Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Minerals (Notes)
Minerals (Notes)
Uploaded by
Jalen Montefalco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pagesThis document discusses minerals and rocks. It defines minerals as naturally occurring inorganic solids with definite chemical compositions and atomic structures. It outlines 5 criteria that define a mineral and describes several techniques for identifying minerals based on characteristics like color, hardness, luster, streak, cleavage, and other properties. It also defines the three main types of rocks as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic; and provides examples to describe how each type forms.
Original Description:
Earth & Life Science - minerals
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses minerals and rocks. It defines minerals as naturally occurring inorganic solids with definite chemical compositions and atomic structures. It outlines 5 criteria that define a mineral and describes several techniques for identifying minerals based on characteristics like color, hardness, luster, streak, cleavage, and other properties. It also defines the three main types of rocks as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic; and provides examples to describe how each type forms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pagesMinerals (Notes)
Minerals (Notes)
Uploaded by
Jalen MontefalcoThis document discusses minerals and rocks. It defines minerals as naturally occurring inorganic solids with definite chemical compositions and atomic structures. It outlines 5 criteria that define a mineral and describes several techniques for identifying minerals based on characteristics like color, hardness, luster, streak, cleavage, and other properties. It also defines the three main types of rocks as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic; and provides examples to describe how each type forms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
MINERALS
- BUILDING BLOCKS OR ROCKS
2000 various of minerals
Minerals have quite few uses in our life
Ex. diamond
Fluorite - toothpaste
Talc - baby powder
What makes a mineral a mineral
5 criteria (snifs)
-solid
-naturally occurring (not man-made)
-inorganic (not living or made from living things)
-fixed chemical formula
-specific atomic arrangement
Mineral Color - not a reliable characteristic for identification
Testing hardness - (scratch the glass w/ mineral); scratch - hard
greater 5.5 , not - less than 5.5
Testing luster - how light reflects off of a surface of a mineral;
metallic or non metallic
Testing breakage - hardest property to identify
Fracture - mineral breaks randomly
Cleavage - minerals break predictably
Testing streak - color of a mineral as a powder (use ceramic tile
b&w; streak tiles)
Other characteristics:
Based on taste
Magnetism
Calcite - double refraction
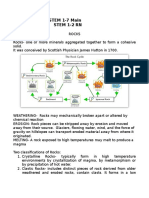
MINERALS AND ROCKS
A mineral is an inorganic, naturally occurring solid that has
definite chemical composition and atomic structure.
Mineral Characteristics
Color
Hardness
Luster
Streak
Cleavage/Fracture
Other (taste, magnetic)
Galena - metallic, very soft 2.5 hardness, silver grey black
streak , compose of lead and sulfur
Olivine - harder mineral fracture, non metallic jewelry
Minerals - building block of rocks
Igneous, sedimnetary, metamorphic
Igneous - cooling solidification of magma or lava
Extrusive (volcanic) - lava cool quickly (small crystal)
Ex. basalt, rhyolite, obsidian
Crystalline or vesicular
The longer the cooling time, the larger the crystal size
Intrusive (plutonic) - lava cool slowly (have large crystals)
Ex. granite, pegmatite
LIGHTER --------------- COLOR ------------- DARKER
LOWER ---------------- DENSITY ------------ HIGHER
FELSIC --------------- COMPOSITION -------MAFIC
(rich in Si, Al) (Iron, Mg)
Sedimentary - compaction and cementation of sediments
Clastic (fragmental)
Crystalline sedimentary rocks - halite dissolved in water
- formed from evaporation or precipitation of minerals in
water
Limestone - bioclastic (formed from the compaction)
METAMORPHIC
- rocks form from exposure to intense heat/or pressure
Foliated ex. gneiss, slate
Minerals alignment - as a result of intense pressure
Banding - under even greater pressure minerals separate
into dark and light stripes called bands
Non-foliated
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document73 pagesChapter 3DjayusmannugrahantoNo ratings yet
- RVWR Earth Science - W2L3-4Document3 pagesRVWR Earth Science - W2L3-4Gabrielle Mari Gratuito PerezNo ratings yet
- EarthLifeScience 2nd SessionDocument58 pagesEarthLifeScience 2nd SessionJohn Peter HuertaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of MineralsDocument34 pagesPhysical Properties of Mineralsjoshua.brussell100% (3)
- Minerals: Rock-Forming in Physical and Chemical Pro PertiesDocument71 pagesMinerals: Rock-Forming in Physical and Chemical Pro PertiesCastor, Mary GraceNo ratings yet
- 0004 Glge2a2 RocksDocument51 pages0004 Glge2a2 RocksAndile MavusoNo ratings yet
- Minerals: A Mineral Is A Naturally Occurring Inorganic Solid With DefiniteDocument32 pagesMinerals: A Mineral Is A Naturally Occurring Inorganic Solid With DefiniteAlipriya ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 2.1 - Minerals and RocksDocument58 pages2.1 - Minerals and RocksTerrence NeptunoNo ratings yet
- Magma: Marble Demo, Rock Specimens, Petrographic Microscope, Olivine Porphyry or GabbroDocument63 pagesMagma: Marble Demo, Rock Specimens, Petrographic Microscope, Olivine Porphyry or GabbroMuhajir_samNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Minerals and ResourcesDocument6 pagesEarth Science Minerals and ResourcesChristian Neri FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument33 pagesRocks and Mineralsjoshua.brussellNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science - HMS12Document24 pagesEarth Life Science - HMS12atienzanorrayneNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument85 pagesRocks and MineralsRowena LupacNo ratings yet
- Notes - MineralsDocument29 pagesNotes - Mineralsapi-243587006No ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument38 pagesRocks and MineralsJuliah PeñalosaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Classification of Igneous RockDocument11 pages5.2 Classification of Igneous RockEDGAR ALEXANDER YATACO ZAMUDIONo ratings yet
- Minerals and RocksDocument37 pagesMinerals and RocksNadz mooreNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Stem 2Document11 pagesEarth Science Stem 2EleanorNo ratings yet
- ES Chapter 2 - Rocks and MineralsDocument50 pagesES Chapter 2 - Rocks and MineralsDiane Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ROCKS ... and How To Identify ThemDocument52 pagesROCKS ... and How To Identify Themvasu7900100% (1)
- Rock & MineralsDocument32 pagesRock & MineralsKathleen Kaye Delos AngelesNo ratings yet
- Igneous Rocks AlternateDocument81 pagesIgneous Rocks AlternateMeldred Manalon100% (1)
- SciencereviewmineralsDocument5 pagesSciencereviewmineralsapi-281100019No ratings yet
- Soil MineralsDocument27 pagesSoil MineralsSumi SubiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2. Soil-Forming Rocks and MineralsDocument58 pagesExercise 2. Soil-Forming Rocks and MineralsJacky Lou GermanoNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument40 pagesMineralsrommel nebrijaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 - Minerals and RocksDocument25 pages2.1 - Minerals and RocksAce CardenoNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCI REVIEWER Q1S2 (John Patrick Pagauitan)Document6 pagesEARTH SCI REVIEWER Q1S2 (John Patrick Pagauitan)timothybadiola99No ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument78 pagesRocks and MineralsAndria EspejoNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument47 pagesRocks and MineralsRoxette Rosete100% (3)
- Applied Geology Lab ManualDocument22 pagesApplied Geology Lab ManualkoloshrabeaaNo ratings yet
- Minerals, Rocks, and Mineral ResourcesDocument55 pagesMinerals, Rocks, and Mineral ResourcesClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Stone and Concrete MasonryDocument80 pagesStone and Concrete MasonryMaria VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 Igneous Rocks UDocument50 pagesLecture 03 Igneous Rocks UCarlos Manuel Changanaqui PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- Ayoko Na PoDocument5 pagesAyoko Na PoAaron Cereneo SibunalNo ratings yet
- Minerals - RocksDocument52 pagesMinerals - Rocksleann.paguio.03No ratings yet
- 2020 BUILDING TECHNOLOGY 1 Module 1 Lecture 2a - Stone and Concrete MasonryDocument41 pages2020 BUILDING TECHNOLOGY 1 Module 1 Lecture 2a - Stone and Concrete Masonrylia immie rigoNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals: Focus QuestionsDocument45 pagesRocks and Minerals: Focus QuestionsWilfredo Martinez CruzNo ratings yet
- 3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYDocument40 pages3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYFARAH HIDAYAHNo ratings yet
- Rock Mineral IntroDocument27 pagesRock Mineral IntroCharles BualeNo ratings yet
- Minerals and RocksDocument30 pagesMinerals and RocksAngelica SeñaNo ratings yet
- Rock MineralsDocument7 pagesRock MineralsChristy RowmanNo ratings yet
- G8 Q4 Rocks and MineralsDocument49 pagesG8 Q4 Rocks and MineralsLocal ClownNo ratings yet
- 4 - Rock Cycle & Igneous Rocks (B)Document13 pages4 - Rock Cycle & Igneous Rocks (B)Saad AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Examining Minerals and RocksDocument27 pagesExamining Minerals and RocksminingnovaNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument41 pagesMineralsalbert pontusNo ratings yet
- Earth S Materials and Resources-1Document83 pagesEarth S Materials and Resources-1Carlos TuazonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Sequence Di - Rocks and Mineral PropertiesDocument74 pagesLesson Sequence Di - Rocks and Mineral Propertiesapi-573363616No ratings yet
- Minerals and RocksDocument24 pagesMinerals and Rocksmusic loverNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument40 pagesMineralsGhillian Mae GuiangNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and Processes Part 1Document25 pagesEarth Materials and Processes Part 1Glyneth Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Little Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksFrom EverandLittle Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Best LGU in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesBest LGU in The PhilippinesJalen MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Importance of SolidarityDocument1 pageImportance of SolidarityJalen MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Having Numerous Holidays in The Country To The Work IndustryDocument1 pageImpact of Having Numerous Holidays in The Country To The Work IndustryJalen MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms BookkeepingDocument6 pagesDefinition of Terms BookkeepingJalen MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Taking A Step Out of My Comfort ZoneDocument3 pagesTaking A Step Out of My Comfort ZoneJalen MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Bone StrengtheningDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Bone StrengtheningJalen MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- 21st Literary AuthorsDocument10 pages21st Literary AuthorsJalen MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Jennifer Doudna MonologueDocument2 pagesJennifer Doudna MonologueJalen MontefalcoNo ratings yet