Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gallstones in Sickle Cell Disease
Gallstones in Sickle Cell Disease
Uploaded by
Vinna Marie LaridoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- English Gastroenteritis PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish Gastroenteritis PDFkatyweymNo ratings yet
- 5263 Gallbladder - tcm28 552977Document2 pages5263 Gallbladder - tcm28 552977Beverly SANo ratings yet
- HT 0114 InfoGraphicDocument1 pageHT 0114 InfoGraphicrizka rahmanitaNo ratings yet
- Malrotation and Volvulus Great Ormond Street HospitalDocument1 pageMalrotation and Volvulus Great Ormond Street Hospitalghy7jbj96sNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsDocument20 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsruthmindosiahaanNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea and Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesDiarrhea and Acute GastroenteritisAkasa DudungNo ratings yet
- 65 HTTP Familydoctor Org Familydoctor en Health Tools Search by Symptom Abdominal Pain Long Term HTMLDocument5 pages65 HTTP Familydoctor Org Familydoctor en Health Tools Search by Symptom Abdominal Pain Long Term HTMLYasaan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Surg107 4-Cholecystitis-04 04 17-HLDocument6 pagesSurg107 4-Cholecystitis-04 04 17-HLOktavia PutriNo ratings yet
- Gallstone e BookDocument107 pagesGallstone e Bookee1993100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal Problems in Children With Down's Syndrome: by DR Liz MarderDocument5 pagesGastrointestinal Problems in Children With Down's Syndrome: by DR Liz MarderNur Haziq HasNo ratings yet
- Bowel Preparation: Information AboutDocument3 pagesBowel Preparation: Information AboutBobyHarmoyoNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Cholestasis (Itching Liver Disorder) : Day Assessment Unit, Women's CentreDocument0 pagesObstetric Cholestasis (Itching Liver Disorder) : Day Assessment Unit, Women's CentrenajmulNo ratings yet
- Parasite Herbal RemediesDocument10 pagesParasite Herbal Remediesdonaldbrown16No ratings yet
- Group 2 Case Study MergedDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Case Study MergedKobe Bryan GermoNo ratings yet
- DIARRHEADocument39 pagesDIARRHEAJessa RedondoNo ratings yet
- BF Checklist EnglishDocument1 pageBF Checklist EnglishYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- Importance of DigestionDocument5 pagesImportance of DigestionChrezza Elicyyenette Bio PalecpecNo ratings yet
- Infant of Diabetic MotherDocument14 pagesInfant of Diabetic MothersreekalaNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux What Is Gastroesophageal Reflux?Document18 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux What Is Gastroesophageal Reflux?Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Yakult StakeholdersDocument4 pagesYakult StakeholdersLuisRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Keep Your Teeth and Gums HealthyDocument20 pagesKeep Your Teeth and Gums HealthydrjperumalNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis (Gastro) : Signs and Symptoms of GastroDocument2 pagesGastroenteritis (Gastro) : Signs and Symptoms of GastrokatyweymNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Gallstone ThesisDocument4 pagesGallstone Thesisjuliekwhlanchorage100% (2)
- Ped Diabetes BookletDocument22 pagesPed Diabetes Bookletmanoj kananiNo ratings yet
- Notes On ReproductionDocument2 pagesNotes On ReproductionBoris CastilloNo ratings yet
- Gallstones: What Does My Gall Bladder Do?Document3 pagesGallstones: What Does My Gall Bladder Do?a kNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain in AdultsDocument3 pagesAbdominal Pain in Adultshikmah_fajriantiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ActivityDocument13 pagesAnaphy ActivityJonas Tristan Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesDigestive SystemJonas Tristan Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesGestational Diabetes MellitusAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- Complication of Horseshoe KidneyDocument2 pagesComplication of Horseshoe KidneyAnggi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Chapter 1 Learning Activities : Herbal SupplementsDocument5 pagesModule 2: Chapter 1 Learning Activities : Herbal SupplementsEloise GalsimNo ratings yet
- A0100 Constipation in Children 1Document8 pagesA0100 Constipation in Children 1iuliaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Growth Clinic LeafletDocument4 pagesFetal Growth Clinic LeafletogatojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Digestive Problems: A troubleshooting guide to common childhood ailmentsFrom EverandDigestive Problems: A troubleshooting guide to common childhood ailmentsNo ratings yet
- The Australian Kids' Health Book: The Essential A-Z Guide to Emergencies , Baby Care and Common Childhood IllnessesFrom EverandThe Australian Kids' Health Book: The Essential A-Z Guide to Emergencies , Baby Care and Common Childhood IllnessesNo ratings yet
- GST NafldDocument3 pagesGST Naflddavedavids0n8475No ratings yet
- Obstetric Cholestasis (Itching Liver Disorder) : Information For Parents-To-BeDocument12 pagesObstetric Cholestasis (Itching Liver Disorder) : Information For Parents-To-BecccccccNo ratings yet
- Help With DiabetesDocument2 pagesHelp With DiabetesgeekfreedomNo ratings yet
- Pi Obstetric CholestasisDocument5 pagesPi Obstetric CholestasisSanaNo ratings yet
- Pigestational DiabetesDocument6 pagesPigestational DiabetesViona fthNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013Document9 pagesDiarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013emmi_valentinaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-08-03 at 16.34.45Document1 pageScreenshot 2023-08-03 at 16.34.45Shankaron AhmedNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument7 pagesPolycystic Kidney DiseaseBlessing IkangNo ratings yet
- Concerned About ConstipationDocument4 pagesConcerned About Constipationapi-559575515No ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Acute Pancreatitis in ChildrenDocument3 pagesFact Sheet Acute Pancreatitis in ChildrenNikola StojsicNo ratings yet
- Omphalocele Repair Umbilical Hernia: CausesDocument3 pagesOmphalocele Repair Umbilical Hernia: CausesCha-cha UzumakiNo ratings yet
- CostipitationDocument4 pagesCostipitationashmi akberNo ratings yet
- Nhs Highland Gestational DiabetesDocument10 pagesNhs Highland Gestational Diabetesemnatoumi2000No ratings yet
- Constipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationFrom EverandConstipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationNo ratings yet
- Gallstones in AdolescentsDocument2 pagesGallstones in AdolescentsFarah Mega RNo ratings yet
- Biliary Atresia What Is Biliary Atresia?Document5 pagesBiliary Atresia What Is Biliary Atresia?Ruthai LegasteNo ratings yet
- Anti Dumping DietDocument3 pagesAnti Dumping DietFelixDrummaruNo ratings yet
- What Is HirschsprungDocument4 pagesWhat Is HirschsprungMicah SaberNo ratings yet
- About Bowel Cancer - A Quick GuideDocument7 pagesAbout Bowel Cancer - A Quick Guidealvin1445No ratings yet
- FilipinoDocument1 pageFilipinoVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- NXT 2.0 Inventor's Guide Sample PDFDocument14 pagesNXT 2.0 Inventor's Guide Sample PDFVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- The Century CarverDocument2 pagesThe Century CarverVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- Gcfandlcm PDFDocument2 pagesGcfandlcm PDFVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- Gall African With Sickle Cell Anaemia: Preliminary From Yaounde, CameroonDocument3 pagesGall African With Sickle Cell Anaemia: Preliminary From Yaounde, CameroonVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- Batu Belah Batu BertangkupDocument3 pagesBatu Belah Batu BertangkupVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
Gallstones in Sickle Cell Disease
Gallstones in Sickle Cell Disease
Uploaded by
Vinna Marie LaridoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gallstones in Sickle Cell Disease
Gallstones in Sickle Cell Disease
Uploaded by
Vinna Marie LaridoCopyright:
Available Formats
Gallstones in Sickle Cell Disease
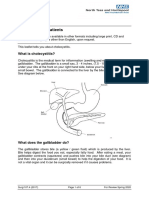
What are gallstones?
The gallbladder is a small sac near the liver. It holds bile which is used to help digest food.
Gallstones are formed in the gallbladder. Some of these stones may cause abdominal pain
and others may not. Many people with sickle cell disease will have gallstones, but usually
not until their teenage years or later. Not everyone with sickle cell disease will develop
gallstones.
What causes gallstones?
Gallstones happen more often in people with sickle cell disease because sickled red blood
cells break down much faster than normal red blood cells. When these break down, they
release bilirubin. Bilirubin turns into bile that then collects in the gallbladder and can form
sludge or gallstones.
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
Pain on the right side of the belly
Nausea (sick to the stomach or queasy)
Vomiting or bloating, especially after eating greasy or spicy foods
Yellow eyes
How are gallstones diagnosed and treated?
Let your child’s doctor know of any of the above symptoms.
X-rays or an ultrasound may be done to look for gallstones.
If symptoms are mild, your child may just be watched over time.
If symptoms are worse, surgery may be needed to take out the gallbladder.
Your child should avoid greasy and spicy foods if this causes stomach pain.
Call the sickle cell nurse or doctor at (816) 234-3265 (Monday through Friday,
8 am to 5 pm) for any questions about the gallbladder or gallstones.
HEM-07-325 (12/11) Page 1 of 1 Content Expires on 12/31/2013
Copyright © 2000-2010 The Children's Mercy Hospital
Kansas City, Missouri Overland Park, Kansas
This card is provided as a public education service. The information does not replace instructions
your physician gives you. If you have questions about your child's care, please call your physician.
You might also like
- English Gastroenteritis PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish Gastroenteritis PDFkatyweymNo ratings yet
- 5263 Gallbladder - tcm28 552977Document2 pages5263 Gallbladder - tcm28 552977Beverly SANo ratings yet
- HT 0114 InfoGraphicDocument1 pageHT 0114 InfoGraphicrizka rahmanitaNo ratings yet
- Malrotation and Volvulus Great Ormond Street HospitalDocument1 pageMalrotation and Volvulus Great Ormond Street Hospitalghy7jbj96sNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsDocument20 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsruthmindosiahaanNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea and Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesDiarrhea and Acute GastroenteritisAkasa DudungNo ratings yet
- 65 HTTP Familydoctor Org Familydoctor en Health Tools Search by Symptom Abdominal Pain Long Term HTMLDocument5 pages65 HTTP Familydoctor Org Familydoctor en Health Tools Search by Symptom Abdominal Pain Long Term HTMLYasaan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Surg107 4-Cholecystitis-04 04 17-HLDocument6 pagesSurg107 4-Cholecystitis-04 04 17-HLOktavia PutriNo ratings yet
- Gallstone e BookDocument107 pagesGallstone e Bookee1993100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal Problems in Children With Down's Syndrome: by DR Liz MarderDocument5 pagesGastrointestinal Problems in Children With Down's Syndrome: by DR Liz MarderNur Haziq HasNo ratings yet
- Bowel Preparation: Information AboutDocument3 pagesBowel Preparation: Information AboutBobyHarmoyoNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Cholestasis (Itching Liver Disorder) : Day Assessment Unit, Women's CentreDocument0 pagesObstetric Cholestasis (Itching Liver Disorder) : Day Assessment Unit, Women's CentrenajmulNo ratings yet
- Parasite Herbal RemediesDocument10 pagesParasite Herbal Remediesdonaldbrown16No ratings yet
- Group 2 Case Study MergedDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Case Study MergedKobe Bryan GermoNo ratings yet
- DIARRHEADocument39 pagesDIARRHEAJessa RedondoNo ratings yet
- BF Checklist EnglishDocument1 pageBF Checklist EnglishYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- Importance of DigestionDocument5 pagesImportance of DigestionChrezza Elicyyenette Bio PalecpecNo ratings yet
- Infant of Diabetic MotherDocument14 pagesInfant of Diabetic MothersreekalaNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux What Is Gastroesophageal Reflux?Document18 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux What Is Gastroesophageal Reflux?Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Yakult StakeholdersDocument4 pagesYakult StakeholdersLuisRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Keep Your Teeth and Gums HealthyDocument20 pagesKeep Your Teeth and Gums HealthydrjperumalNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis (Gastro) : Signs and Symptoms of GastroDocument2 pagesGastroenteritis (Gastro) : Signs and Symptoms of GastrokatyweymNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Gallstone ThesisDocument4 pagesGallstone Thesisjuliekwhlanchorage100% (2)
- Ped Diabetes BookletDocument22 pagesPed Diabetes Bookletmanoj kananiNo ratings yet
- Notes On ReproductionDocument2 pagesNotes On ReproductionBoris CastilloNo ratings yet
- Gallstones: What Does My Gall Bladder Do?Document3 pagesGallstones: What Does My Gall Bladder Do?a kNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain in AdultsDocument3 pagesAbdominal Pain in Adultshikmah_fajriantiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ActivityDocument13 pagesAnaphy ActivityJonas Tristan Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesDigestive SystemJonas Tristan Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesGestational Diabetes MellitusAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- Complication of Horseshoe KidneyDocument2 pagesComplication of Horseshoe KidneyAnggi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Chapter 1 Learning Activities : Herbal SupplementsDocument5 pagesModule 2: Chapter 1 Learning Activities : Herbal SupplementsEloise GalsimNo ratings yet
- A0100 Constipation in Children 1Document8 pagesA0100 Constipation in Children 1iuliaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Growth Clinic LeafletDocument4 pagesFetal Growth Clinic LeafletogatojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Digestive Problems: A troubleshooting guide to common childhood ailmentsFrom EverandDigestive Problems: A troubleshooting guide to common childhood ailmentsNo ratings yet
- The Australian Kids' Health Book: The Essential A-Z Guide to Emergencies , Baby Care and Common Childhood IllnessesFrom EverandThe Australian Kids' Health Book: The Essential A-Z Guide to Emergencies , Baby Care and Common Childhood IllnessesNo ratings yet
- GST NafldDocument3 pagesGST Naflddavedavids0n8475No ratings yet
- Obstetric Cholestasis (Itching Liver Disorder) : Information For Parents-To-BeDocument12 pagesObstetric Cholestasis (Itching Liver Disorder) : Information For Parents-To-BecccccccNo ratings yet
- Help With DiabetesDocument2 pagesHelp With DiabetesgeekfreedomNo ratings yet
- Pi Obstetric CholestasisDocument5 pagesPi Obstetric CholestasisSanaNo ratings yet
- Pigestational DiabetesDocument6 pagesPigestational DiabetesViona fthNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013Document9 pagesDiarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013emmi_valentinaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-08-03 at 16.34.45Document1 pageScreenshot 2023-08-03 at 16.34.45Shankaron AhmedNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument7 pagesPolycystic Kidney DiseaseBlessing IkangNo ratings yet
- Concerned About ConstipationDocument4 pagesConcerned About Constipationapi-559575515No ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Acute Pancreatitis in ChildrenDocument3 pagesFact Sheet Acute Pancreatitis in ChildrenNikola StojsicNo ratings yet
- Omphalocele Repair Umbilical Hernia: CausesDocument3 pagesOmphalocele Repair Umbilical Hernia: CausesCha-cha UzumakiNo ratings yet
- CostipitationDocument4 pagesCostipitationashmi akberNo ratings yet
- Nhs Highland Gestational DiabetesDocument10 pagesNhs Highland Gestational Diabetesemnatoumi2000No ratings yet
- Constipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationFrom EverandConstipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationNo ratings yet
- Gallstones in AdolescentsDocument2 pagesGallstones in AdolescentsFarah Mega RNo ratings yet
- Biliary Atresia What Is Biliary Atresia?Document5 pagesBiliary Atresia What Is Biliary Atresia?Ruthai LegasteNo ratings yet
- Anti Dumping DietDocument3 pagesAnti Dumping DietFelixDrummaruNo ratings yet
- What Is HirschsprungDocument4 pagesWhat Is HirschsprungMicah SaberNo ratings yet
- About Bowel Cancer - A Quick GuideDocument7 pagesAbout Bowel Cancer - A Quick Guidealvin1445No ratings yet
- FilipinoDocument1 pageFilipinoVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- NXT 2.0 Inventor's Guide Sample PDFDocument14 pagesNXT 2.0 Inventor's Guide Sample PDFVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- The Century CarverDocument2 pagesThe Century CarverVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- Gcfandlcm PDFDocument2 pagesGcfandlcm PDFVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- Gall African With Sickle Cell Anaemia: Preliminary From Yaounde, CameroonDocument3 pagesGall African With Sickle Cell Anaemia: Preliminary From Yaounde, CameroonVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet
- Batu Belah Batu BertangkupDocument3 pagesBatu Belah Batu BertangkupVinna Marie LaridoNo ratings yet