Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Water We Drink
The Water We Drink
Uploaded by
Chris0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pageChemical engineers treat water to make it safe for drinking. They place water in a settling basin and treat it with slaked lime and aluminum sulfate, which forms a gelatinous mass that carries down dirt particles and bacteria to purify the water. Many communities add fluoride to their water between 0.7 to 1.0 ppm, which can significantly reduce tooth decay in children. Some smaller communities obtain water from wells, but may have contamination issues if the groundwater contains nitrates above the maximum safe level of 1.0 ppm from agricultural fertilizers or organic wastes.
Original Description:
Texto para interpretação.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChemical engineers treat water to make it safe for drinking. They place water in a settling basin and treat it with slaked lime and aluminum sulfate, which forms a gelatinous mass that carries down dirt particles and bacteria to purify the water. Many communities add fluoride to their water between 0.7 to 1.0 ppm, which can significantly reduce tooth decay in children. Some smaller communities obtain water from wells, but may have contamination issues if the groundwater contains nitrates above the maximum safe level of 1.0 ppm from agricultural fertilizers or organic wastes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pageThe Water We Drink
The Water We Drink
Uploaded by
ChrisChemical engineers treat water to make it safe for drinking. They place water in a settling basin and treat it with slaked lime and aluminum sulfate, which forms a gelatinous mass that carries down dirt particles and bacteria to purify the water. Many communities add fluoride to their water between 0.7 to 1.0 ppm, which can significantly reduce tooth decay in children. Some smaller communities obtain water from wells, but may have contamination issues if the groundwater contains nitrates above the maximum safe level of 1.0 ppm from agricultural fertilizers or organic wastes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
ATIVIDADE INGLÊS – FAVOR NÃO ESCREVER NA FOLHA.
THE WATER WE DRINK
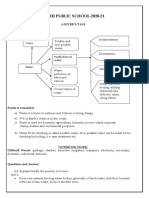
The water we drink usually comes from reservoirs, lakes, or rivers. A large number of cities uses river
water and dumps it back into the river. Sometimes another city downstream uses the same water. This water
may be badly polluted with chemicals and pathogenic bacteria. Many different chemical treatments are
necessary to make it safe and palatable.
Chemical engineers usually place the water into a settling basin to purify it. Then, they treat it with
slaked lime and aluminum sulfate. The chemical reaction of these elements forms a gelatinous mass. This
mass carries down dirt particles and bacteria.
Many communities add some form of fluoride to their water. Fluoride in concentrations of 0.7 to 1.0
ppm (parts per million) can significantly reduce tooth decay in children.
Some communities, usually the smaller ones, obtain water from wells. Even they have problems
because sometimes the ground water is contaminated. In some parts of the country the contamination of
nitrates in well water is above the maximum safe level of 1.0 ppm. These nitrates come from agricultural
fertilizers and from the decomposition of organic wastes.
What can we do? We can fight for clear water and convince our neighbors to do the same. We can
demand an end to water pollution by industries and cities. And finally, we must know how to use the water of
the earth because that is all we have.
VOCABULARY
dumps: despeja dowstream: rio abaixo , corrente abaixo
badly: mal; muito (sentido negativo, de coisa ruim) fluorine: flúor nitrate; nitrato
smaller: menores wells; poços
demand: exigência tooth decay; carie nos dentes
place the water into a settling basin: colocar a água em uma bacia de decantação
COMPREHENSION
A. Choose the correct alternative.
1. Aluminum sulfate reacts with: 2. A gelatinous mass:
a) ( ) a gelatinous mass. a) ( ) reduces tooth decay.
b) ( ) bacteria. b) ( ) purifies the settling basing.
c) ( ) slaked lime. c) ( ) contaminates ground water.
d) ( ) nitrates. d) ( ) carries down dirt particles and bacteria.
3. We obtain safe and palatable water: 4. We can:
a) ( ) from wells. a) ( ) demand an end to water pollution.
b) ( ) after chemical treatments. b) ( ) stop the decomposition of organic wasters.
c) ( ) from lakes. c) ( ) use river water.
d) ( ) from agricultural fertilizers. d) ( ) convince our neighbors to use fluoride.
5. Some small communities:
a) ( ) obtain nitrates from wells.
b) ( ) have purified well water.
c) ( ) also have problems with their water.
d) ( ) obtain agricultural fertilizers from nitrates.
B. Write T for True and F for False:
1. Nitrates pollute the water. ( )
2. People dump purified water into the river. ( )
3. We drink water from reservoirs. ( )
4. Fertilizers purify the water. ( )
5. Chemical reactions carry bacteria into a settling basing. ( )
6. Fluoride doesn't reduce tooth decay. ( )
7. The smaller communities obtain water from lakes. ( )
8. Many cities use river water. ( )
9. Chemical treatments are necessary to make water palatable. ( )
10. The maximum safe level of nitrate in water is 1.0 ppm. ( )
You might also like
- German Dwa Rules and Standards: Standard DWA-A 117EDocument6 pagesGerman Dwa Rules and Standards: Standard DWA-A 117EMehmet Emre Bastopcu100% (1)
- Plumbing Exam #2Document13 pagesPlumbing Exam #2Nestor Cantilang MalinaoNo ratings yet
- May 3 2021 Grand Forks Wastewater Treatment Facility PlanDocument22 pagesMay 3 2021 Grand Forks Wastewater Treatment Facility PlanJoe BowenNo ratings yet
- Atividade 8º - Inglês - Semana 22Document3 pagesAtividade 8º - Inglês - Semana 22Maria ClaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic: Wastewater TreatmentDocument7 pagesAssignment Topic: Wastewater TreatmentUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Water AssignDocument5 pagesWater AssignArka PramanikNo ratings yet
- Water Terms NotesDocument7 pagesWater Terms Notesyhalz mathyNo ratings yet
- SC Water PollutionDocument16 pagesSC Water Pollutionnor syazwani67% (3)
- Unit 4. Water Technology - 2022Document21 pagesUnit 4. Water Technology - 2022EeraúNo ratings yet
- Irreogatins Water Noteses ChapeteDocument12 pagesIrreogatins Water Noteses ChapetesreyrnNo ratings yet
- Scimich WQ TestDocument12 pagesScimich WQ TestShita AlemieNo ratings yet
- Effectof Aquatic Pollutionon Fish Fisheries 2Document17 pagesEffectof Aquatic Pollutionon Fish Fisheries 2Nusrat Jahan RiteNo ratings yet
- MOWR Media Fellowship Program: Lecture byDocument22 pagesMOWR Media Fellowship Program: Lecture bybudhnabamNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument24 pagesChemistryBushra Amir X-G-ANo ratings yet
- Environment 100 Important Questions 70Document28 pagesEnvironment 100 Important Questions 70Muhammad Ibrar Akbar Ali JanNo ratings yet
- MCQ Che541 Final Exam Fall 2019Document7 pagesMCQ Che541 Final Exam Fall 2019Mohamed ElbehlilNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment TechnologyDocument37 pagesWater Treatment TechnologyDeepak RajendarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The EnvironmentDocument14 pagesChemistry of The EnvironmentAyeyie Amankwah AndohNo ratings yet
- ZIMSEC O Level Combined Science Question Paper For Environmental HealthDocument7 pagesZIMSEC O Level Combined Science Question Paper For Environmental Healthchristinah mutikaNo ratings yet
- Water Technology1Document4 pagesWater Technology1Tejas YadavNo ratings yet
- BCEN 213 Construction Tech - Water SupplyDocument4 pagesBCEN 213 Construction Tech - Water SupplyTamir AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document90 pagesUnit 1pthangarasu sctengNo ratings yet
- Class 6 WaterDocument7 pagesClass 6 WaterBranded HackerNo ratings yet
- Pemeliharaaan Kualiti AirDocument15 pagesPemeliharaaan Kualiti AirCaroline LawNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Engineering New Ocr FormatDocument41 pagesWater Supply Engineering New Ocr FormatIES-GATEWizNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document5 pagesTest 1AMAN THAKARNo ratings yet
- Heep 118Document6 pagesHeep 118dkclarkNo ratings yet
- Water (Ctca)Document47 pagesWater (Ctca)Tanvir HasnatNo ratings yet
- Water Technology Characteristics of Hard Water - Hardness, DO, TDS in WaterDocument38 pagesWater Technology Characteristics of Hard Water - Hardness, DO, TDS in Waternirbhay gandhiNo ratings yet
- APES Water Test AssignmentDocument7 pagesAPES Water Test AssignmentNelson OkunlolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 ChemistryDocument8 pagesGrade 11 ChemistryMarcusKlahnTokoeJr.No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Water (H O) : Impurities in Natured WaterDocument33 pagesUnit - 1 Water (H O) : Impurities in Natured WaterTejas ChavanNo ratings yet
- LP A Rivers Tale 1Document3 pagesLP A Rivers Tale 1Pramsu ShauryaNo ratings yet
- Activity On Water Pollution: P NP NP PDocument2 pagesActivity On Water Pollution: P NP NP PAmae LababitNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-06-11 at 7.27.50 AMDocument14 pagesScreenshot 2024-06-11 at 7.27.50 AMsddypofficeNo ratings yet
- Design Aspects of Drinking Water PlantDocument32 pagesDesign Aspects of Drinking Water PlantVenkatesh Kumar RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Industrial Discharge Pollutes WaterDocument3 pagesIndustrial Discharge Pollutes WatervarshavishuNo ratings yet
- AE Civil - Environmental Engineering - With Answer KeyDocument14 pagesAE Civil - Environmental Engineering - With Answer KeyVishnu Nandakumar100% (1)
- Water Pollution For Environmental ScienceDocument21 pagesWater Pollution For Environmental Scienceobaid kuraishyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 WaterDocument32 pagesModule 1 WatervamshiNo ratings yet
- Ee Mid-2 Quiz BitsDocument13 pagesEe Mid-2 Quiz Bitsa manikantaNo ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument53 pagesWater PollutionDileep1489No ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument40 pagesWater PollutionSurendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Water-Treatment Book PDFDocument42 pagesWater-Treatment Book PDFAARYAN 9No ratings yet
- Effect of Aqatic Pollution On Fish & FisheriesDocument15 pagesEffect of Aqatic Pollution On Fish & Fisheriesapi-380337193% (14)
- Natural Raw Water ImpuritiesDocument54 pagesNatural Raw Water ImpuritiesUnc StappyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Section 5Document8 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Section 5Cire OmalinNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii-Iv & V 26-02-2021Document94 pagesUnit Ii-Iv & V 26-02-2021vgangire3No ratings yet
- Water Pollution LectureDocument46 pagesWater Pollution LectureSohail AslamNo ratings yet
- Water Technology Notes - Unit 1Document38 pagesWater Technology Notes - Unit 1AdharshNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Chemistry - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Chemistry - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT I WaterDocument25 pagesUNIT I WaterYERIPINA SATEESH CHANDRA DEV 19-206100% (1)
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 7 Science Chapter 18Document13 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 7 Science Chapter 18Shaurya Maniktala100% (1)
- 2 WaterDocument28 pages2 WaterAli HarbNo ratings yet
- Artificial Kidneys of SoilDocument23 pagesArtificial Kidneys of SoilChithira P UNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii Water and Its TreatmentDocument110 pagesUnit-Iii Water and Its TreatmentDinesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 CHP 18Document3 pagesClass 7 CHP 18GiteshNo ratings yet
- Did Your Can of Soda Kill A Whale? Water Pollution for Kids | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandDid Your Can of Soda Kill A Whale? Water Pollution for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- Ativ Simple PresentDocument1 pageAtiv Simple PresentChrisNo ratings yet
- Aula 10 de Agosto EJADocument2 pagesAula 10 de Agosto EJAChrisNo ratings yet
- Exercícios Present Continuous 1Document2 pagesExercícios Present Continuous 1ChrisNo ratings yet
- 1º Atividade para Os 4º Anos - GABARITODocument3 pages1º Atividade para Os 4º Anos - GABARITOChrisNo ratings yet
- 1º Atividade para Os 2º AnosDocument5 pages1º Atividade para Os 2º AnosChrisNo ratings yet
- Historic Flooding in The Prut-Bârlad Catchments: Hydrology and Water ResourcesDocument9 pagesHistoric Flooding in The Prut-Bârlad Catchments: Hydrology and Water ResourcesIsabela BalanNo ratings yet
- Identifying Signs of Water NearbyDocument3 pagesIdentifying Signs of Water NearbyZerotheoryNo ratings yet
- Emeai SSF - Atkins Reigate Case StudyDocument8 pagesEmeai SSF - Atkins Reigate Case StudymaanurayaNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi AquadesDocument1 pageSpesifikasi AquadesasiapesonamutiaraNo ratings yet
- Partido State University: Camarines Sur College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument3 pagesPartido State University: Camarines Sur College of Engineering and TechnologyMoriel PradoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Water Resources Engineering: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Water Resources Engineering: Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpuranirban dasNo ratings yet
- SWTP Operation ManualDocument131 pagesSWTP Operation ManualKASHIFNo ratings yet
- Chapter - VII Infrastructure Water SupplyDocument25 pagesChapter - VII Infrastructure Water Supplydreamboy87No ratings yet
- DILG Memorandum Circular 2023 065 1 22 2024Document8 pagesDILG Memorandum Circular 2023 065 1 22 2024Aris R. AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Design of Swro PlantDocument10 pagesDesign of Swro PlantAbdelrahman MohamedNo ratings yet
- Types and Properties of WaterDocument4 pagesTypes and Properties of WaterQdlm KnocNo ratings yet
- Design Report On Sanitary Installation DesignDocument12 pagesDesign Report On Sanitary Installation DesignNatanNo ratings yet
- Dehoust Greywater Brochure - 2013Document12 pagesDehoust Greywater Brochure - 2013Danyal HaiderNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document26 pagesLecture 1Pee JayNo ratings yet
- Pagal. Jayson J. Bsce3-Ec (Ce 327)Document1 pagePagal. Jayson J. Bsce3-Ec (Ce 327)Jayson PagalNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Water UseDocument18 pagesSustainable Water UseGiorgio Louis BascoNo ratings yet
- Water MGT in HillDocument15 pagesWater MGT in HillIrfan HyderNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Water Treatment (Ceng 5403)Document1 pageAssignment 1: Water Treatment (Ceng 5403)አድሜ ልስልሱNo ratings yet
- UAE Cooling Tower Blow DownDocument3 pagesUAE Cooling Tower Blow DownRamkiNo ratings yet
- Ajol File Journals - 483 - Articles - 197647 - Submission - Proof - 197647 5701 497764 1 10 20200717Document8 pagesAjol File Journals - 483 - Articles - 197647 - Submission - Proof - 197647 5701 497764 1 10 20200717derrickclarke2990No ratings yet
- Final Report Vol3-River Basin StudyDocument159 pagesFinal Report Vol3-River Basin StudySorn SomolineNo ratings yet
- Water Resources: Edward D. SchroederDocument31 pagesWater Resources: Edward D. SchroederAdrian LozadaNo ratings yet
- National Register of Large Dams 2015Document207 pagesNational Register of Large Dams 2015Thapa S100% (1)
- Module 3Document8 pagesModule 3Xandra Patricia BarreraNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment From Flooding in The Rivers of AlbaniaDocument1 pageRisk Assessment From Flooding in The Rivers of AlbaniaMscAlbanNo ratings yet
- Development of Water Quality Index of Sindh River by Using Weighted Arithmetic Method at Dabra, M.P., IndiaDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Water Quality Index of Sindh River by Using Weighted Arithmetic Method at Dabra, M.P., IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Concept Note by BBAGROUPDocument4 pagesConcept Note by BBAGROUPTanmay ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Rishi Thariani PPT Earth ConversationDocument7 pagesRishi Thariani PPT Earth ConversationMayank VachherNo ratings yet