liver, bone marrow, and endocrine
glands
You might also like
- Water MucilagesDocument11 pagesWater MucilagesPNo ratings yet
- 07-Cell Cycle Virtual Lab Handout SolutionsDocument4 pages07-Cell Cycle Virtual Lab Handout Solutionschuckly100% (2)
- L2 EpitheliumDocument4 pagesL2 EpitheliumGlysa MaeNo ratings yet
- Histo 1 PDFDocument14 pagesHisto 1 PDFSamantha Cruz BlancoNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023Document5 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023VERONICA ROSE MAGPOCNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument7 pagesConnective TissueSaif AliNo ratings yet
- Human Tissues Structure, Function and LococationDocument4 pagesHuman Tissues Structure, Function and Lococationxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TissueDocument7 pagesChapter 4 TissueVince De PanoNo ratings yet
- Tissues UnfinishedDocument5 pagesTissues UnfinishedPessimus KidNo ratings yet
- Apr 1Document9 pagesApr 1KEISHA CZARELLE POBRENo ratings yet
- Basic HistologyDocument2 pagesBasic HistologyAngel DumalagNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: Dr. Lalit MehraDocument39 pagesEpithelium: Dr. Lalit Mehramus zaharaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 TRANS AnaphyDocument8 pagesWEEK 4 TRANS AnaphygazzyngsalvadorNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument2 pagesAnimal TissuesMami AmihanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Tissues, Part 1: Tissue A Collection of Cells That Perform RelatedDocument23 pagesChapter 4: Tissues, Part 1: Tissue A Collection of Cells That Perform RelatedSajid NadafNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals Mind MapDocument3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals Mind MapAstha Agrawal75% (4)
- Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumDocument18 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumKamal Hameed Al-taiyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 2 The Epithelial TissueDocument3 pagesLaboratory 2 The Epithelial TissueJoshtwotown EarnshawNo ratings yet
- Forms and Characteristics of Epithelial Cells: Basement MembranesDocument5 pagesForms and Characteristics of Epithelial Cells: Basement MembranesA18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- Histology EpitheliumsDocument4 pagesHistology EpitheliumsNORHANA PHARINo ratings yet
- Epithelial: Type of Tissue CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesEpithelial: Type of Tissue CharacteristicsGlanela ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Echinoderm at ADocument27 pagesEchinoderm at AdidaagunalaysaNo ratings yet
- Epithelia & Glands: Dr. Madhan KumarDocument49 pagesEpithelia & Glands: Dr. Madhan KumarTan DesmondNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Blok 18Document236 pagesPraktikum Blok 18Sherly MydoNo ratings yet
- Epithelia N Connective FunctionsDocument2 pagesEpithelia N Connective Functionsmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Epithelial-Cells 2Document5 pagesEpithelial-Cells 2Edeilaine JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Tissues: DR - Tooba Rehan Pharm-DDocument42 pagesTissues: DR - Tooba Rehan Pharm-DShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Zoology by Harsh KaushikDocument136 pagesZoology by Harsh KaushikSamarth KhatorNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument8 pagesCell TypesMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- Jaringan Dasar 1 BDocument20 pagesJaringan Dasar 1 BJIHAN ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Tissues Pre LabDocument43 pagesTissues Pre LabCindy-chan DelfinNo ratings yet
- Zygote Embryo: TissuesDocument3 pagesZygote Embryo: TissuesChelsea NacinoNo ratings yet
- 5th Learning Check (Anaphy)Document2 pages5th Learning Check (Anaphy)Carl Warren RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 19 JulyDocument39 pages19 JulySubhash YadavNo ratings yet
- Epithelium Tissue Q&ADocument5 pagesEpithelium Tissue Q&ANo NameNo ratings yet
- Histology Nutshell - Notespaedia Elite NotesDocument28 pagesHistology Nutshell - Notespaedia Elite NotesShyamPrashadNo ratings yet
- The Tissues of The Body - The Epithelium: DR Iram IqbalDocument144 pagesThe Tissues of The Body - The Epithelium: DR Iram Iqbalimmmi100% (1)
- 07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterDocument12 pages07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterexercisestartNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumDocument22 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumMahmoud IdlbiNo ratings yet
- 1 EpithelialTissueWEBDocument27 pages1 EpithelialTissueWEBJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- Simple and Stratified EpitheliumDocument24 pagesSimple and Stratified EpitheliumAltaf HussainNo ratings yet
- Histology Table ReviewerDocument4 pagesHistology Table ReviewerDaNicaRaylaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 TissuesDocument15 pagesWEEK 4 TissuesMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument13 pagesHistologyangelo davidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Image-Forming EyeDocument23 pagesAnatomy of The Image-Forming EyekupukupuNo ratings yet
- Module # Epitheleal TransDocument5 pagesModule # Epitheleal TransLara VanessNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument6 pagesEpithelial TissueHM ChuaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesLesson 2 TissuesRodefe AmitNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024Document3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024thakur.shrish.singhNo ratings yet
- Fit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesDocument3 pagesFit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesCaithlyn KirthleyNo ratings yet
- Type of Epithelium CellDocument3 pagesType of Epithelium CellHo Shi XianNo ratings yet
- Os 201 Histo Lab CellsDocument33 pagesOs 201 Histo Lab CellsJoyce TLeeNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY 1 2022 Materials Part 3Document29 pagesHISTOLOGY 1 2022 Materials Part 3Mutahir AliNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument40 pagesEpithelial TissueTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- 04 EpitheliumDocument39 pages04 EpitheliumMartha Orendu Oche AttahNo ratings yet
- T I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueDocument6 pagesT I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueMarla TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tissues: Microscopic Human Structural BiologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Tissues: Microscopic Human Structural BiologyKeith Arleigh JosonNo ratings yet
- The Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan KianiDocument74 pagesThe Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan Kianiviya7No ratings yet
- Animal Tissue SLDocument181 pagesAnimal Tissue SLkrhimkrNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Low-FODMAP Diet: Definition/IntroductionDocument2 pagesLow-FODMAP Diet: Definition/IntroductionPNo ratings yet
- Carbon 60 Sp2 OrbitalDocument4 pagesCarbon 60 Sp2 OrbitalPNo ratings yet
- 10 Most Common Diseases: InfantDocument6 pages10 Most Common Diseases: InfantPNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Agonist and Antagonist 23Document12 pagesSympathetic Agonist and Antagonist 23PNo ratings yet
- Emulsions ExtractivesDocument9 pagesEmulsions ExtractivesPNo ratings yet
- Adr Manor NotesDocument7 pagesAdr Manor NotesPNo ratings yet
- Ward Quiz 1 Musculoskeletal PDFDocument3 pagesWard Quiz 1 Musculoskeletal PDFPNo ratings yet
- Module 6.2 AntibioticsDocument6 pagesModule 6.2 AntibioticsPNo ratings yet
- Module 6.4 ParasitesDocument6 pagesModule 6.4 ParasitesPNo ratings yet
- Ceutics 1Document2 pagesCeutics 1PNo ratings yet
- AkapulkoDocument2 pagesAkapulkoPNo ratings yet
- Module 6.2 AntibioticsDocument6 pagesModule 6.2 AntibioticsPNo ratings yet
- Module 6.5 MycologyDocument4 pagesModule 6.5 MycologyPNo ratings yet
- Module 6.1 MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesModule 6.1 MicrobiologyPNo ratings yet
- Prelim Quiz 1 - Attempt ReviewDocument5 pagesPrelim Quiz 1 - Attempt ReviewAshnesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Kejang MioklonikDocument26 pagesKejang MioklonikDhamara AdhityaNo ratings yet
- TPR Sheet - Bito-OnDocument2 pagesTPR Sheet - Bito-OnBryle James Bito-on100% (1)
- RiversideDocument58 pagesRiversideMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IINo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISDocument22 pagesCHOLECYSTOLITHIASISMc N Mi KabilingNo ratings yet
- Zoo Lab Frog ActivityDocument12 pagesZoo Lab Frog ActivityAdznaira AmilussinNo ratings yet
- Kasus Non Spesialitik (KNS)Document4 pagesKasus Non Spesialitik (KNS)Ken DadangNo ratings yet
- Cancer Care 2023 06 28Document146 pagesCancer Care 2023 06 28oglasi oglasiNo ratings yet
- The British Journal of Cardiology May-June 2010, Volume 17 Supplement 2Document16 pagesThe British Journal of Cardiology May-June 2010, Volume 17 Supplement 2mbarrales_4No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Pain (Unit 4)Document28 pagesLesson Plan - Pain (Unit 4)Jincy JohnyNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Unit 2, Topic 1Document24 pagesHomeostasis: Unit 2, Topic 1qwertNo ratings yet
- Contrast-Induced Nephropathy Following Angiography and Cardiac InterventionsDocument11 pagesContrast-Induced Nephropathy Following Angiography and Cardiac InterventionsReioctabianoNo ratings yet
- Mesh No00Document12 pagesMesh No00novanoktawNo ratings yet
- Program Schdule2021 - FinalDocument4 pagesProgram Schdule2021 - FinalishupandiNo ratings yet
- John Chitty - The TRIUNE Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesJohn Chitty - The TRIUNE Autonomic Nervous SystemadamiamNo ratings yet
- Isometric Power Revolution Part2Document86 pagesIsometric Power Revolution Part2Smriti Ichopra100% (15)
- Peterson Et Al, 2004Document6 pagesPeterson Et Al, 2004Bernardo Ravanello da CostaNo ratings yet
- Genetics of The Ebony Body MutantDocument3 pagesGenetics of The Ebony Body MutantDaniela Seczon0% (1)
- HemofagocitoseDocument9 pagesHemofagocitoseThais BenevidesNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Gingival Form Following Implant PlacementDocument4 pagesMaintenance of Gingival Form Following Implant PlacementRomina BitaNo ratings yet
- Iea MSKDocument48 pagesIea MSKAlex WalshNo ratings yet
- 02 Cell PhysiologyDocument28 pages02 Cell PhysiologyZaw Lin TheinNo ratings yet
- Combination Syndrome !: By: DR - Pawanjeet Singh Chawla Rama Dental College, Hospital, Kanpur Guided byDocument26 pagesCombination Syndrome !: By: DR - Pawanjeet Singh Chawla Rama Dental College, Hospital, Kanpur Guided byDrShweta SainiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis ListDocument17 pagesNursing Diagnosis ListShelby SheppardNo ratings yet
- Demystifying The Diagnosis and Classification of Lymphoma - Gabriel C. Caponetti, Adam BaggDocument6 pagesDemystifying The Diagnosis and Classification of Lymphoma - Gabriel C. Caponetti, Adam BaggEddie CaptainNo ratings yet
- Solomon cb09 PPT 02Document32 pagesSolomon cb09 PPT 02kambar123No ratings yet
- Neuroimage: Conghui Su, Hui Zhou, Liangyu Gong, Binyu Teng, Fengji Geng, Yuzheng HuDocument11 pagesNeuroimage: Conghui Su, Hui Zhou, Liangyu Gong, Binyu Teng, Fengji Geng, Yuzheng HuGînțăgan Denisa GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Zoology Practical Exam Tips 2024Document62 pagesZoology Practical Exam Tips 2024sureshsooraj426No ratings yet
- Psych Final Exam ReviewerDocument49 pagesPsych Final Exam ReviewerDAVID BAYANI AGCAOILINo ratings yet