Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Drug
Drug Study Drug
Uploaded by
jl frusaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Drug
Drug Study Drug
Uploaded by
jl frusaCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Drug
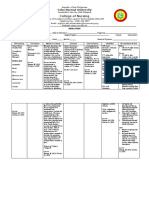
I. Generic Name Acetylcysteine
II. Brand Name
III. Drug Classification Respiratory
inhalant,
IV. Dosage/ Stock Dose Bronchodilators should be
given 10–15 min before acetylcysteine.
ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN:╇ 3–5 ml
(20%
solution) 3–4 times a day or 6–10 ml (10%
solution) 3–4 times a day. Range: 1–10 ml
(20% solution) q2–6h or 2–20 ml (10%
solution) q2–6h. INFANTS:╇ 1–2 ml (20%)
or 2–4 ml (10%) 3–4 times a day.
Intratracheal:╇ ADULTS, CHILDREN:╇ 1–2
ml of 10% or 20% solution instilled into
tracheostomy q1–4h.
V. Indication Adjunctive treatment for abnormally
viscid mucous secretions present
in acute and chronic bronchopulmonary
disease and pulmonary complications
of cystic fibrosis and surgery, diagnostic
bronchial studies.
VI. Drug Action/ Therapeutic Effort Mucolytic splits linkage of mucoproteins,
reducing viscosity of pulmonary secretions.
Therapeutic Effect:╇ Facilitates
removal of pulmonary secretions by
coughing, postural drainage, mechanical
means. Protects against acetaminophen
overdose-induced hepatotoxicity.
VII. Contraindications Cautions: Pts with bronchial asthma; debilitated
pts
with severe respiratory insufficiency (increases
risk of anaphylactoid reaction).
VIII. Drug Interactions none
IX. Side Effects Inhalation: Stickiness
on face, transient unpleasant odor.
Occasional:╇ Inhalation: Increased
bronchial secretions, throat irritation,
nausea, vomiting, rhinorrhea. Rare:╇ Inhalation:
Rash. PO: Facial edema, bronchospasm,
wheezing, nausea, vomiting.
X. Adverse Effects Large doses may produce severe nausea/
vomiting. (Less than 2%): Serious anaphylactoid
reactions including cough,
wheezing, stridor, respiratory distress,
bronchospasm, hypotension, and death
have been known to occur with IV administration.
XI. Nursing Responsibilities Assessment
Assess pretreatment respirations
for rate, depth, rhythm. IV antidote:
Obtain baseline labs and drug
screen. For use as antidote, obtain acetaminophen
level to determine need for
treatment with acetylcysteine.
Intervention
If bronchospasm occurs, discontinue
treatment, notify physician; bronchodilator
may be added to therapy. Monitor
rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration
(abdominal, thoracic). Observe sputum
for color, consistency, amount. IV antidote:
Administer within 8 hrs of acetaminophen
ingestion for maximal hepatic
protection; ideally, within 4 hrs
after immediate-A�release and 2 hrs after
liquid acetaminophen formulations.
Teaching point
Slight, disagreeable sulfuric odor from
solution may be noticed during
initial administration but disappears
quickly.
Adequate hydration is important part of
therapy.
Follow guidelines for proper coughing and
deep breathing techniques.
Drug Study Drug
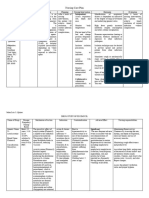
I. Generic Name Carbocisteine
II. Brand Name
III. Drug Classification Respiratory
inhalant,
IV. Dosage/ Stock Dose PO Initial: 2.25 g/day in 3-4 divided doses, then
reduce dose to 1.5 g/day in divided doses as
condition improves.
V. Indication Acts as mucolytic
VI. Drug Action/ Therapeutic Effort Carbocisteine is a mucolytic agent that reduces
goblet cell hyperplasia in the management of
respiratory disorders associated with abnormally
excessive or viscous mucus secretion.
VII. Contraindications Active peptic ulceration
VIII. Drug Interactions
IX. Side Effects Immune system disorders (there are reported cases
of anaphylactic shock in patients who have been
treated with this drug)
Gastrointestinal bleeding
X. Adverse Effects Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, diarrhoea,
abdominal pain, vomiting, gastrointestinal
bleeding.
Surgical and medical procedures: Skin rashes,
itching, bullous dermatitis (e.g. Stevens-Johnson
syndrome, erythema multiforme).
XI. Nursing Responsibilities Assessment
Assess pretreatment respirations
for rate, depth, rhythm. IV antidote:
Obtain baseline labs and drug
screen. For use as antidote, obtain acetaminophen
level to determine need for
treatment with acetylcysteine.
Intervention
If bronchospasm occurs, discontinue
treatment, notify physician; bronchodilator
may be added to therapy. Monitor
rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration
(abdominal, thoracic). Observe sputum
for color, consistency, amount. IV antidote:
Administer within 8 hrs of acetaminophen
ingestion for maximal hepatic
protection; ideally, within 4 hrs
after immediate-A�release and 2 hrs after
liquid acetaminophen formulations.
Teaching point
Slight, disagreeable sulfuric odor from
solution may be noticed during
initial administration but disappears
quickly.
Adequate hydration is important part of
therapy.
Follow guidelines for proper coughing and
deep breathing techniques.
Drug Study Drug
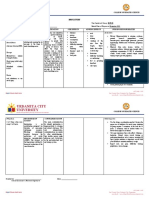
I. Generic Name Ambroxol
II. Brand Name
III. Drug Classification mucolytic
IV. Dosage/ Stock Dose Ambroxol 15 mg/5 ml syrup, 30 mg/5 ml syrup, 60
mg effervescent tablets, 30 mg tablets and
Ambroxol 10 mg/dose spray.
V. Indication It is used to treat acute and chronic respiratory
diseases accompanied by an increased mucus
production.
VI. Drug Action/ Therapeutic Effort This medicine works by helping to break down the
structure of mucus in the lungs and therefore
facilitates expectoration.
VII. Contraindications Hypersensitivity
VIII. Drug Interactions None
IX. Side Effects nausea,
vomiting,
diarrhea,
abdominal pain,
digestive disorders,
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (a life-threatening skin
disorder),
allergy and others.
X. Adverse Effects GI disturbances, allergic reaction
XI. Nursing Responsibilities Assessment
Assess pretreatment respirations
for rate, depth, rhythm. IV antidote:
Obtain baseline labs and drug
screen. For use as antidote, obtain acetaminophen
level to determine need for
treatment with acetylcysteine.
Intervention
If bronchospasm occurs, discontinue
treatment, notify physician; bronchodilator
may be added to therapy. Monitor
rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration
(abdominal, thoracic). Observe sputum
for color, consistency, amount. IV antidote:
Administer within 8 hrs of acetaminophen
ingestion for maximal hepatic
protection; ideally, within 4 hrs
after immediate-A�release and 2 hrs after
liquid acetaminophen formulations.
Teaching point
Slight, disagreeable sulfuric odor from
solution may be noticed during
initial administration but disappears
quickly.
Adequate hydration is important part of
therapy.
Follow guidelines for proper coughing and
deep breathing techniques.
Drug Study Drug
I. Generic Name Guaifenesin
II. Brand Name
III. Drug Classification Respiratory
expectorant.
IV. Dosage/ Stock Dose Ambroxol 15 mg/5 ml syrup, 30 mg/5 ml syrup, 60
mg effervescent tablets, 30 mg tablets and
Ambroxol 10 mg/dose spray.
V. Indication Helps loosen phlegm and thin bronchial
secretions, making cough more
productive.
VI. Drug Action/ Therapeutic Effort Stimulates respiratory tract secretions
by decreasing adhesiveness, viscosity of
mucus. Therapeutic Effect:╇ Promotes
removal of viscous mucus.
VII. Contraindications Contraindications:╇ None known.╇
Cautions:╇
Avoid OTC use in children younger than
2 yrs.
VIII. Drug Interactions None
IX. Side Effects Dizziness, headache, rash, diarrhea,
nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
X. Adverse Effects Overdose may produce nausea, vomiting.
XI. Nursing Responsibilities Assessment
Assess type, severity, frequency of cough.
Increase fluid intake, environmental humidity
to lower viscosity of lung secretions.
Intervention
Initiate deep breathing, coughing exercises,
particularly in pts with pulmonary
impairment. Assess for clinical improvement;
record onset of relief of cough.
Health Teaching
Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor
skills until response to drug is established.
Do not take for chronic cough.
Report persistent cough if
fever, rash, headache, sore throat is present
with cough.
Maintain adequate hydration.
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Case 1 - Eli Lilly CompanyDocument12 pagesCase 1 - Eli Lilly CompanyPau G100% (2)
- PMS PMCF CER RelationshipDocument1 pagePMS PMCF CER RelationshipMohammed HammedNo ratings yet
- Should You Get VaccinatedDocument159 pagesShould You Get Vaccinatedmario_kgl0% (1)
- Atrovent (Ipratropium)Document1 pageAtrovent (Ipratropium)E100% (2)
- ALBUTEROL Drug StudyDocument4 pagesALBUTEROL Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- Egyptian Guideline On PharmacovigilanceDocument194 pagesEgyptian Guideline On Pharmacovigilancedr3azzam0% (2)
- Drug Study #3Document8 pagesDrug Study #3James Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- Ipratroprium Drug CardDocument3 pagesIpratroprium Drug CardXiaoDuckyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document2 pagesDrug Study 2Joshua Selwyn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaDocument4 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- AcetylcysteineDocument2 pagesAcetylcysteineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- Final AcetylcysteineDocument2 pagesFinal AcetylcysteineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Pulmo)Document3 pagesRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Pulmo)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Acetylcysteine: Mucolytic Adult: Inhalation 1-10 ML of 20% Solution q4-6h or 2-20 ML of 10%Document3 pagesAcetylcysteine: Mucolytic Adult: Inhalation 1-10 ML of 20% Solution q4-6h or 2-20 ML of 10%Aubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- ACETYLCYSTEINEDocument2 pagesACETYLCYSTEINEAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Flovent (Fluticasone)Document3 pagesFlovent (Fluticasone)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- BeclomethasoneDocument2 pagesBeclomethasoneDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin (Hospital Formulary) - LexicompDocument1 pageVancomycin (Hospital Formulary) - Lexicompsalmanul farisNo ratings yet
- Tiotropium Bromide - Spiriva - BronchodilDocument2 pagesTiotropium Bromide - Spiriva - Bronchodil1adie1907No ratings yet
- Faeldonea, PJ - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFaeldonea, PJ - Drug StudyPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- CefepimeDocument3 pagesCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Anasthesia & AsthmaDocument30 pagesAnasthesia & AsthmafadhiliNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - CopdDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - CopdMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument19 pagesRespiratory DrugsBryan MedranoNo ratings yet
- COPD - Drug FormularyDocument32 pagesCOPD - Drug FormularyCharles BayogNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyMec AmilasanNo ratings yet
- ASTHMA RestriveraDocument18 pagesASTHMA RestriveraAoi ShinNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument5 pagesName of DrugJoann BeriñoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Sympathomime Tic, Beta2-Selective Adrenergic Agonist, Bronchodilator, AntiasthmaticDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Sympathomime Tic, Beta2-Selective Adrenergic Agonist, Bronchodilator, AntiasthmaticJichutreasure100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument186 pagesDrug StudyTheresa Sombilla FacunlaNo ratings yet
- Acetylcysteine Drug Study - FranciscoDocument4 pagesAcetylcysteine Drug Study - FranciscoFaye Andrea Francisco100% (1)
- Drug Study Copd FinalDocument3 pagesDrug Study Copd FinalMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- Drug BookDocument30 pagesDrug BookLindy JaneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument5 pagesDrug Study Pediajulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: Anti-Infectives and Anti-Inflammatory: Ncm106 - Pharmacology 2 Semester, AY 2020-2021Document34 pagesAntifungal Drugs: Anti-Infectives and Anti-Inflammatory: Ncm106 - Pharmacology 2 Semester, AY 2020-2021imnas100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCee-jay SalesNo ratings yet
- Beclomethasone DipropionateDocument3 pagesBeclomethasone Dipropionateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Copd Drug StudyDocument9 pagesCopd Drug StudyJoegie Ario100% (1)
- Drug Study: Alvarado. Marivil C. Bsn-IvDocument1 pageDrug Study: Alvarado. Marivil C. Bsn-IvAlejandro Lucena TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Beractant: Drug Class Therapeutic ActionsDocument4 pagesBeractant: Drug Class Therapeutic ActionsPrincess BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ufc FPDocument11 pagesCase Study Ufc FPMicah MagallanoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityShiva TorinsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanJehan Lois QuinesNo ratings yet
- Case: Pulmonary Tuberculosis Group D: NCM 104 Rle-Cd BSN 3Y2-1 SUBMITTED TO: Gerardo Nicolas, RN, MANDocument18 pagesCase: Pulmonary Tuberculosis Group D: NCM 104 Rle-Cd BSN 3Y2-1 SUBMITTED TO: Gerardo Nicolas, RN, MANJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Op PoisoningDocument6 pagesOp PoisoningSid DhayriNo ratings yet
- V. Drug StudyDocument5 pagesV. Drug StudyJopaii TanakaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Shortness of Breath)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Shortness of Breath)Michelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 6 Asma 2018Document45 pages6 Asma 2018Visco Da GamaNo ratings yet
- Antifungals Student'sDocument34 pagesAntifungals Student'sapril jholynna garroNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- PDF Changes2Document1 pagePDF Changes2Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Pharma Reviewer (Midterm)Document7 pagesPharma Reviewer (Midterm)SaidinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Book SkillabDocument38 pagesDrug Book SkillabSnehal SharmaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Work On The Following QuestionsDocument7 pagesWork On The Following QuestionsCenn Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument11 pagesCHF Drug StudySeth Michael Daniel BenauroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Prophylaxis Action: Tetanus: Injection: 5 To 10 LF Units ofDocument10 pagesProphylaxis Action: Tetanus: Injection: 5 To 10 LF Units ofElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Intra ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntra Reviewerjl frusaNo ratings yet
- Frusa, Jasmine Liezet S. BSN 2-2 CWTS (Sept. 22, 2019)Document1 pageFrusa, Jasmine Liezet S. BSN 2-2 CWTS (Sept. 22, 2019)jl frusaNo ratings yet
- Symph A To Mimetic SDocument27 pagesSymph A To Mimetic Sjl frusaNo ratings yet
- CHN FNCPDocument8 pagesCHN FNCPjl frusaNo ratings yet
- Drugs of OphthalmologyDocument9 pagesDrugs of OphthalmologyPutri KartiniNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Patient Medication Review: September 2003Document33 pagesA Guide To Patient Medication Review: September 2003Muhamad GunturNo ratings yet
- Pycnogenol Consumer/Patient Information SheetDocument1 pagePycnogenol Consumer/Patient Information SheetDeboraNainggolanNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Antara Ceftriaxone Dengan Infus RLDocument7 pagesReaksi Antara Ceftriaxone Dengan Infus RLNaila Nak'z FarmaziNo ratings yet
- Efficacy & Safety of Trad Plant MedicinesDocument41 pagesEfficacy & Safety of Trad Plant MedicinesBiol. Miguel Angel Gutiérrez DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Medical Biotechnology: A Resource Guide For Biotechnology Club SponsorsDocument39 pagesMedical Biotechnology: A Resource Guide For Biotechnology Club Sponsorsim_mogerzNo ratings yet
- Mccuistion: Pharmacology: A Patient-Centered Nursing Process Approach, 9Th EditionDocument3 pagesMccuistion: Pharmacology: A Patient-Centered Nursing Process Approach, 9Th EditionfaizaNo ratings yet
- Dorota Ceglinska ResumeDocument2 pagesDorota Ceglinska Resumeapi-329517148No ratings yet
- Template MEDDEV271Rev4 Clinical Evaluation ReportDocument15 pagesTemplate MEDDEV271Rev4 Clinical Evaluation Reportkrishna bhargavNo ratings yet
- Role of Pharmacogenomics in Drug Discovery and Development: Review ArticleDocument7 pagesRole of Pharmacogenomics in Drug Discovery and Development: Review ArticleDrishti MohleyNo ratings yet
- Use of Contrast Media in Diagnostic Imaging: Medico Legal ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesUse of Contrast Media in Diagnostic Imaging: Medico Legal Considerationscrisvbarros8865No ratings yet
- Toxicology in The Drug Discovery and Development Process: UNIT 10.3Document35 pagesToxicology in The Drug Discovery and Development Process: UNIT 10.3Nilabh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Research - HandbookDocument22 pagesClinical Research - HandbookRathi PriyaNo ratings yet
- 2016 01 Pengantar Farmasi KlinikDocument39 pages2016 01 Pengantar Farmasi KlinikDhearara W RizkyNo ratings yet
- Approach by Health Professionals To The Side Effects of Antihypertensive Therapy: Strategies For Improvement of AdherenceDocument10 pagesApproach by Health Professionals To The Side Effects of Antihypertensive Therapy: Strategies For Improvement of AdherenceSabrina JonesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Trials Flow ProcessDocument77 pagesClinical Trials Flow ProcessAnonymous Qr9nZRb100% (2)
- Drug StudiesDocument32 pagesDrug StudiesKelly ChanNo ratings yet
- ADR FormDocument1 pageADR Formultimate_2226252No ratings yet
- PharmacodynamicsDocument3 pagesPharmacodynamicsCha SahiddanNo ratings yet
- Safety of Magnesium Sulfate For Management of Severe Pre-Eclampsia and Eclampsia: A Practical Review of Research FindingsDocument15 pagesSafety of Magnesium Sulfate For Management of Severe Pre-Eclampsia and Eclampsia: A Practical Review of Research FindingsJhpiegoNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Care PlanDocument8 pagesSickle Cell Care Planoguitekim1No ratings yet
- Report On Suspected Adverse Drug ReactionsDocument2 pagesReport On Suspected Adverse Drug Reactionsyw100% (1)
- Solution 1Document3 pagesSolution 1mabarcauNo ratings yet
- 8Document244 pages8Marcovici AdrianNo ratings yet
- PSPTIS002 Build Glossaries For Translating and Interpreting AssignmentsDocument16 pagesPSPTIS002 Build Glossaries For Translating and Interpreting AssignmentsGRACENo ratings yet
- Drug Benefits and Risks - 2Document31 pagesDrug Benefits and Risks - 2David KonnehNo ratings yet