Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GUIDE DEVELOPMENT # 1 Workshop Entry Conducts
GUIDE DEVELOPMENT # 1 Workshop Entry Conducts
Uploaded by
Brayan AgudeloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GUIDE DEVELOPMENT # 1 Workshop Entry Conducts
GUIDE DEVELOPMENT # 1 Workshop Entry Conducts
Uploaded by
Brayan AgudeloCopyright:
Available Formats
GUIDE DEVELOPMENT # 1 workshop
ENTRY CONDUCTS
STUDENTS : linda mosquera 130004019
laura humoa
angelica mantilla
Cristian valencia
Karoline
OBJETIVES
Strengthen the skills acquired in previous semesters related to Sexual and
Reproductive Health.
METODOLOGY
Develop guidance workshop and upload it to the platform in the time required.
CONTENT
1. As for the functions of the various reproductive organs, complete the following
table below.
ORGAN FUNCTION(S)
PROSTATE
UTERO
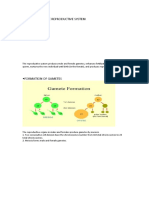
2. What is the purpose of gametogenesis?
3. The chromosomes in females sex are distributed as follows:
(#)_______ Autosomes and (#) ______ sex chromosomes
4. Describe the features and functions:
Amniotic fluid Placenta
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 5 TO 8 MUST BE JUSTIFIED.
5. Semen or seminal fluid is composed of synthesized secretions by
A. Seminal vesicles.
B. Prostate.
C. Bulbourethral glands.
D. All of the above.
6. What are the ovarian hormones produced by the follicle Graff and yellow body
cells?
A. Progesterone and gonadotropin.
B. Estrogen and progesterone.
C. Gonadotropin and follicle stimulating hormone.
D. Estrogen and follicle stimulating hormone.
7. The only direct connection between the fetus and any structure, is the umbilical
cord. Which of the following components contain?
A. An artery and a vein
B. Two arteries and a vein
C. A vein and Wharton jelly
D. Two veins and a Wharton artery
8. What is the role of the epididymis?
A. Sperm formation.
B. Secretion of part of the seminal fluid.
C. Testosterone ejaculation during coition.
D. Storage of sperm.
RTA:
D. Sperm storage.
The epididymis has the function of receiving and storing sperm produced by the
testicles. The epididymis is divided into three parts:
The head: receives the sperm from the testicles to store them.
The body: is where sperm maturation occurs.
The tail: the mature sperm accumulate in the tail of the epididymis, waiting to be
thrown next to the sperm or phagocytes.
9. Progesterone is produced in the ovary: through the body luteo, during the phase
of the menstrual cycle: lutea phase of the uterus, prepares the uterus if an embryo
is implanted, causes the endometrium to thicken and accumulate fluid and nutrients
to feed a possible embryo
10. Providing nutrients to support sperm metabolism, it is a function of fluid secreted
by:
Sertoli cells provide them with nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins
and minerals), in addition to secreting specific factors necessary for their survival
and development.
11. Describe the ovarian cycle. :
The process of formation of the ovules, the ovogenesis develops inside the follicles
of the ovary before the birth of the female being, in the proliferation phase the germ
cells multiply by mitosis and originate ovogonias cells of 46 chromosomes.
During the phase of growth, ovogonias increase in size, transform into first-order
oocytes, surround themselves with follicular cells and give rise to primordial follicles
that paralyze their activity,
These primary oocytes remain preserved without activity until the woman reaches
puberty and restarts in the process; the oocytes are first divided by meiosis and
become cells with 26 chromosomes releasing a polar corpuscle.
In the next division, the oocyte releases another corpuscle and the ovule is
transformed. This is when the follicle breaks and the ovum leaves the ovary.
Ovulation Process stimulated by the sharp increase in LH, consists in the rupture of
the follicular wall and the discharge of the oocyte, which restarts the meiotic division.
The differentiation of teak and granulosa cells to luteal cells also occurs.
Luteogenesis It implies a morphological change of the cells and a remodeling in the
enzymatic systems involved in steroidogenesis that allows the synthesis and
secretion of progesterone. There is a local angiogenesis process due to the great
Metabolic demand of these cells and the disappearance of the basement membrane,
which leads to vascular invasion of the granulose. Unless embryonic signals appear
in the maternal circulation, a regressive process begins between the 8th and 10th
after postovulation, which leads to a decrease in the amount of circulating cells and
hormones, which ultimately leads to menstruation.
12. Describe the uterine or hemorrhage cycle:
If implantation does not occur, no There is hGC, the body wrestling is not sustained
for a long time and decreases the E2 and the Progesterone. This decrease induces
a increase in FSH that begins to recruit follicles for the next cycle w Mention appears
because progesterone levels drop to those required to maintain the secretory
endometrium
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Brainly https://brainly.lat/tarea/4375921
2. Celula sertoli https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/C%C3%A9lula_de_Sertoli
3. MANUAL MSD Versión para público
generalhttps://www.msdmanuals.com/es-co/hogar/salud-
femenina/biolog%C3%ADa-del-aparato-reproductor-femenino/ciclo-
menstrual
4. Centro de Reproducción Humana y Planificación Familiar DR. CESAR LUIS
BERTAhttps://www.gfmer.ch/Educacion_medica_Es/Pdf/Ciclo_menstrual.pd
f
5. Miguel hermandes, universitas http://las-hormonas.blogspot.com/2013/12/la-
fabrica-de-espermatozoides.html
You might also like
- Preclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- End of Course Assessment Review PracticeDocument194 pagesEnd of Course Assessment Review PracticeyoniNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Answer KeyDocument7 pagesReproductive System Answer Keyapi-209542414No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionTheLost GuyNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionDocument17 pagesImportant Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionYuvraj MehtaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproductionjiya jainNo ratings yet
- Biology Class-12 Chapter-3Document9 pagesBiology Class-12 Chapter-3mokanrajan141106No ratings yet
- LAS 3rd Quarter FINALDocument58 pagesLAS 3rd Quarter FINALJustine Emilia100% (1)
- Ran Ii - Reproductive - 083648Document17 pagesRan Ii - Reproductive - 083648joykibaki066No ratings yet
- Marks Wise Questions CH-2Document22 pagesMarks Wise Questions CH-2lakshshah5116No ratings yet
- XII Bio Chp-3 Ques-AnsDocument7 pagesXII Bio Chp-3 Ques-Ans3humika24No ratings yet
- LN 3 - Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesLN 3 - Human ReproductionZara KNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument32 pagesFertilizationAngel Joshua PauliteNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan (The Roles of Hormoes)Document8 pagesLesson Plan (The Roles of Hormoes)Marie Cris CabrillosNo ratings yet
- Female Reproduction Female Reproductive Parts and Functions II. Oogenesis and OvulationDocument4 pagesFemale Reproduction Female Reproductive Parts and Functions II. Oogenesis and OvulationLana GalloNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet (Las) : Department of EducationDocument15 pagesLearning Activity Sheet (Las) : Department of EducationJoeffrie G. Costales100% (1)
- Q & A Notebook Chap 03Document13 pagesQ & A Notebook Chap 03umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 - Module 1 For EditedDocument14 pagesScience 10 Q3 - Module 1 For Editedtaylorsheesh64No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Exercises Reproduction SolutionDocument10 pagesUnit 5 Exercises Reproduction SolutionxdryzzyNo ratings yet
- Atg Quiz PresentperfectDocument30 pagesAtg Quiz PresentperfectfirstclassNo ratings yet
- Cabalan - Sas-Lecture #23Document8 pagesCabalan - Sas-Lecture #23kierstyn cabalanNo ratings yet
- PPT1 BioDocument53 pagesPPT1 BioRalph NilloNo ratings yet
- Repro Q N A PDFDocument8 pagesRepro Q N A PDFtrust zimunyaNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 7 For Students PDFDocument118 pagesMod 2 7 For Students PDFpetergomez0119No ratings yet
- Unit 12Document45 pagesUnit 12saurin.tailor425No ratings yet
- 3rd QTR Multiple Choice Work Sheet BIO X LearnersDocument11 pages3rd QTR Multiple Choice Work Sheet BIO X LearnersIan DibNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Biology - Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesClass 12 - Biology - Human ReproductionAstha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument3 pagesA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceI AM ANONYMOUSNo ratings yet
- Makalah Ingris SindyDocument16 pagesMakalah Ingris SindyRatna SusantiNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentvetsahidulNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual CycleDocument26 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual CycleViktor InocNo ratings yet
- Third Departmental Test G10Document4 pagesThird Departmental Test G10joy grace jaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Human Reproductionlavishbhati691No ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 M1 W2Document6 pagesScience10 Q3 M1 W2Chris John SantosNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science 10 Module 2Document19 pagesQ3 Science 10 Module 2Rizalyn Patalinghug50% (2)
- Nur 194 Sas 2Document2 pagesNur 194 Sas 2Orange AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Biology M13 Human Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesBiology M13 Human Reproductive SystemEunice CorreaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 To 7Document35 pagesLesson 4 To 7Macario estarjerasNo ratings yet
- Q3-DLL Week 2Document5 pagesQ3-DLL Week 2Jun Dadiahon AlindayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Human Reproduction: 1. Draw A Neat Labelled Diagram of Male Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesChapter-3: Human Reproduction: 1. Draw A Neat Labelled Diagram of Male Reproductive SystemSanaullah M SultanpurNo ratings yet
- Day 3Document9 pagesDay 3Kinberly AnnNo ratings yet
- Hormones and ReproductionDocument4 pagesHormones and ReproductionJNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AssignmentDocument58 pagesAnatomy AssignmentChonnetteAshlynKingNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions-Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesNcert Solutions-Human ReproductionSHAIKH YUNUS ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Reproduction (2019) Notes:: Provided by Yvonne HodgsonDocument14 pagesPhysiology of Reproduction (2019) Notes:: Provided by Yvonne HodgsonBảoChâuNo ratings yet
- Answer - PASS Worksheet Week 7Document4 pagesAnswer - PASS Worksheet Week 7Juan Manuel MairnNo ratings yet
- Science 10: Prepared By: Jergen A. Romulo Sst-IiiDocument8 pagesScience 10: Prepared By: Jergen A. Romulo Sst-IiiRona May EsperanzateNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 43Document5 pagesLab Exercise 43BEBE BEBENo ratings yet
- CH - 3 - Ncert SolutionsDocument6 pagesCH - 3 - Ncert SolutionsJanani VijayarajNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SDocument15 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SSrajanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam Science 10Document5 pages3rd Quarter Exam Science 10ROMELYN GRACE BORBENo ratings yet
- Q3 Science 10 Module 2 - NK4ADocument17 pagesQ3 Science 10 Module 2 - NK4ALyzhafel AlingalanNo ratings yet
- Nzary El 3maliDocument13 pagesNzary El 3maliGana KhaledNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYSIODocument5 pagesANAPHYSIOCarol Lopez DauagNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 2Document16 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 2Fernadez Rodison100% (3)
- Bio Investment BankingDocument10 pagesBio Investment BankingGoutham shetty MNo ratings yet
- 2024 GRADE 12 Notes Term 1Document32 pages2024 GRADE 12 Notes Term 1simwingaelvis37No ratings yet
- Chapter 9/MCQ/Answer SchemeDocument9 pagesChapter 9/MCQ/Answer SchemeALIAH AYUNI AIMAN BINTI MOHAMED NIZAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-3Document4 pagesSci.10 Weeks 1-3Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Wella S, VIRINA Bsn-I: Review Question Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesWella S, VIRINA Bsn-I: Review Question Reproductive SystemEllee HadesNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet
- B&S2011catalog VprintDocument179 pagesB&S2011catalog Vprinttammy_detrich100% (1)
- NBME 15 QuizletDocument12 pagesNBME 15 Quizletrmelendez00192% (12)
- Locomotion and Movement: SolutionsDocument11 pagesLocomotion and Movement: SolutionsEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- IridologyDocument6 pagesIridologyIonel-florin HritcuNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 1Document4 pagesActivity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 1dinnes masubay100% (3)
- Yogic Sukshma Vyayama CompressDocument60 pagesYogic Sukshma Vyayama CompressSyeda Shahida SultanaNo ratings yet
- History of BrainDocument3 pagesHistory of BrainMaria TountaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Palpation Lesson PDFDocument12 pagesPregnancy and Palpation Lesson PDFGyanesh VermaNo ratings yet
- 11444.muscle Injuries in Sport Medicine by Gian Nicola BisciottiDocument331 pages11444.muscle Injuries in Sport Medicine by Gian Nicola BisciottiPaisan Ngerndee100% (1)
- A Case Study of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVD) : School of Nursing and MidwiferyDocument13 pagesA Case Study of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVD) : School of Nursing and Midwiferyhsiria100% (2)
- Lesson Plan No 3Document5 pagesLesson Plan No 3hafeez ahmed100% (1)
- Unit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleDocument76 pagesUnit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleBAYAN NADER YOSRI JABARI 22010404No ratings yet
- LO Week 5 Tutorial 2Document7 pagesLO Week 5 Tutorial 2Hizkia MarlissaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Presentation - Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base BalanceDocument16 pagesLecture Presentation - Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base Balancehendra_darmawan_4100% (2)
- Module 7 ProjectDocument30 pagesModule 7 ProjectLeena KamranNo ratings yet
- Cell ActivityDocument1 pageCell ActivitySheryl BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Sistem Perkemihan: Indargairi Universitas Mega RezkyDocument46 pagesSistem Perkemihan: Indargairi Universitas Mega RezkyMaria GabrielaNo ratings yet
- MS Etiology & PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesMS Etiology & PathophysiologyZgama AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- RH System PPDocument38 pagesRH System PPتجربة أولىNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies of The Kidney and The Urinary Tract: Dr. Işın Doğan Ekici PathologyDocument27 pagesCongenital Anomalies of The Kidney and The Urinary Tract: Dr. Işın Doğan Ekici PathologyRobbertNo ratings yet
- P.E 101 Mod. 1 First Sem PDFDocument14 pagesP.E 101 Mod. 1 First Sem PDFabcdNo ratings yet
- Muscle Spindle by CKDocument23 pagesMuscle Spindle by CKChaman Lal KarotiaNo ratings yet
- Clasification of Odontogenic Tumours A ReviewDocument6 pagesClasification of Odontogenic Tumours A ReviewJuan Carlos MeloNo ratings yet
- Pharyngitis 2Document16 pagesPharyngitis 2Reisabelle LabianoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Week 1 - Lesson 1 (Autosaved)Document31 pagesQuarter 2 - Week 1 - Lesson 1 (Autosaved)Glen Grace GorgonioNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell ProjectDocument23 pagesStem Cell ProjectTD Harini0% (1)
- Icell Activity: Part One: Animal Cell Organelle FunctionDocument6 pagesIcell Activity: Part One: Animal Cell Organelle FunctionDanielle ruffNo ratings yet
- Langer1985 Sub Epithelial Connective Tissue GraftDocument6 pagesLanger1985 Sub Epithelial Connective Tissue GraftAna Maria Montoya GomezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy at A GlanceDocument327 pagesAnatomy at A GlanceANo ratings yet