Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: Brillian Nala Chandra Divella NIM: 18930068/PHARMACY C
Name: Brillian Nala Chandra Divella NIM: 18930068/PHARMACY C
Uploaded by
cantika berlianOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Brillian Nala Chandra Divella NIM: 18930068/PHARMACY C
Name: Brillian Nala Chandra Divella NIM: 18930068/PHARMACY C
Uploaded by
cantika berlianCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: BRILLIAN NALA CHANDRA DIVELLA
NIM: 18930068/PHARMACY C
Basic Chemistry “Ion Bonding”
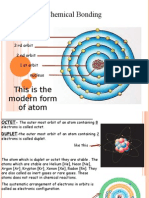
Ionic bonds are bonds that occur because of the transfer of electrons from one atom to
another (James E. Brady, 1990). Ionic bonds are formed between the atoms that release
electrons (metals) and atoms that accept electrons (not metals). Metal atoms, after releasing
electrons, turn into positive ions. The ions opposite the charge occur attraction (electrostatic
forces) called ionic bonds (electrovalent bonds). Compounds that have ionic bonds are called
ionic compounds. Ionic compounds are usually formed between metal atoms and non-metal
elements.
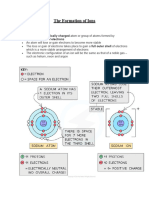
Example of the process of forming ionic bonds through the formation of NaCl.
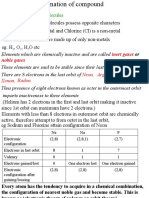
Sodium (Na) has an electron configuration (2,8,1) will become stable if it releases 1 electron
so that the electron configuration changes to (2.8). While Chlorine (Cl), has a configuration
(2,8,7), it becomes stable if it receives 1 electron so the configuration becomes (2,8,8). So
both of them become stable if sodium accounts for one electron and chlorine gets one
electron from sodium. When transferring electrons, (Na will be positively charged (Na +) and
Cl will be negatively charged (Cl-). Then there is an electronegative force between Na + and
Cl- making an ionic bond.
Ion bonds have several characteristics, including:
1. a common ionic bond between metals and non-metals.
2. Naming the ionic bond, the name of the metal always comes first and the name of the non-
metal comes second. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium is a metal while chlorine
is a non-metal.
3. Ionic bonds dissolve easily in water and some other polar solvents.
4. the benefits to conduct electricity.
You might also like
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Chemical BondingDe AktivedNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument59 pagesChemical BondingBbg FeeruwuNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument3 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazmatshahzad786786No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding - Compounds and PropertiesDocument21 pagesIonic Bonding - Compounds and PropertiesJawaid IqbalNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.Document34 pagesIonic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.allenbrien077No ratings yet
- Introduction To BondingDocument9 pagesIntroduction To BondingTheonie DavisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry NotesfezthebombNo ratings yet
- Atoms Unite To From Molecules: Inert Gases Noble GasesDocument6 pagesAtoms Unite To From Molecules: Inert Gases Noble GasesIMPACTTutorials Mathematics and ScienceNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Bonding in SolidsDocument14 pagesPresentation of Bonding in SolidsRohit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Chemical CombinationDocument4 pagesChemical CombinationGodspower OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision Notes-LibreDocument17 pagesChemistry Revision Notes-LibreShridhar MathadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Hu-1Document59 pagesCHAPTER 2 Hu-1Lelo DEMENo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument44 pagesChemical Bondingjas_ong_man_ling1996No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Notes 2Document32 pagesChemical Bonding Notes 2arun iyer BitcoinminerandmathematicianNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Chemical BondsDocument23 pagesModule 5 Chemical BondsAjay WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-NotesDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding-NotesHimanshu Meena100% (3)
- Chemical BondingDocument1 pageChemical Bondingramghotra77No ratings yet
- Primary Bonds: Chemical BondDocument1 pagePrimary Bonds: Chemical BondDhanushka WarnakulasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Prepared By: Asuda Taha Mhamad Mahdi Helin Salh Miran Bakr Zhwan OmarDocument24 pagesChemical Bonding: Prepared By: Asuda Taha Mhamad Mahdi Helin Salh Miran Bakr Zhwan OmarLana OmarNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocument10 pagesBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5Hina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Types of Chemical BondsDocument12 pages4.1 Types of Chemical BondsNeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 2 G - 11 NoteDocument17 pagesUNIT - 2 G - 11 Notely8623013No ratings yet
- CH No 3Document22 pagesCH No 3Ultimate chemistryNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PHY 351Document14 pagesTutorial 1 PHY 351MUHAMMAD AMMIRUL HAFIZ MD ZAININo ratings yet
- Y10B (AP) Bonding 2022Document41 pagesY10B (AP) Bonding 2022Mulki MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table (PT) : O-LevelDocument23 pagesThe Periodic Table (PT) : O-Levelleticia karungiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document104 pagesUnit 73U30CHRISTINA CHI YEE WONGNo ratings yet
- Pert 13 Gaya IntermolekulerDocument138 pagesPert 13 Gaya IntermolekulerNatasyaxoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Chemical Bond Stability of Noble GasesDocument20 pagesChapter 5: Chemical Bond Stability of Noble GasesLuna LatisyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry: Chapter OutlineDocument68 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry: Chapter OutlineMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument5 pagesChemical Bondscharshadali2004No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument12 pagesChemical BondingdharanicrrNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chemistry Chapter 5Document37 pagesForm 4 Chemistry Chapter 5SF CHENGNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 3A1 NotesDocument9 pagesIonic Bonding 3A1 NotesmunasheNo ratings yet
- Fbise Chapter 4 (I)Document7 pagesFbise Chapter 4 (I)Zarish ZubairNo ratings yet
- 10 ChemDocument5 pages10 ChemSachin GargNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Solids: RK ChowdaryDocument27 pagesThe Structure of Solids: RK Chowdaryrkchowdary007No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 9th Class Long QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 4 9th Class Long Questionssomerakhan2023No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (1) AS1C6Document29 pagesChemical Bonding (1) AS1C6tzeina578No ratings yet
- Class 10 Concise Chemistry Chemical Bonding SolutionsDocument30 pagesClass 10 Concise Chemistry Chemical Bonding SolutionsPIYUSH DikshitNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563No ratings yet
- What Is The Atomic NumberDocument31 pagesWhat Is The Atomic NumberMennatallah Mohamed HamedNo ratings yet
- Science Test 2nd QuarterDocument8 pagesScience Test 2nd QuarterAbbychel AlmarioNo ratings yet
- CH No 3Document22 pagesCH No 3Ultimate chemistryNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondsDocument4 pagesAtomic Bondsfatiman333333No ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- GCFGCGCFGFDGDocument15 pagesGCFGCGCFGFDGZabrinaRuizNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document42 pagesUnit 2Muktaar HassenNo ratings yet
- 03 BondingDocument22 pages03 BondingafshinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding - Occurs When Two or More Ions Combine To Form An Electrically-NeutralDocument28 pagesChemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding - Occurs When Two or More Ions Combine To Form An Electrically-NeutralananntsharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocument6 pagesChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding PDFDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding PDFqadir7863574No ratings yet
- The Ionic Bond: How Sodium and Chlorine Atoms Bond TogetherDocument1 pageThe Ionic Bond: How Sodium and Chlorine Atoms Bond TogetherAshrafNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument2 pagesChemistry-Ionic and Covalent Bondingifaitchwould2No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Is A Type ofDocument5 pagesIonic Bonding Is A Type ofNadya IkaNo ratings yet
- Tema 7 - Enlace MetalicoDocument39 pagesTema 7 - Enlace MetalicoLuchinPozo100% (2)
- Bonds in SolidsDocument729 pagesBonds in Solids1553No ratings yet