Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STPM 2014 Sem 1 Real
STPM 2014 Sem 1 Real
Uploaded by
evacuate clash0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
496 views2 pages1) Ammonia has weak intermolecular forces between its polar molecules, giving it a low boiling point despite its large molecular size.
2) The electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s22s22p3, with the 2p orbitals each filled with a single electron of parallel spin according to Hund's rule.
3) The reaction of 4-hexene is second order with respect to 4-hexene concentration. The rate constant was determined to be 0.040 mol-1dm3s-1 from the slope of a plot of 1/[4-hexene] versus time.
Original Description:
Tt
Original Title
Stpm 2014 Sem 1 Real
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Ammonia has weak intermolecular forces between its polar molecules, giving it a low boiling point despite its large molecular size.
2) The electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s22s22p3, with the 2p orbitals each filled with a single electron of parallel spin according to Hund's rule.
3) The reaction of 4-hexene is second order with respect to 4-hexene concentration. The rate constant was determined to be 0.040 mol-1dm3s-1 from the slope of a plot of 1/[4-hexene] versus time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
496 views2 pagesSTPM 2014 Sem 1 Real
STPM 2014 Sem 1 Real
Uploaded by
evacuate clash1) Ammonia has weak intermolecular forces between its polar molecules, giving it a low boiling point despite its large molecular size.
2) The electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s22s22p3, with the 2p orbitals each filled with a single electron of parallel spin according to Hund's rule.
3) The reaction of 4-hexene is second order with respect to 4-hexene concentration. The rate constant was determined to be 0.040 mol-1dm3s-1 from the slope of a plot of 1/[4-hexene] versus time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
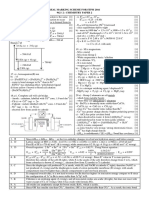
MARKING SCHEME
STPM SEMESTER 1 2013 / 14 962 / 1 (CHEMISTRY)
Section B and C
16 a) - Ammonia has attraction forces / polar molecules / hydrogen b) i. m1 : - Hund's rule : orbitals with the same energy levels are
bond / weak Van Der Waals forces / intermolecular forces [1] each filled with 1e- singly / parallel spins @ degenerate orbitals
- particle has volume / large molecular size / occupied space [1] with maximum number of parallel e- are more stable [1]
b) - low pressure ; high temperature [1] m2 : - electronic configuration X = 1s22s22p3 @ diagram [1]
c) - PV = nRT @ PV = mRT / MR [1] - 2px , 2py , 2pz must be filled with single e-/ parallel spin [1]
PM R m MR [1] ii. m1 : 2s [1] 2py 2pz 2px
ρ= / ρ= y y
m2 : shape [1]
RT V RT m3 : label 2px [1]
d) Total MR = 17.0 + 4.0 + 28.0 = 49.0 [1] x x
(1.01 × 105 )(49.0) [1] z z
ρ= (ins 49.0)
(8.31)(30 + 273)
In g dm-3 ; p = 1.97 g dm-3 (3 s.f.) [1] 19 a) i. m1 : - Electron pair repulse as far apart as possible. [1]
m2 : - lone-pair & lone-pair repulsion > lone-pair & bond-pair
17 a) Calculate 1/ [C4H6] and place in graph accordingly [1] repulsion > bond-pair & bond-pair repulsion [1]
Time / s 0 1000 1800 3000 4000 ii. Alt : (If CF2I+ ; m1 - 3 b.p.e ; m2 : trigonal planar ; m3 : 1200)
[C4H6] / 10-3 ClF2+ SF4
13.3 8.54 6.67 5.00 4.17
mol dm-3 Structure @
1/ [C4H6] / description [1] [1]
75.2 117 150 200 240
mol-1 dm3
Bond pair m1 : 2 b.p.e- / 1 l.p.e- m4 : 4 b.p.e- / 1 l.p.e-
b) Axis [1] (with unit) ; plotting points [1] ; linear plot [1] & Lone pair m2 : bent [1] m5 : see-saw [1]
300 Angle m3 : 104.5 ≤ x < 109.5 m6 : y < 1800
b) i. m1 : - MgCl2 has ionic bond / fix position / no mobile e- [1]
1/[C4H6] / mol-1 dm 3
250 m2 : - molten MgCl2 contain free mobile ions [1]
200 m3 : - Cu can delocalise e- in solid and molten state [1]
ii. m1 : - Ice has open lattice structure @ diagram contain 5 H2O [1]
150 m2 : - Ice occupied larger volume than water (or reverse) [1]
100 m3 : - when ice melt, the hydrogen bond broken [1]
m4 : - hence water molecule become closer / distance smaller [1]
50
0 20. a) * For m3 : KC is inverse of KC'
[ AB]2 [ A ][ B ] 1
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 m1 : K C = [1] m 2 : K 'C = 2 22 [1] m3 : K C = ' [1]
[ A 2 ][ B 2 ] [AB] Kc
time / s b) A + 2B ↔ 2C
Initial 1.0 / 2.0 1.5 / 2.0 0
c) i. second order [1] Changes - 0.35 / 2 - 0.35 + 0.35
ii. gradient = rate constant (ins gradient / k ) 0.5 - x @ 0.75 - 2x @ 0 + 2x
240 − 200 At eq. m1 : 0.325 [1] m2 : 0.40 [1] 0.35
k= [1] ; k = 0.040 mol −1dm 3s −1 [1]
4000 − 3000 [C]2 (0.35) 2
m3 : K C = [1] m4 : K C = [1]
iii. rate equation ; rate = k [C4H6]2 (follow through i. order) [1] [ A][B]2 (0.325)(0.40) 2
m5 : Kc = 2.4 mol-1 dm3 [1]
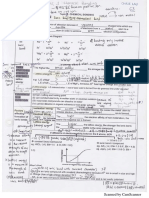
18. a) Energy (m1)
n=∞ b) ii. Using Van't Hoff equation [1]
n= 5 m1 : ∆H 1
ln K = +C
n= 4 R T1
m2 : K 2 ∆H 1 1 [1]
n= 3 ln = −
K1 R T1 T2
n= 2 m3 : K 2 − 20000 1 1 [1]
ln = −
2.4 8.31 1000 1300
n= 1 m4 : K2 = 1.4 mol-1 dm3 (accept : 1 mol-1 dm3) [1]
Lyman Series (m2) Balmer Series (m3)
* Show at least 1 electron transfer) iii. m1 : - Since forward reaction is exothermic,
m4 : energy level converge (become closer) m2 : - equilibrium shift to left [1]
ii. m1 : f = 3.00 x 108 / 121.6 x 10-9 [1] m2 : 2.47 x 1015 s-1 [1] m3 : - [C] decrease [1]
m3 : f = c / λ or ∆E = hf [1]
m4 : ∆E = 6.63 x 10-34 x 2.47 x 1015 s [1]
m5 : E = 1.64 x 10-18 J [1]
Alternative : ∆E = hf @ h c / λ [m1 + m2] (if only E = hf [m2])
(6.63 × 10 −34 ) (3.00 × 108 ) [ m3] m5 : E = 1.64 x 10-18 J [1]
∆E =
121.6 × 10 −9 [m 4]
You might also like
- Scissor Hydraulic Jack@Wachamo UniversityDocument49 pagesScissor Hydraulic Jack@Wachamo UniversityMuluken Filmon75% (4)
- STPM Past Year QuestionDocument34 pagesSTPM Past Year QuestionChris Ng Kien Siong100% (2)
- Introduction Coursework STPMDocument4 pagesIntroduction Coursework STPMSarath KumarNo ratings yet
- STPM 2023 SEM 2 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2023 SEM 2 Mock AnsHannah KaienNo ratings yet
- Chem Sem 1 SMK Taman Johor Jaya AnsDocument2 pagesChem Sem 1 SMK Taman Johor Jaya Ansevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- STPM 2016 Physics 1Document16 pagesSTPM 2016 Physics 1Abdul ShariffNo ratings yet
- STPM 2022 SEM 2 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2022 SEM 2 Mock Ansm-4306022No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3Viola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- 2021 STPM 954-P1 AnsDocument5 pages2021 STPM 954-P1 AnsPavitraNo ratings yet
- 2020 2 Joh Batu Pahat ADocument11 pages2020 2 Joh Batu Pahat AMohamad Afiq AnuarNo ratings yet
- STPM 2018 Sem 2 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2018 Sem 2 Mock Anstee hcNo ratings yet
- Ace Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5Document10 pagesAce Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5James OoiNo ratings yet
- Chem Sem 1 Percubaan SMK Pusat Bandar PuchongDocument12 pagesChem Sem 1 Percubaan SMK Pusat Bandar Puchongevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- Math Viva Sem 3Document21 pagesMath Viva Sem 3Xiangjun Woo50% (2)
- STPM 2019 Sem 2 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2019 Sem 2 Mock AnsNicholson NicholsonNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFChris LauNo ratings yet
- 2 Electrochemistry (Semester 2)Document49 pages2 Electrochemistry (Semester 2)Esther Ngieng100% (1)
- 1 3 0 X 2, 2 3 (3 X), 2 X 3, 0, OtherwiseDocument9 pages1 3 0 X 2, 2 3 (3 X), 2 X 3, 0, OtherwiseWendy LohNo ratings yet
- STPM 2013 Sem 1Document7 pagesSTPM 2013 Sem 1nurulNo ratings yet
- Real Marking Scheme For STPM 2016 962 / 2: Chemistry Paper 2Document2 pagesReal Marking Scheme For STPM 2016 962 / 2: Chemistry Paper 2PAVITRA A/P THEVINDRAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Biology Esei STPM 2017@ 2018Document43 pagesBiology Esei STPM 2017@ 2018Wei Yuen100% (1)
- SUGGESTED ANSWER STPM 2011 MATHEMATICS T Paper 2Document6 pagesSUGGESTED ANSWER STPM 2011 MATHEMATICS T Paper 2SKNo ratings yet
- Maths T Coursework PowerPoint 2017 (Vers. 2)Document38 pagesMaths T Coursework PowerPoint 2017 (Vers. 2)bendanNo ratings yet
- 2018 1 NS Spi Q&aDocument8 pages2018 1 NS Spi Q&aXue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- 06AAMathT FWS Chapter 06Document21 pages06AAMathT FWS Chapter 06Selina WongNo ratings yet
- Guide To STPM Pratical Ace Ahead Biology Third Term PDFDocument17 pagesGuide To STPM Pratical Ace Ahead Biology Third Term PDFViola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 2015Document4 pagesExperiment 1 2015UngHHNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Experiment 7 Wheatstone Bridge Second TermDocument2 pagesSTPM Physics Experiment 7 Wheatstone Bridge Second TermShapelessNo ratings yet
- STPM 2020 Sem 1Document9 pagesSTPM 2020 Sem 1fathin100% (1)
- STPM 2021 Sem 3 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2021 Sem 3 Mock AnsNATASHA NADIA BINTI ABDULLAH MoeNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second Term PDFDocument2 pagesSTPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second Term PDFVishalinie RamanNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 2022 Manual ChemistryDocument9 pagesSem 1 2022 Manual ChemistryVZYFVVZHVMNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Sem 3 Definition ListDocument4 pagesSTPM Physics Sem 3 Definition ListredroseNo ratings yet
- Project Report Chemistry (MAIN BODY)Document16 pagesProject Report Chemistry (MAIN BODY)Ung Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 ProjectileDocument9 pagesExperiment 2 ProjectilevimalNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document3 pagesTask 1Cherry T CYNo ratings yet
- PROPOSAL FOR CHEMISTRY PROJECT STPM 2023 New-1Document6 pagesPROPOSAL FOR CHEMISTRY PROJECT STPM 2023 New-1Thurgahini KikaNo ratings yet
- STPM Chem Project Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesSTPM Chem Project Literature ReviewXiangjun WooNo ratings yet
- Endothermic.: A The Forward Reaction IsDocument9 pagesEndothermic.: A The Forward Reaction IsSatyrKuangNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 ChemistryDocument3 pagesExperiment 5 ChemistryJack OngNo ratings yet
- 962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDocument13 pages962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics 2008Document26 pagesSTPM Physics 2008Tang Siew Eng100% (2)
- Itmti Chemistry Term 2 STPM Chapter 7 Chemical EnergeticsDocument47 pagesItmti Chemistry Term 2 STPM Chapter 7 Chemical EnergeticsCherry T CYNo ratings yet
- STPM Maths T Assignment (Semester 1) 2012Document10 pagesSTPM Maths T Assignment (Semester 1) 2012Nicholas Chong0% (2)
- STPM Che1 Ans (SBH)Document1 pageSTPM Che1 Ans (SBH)SimPorNo ratings yet
- Physic Experiment 6Document2 pagesPhysic Experiment 6JasonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (T) VIvaDocument11 pagesMathematics (T) VIvaJinJinKiraie0% (1)
- Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia EditDocument75 pagesSijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia EditDiana Ana0% (2)
- Biology STPM Report 2012Document63 pagesBiology STPM Report 2012Zahidah Husna Zulkifli100% (2)
- Physics STPM Sem 1 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 1 DefinitionBen40% (5)
- Uppp2 2022 Sem 1 AnsDocument1 pageUppp2 2022 Sem 1 AnsyijieeNo ratings yet
- Ans Gerak Gempue Sem 1 2023Document2 pagesAns Gerak Gempue Sem 1 2023revathy varatharajahNo ratings yet
- STPM 2021 Sem 1 Mock AnsDocument3 pagesSTPM 2021 Sem 1 Mock Ansm-7319562No ratings yet
- STPM 2020 Sem 1 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2020 Sem 1 Mock AnsNicole LimNo ratings yet
- STPM 2018 Sem 1 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2018 Sem 1 Mock Ansm-7319562No ratings yet
- L STPM 2019 SEM 1 MOCK ANSDocument2 pagesL STPM 2019 SEM 1 MOCK ANSm-7319562No ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument11 pagesPhysics Paper 2 SL MarkschemeAbdul RaqeebNo ratings yet
- Math Record1Document12 pagesMath Record1SABARISH SABARISHNo ratings yet
- STPM Che2 Ans (SBH)Document8 pagesSTPM Che2 Ans (SBH)SimPor100% (3)
- Chapter 06Document20 pagesChapter 06madee024No ratings yet
- pg308-311 ExtrasDocument5 pagespg308-311 Extrasevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- The Signs of Sine, Cosine and Tangent of Any Angle: Tanda-Tanda Bagi Sinus, Kosinus Dan Tangen Bagi Sebarang SudutDocument1 pageThe Signs of Sine, Cosine and Tangent of Any Angle: Tanda-Tanda Bagi Sinus, Kosinus Dan Tangen Bagi Sebarang Sudutevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- Chem Sem 1 Percubaan SMK Pusat Bandar PuchongDocument12 pagesChem Sem 1 Percubaan SMK Pusat Bandar Puchongevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - HOTS ExtraDocument3 pagesChapter 3 - HOTS Extraevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- Chem Sem 1 Q &A PDFDocument9 pagesChem Sem 1 Q &A PDFevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- Chem Sem 1 SMK Taman Johor Jaya AnsDocument2 pagesChem Sem 1 SMK Taman Johor Jaya Ansevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-07-20 15.52.49Document1 pageNew Doc 2019-07-20 15.52.49evacuate clashNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-07-31 23.03.44Document11 pagesNew Doc 2019-07-31 23.03.44evacuate clashNo ratings yet
- Detective Conan QuotesDocument1 pageDetective Conan Quotesevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- English Study MaterialsDocument5 pagesEnglish Study Materialsevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- Ozone DepletionDocument5 pagesOzone Depletionevacuate clash0% (1)
- Tiny Foods For Small Fry - EditedDocument5 pagesTiny Foods For Small Fry - Editedevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- June 2003 QP - Paper 1 CIE Physics IGCSE PDFDocument20 pagesJune 2003 QP - Paper 1 CIE Physics IGCSE PDFύπατίαNo ratings yet
- Non Metallic Materials Used For Machine ElementsDocument25 pagesNon Metallic Materials Used For Machine ElementsRajanikantJadhav50% (4)
- Steel Design: Engr. Jeric P. SarteDocument18 pagesSteel Design: Engr. Jeric P. SartePatrikNo ratings yet
- 2100Q Sales TrainingDocument27 pages2100Q Sales TrainingHien NguyenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0378517317310736 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0378517317310736 MaingabrielpoulsonNo ratings yet
- Silane Grafted Graphene Oxide Papers ForDocument29 pagesSilane Grafted Graphene Oxide Papers ForSolomon Jones SNo ratings yet
- Us1665267 PDFDocument3 pagesUs1665267 PDFmien namNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide Storage TanksDocument18 pagesSodium Hydroxide Storage TanksMudassar HassanNo ratings yet
- Igcse 41 EnergytransfersDocument32 pagesIgcse 41 EnergytransfersHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- 08chapter 3 FiberDocument8 pages08chapter 3 FiberAhmed AbdulazeezNo ratings yet
- Exercise-4 Part - 1: Single Option Correct Type: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument23 pagesExercise-4 Part - 1: Single Option Correct Type: Newton's Laws of MotionDebraj SahaNo ratings yet
- Work - Energy and Pressure in FluidsDocument7 pagesWork - Energy and Pressure in FluidsNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Physics Core 2017 With SolutionDocument62 pagesPhysics Core 2017 With Solutional_helu260% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: Si Units Thermodynamics 6 EditionDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Si Units Thermodynamics 6 EditionIllion IllionNo ratings yet
- Book Manual 103 BapatlaDocument80 pagesBook Manual 103 BapatlaAjay ReddyNo ratings yet
- Multistage Centrifugal Pump Operation & Maintenance ManualDocument11 pagesMultistage Centrifugal Pump Operation & Maintenance ManualHazrin HasanNo ratings yet
- Carbon Black - EncapsulationDocument10 pagesCarbon Black - EncapsulationWaltoy DinizNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem Chemistry Grade 12thDocument7 pages2nd Sem Chemistry Grade 12thDesta LelagoNo ratings yet
- CFD Request For QuotationDocument1 pageCFD Request For QuotationHedi Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- 2010 08 14 NotesOnFluidMechanicsAndGasDynamics Wassgren PDFDocument723 pages2010 08 14 NotesOnFluidMechanicsAndGasDynamics Wassgren PDFRaji0% (1)
- Best Practice Material in Palm Oil Mill - 2022-Final PDFDocument41 pagesBest Practice Material in Palm Oil Mill - 2022-Final PDFMarel LawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Fundamental ConceptsDocument24 pagesChapter 1 - Fundamental ConceptsHasri AzizNo ratings yet
- Design of CouplingsDocument10 pagesDesign of CouplingsvrajendraupadhyayNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis: Structures and LoadsDocument13 pagesStructural Analysis: Structures and LoadsWint Thu HtunNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure ChemistryDocument3 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure ChemistryAbhisiktaNo ratings yet
- Water AbsorbencyDocument3 pagesWater AbsorbencysalehaupmNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument116 pagesChemical KineticsSai Vishnu GainiNo ratings yet
- Initial Soil Springs Stiffness For Laterally Loaded Piles PDFDocument7 pagesInitial Soil Springs Stiffness For Laterally Loaded Piles PDFmagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Drag Reduction by Microbubble - ShipDocument6 pagesDrag Reduction by Microbubble - ShipKURNIAWANNo ratings yet