Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Objective Theory: Darcy's Law in Petroleum Engineering
Objective Theory: Darcy's Law in Petroleum Engineering
Uploaded by
tariq khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document discusses measuring permeability using a gas permeameter. It defines permeability as the ability of a formation to transmit fluids, measured in darcys or millidarcys. Darcy's law is used to determine flow through permeable media based on permeability, cross-sectional area, fluid viscosity, and pressure change over length. The experiment involves forcing a fluid through a core sample of known length and area and measuring the pressure drop to calculate permeability.
Original Description:
permeability
Original Title
Permeability Measurement
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses measuring permeability using a gas permeameter. It defines permeability as the ability of a formation to transmit fluids, measured in darcys or millidarcys. Darcy's law is used to determine flow through permeable media based on permeability, cross-sectional area, fluid viscosity, and pressure change over length. The experiment involves forcing a fluid through a core sample of known length and area and measuring the pressure drop to calculate permeability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesObjective Theory: Darcy's Law in Petroleum Engineering
Objective Theory: Darcy's Law in Petroleum Engineering
Uploaded by
tariq khanThis document discusses measuring permeability using a gas permeameter. It defines permeability as the ability of a formation to transmit fluids, measured in darcys or millidarcys. Darcy's law is used to determine flow through permeable media based on permeability, cross-sectional area, fluid viscosity, and pressure change over length. The experiment involves forcing a fluid through a core sample of known length and area and measuring the pressure drop to calculate permeability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
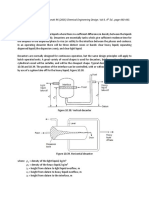
Objective
To measure the permeability of given core sample using Gas Permeameter
Theory
Permeability Measurement
The ability of a formation to transmit fluids is termed permeability; its unit is
the darcy (µm2). This unit has been subdivided into 1000 smaller units,
called millidarcies, and these units are used in reporting core analysis
measured values. A darcy has been defined as that permeability which
permits a fluid of one centipoise viscosity to flow at a rate of one cubic
centimeter per second through a porous medium with a cross-sectional area
of one square centimeter under a pressure gradient of one atmosphere per
centimeter. Its value is determined in the laboratory.
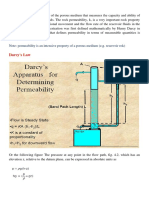
Darcy's law in petroleum engineering[edit]
Another derivation of Darcy's law is used extensively in petroleum engineering to
determine the flow through permeable media — the most simple of which is for a
one-dimensional, homogeneous rock formation with a single fluid phase and
constant fluid viscosity.
where Q is the flowrate of the formation (in units of volume per unit
time), k is the permeability of the formation (typically in millidarcys), A is
the cross-sectional area of the formation, μ is the viscosity of the fluid
(typically in units of centipoise). ∂p/∂x represents the pressure change per
unit length of the formation. This equation can also be solved for
permeability and is used to measure it, forcing a fluid of known viscosity
through a core of a known length and area, and measuring the pressure drop
across the length of the core.
You might also like
- Lab 2 Determing Fluid Velocity and Discharge Coefficient-Converted NewwwDocument11 pagesLab 2 Determing Fluid Velocity and Discharge Coefficient-Converted Newwwkashvin rajNo ratings yet
- Objective Theory: Darcy's Law in Petroleum EngineeringDocument2 pagesObjective Theory: Darcy's Law in Petroleum EngineeringShehzad khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 3 PDFMohd Khalid AnsariNo ratings yet
- TL2 - DecanterDocument3 pagesTL2 - DecanterAfif RuzainiNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law: BackgroundDocument10 pagesDarcy's Law: BackgroundJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Group 5.0Document25 pagesGroup 5.0Alhaj MassoudNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument16 pagesPDFŘïśhåbh ÇhåţúŕvëđîNo ratings yet
- Darcy-Law (Rock)Document9 pagesDarcy-Law (Rock)Maqsood IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture (9-10) Permeability & Capillary PressureDocument23 pagesLecture (9-10) Permeability & Capillary PressureKetone PropanonNo ratings yet
- The Vertical Sweep EfficiencyDocument4 pagesThe Vertical Sweep EfficiencyASaifulHadi100% (1)
- PermeabilityDocument2 pagesPermeabilityPipit IrfaniNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law & ApplicationsDocument10 pagesDarcy's Law & ApplicationsEmad AamerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3/ Reservoir Engineering: The Fundamentals of Fluid Flow Through Porous Medium (Darcy's Law)Document21 pagesLecture 3/ Reservoir Engineering: The Fundamentals of Fluid Flow Through Porous Medium (Darcy's Law)منتظر ال سلمانNo ratings yet
- REN5415 - Y19 - Lec5 &6Document76 pagesREN5415 - Y19 - Lec5 &6Abdulla MohammadNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 1: To Determine The Permeability of A Granular Soil by Constant Head Permeameter. PermeabilityDocument5 pagesExperiment # 1: To Determine The Permeability of A Granular Soil by Constant Head Permeameter. Permeabilityhafsazaq2003No ratings yet
- PERMEABILITYDocument8 pagesPERMEABILITYSaroo BastkyNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICSDocument10 pagesHYDRAULICSLuisito Sta InesNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics of Slurries: (Term Project Report)Document18 pagesFluid Mechanics of Slurries: (Term Project Report)Ashok Roy100% (1)
- Hydraulics: The Science of Hydraulics. Hydraulics Is Defined As That Branch of Science Which Treats ofDocument24 pagesHydraulics: The Science of Hydraulics. Hydraulics Is Defined As That Branch of Science Which Treats ofAj SobremonteNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering CourseDocument129 pagesReservoir Engineering CourseLeonardo Barrios CarreraNo ratings yet
- Numerical Investigations of Liquid-Solid Slurry Ows in A Fully Developed Turbulent Ow RegionDocument10 pagesNumerical Investigations of Liquid-Solid Slurry Ows in A Fully Developed Turbulent Ow RegionPrantik DasNo ratings yet
- Calgary University - Introduction To Reservoir Engineering - Course NotesDocument129 pagesCalgary University - Introduction To Reservoir Engineering - Course NotesSalaheldin TawfigNo ratings yet
- 2 Hydraulic FundamentalsDocument6 pages2 Hydraulic FundamentalsMohamed SokarNo ratings yet
- Mal1033: Groundwater Hydrology: Principles of Groundwater FlowDocument53 pagesMal1033: Groundwater Hydrology: Principles of Groundwater Flowomed muhammadNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 Reynolds NumberDocument18 pagesTopic 1.2 Reynolds Numberethandleon4No ratings yet
- LabDocument4 pagesLabgetsweetNo ratings yet
- Viscosity Is Another Type of Bulk Property Defined As A Liquid's Resistance To Flow. When TheDocument2 pagesViscosity Is Another Type of Bulk Property Defined As A Liquid's Resistance To Flow. When TheUmer AizazNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 and Unit 5 UpdatedDocument86 pagesUnit 3 and Unit 5 UpdatedDebanga BoruahNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Hydraulics: Answer Atleast 10 (Ten) QuestionsDocument2 pagesAssignment On Hydraulics: Answer Atleast 10 (Ten) QuestionsDipankar NathNo ratings yet
- MESD311-Velocity and Discharge CoefficientDocument9 pagesMESD311-Velocity and Discharge Coefficienthaslina matzianNo ratings yet
- Distributor Plate and Evaporator TubesDocument5 pagesDistributor Plate and Evaporator TubesKevinNo ratings yet
- Fisika 1 - Kelas B - Grup 4Document12 pagesFisika 1 - Kelas B - Grup 4faridNo ratings yet
- EXP 5kuuDocument12 pagesEXP 5kuuazym94No ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of The Inertial Effects of Flow Through Porous MediaDocument6 pagesExperimental Investigation of The Inertial Effects of Flow Through Porous MediaRosa K Chang HNo ratings yet
- Ydrology Ecture Ifteen: G: D ' L F N D - K A. RDocument37 pagesYdrology Ecture Ifteen: G: D ' L F N D - K A. Rakshay sewcharanNo ratings yet
- Darcy (Unit) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesDarcy (Unit) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaChristian PaterninaNo ratings yet
- Notes Grit RemovalDocument16 pagesNotes Grit RemovalrojanmathewNo ratings yet
- PermeabilityDocument34 pagesPermeabilitytalbkhfajy4No ratings yet
- PermeabilityDocument34 pagesPermeabilityhussein alsaedeNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Lab (PermeabilityDocument12 pagesReservoir Lab (PermeabilityAhmed AmirNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument14 pagesNOTESEzioSilvestreNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic ConductivityDocument7 pagesHydraulic ConductivityDragomir Gabriela MarianaNo ratings yet
- Determining Fluid Velocity LabDocument19 pagesDetermining Fluid Velocity Labtk_atiqah100% (2)
- Lab Report For Permeability and PorosityDocument30 pagesLab Report For Permeability and PorosityMohammed Erwaiha67% (3)
- AbhishekDocument29 pagesAbhishekabhishek_negi_41No ratings yet
- 60ce52bd93c21a001fa11df0 - ## - FLUID MECHANICSDocument158 pages60ce52bd93c21a001fa11df0 - ## - FLUID MECHANICSDev SoniNo ratings yet
- ENM200 Reservoir Rock Properties NotesDocument13 pagesENM200 Reservoir Rock Properties NotesAdekunle John AdejumoNo ratings yet
- CENTRIFUGATIONDocument2 pagesCENTRIFUGATIONLily Antonette AgustinNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Designing An Experiment To Calculate Permeability of Porous MediumDocument17 pagesPresentation On Designing An Experiment To Calculate Permeability of Porous MediumMohita JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Ad2 IA-3 Assignment 2015Document2 pagesAd2 IA-3 Assignment 2015Supreeth RNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics (QUESTION BANK)Document5 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics (QUESTION BANK)Zohaib ShahidNo ratings yet
- Averaging Absolute PermeabilityDocument7 pagesAveraging Absolute PermeabilitySaroo BastkyNo ratings yet
- Flow in Pipe: Characteristic LengthDocument9 pagesFlow in Pipe: Characteristic Lengthguapo93No ratings yet
- Hydrau Handout.Document57 pagesHydrau Handout.Rhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics I Laboratory Class 2: Permeability, Hydraulic ConductivityDocument2 pagesSoil Mechanics I Laboratory Class 2: Permeability, Hydraulic ConductivityRobert PrinceNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet