Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geologic Time: Earth'S Historical Past Divisons and Summary of Events
Geologic Time: Earth'S Historical Past Divisons and Summary of Events
Uploaded by
Katrina SooOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geologic Time: Earth'S Historical Past Divisons and Summary of Events
Geologic Time: Earth'S Historical Past Divisons and Summary of Events
Uploaded by
Katrina SooCopyright:
Available Formats
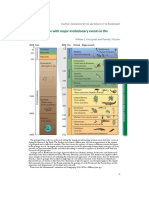
GEOLOGIC TIME: EARTH’S HISTORICAL PAST
DIVISONS AND SUMMARY OF EVENTS
Accretion (planetesimal to protoplanet)
Earth collided with a Mars-sized object; debris
formed the moon
Chemical differentiation established Earth’s three
major layers (primitive crust, mantle and core)
Archean Eon Outgassing produced primitive atmosphere
First unicellular organisms
Precambrian Eon
Cyanobacteria released oxygen into the oceans as a
by-product of photosynthesis
Formation of continental crust
Oxygen molecules accumulated in the atmosphere,
then rearranged themselves to form ozone
protecting Earth’s surface from solar radiation
Proterozoic Eon First multicellular organisms
Supercontinent Rodinia formed, then dispersed into
separate landmasses, and later reassembled into
Gondwana plus other continental fragments
Cambrian explosion
(huge expansion in biodiversity)
Invertebrates”
Cambrian Period
Emergence of major invertebrate groups
“Age of
Golden age of trilobites
Appearance of cephalopods
Ordovician Period Fishes perfected their internal skeleton
and were the first creatures to have jaws
First, tiny, leafless, spiky, upright land plants
Paleozoic Era
Silurian Period
about the size of a human index finger
“Age of
Fishes”
Fishes flourished
Devonian Period First amphibians
First tree-sized land plants
Amphibians were dominant
Extensive forests that would later become coal
Amphibians”
Carboniferous Mississippian
Phanerozoic Eon
beds
“Age of
Period
Highest levels of atmospheric oxygen
Pennsylvanian Continents collided to form Pangaea
Great Permian extinction wiped out 70% of land-
Permian Period
dwelling vertebrates and 90% of marine life
Pangaea began to rift
Much of the world’s continents were above sea
level, exposing Triassic strata
Archosaurs and Therapsids were the dominant
Triassic Period terrestrial vertebrates
“Age of Reptiles”
Triassic-Jurassic extinction event wiped out 34% of
Mesozoic Era
marine species, made many of the large amphibians
extinct, and allowed dinosaurs to assume
dominance
Dinosaurs dominated
Jurassic Period Pangaea separated into Laurasia and Gondwana
First known bird (Archaeopteryx)
Relatively warm climate
Cretaceous Period Appearance of new groups of mammals,
angiosperms, insects and birds
STEM-Lecture Notes in Earth Science
Completion of Pangaea’s breakup into present-day
continents (with positions very different from their
current locations)
Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event wiped out
the dinosaurs but opened habitats for mammals
Mammals branched out into marsupial and
placental mammals
Expansion of grasslands
Paleocene Separation of Australia from South America
resulting in diversified evolutionary processes
Epoch
Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum
Temperatures rose by 8° C
Water transferred to near the poles
Increased precipitation
Warm temperatures and moist environment
Thriving forests throughout the planet
Paleogene Period Continued diversification and abundance of
mammals
Eocene
Epoch Eocene-Oligocene extinction event or Grande
Coupre wherein atmospheric carbon dioxide
decreased, resulting in decreased global
temperatures, which led to the formation of ice
sheets on the poles
Extensive grasslands
“Age of Mammals”
Temperature deciduous forests replaced tropical
Cenozoic Era
Oligocene and subtropical forests
Epoch Antarctica developed an ice cap due to the
Antarctic circumpolar current keeping warm ocean
waters away from the continent’s ice sheets
Apes diversified; split evolutionary path
Kelp forest and grassland biomes formed
Miocene Middle Miocene Climate Transition or Middle
Epoch Miocene extinction (peak) wiped out terrestrial and
aquatic life forms
First hominins appeared
Neogene Period
First recognizable hominid appeared
Continued drifting of the continents
Pliocene Sea levels changed; oceans continued cooling
Epoch Mild latitude glaciation occurred
Grasslands spread across all continents
Deserts formed in some areas
Continued tectonic activity and volcanism
Pleistocene Widespread glaciation
Epoch
Quaternary Lowered sea levels and cooler climates
Period Evolution of human lineage (genus Homo)
Holocene Civilizations and transition toward urban living
Epoch (continues to the present)
STEM-Lecture Notes in Earth Science
You might also like
- GENBIO2 MOD3 Howlifebeganonearth Forfinalcheck.Document26 pagesGENBIO2 MOD3 Howlifebeganonearth Forfinalcheck.Kris LaglivaNo ratings yet
- Bio2 RRCDocument7 pagesBio2 RRCRodel CalmaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Pre Lim PDFDocument8 pagesGen Bio 2 Pre Lim PDFMark CagasNo ratings yet
- EON and ERADocument3 pagesEON and ERAJanah JanahNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time An IntroductionDocument28 pagesGeologic Time An IntroductionIan Jay AntipuestoNo ratings yet
- Geological TS ModuleDocument20 pagesGeological TS ModuleSandara AsinguaNo ratings yet
- GenBio 2Document17 pagesGenBio 2hernandezlovenson65No ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument1 pageGeologic Time Scaleanon_114803412No ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Week 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Week 2Danikyl Villamonte LukbanNo ratings yet
- NP - General Biology 2 11 & 12 - Q3 - W2 BDocument9 pagesNP - General Biology 2 11 & 12 - Q3 - W2 BIrrah Sheene De VegaNo ratings yet
- Description Life: Eon Era Period Epoch Age YearDocument1 pageDescription Life: Eon Era Period Epoch Age YearsubhaNo ratings yet
- History of The EarthDocument7 pagesHistory of The EarthMary JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Maktesh Ramon CraterDocument1 pageMaktesh Ramon CraterSt. Giuseppe MoscatiNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Geologic Time: Mesozoic Era (252 To 66 Million Years Cenozoic Era (66 Million Years AgoDocument1 pageTimeline of Geologic Time: Mesozoic Era (252 To 66 Million Years Cenozoic Era (66 Million Years AgoRenz TacastacasNo ratings yet
- GenBio2 - Geologic Time ScaleDocument6 pagesGenBio2 - Geologic Time Scalesalabsabhga0529No ratings yet
- Fossils & Geologic TimeDocument32 pagesFossils & Geologic TimeYolanda Jane PagtamaanNo ratings yet
- Bio ReportingDocument3 pagesBio ReportingJessica ApolonioNo ratings yet
- 158 EarthandLifeSci12 Q1 Mod6 Geologic Time Scale and Geohazards v3Document16 pages158 EarthandLifeSci12 Q1 Mod6 Geologic Time Scale and Geohazards v3Sweet MintNo ratings yet
- Geological Time With Major Evolutionary Events in The Fossil RecordDocument1 pageGeological Time With Major Evolutionary Events in The Fossil RecordMubarun100% (1)
- ESCI - TimelineDocument3 pagesESCI - TimelineVicki Punzalan100% (1)
- Earth History and Geologic TimeDocument1 pageEarth History and Geologic TimeRemil CastañedaNo ratings yet
- History of Life On Earth 1Document66 pagesHistory of Life On Earth 1Bukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- Geological_Time_ScaleDocument1 pageGeological_Time_ScaleAnkesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Geologic TimeDocument32 pagesGeologic TimeAxel Jhon CaterNo ratings yet
- 3rd QUARTER REVIEWERDocument6 pages3rd QUARTER REVIEWERlorieferpaloganNo ratings yet
- Historia Del TiempoDocument11 pagesHistoria Del TiempoMireia LongNo ratings yet
- Escie W7 8Document3 pagesEscie W7 8Angel CheungNo ratings yet
- Geo - CH-2Document42 pagesGeo - CH-2mbambuNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 Lesson 2Document5 pagesBio 2 Lesson 2rharpienNo ratings yet
- Actividad Grupal No. 1Document5 pagesActividad Grupal No. 1KGAMER47 KGamer47No ratings yet
- THE Earth: MYA MYA Precambrean EonDocument1 pageTHE Earth: MYA MYA Precambrean EonMigolits DalanginNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Quarter 3: Week 2 - Module 2: Evolution and Origin of BiodiversityDocument24 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Quarter 3: Week 2 - Module 2: Evolution and Origin of Biodiversitycristina maquinto0% (1)
- THE-CENOZOIC-ERA SchoolDocument4 pagesTHE-CENOZOIC-ERA SchooljungcolemerjerihNo ratings yet
- GENBIO2Document16 pagesGENBIO2Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Description Life: Eo N Era Period Epoch Age YearDocument1 pageDescription Life: Eo N Era Period Epoch Age YearsubhaNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 Lesson 2Document7 pagesBio 2 Lesson 2rharpienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Canada's Geological HistoryDocument8 pagesChapter 11 - Canada's Geological HistoryRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- GTSDocument14 pagesGTSMariel LolincoNo ratings yet
- ELS Geologic Time DLLDocument84 pagesELS Geologic Time DLLLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- Geo Assignment No.1Document2 pagesGeo Assignment No.1Angelika HernandezNo ratings yet
- Time ScaleDocument2 pagesTime ScaleKitty AlipioNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument2 pagesGeologic Time ScaleJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- BIO 140 Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesBIO 140 Lecture NotesChristian Anthony DonosoNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument51 pagesGeologic Time ScaleLance Francis DanielesNo ratings yet
- History of The EarthDocument2 pagesHistory of The Earthsara.gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument3 pagesGeologic Time ScaleJohn Andrae MangloNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument22 pagesGeologic Time ScaleJuby Ann EnconadoNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Life On EarthDocument3 pagesA Brief History of Life On EarthJohn Lloyd EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio PosterDocument3 pagesGen Bio PosterJasmin MateoNo ratings yet
- Geo TimeDocument25 pagesGeo TimeClint DuglasNo ratings yet
- Part II - Chapter 1 - GME I @2022Document58 pagesPart II - Chapter 1 - GME I @2022Temesgen SilabatNo ratings yet
- Factsheets of Earth ScienceDocument7 pagesFactsheets of Earth ScienceBok ManNo ratings yet
- Earth HistoryDocument3 pagesEarth HistoryRicarla Faith TuyacNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time and Earth's Biological HistoryDocument32 pagesGeologic Time and Earth's Biological HistoryJoyae ChavezNo ratings yet
- Geological Time Scale: Index Fossils Are Remains That Represent Short Lived Species That Only AppearDocument5 pagesGeological Time Scale: Index Fossils Are Remains That Represent Short Lived Species That Only AppearMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Geological TimescaleDocument3 pagesGeological TimescaleyxrizipNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Origin and Evolution of Life Prior To The Appearance of Human BeingsDocument2 pages1.4 Origin and Evolution of Life Prior To The Appearance of Human BeingsHema Mani Kiran PathuriNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument2 pagesGeologic Time ScalemarkarlofriasNo ratings yet
- FINALS ELS Made Easy 1Document9 pagesFINALS ELS Made Easy 1Argueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- History of LifeDocument17 pagesHistory of LifeKienth Vincent LopeñaNo ratings yet
- Mesozoic PeriodDocument3 pagesMesozoic PeriodLeonardoNo ratings yet
- Phanerozoic EON: Consist of 3 Eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and CenozoicDocument17 pagesPhanerozoic EON: Consist of 3 Eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and CenozoicSamantha BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciences Week 6Document49 pagesEarth and Life Sciences Week 6syrine mendozaNo ratings yet
- Tunisian Stratigraphic ChartDocument1 pageTunisian Stratigraphic ChartKhaled Ben Rached100% (4)
- Chrono Strat Chart 2012Document1 pageChrono Strat Chart 2012car28morNo ratings yet
- Kutai Basin Stratigraphy ColumnDocument1 pageKutai Basin Stratigraphy ColumnAkarius MagersNo ratings yet
- Escala de Tiempo Geologico 2009 - INTERNATIONAL STRATIGRAPHIC CHART 2009Document1 pageEscala de Tiempo Geologico 2009 - INTERNATIONAL STRATIGRAPHIC CHART 2009edwardNo ratings yet
- GSSP of All Periods Table 2013Document14 pagesGSSP of All Periods Table 2013Galaxad GarcíaNo ratings yet
- IndexfossilsDocument27 pagesIndexfossilsかな どなりNo ratings yet
- Kiessling Et Al., 2003 Pattern of Phanerozoic Carbonate PlatformDocument31 pagesKiessling Et Al., 2003 Pattern of Phanerozoic Carbonate PlatformsofienehaddadNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity - WikipediaDocument278 pagesBiodiversity - WikipediaSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- PDF PanderDocument53 pagesPDF PanderKhadija RvNo ratings yet
- Bio2 11 - 12 Q3 0301 PF FDDocument40 pagesBio2 11 - 12 Q3 0301 PF FDdanarturo18No ratings yet
- ELS Final Module 14 08082020Document26 pagesELS Final Module 14 08082020strawberryNo ratings yet
- Mapa Geologico HuacaretaDocument1 pageMapa Geologico Huacaretavanesa100% (1)
- Stratigraphy of PakistanDocument4 pagesStratigraphy of Pakistanbilal afzalNo ratings yet
- 02192022093949GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 - Third Quarter-Module 3Document6 pages02192022093949GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 - Third Quarter-Module 3ejNo ratings yet
- The Paleozoic Era Diversification of Plant and Animal Life (J.P. Rafferty 2011)Document341 pagesThe Paleozoic Era Diversification of Plant and Animal Life (J.P. Rafferty 2011)Fabian Martinez100% (9)
- DinosaursDocument2 pagesDinosaursDerdy JanliNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Quarter 3-Module 2: History of Life On EarthDocument21 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 3-Module 2: History of Life On EarthJohn Michael RomarezNo ratings yet
- ELSCIDocument11 pagesELSCIMeyenNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Word - Foundation5Document73 pagesCritical Thinking Word - Foundation5Saraswati Learning Center SLCNo ratings yet
- Chronostrat Scale EuropeDocument2 pagesChronostrat Scale EuropeIonut Stiuj100% (2)
- ChronostratChart2017 02NLDutchDocument1 pageChronostratChart2017 02NLDutchDafne Ramírez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument2 pagesGeologic Time ScaleAngela Pearl AngelesNo ratings yet
- Trinidad FormationsDocument3 pagesTrinidad FormationsZephrine T MillardNo ratings yet
- Mapa Geologico TrujilloDocument1 pageMapa Geologico TrujilloḌēniyalPānsNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphic Column For Gulf of Suez, Western Desert and Nile Delta, Egypt-M.M.badawyDocument1 pageStratigraphic Column For Gulf of Suez, Western Desert and Nile Delta, Egypt-M.M.badawyOmarMokhtarZayed100% (1)
- Geologic Time Worksheet - ANSWERSDocument2 pagesGeologic Time Worksheet - ANSWERSOG Dreadful Official100% (1)