Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6
Uploaded by
della salsabila0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pages1. The document contains 6 group assignments on economics problems. The assignments cover topics such as using Cramer's Rule to solve national income models, finding derivatives and difference quotients, solving absolute value and inequality equations, and differentiating total cost and revenue functions.
2. Each group is assigned a different economics problem to solve involving concepts like national income models, derivatives, absolute values, inequalities, and cost and revenue functions. The groups must use techniques like Cramer's Rule, differentiation, and algebraic manipulation to solve their assigned problems.
3. The document provides high-level overviews of the problems each group is to solve without showing the step-by-step workings, focusing instead on the key economic
Original Description:
Matek
Original Title
Mathecs, Assignment4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document contains 6 group assignments on economics problems. The assignments cover topics such as using Cramer's Rule to solve national income models, finding derivatives and difference quotients, solving absolute value and inequality equations, and differentiating total cost and revenue functions.
2. Each group is assigned a different economics problem to solve involving concepts like national income models, derivatives, absolute values, inequalities, and cost and revenue functions. The groups must use techniques like Cramer's Rule, differentiation, and algebraic manipulation to solve their assigned problems.
3. The document provides high-level overviews of the problems each group is to solve without showing the step-by-step workings, focusing instead on the key economic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesGroup 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6
Uploaded by
della salsabila1. The document contains 6 group assignments on economics problems. The assignments cover topics such as using Cramer's Rule to solve national income models, finding derivatives and difference quotients, solving absolute value and inequality equations, and differentiating total cost and revenue functions.
2. Each group is assigned a different economics problem to solve involving concepts like national income models, derivatives, absolute values, inequalities, and cost and revenue functions. The groups must use techniques like Cramer's Rule, differentiation, and algebraic manipulation to solve their assigned problems.
3. The document provides high-level overviews of the problems each group is to solve without showing the step-by-step workings, focusing instead on the key economic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
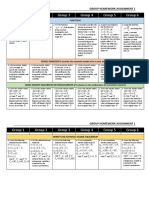
GROUP HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 4
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6
FINDING SOLUTION OF ECONOMIC PROBLEM USING CRAMER’S RULE
1. Given the following 1. Let the national-income 1. Given the following 1. A two-commodity 1. A two-commodity 1. Given the following
national-income model: model be: national-income model: market model is given: market model is given: national-income model:
𝑌 = 𝐶 + 𝐼0 + 𝐺0 𝑌 = 𝐶 + 𝐼0 + 𝐺 𝑌 = 𝐶 + 𝐼0 + 𝐺0 𝑄𝑑1 = 18 − 3𝑃1 + 𝑃2 𝑄𝑑1 = 470 − 5𝑃1 − 2𝑃2 𝑌 = 𝐶 + 𝐼0 + 𝐺0
𝐶 = 𝐶0 + 𝑐(𝑌 − 𝑇); 𝐶 = 𝑎 + 𝑏(𝑌 − 𝑇0 ); 𝐶 = 𝑎 + 𝑏(𝑌 − 𝑇); 𝑄𝑠1 = −2 + 4𝑃1 𝑄𝑠1 = −60 + 3𝑃1 𝐶 = 𝑎 + 𝑏(𝑌 − 𝑇);
(0 < 𝑐 < 1) (𝑎 > 0,0 < 𝑏, 1) (𝑎 > 0,0 < 𝑏, 1) 𝑄𝑑2 = 12 + 𝑃1 − 2𝑃2 𝑄𝑑2 = 295 − 𝑃1 − 3𝑃2 (𝑎 > 0,0 < 𝑏 < 1)
𝑇 = 𝑇0 + 𝑡𝑌; 𝐺 = 𝑔𝑌; (0 < 𝑔 < 1) 𝑇 = 𝑡𝑌; (0 < 𝑡 < 1) 𝑄𝑠2 = −2 + 3𝑃2 𝑄𝑠2 = −120 + 2𝑃2 𝑇 = 𝑡𝑌; (0 < 𝑡 < 1)
(0 < 𝑡 < 1) Find 𝑌 ∗ , 𝐶 ∗ , and 𝐺 ∗ in Find 𝑌 ∗ , 𝐶 ∗ , and 𝑇 ∗ using Find 𝑃𝑖∗ and 𝑄𝑖∗ (𝑖 = 1.2) Find 𝑃𝑖∗ and 𝑄𝑖∗ (𝑖 = 1.2) Find 𝑌 ∗ , 𝐶 ∗ , and 𝑇 ∗ in
Find 𝑌 ∗ , 𝐶 ∗ , and 𝑇 ∗ using reduced-forms using Cramer’s Rule if 𝐼0 = using Cramer’s Rule and using Cramer’s Rule and reduced-forms using
Cramer’s Rule if 𝐶0 = Cramer’s Rule. 5,000; 𝐺0 = 2,500; 𝑎 = substitution. substitution. Cramer’s Rule.
30; 𝐼0 = 60, 𝐺0 = 1,000; 𝑏 = 0,2; 𝑡 =
5; 𝑇0 = 20; 𝑐 = 25%.
0.75; 𝑡 = 20%.
DIFFERENCE QUOTIENT AND DERIVATIVE
2. Given the function 2. Given the function 2. Given the function 2. Given the function 2. Given the function 2. Given the function
𝑦 = 3𝑥 2 + 5, find: 𝑦 = 𝑥 2 + 5𝑥, find: 𝑦 = 5𝑥 − 3, 𝑦 = 2𝑥 2 + 3, find: 𝑦 = 4𝑥 2 + 𝑥, find: 𝑦 = 5 + 2𝑥,
(1) the difference (1) the difference (1) find the difference (1) the difference (1) the difference (1) find the difference
quotient (as a function quotient (as a function quotient (as a function quotient (as a function quotient (as a function quotient (as a function
of 𝑥 or 𝑥0 and ∆𝑥) and of 𝑥 or 𝑥0 and ∆𝑥) and of 𝑥 or 𝑥0 and ∆𝑥) and of 𝑥 or 𝑥0 and ∆𝑥) and of 𝑥 or 𝑥0 and ∆𝑥) and of 𝑥 or 𝑥0 and ∆𝑥) and
the derivative (𝑑𝑦⁄𝑑𝑥 ); the derivative (𝑑𝑦⁄𝑑𝑥 ); the derivative (𝑑𝑦⁄𝑑𝑥 ); the derivative (𝑑𝑦⁄𝑑𝑥 ); the derivative (𝑑𝑦⁄𝑑𝑥 ); the derivative (𝑑𝑦⁄𝑑𝑥 );
(2) 𝑓 ′ (3) and 𝑓 ′ (4). (2) 𝑓 ′ (3) and 𝑓 ′ (4). (2) what type of function (2) 𝑓 ′ (3) and 𝑓 ′ (4). (2) 𝑓 ′ (3) and 𝑓 ′ (4). (2) what type of function
are your results? What are your results? What
can you observe? can you observe?
ABSOLUTE VALUES AND INEQUALITIES
3. Solve the followings: 3. Solve the followings: 3. Solve the followings: 3. Solve the followings: 3. Solve the followings: 3. Solve the followings:
(1) 3𝑥 − 2 < 7𝑥 + 2, (1) 2𝑥 − 5 < 𝑥 + 4, (1) 3𝑥 − 5 < 2𝑥 + 1, (1) 3𝑥 − 5 < 4𝑥 + 2, (1) 𝑥 − 2 < 7𝑥 + 5, (1) 2𝑥 + 5 < 3𝑥 − 2,
(2)|𝑥 + 2| < 4. (2)|4𝑥 + 1| < 4. (2)|𝑥 + 2| > 4. (2)|𝑥 + 2| ≤ 4. (2)|2𝑥 + 2| < 3. (2)|𝑥 + 2| ≥ 2.
DIFFERENTIATION WITH SINGLE VARIABLE CASE
4. Write out a variable-cost 4. Given the average- 4. Given the average-cost 4. Write out a variable-cost 4. Given the average- 4. Given the average-cost
of the total-cost function revenue function 𝐴𝑅 = function 𝐴𝐶 = 𝑄2 − of the total-cost function revenue function 𝐴𝑅 = function 𝐴𝐶 = 𝑄2 −
Page 1 of 2
GROUP HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 4
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6
3 2 3 2
𝐶 = 𝑄 − 5𝑄 + 12𝑄 + 45 − 3𝑄, find the total- 4𝑄+174, find the total- 𝐶 = 𝑄 − 5𝑄 + 12𝑄 + 20 − 3𝑄, find the total- 5𝑄+12, find the total-
75, then find the deriva- revenue (R) and the cost (C) and the 75, then find the deriva- revenue (R) and the cost (C) and the
tives of both the total- marginal-revenue (MR) marginal-cost (MC) tives of both the total- marginal-revenue (MR) marginal-cost (MC)
cost and variable-cost functions. What can you functions. What can you cost and variable-cost functions. What can you functions. What can you
functions. What can you conclude about the observe about the shape functions. What can you conclude about the observe about the shape
observe? slopes of AR and MR? of AC and MC? observe? slopes of AR and MR? of AC and MC?
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Limb Volume CalculatorDocument6 pagesLimb Volume CalculatorYudhi HuseinNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry CH 9 To 14 Test Part 1 FSCDocument2 pagesTrigonometry CH 9 To 14 Test Part 1 FSCfawwad93386% (14)
- Chapter 9 AssignmentDocument3 pagesChapter 9 Assignmentapi-528144614No ratings yet
- 5-1 Study Guide and Intervention: Operations With PolynomialsDocument2 pages5-1 Study Guide and Intervention: Operations With PolynomialsasdfasdfasdfasdfasdfNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 The Antiderivative of A Function PDFDocument33 pagesLesson 11 The Antiderivative of A Function PDFtrisha paclebNo ratings yet
- Multiply Whole Numbers: InvestigateDocument44 pagesMultiply Whole Numbers: InvestigateShahla Ali100% (1)
- PDP Namuna-1Document6 pagesPDP Namuna-1asadbektoshpolatov913No ratings yet
- MatematikaDocument6 pagesMatematikaasadbektoshpolatov913No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mat455Document36 pagesChapter 2 Mat455Ajaq 98No ratings yet
- Practica 1102Document4 pagesPractica 1102Edgar Sipe QuispeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Function Mapping and Limits by Dr. AjijolaDocument11 pagesLecture Notes On Function Mapping and Limits by Dr. AjijolasmartruthieNo ratings yet
- Practica 1102 ......... - 2Document4 pagesPractica 1102 ......... - 2Edgar Sipe QuispeNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Study Guide + Answers gr.11Document2 pages8.1 Study Guide + Answers gr.11LLLNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6Document2 pagesGroup 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6NelsonFernandoNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Math Notes PDF Download Chapther 5Document11 pages9th Class Math Notes PDF Download Chapther 5Owi ShahNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Quadratic FactorizationDocument32 pagesWeek 7 - Quadratic Factorizationrheanna0076No ratings yet
- Ch-4 - Introduction To CalculusDocument51 pagesCh-4 - Introduction To Calculus5hbsb7mc68No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Measuring Change - Differentiation UpdatedDocument114 pagesChapter 5 Measuring Change - Differentiation UpdatedOld NewbornNo ratings yet
- Statistics Formulae BookletDocument36 pagesStatistics Formulae BookletKarl LewisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (2.1)Document28 pagesChapter 2 (2.1)Farish IskandarNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tambahan: Modul Mas (Minimum Adequate Syllabus) SPM 2019Document37 pagesMatematik Tambahan: Modul Mas (Minimum Adequate Syllabus) SPM 2019Jinny NeutrollNo ratings yet
- TypingDocument6 pagesTypingAleem AliNo ratings yet
- 15 Ex 4K The Quotient RuleDocument13 pages15 Ex 4K The Quotient RuleRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Module2 - R&W - Content%nlDocument20 pagesModule2 - R&W - Content%nlSangcad M AmboloNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Chapter # 5 Factorization Class 9TH (KPK)Document13 pagesMathematics: Chapter # 5 Factorization Class 9TH (KPK)ShEzzZyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 FKB 11102Document31 pagesLesson 4 FKB 11102Muhd ShazanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. ODEDocument7 pagesChapter 6. ODEAvese ISONo ratings yet
- Formulas 1ST SemDocument7 pagesFormulas 1ST Semibdeveterbo.nhcsNo ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting FunctionsDocument26 pagesAdding and Subtracting FunctionsJustmeNo ratings yet
- Sections 2.4-2.5Document14 pagesSections 2.4-2.5samueldeegan0130No ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 - Ellipses & Vector - 1 Answer SchemeDocument9 pagesTutorial 7 - Ellipses & Vector - 1 Answer Schemefiqah BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Article: Indexing Agency: July 2018Document9 pagesArticle: Indexing Agency: July 2018UMT JournalsNo ratings yet
- Limit and Continuty (S)Document6 pagesLimit and Continuty (S)Zuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Algebraic SubstitutionDocument6 pagesAlgebraic SubstitutionIchiroue Whan GNo ratings yet
- Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Senior High School Grade Basic CalculusDocument32 pagesWhole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Senior High School Grade Basic CalculusKayrell AquinoNo ratings yet
- Fiche D'exercice N°5 3eme Calcul Nulérique PDFDocument4 pagesFiche D'exercice N°5 3eme Calcul Nulérique PDFEric LegerNo ratings yet
- Rules For DifferentiationDocument7 pagesRules For DifferentiationPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Week 13-14 - CalcDocument3 pagesWeek 13-14 - CalcFlorenceNo ratings yet
- Exam3 SolutionDocument6 pagesExam3 Solutionowronrawan74No ratings yet
- Solución Semana 8 Análisis MatemáticoDocument16 pagesSolución Semana 8 Análisis MatemáticoElvis CalderonNo ratings yet
- Calculus Module 3Document22 pagesCalculus Module 3Karl AngcananNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Related RatesDocument5 pagesLesson 2 Related RatesG02 - BALACANAO JHERICE A.No ratings yet
- ATHENS BookDocument392 pagesATHENS Bookrspapel1732antNo ratings yet
- MODUL (1) Analisis Teknik Pengukuran: TME 142 - Praktikum FisikaDocument9 pagesMODUL (1) Analisis Teknik Pengukuran: TME 142 - Praktikum FisikaYudi YunaputraNo ratings yet
- MeetLearn 575 Mark GuideDocument5 pagesMeetLearn 575 Mark GuideLukong EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Self Learning Module Basic Calculus q3 Week5Document24 pagesSelf Learning Module Basic Calculus q3 Week5Kayrell AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document13 pagesLecture 7Aliza FatymaNo ratings yet
- Cal 11 Q3 0502 Final PDFDocument20 pagesCal 11 Q3 0502 Final PDFKat DumpNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8.1:: Rizal National Science High SchoolDocument18 pagesLESSON 8.1:: Rizal National Science High Schooltrisha paclebNo ratings yet
- 2nd Basiccal Differentiation RulesDocument35 pages2nd Basiccal Differentiation RulesBernadette BaduaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Calculus (Derivatives of Functions)Document16 pagesModule 3 Calculus (Derivatives of Functions)Michael AliagaNo ratings yet
- Calc 3.3 PacketDocument4 pagesCalc 3.3 PacketShubham PardeshiNo ratings yet
- Model Q Paper - V Cbse PatternDocument6 pagesModel Q Paper - V Cbse PatternMUKESH DHALNo ratings yet
- Class 01 AdvancedFunctions HandoutSOLDocument6 pagesClass 01 AdvancedFunctions HandoutSOLRonan ZhongNo ratings yet
- Answer: Rise Time Answer: Equal Real Answer: Mass Spring Damper System U-Tube Manometer Pneumatic ValvesDocument2 pagesAnswer: Rise Time Answer: Equal Real Answer: Mass Spring Damper System U-Tube Manometer Pneumatic ValvesLois ReyesNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument25 pagesParabolaNorman JadumasNo ratings yet
- Actividad 5Document6 pagesActividad 5YaretziNo ratings yet
- DDP - Solutions - JEE ADVANCED - Quadratic & ComplexDocument7 pagesDDP - Solutions - JEE ADVANCED - Quadratic & ComplexArtisticNo ratings yet
- Continuidade de Funções - RESOLUÇÃODocument4 pagesContinuidade de Funções - RESOLUÇÃOAndrew Ribeiro Candido de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Applicaton of Laplace TransformDocument10 pagesApplicaton of Laplace TransformJohn Reda100% (1)
- ChristianDocument7 pagesChristianJohnny JanulgueNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - FunctionsDocument35 pagesLesson 1 - FunctionsQyndel Zach BiadoNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other EntitiesDocument21 pagesChapter 01 - Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other Entitiesdella salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other EntitiesDocument21 pagesChapter 01 - Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other Entitiesdella salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Uas MPSDMDocument26 pagesRangkuman Uas MPSDMdella salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Advanced Accounting 8e by Baker 06 Chapter 18 42Document25 pagesTest Bank Advanced Accounting 8e by Baker 06 Chapter 18 42della salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Advanced Accounting 8e by Baker 06 ChapterDocument42 pagesTest Bank Advanced Accounting 8e by Baker 06 Chapterdella salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Essay AssignmentDocument3 pagesEssay Assignmentdella salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Mathecs, Assignment7.2Document3 pagesMathecs, Assignment7.2della salsabilaNo ratings yet
- NDCE (Final Accredited) - 2Document97 pagesNDCE (Final Accredited) - 2Xris AthensNo ratings yet
- Solution of Heat and Wave Equations Using Mahgoub Adomian Decomposition MethodDocument5 pagesSolution of Heat and Wave Equations Using Mahgoub Adomian Decomposition MethodiajerNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Probability: Solutions To Self-Quizzes and Self-TestsDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Probability: Solutions To Self-Quizzes and Self-TestsRaul Santillana QuispeNo ratings yet
- R - (Z/R,) (1 + Ao o + E " (Z/R,) " (A. - Ib.)Document6 pagesR - (Z/R,) (1 + Ao o + E " (Z/R,) " (A. - Ib.)Srinivas JangiliNo ratings yet
- Section Quiz 3-2 - Schools of The Sacred HeartDocument3 pagesSection Quiz 3-2 - Schools of The Sacred HeartAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Glencoe CH 3 EditDocument93 pagesGlencoe CH 3 EditVenkat KrishnanNo ratings yet
- QA BookDocument130 pagesQA BookKish Catclasses67% (9)
- JPWPKL Trial 2010 p2 Mark SchemeDocument11 pagesJPWPKL Trial 2010 p2 Mark Schemetan_wooichoongNo ratings yet
- Genmath q1 Mod2 Evaluatingfunctions v2 PDFDocument29 pagesGenmath q1 Mod2 Evaluatingfunctions v2 PDFJohnreyDelosSantosNo ratings yet
- A Bridged CurriculumDocument86 pagesA Bridged Curriculumkaziba stephen100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3: Least Common MultipleDocument29 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3: Least Common MultipleEmman Fernandez100% (1)
- TeachingSampling PackagerDocument101 pagesTeachingSampling PackagerANGÉLICA GUARÍNNo ratings yet
- Ece-V-Digital Signal Processing U1 PDFDocument16 pagesEce-V-Digital Signal Processing U1 PDFlathavenkyNo ratings yet
- Picking Winners: A Framework For Venture Capital InvestmentDocument30 pagesPicking Winners: A Framework For Venture Capital InvestmentkaltsturmNo ratings yet
- Temporal and Spatial LocalityDocument24 pagesTemporal and Spatial LocalityAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- GrecoImpolloniaCuomo StaticAnalysis PDFDocument14 pagesGrecoImpolloniaCuomo StaticAnalysis PDFKrebs ChouaibNo ratings yet
- Mean and Random VariableDocument4 pagesMean and Random VariabledfgftjhfjsNo ratings yet
- Tle-10 Ict Quarter 1 Module 1 (Babatuan)Document14 pagesTle-10 Ict Quarter 1 Module 1 (Babatuan)Shua HongNo ratings yet
- Cse 321 HW05Document2 pagesCse 321 HW05tubaNo ratings yet
- Inverted PendulumDocument9 pagesInverted PendulumMahmoud Samir MahmoudNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology: Approved Per BOR Res. No.29 Series 1981Document1 pageCollege of Engineering, Architecture and Technology: Approved Per BOR Res. No.29 Series 1981Miko F. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Use of Symbols in Mathematics and Logic: Sundar SarukkaiDocument22 pagesThe Use of Symbols in Mathematics and Logic: Sundar SarukkaidominicNo ratings yet
- Modeling The Motion of A SpringDocument5 pagesModeling The Motion of A Springapi-253477911No ratings yet
- IMO 2015 ShorlistDocument7 pagesIMO 2015 ShorlistAxelNo ratings yet
- Model Paper For Calculus I Midterm Exam. 2021-2022-1: y Sin X y Cos XDocument4 pagesModel Paper For Calculus I Midterm Exam. 2021-2022-1: y Sin X y Cos XmugahedNo ratings yet
- Mat495 Chapter 5Document10 pagesMat495 Chapter 5MuhamadSadiqNo ratings yet