Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Changes: Hydrogen Gas (H) Oxygen Gas (O)
Chemical Changes: Hydrogen Gas (H) Oxygen Gas (O)
Uploaded by
Joy Glynis Celebrado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageWater molecules can be split into hydrogen and oxygen gas through electrolysis. When an electric current is passed through water, the water molecules break apart into hydrogen and oxygen atoms. These atoms then recombine into H2 and O2 gas molecules. The original water is changed into different substances through this chemical reaction.
Original Description:
Original Title
page_273.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWater molecules can be split into hydrogen and oxygen gas through electrolysis. When an electric current is passed through water, the water molecules break apart into hydrogen and oxygen atoms. These atoms then recombine into H2 and O2 gas molecules. The original water is changed into different substances through this chemical reaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageChemical Changes: Hydrogen Gas (H) Oxygen Gas (O)
Chemical Changes: Hydrogen Gas (H) Oxygen Gas (O)
Uploaded by
Joy Glynis CelebradoWater molecules can be split into hydrogen and oxygen gas through electrolysis. When an electric current is passed through water, the water molecules break apart into hydrogen and oxygen atoms. These atoms then recombine into H2 and O2 gas molecules. The original water is changed into different substances through this chemical reaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
s8pe-30901-ca 12/6/05 4:29 PM Page 273 MAZER PDF
Chemical Changes Electrolysis of Water
Water can also undergo a chemical change. Water
molecules can be broken down into hydrogen and hydrogen gas (H2)
oxygen molecules by a chemical reaction called oxygen gas (O2)
electrolysis. When an electric current is passed through
liquid water (H2O), it changes the water into two water (H2O)
gases—hydrogen and oxygen. The molecules of water
break apart into individual atoms. These atoms then
recombine into hydrogen molecules (H2) and oxygen
molecules (O2). The original material (water) changes
into different substances through a chemical reaction.
Hydrogen and oxygen are used as rocket fuel for the
space shuttle. During liftoff, liquid hydrogen and liquid
oxygen are combined in a reaction that is the opposite of
electrolysis. This reaction produces water and a large
amount of energy that helps push the shuttle into orbit.
Check Your Reading How does a chemical change differ from
a physical change? Water molecules can be split apart to form
separate hydrogen and oxygen molecules.
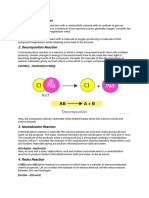
Reactants and Products
Reactants are the substances present at the beginning of a chemical
reaction. In the burning of natural gas, for example, methane (CH4) and
oxygen (O2) are the reactants in the chemical reaction. Products are the
substances formed by a chemical reaction. In the burning of natural gas,
carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) are the products formed by
the reaction. Reactants and products can be elements or compounds,
depending on the reaction taking place.
During a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in the reactants
are broken and new bonds are formed in the products. When natural
gas is burned, bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms in meth-
ane are broken. Bonds between the oxygen atoms in oxygen molecules
are broken. New bonds are formed between carbon and oxygen in
carbon dioxide gas and between hydrogen and oxygen in water vapor.
Reactants—bonds broken Products—new bonds formed
methane + oxygen carbon dioxide + water
(CH4) (O2) (CO2) (H2O)
H O O O
C H H
O C O
H H H
O O O
H H
Check Your Reading What must happen for reactants to be changed into products?
Chapter 9: Chemical Reactions 273
You might also like
- Oman O&G Blocks PDFDocument1 pageOman O&G Blocks PDFSathishNo ratings yet
- TUGAS 5 (Revisi Format) - Kelompok 6Document3 pagesTUGAS 5 (Revisi Format) - Kelompok 6Jenny AzzahraNo ratings yet
- 7 CH 3 Sec 2 Physical and Chemical Changes UploadDocument25 pages7 CH 3 Sec 2 Physical and Chemical Changes Uploadapi-294483847No ratings yet
- Global Natural Gas Reserves-A Heuristic ViewpointDocument13 pagesGlobal Natural Gas Reserves-A Heuristic ViewpointChris NwokoloNo ratings yet
- Aakash Chemistry Module 1Document152 pagesAakash Chemistry Module 1ASHISH NAIK100% (1)
- Balancing Equation: Chemical ReactionDocument1 pageBalancing Equation: Chemical ReactionGrace Anne AlaptoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Chemical Reaction and TypesDocument18 pagesChapter 9 Chemical Reaction and TypesAbie BarceloNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q4 Week 5Document13 pagesScience 10 Q4 Week 5Smb05 PlaylistNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions PresentationDocument25 pagesChemical Reactions PresentationRolanel L. EscobiaNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam 4 Study GuideDocument12 pagesBiology Exam 4 Study GuideKhusbu PatelNo ratings yet
- CERP Electroysis (200305) - Final2 - CleanDocument26 pagesCERP Electroysis (200305) - Final2 - Cleansaul coronaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations: Interpreting A Chemical EquationDocument8 pagesChemical Reactions and Chemical Equations: Interpreting A Chemical EquationJoël Fleur Nzamba KombilaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 - Chapters (1,2,3,4)Document10 pagesUnit-4 - Chapters (1,2,3,4)Farah AounNo ratings yet
- Byju-Chemical ReactionDocument7 pagesByju-Chemical ReactionsangitaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesChemical ReactionscristiansibisanNo ratings yet
- 1 - NOTES Reactions and Stoichiometry PreAP ReviewDocument5 pages1 - NOTES Reactions and Stoichiometry PreAP ReviewspamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 9 HydrogenDocument13 pagesChemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 9 HydrogenKalpesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes: Measuring A Chemical ReactionDocument6 pagesChemical Changes: Measuring A Chemical ReactionSarah GraceNo ratings yet
- Charold Paulus Inorganic ChemistDocument10 pagesCharold Paulus Inorganic ChemistCharold S. Paulus Pendidikan Kimia ANo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction 111Document48 pagesOxidation Reduction 111moskovbringerNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and S-Block ElementsDocument72 pagesHydrogen and S-Block ElementsGuru BhatNo ratings yet
- Sci. 411 Chemical Reactions Edleen AquinoDocument26 pagesSci. 411 Chemical Reactions Edleen Aquinojoebane capapas jr.No ratings yet
- Module 7 Aquatic Chemistry and Water PollutionDocument19 pagesModule 7 Aquatic Chemistry and Water PollutionMido IzukuNo ratings yet
- 16 Water ChemistryDocument21 pages16 Water ChemistryMohit KambojNo ratings yet
- Organic Review Worksheet and Problem SetDocument20 pagesOrganic Review Worksheet and Problem SetNelNo ratings yet
- GR 12 A1 - 2 Add NotesDocument2 pagesGR 12 A1 - 2 Add NotesShaimaa SalamaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CH 1 & 2Document17 pagesChemistry CH 1 & 2Mallesh RaoNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument11 pagesRedox ReactionAin AwangNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes WorkbookDocument11 pagesChemical Changes WorkbookKaitlyn DuarteNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Module 7-Module 8Document18 pagesInorganic Chemistry Module 7-Module 8Novelyn LumboyNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument6 pagesScience NotesKhushal BachwaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument52 pagesChemical ReactionsABEGAIL ARCIAGANo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Week 3 Chemical Equations CompilerDocument11 pagesChem 1 Week 3 Chemical Equations CompilerMelcorr MontesclarosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationDocument15 pagesChemical Reaction and Equationsanjayjoshi.jnvNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen-Book Back QuestionsDocument7 pagesHydrogen-Book Back QuestionsNitishNo ratings yet
- Physical Science AssessmentDocument4 pagesPhysical Science AssessmentridokundatshishongaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in MedicinesDocument46 pagesChemistry in MedicinesVIVEK KAUSHIKNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument25 pagesChemical ReactionsDonnafe AganonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsEric ArtocilloNo ratings yet
- Weak ForcesDocument17 pagesWeak Forcesbiri.melisa.105No ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 2Document81 pagesInorganic Chem 2et0191zemeneNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-Chemical Reaction and Equation NotesDocument7 pagesChapter1-Chemical Reaction and Equation Notesluv manotNo ratings yet
- Atom 1Document21 pagesAtom 1otuse557No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Complete NOTESDocument7 pagesHydrogen Complete NOTESAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations2Document28 pagesChemical Equations2Saleem BashaNo ratings yet
- Class11 Hydrogen Important Question With Answers - Chemistry TutorialsDocument12 pagesClass11 Hydrogen Important Question With Answers - Chemistry TutorialsParanjay DasNo ratings yet
- ReactionDocument7 pagesReactionSaravana ChandranNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 1Document8 pagesLecture No 1iman.aliNo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument35 pagesHydrogenRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is Chemical Reaction and Its TypeDocument9 pagesWhat Is Chemical Reaction and Its TypekamilbismaNo ratings yet
- Factors of Rate of ReactionDocument4 pagesFactors of Rate of ReactionHewa GiorgioNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument190 pagesChemical ReactionsAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (2)
- Reaksi KimiaDocument39 pagesReaksi KimiaainulavidaNo ratings yet
- AP Chem Adrian DingleDocument32 pagesAP Chem Adrian DingleEliza Salaritan0% (1)
- ScienceDocument220 pagesSciencenightwingklolNo ratings yet
- accurate note Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument5 pagesaccurate note Chemical Reactions & EquationsCuzco CuckooNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen: For XI STD ChemistryDocument139 pagesHydrogen: For XI STD ChemistryVed PrakashNo ratings yet
- English For ChemistsDocument27 pagesEnglish For ChemistsViet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Basic 2012Document58 pagesChemistry Basic 2012peterr1022No ratings yet
- The Dynamic World of Chemical Reactions with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Dynamic World of Chemical Reactions with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Hydrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Hydrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- LS Week 50Document4 pagesLS Week 50capt_rvalerosjrNo ratings yet
- TolueneDocument1 pageTolueneAlliah Mae LumanogNo ratings yet
- Pedosphere PDFDocument15 pagesPedosphere PDFshaziaNo ratings yet
- RNZ Project Experience OffshoreDocument19 pagesRNZ Project Experience OffshoreBich KieuNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Plant Brief DescriptionDocument4 pagesAmmonia Plant Brief DescriptionMohd Adnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Global Warming 2Document5 pagesGlobal Warming 2Akhil De Sa100% (1)
- Apcngi Role in The CNG Industry: Presented by Robbi R. Sukardi, Secretary General APCNGIDocument11 pagesApcngi Role in The CNG Industry: Presented by Robbi R. Sukardi, Secretary General APCNGIPutri VorwantyNo ratings yet
- June 2012 (v1) QP - Paper 2 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument16 pagesJune 2012 (v1) QP - Paper 2 CIE Chemistry IGCSEdovoo lolNo ratings yet
- Hook Up Wokshop P&ID Mark Up - 05 Jul 19Document18 pagesHook Up Wokshop P&ID Mark Up - 05 Jul 19gusyahri001No ratings yet
- 3.2. The LNG Storage Business and Associated Costs Ángel Rojo ENAGÁSDocument26 pages3.2. The LNG Storage Business and Associated Costs Ángel Rojo ENAGÁSFirzaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy Sources and Technologies. Process Design and Operation PDFDocument511 pagesAlternative Energy Sources and Technologies. Process Design and Operation PDFAlicia Gutiérrez del ValleNo ratings yet
- Uae LtledsDocument125 pagesUae Ltledsenergy8001No ratings yet
- Module 3 EdittedDocument15 pagesModule 3 EdittedMARIE ANN DIAMANo ratings yet
- Types of MicroorganismDocument20 pagesTypes of MicroorganismFrances Audrey TagupaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Extractive Metallurgy - MSE 4201Document190 pagesPrinciples of Extractive Metallurgy - MSE 4201eyob100% (1)
- Combined ZnO Reduction and Methane Reforming For Co Product - 2021 - Fuel ProcesDocument15 pagesCombined ZnO Reduction and Methane Reforming For Co Product - 2021 - Fuel ProcesDuvan Leandro Parra VelandiaNo ratings yet
- ANSYS 15.0 Update For Improving Fluids Dynamics SimulationsDocument11 pagesANSYS 15.0 Update For Improving Fluids Dynamics Simulationsrkkumarcpri1No ratings yet
- NT 03 PhysicswallahDocument12 pagesNT 03 PhysicswallahPrashant KhandareNo ratings yet
- 4 Combustion Problems With SolutionsDocument25 pages4 Combustion Problems With SolutionsMunawar Lal JoshiNo ratings yet
- Abb Oltc Dga InterpretDocument4 pagesAbb Oltc Dga Interpretbertovalen0% (1)
- 2014 19 1Document25 pages2014 19 1Afif Samsun BaharunNo ratings yet
- Syngas Synthesis & Its UseDocument18 pagesSyngas Synthesis & Its UseAekkasit SenaartNo ratings yet
- Florinsky 2010dDocument403 pagesFlorinsky 2010dVostjeNo ratings yet
- Energetics Question DatabaseDocument23 pagesEnergetics Question DatabaseKamrul Alam MasumNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument9 pagesPlug Flow ReactorTajTajNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - Tape Script (Homework)Document28 pagesAnswer Key - Tape Script (Homework)Chi Nguyễn ThảoNo ratings yet
- 8-Galvanic 903-Sulphur AnalyserDocument13 pages8-Galvanic 903-Sulphur Analysergudapati9No ratings yet