Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsLiterature Review Table: Bacillus Subtilis As A
Literature Review Table: Bacillus Subtilis As A
Uploaded by
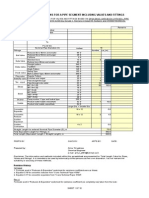
anon_884442402This literature review table summarizes two studies on using bacteria to improve concrete properties. The first study by M.V Seshagiri Rao, et al. investigated using Bacillus subtilis bacteria and found it led to a 16-17% increase in compressive strength, 14-13% increase in split tensile strength, and 30-26% increase in flexural strength for M20 and M40 concrete grades. The second study by C.C Gavimath, et al. examined using B.sphaericus bacteria and found a 30.76-32.21% increase in compressive strength and 13.75-18.35% increase in split tensile strength compared to conventional concrete without
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Through The Eyes of The Masters - David AnriasDocument93 pagesThrough The Eyes of The Masters - David Anriasmalazza95% (21)
- Practica Asist Socialeintre Religios Si SecularDocument12 pagesPractica Asist Socialeintre Religios Si Seculargabriela100% (2)
- Chippewa Park Master Plan ReportDocument28 pagesChippewa Park Master Plan ReportinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Isrm 11congress 2007 155 PDFDocument4 pagesIsrm 11congress 2007 155 PDFCyrillus Arthur SaputraNo ratings yet
- Extended Abstract - Nypa FruiticanDocument3 pagesExtended Abstract - Nypa FruiticanRevilo SilecNo ratings yet
- Fly Ash Concrete PDFDocument5 pagesFly Ash Concrete PDFVishal PanchalNo ratings yet
- Analisis Diameter Gelembung Pada Kerugian Tekanan Aliran Fluida Rachmat Subagyo, I.N.G. Wardana, Agung Widodo., Eko SiswantoDocument4 pagesAnalisis Diameter Gelembung Pada Kerugian Tekanan Aliran Fluida Rachmat Subagyo, I.N.G. Wardana, Agung Widodo., Eko SiswantoLara Aisya ZaharahNo ratings yet
- Simplified Interaction Diagrams: For Single and Bi-Axial MomentsDocument11 pagesSimplified Interaction Diagrams: For Single and Bi-Axial MomentsAhmed EwisNo ratings yet
- Box Culvert Design: Title: Units: KN, M Materials: ConcreteDocument1 pageBox Culvert Design: Title: Units: KN, M Materials: ConcreteDelahan AbatyoughNo ratings yet
- J JMMM 2019 165719Document13 pagesJ JMMM 2019 165719brandt.nickNo ratings yet
- Resistencia de ProbetasDocument11 pagesResistencia de ProbetasAlcides Emerson Cerda GomezNo ratings yet
- BEHAVIOUR AND STRENGTH ASSESSMENT OF Masonry PrismsDocument42 pagesBEHAVIOUR AND STRENGTH ASSESSMENT OF Masonry Prismsmanish_shashikantNo ratings yet
- (IJETA-V11I3P6) :binit Gopal, Hemant Kumar SainDocument4 pages(IJETA-V11I3P6) :binit Gopal, Hemant Kumar SaineditorijetaNo ratings yet
- The Background of The Selected MixturesDocument1 pageThe Background of The Selected MixturesAayu GargNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Micro-Stresses and Interfacial Tractions in Boron Carbide/AA5050 Alloy Metal Matrix CompositesDocument3 pagesEstimation of Micro-Stresses and Interfacial Tractions in Boron Carbide/AA5050 Alloy Metal Matrix CompositesA. Chennakesava ReddyNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Multiscale Quantum Mechanics Modeling of The Mechanical PropertiesDocument16 pagesExperimental and Multiscale Quantum Mechanics Modeling of The Mechanical PropertiesMaribel VirreyraNo ratings yet
- Example TopographyDocument1 pageExample TopographyredhoardianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Week 5 - Updated17.10Document61 pagesChapter 5 - Week 5 - Updated17.10anon_884442402No ratings yet
- ECG426 - Week 3a - I - Soil Classification - Problematic Soil PDFDocument82 pagesECG426 - Week 3a - I - Soil Classification - Problematic Soil PDFanon_884442402No ratings yet
- ECG426 - Week 1a - I - OBE & Intro PDFDocument56 pagesECG426 - Week 1a - I - OBE & Intro PDFanon_884442402No ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument2 pagesApparatusanon_884442402No ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Bendable Concrete Using Natural and Artificial Fibres (Jute and Nylon)Document5 pagesExperimental Investigation On Bendable Concrete Using Natural and Artificial Fibres (Jute and Nylon)anon_884442402No ratings yet
- JACOB ThirdDocument16 pagesJACOB ThirdWendell ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dơnload A Simple Secret 2nd Edition M Brereton Full ChapterDocument24 pagesDơnload A Simple Secret 2nd Edition M Brereton Full Chapterjsfjarbin100% (4)
- Chapter 10b Kinetic Theory For Ideal GasesDocument3 pagesChapter 10b Kinetic Theory For Ideal GasesPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Agribusiness: ExamplesDocument4 pagesAgribusiness: ExamplesAngelo AristizabalNo ratings yet
- Polyphenol Oxidase Activity and Browning of Three Avocado VarietiesDocument6 pagesPolyphenol Oxidase Activity and Browning of Three Avocado VarietiesMiguelArceMonroyNo ratings yet
- Benign Ovarian TumorsDocument16 pagesBenign Ovarian TumorsPatNo ratings yet
- Initial Newborn AssessmentDocument14 pagesInitial Newborn Assessmentaclark831No ratings yet
- Beyond Risk - Bacterial Biofilms and Their Regulating ApproachesDocument20 pagesBeyond Risk - Bacterial Biofilms and Their Regulating ApproachesVictor HugoNo ratings yet
- Star Holman 210HX Conveyor OvenDocument2 pagesStar Holman 210HX Conveyor Ovenwsfc-ebayNo ratings yet
- Biology Q & A Booklet: (English Medium)Document76 pagesBiology Q & A Booklet: (English Medium)La EscenaNo ratings yet
- Quail Farming Business Plan PDF OverviewDocument5 pagesQuail Farming Business Plan PDF OverviewhenrymcdoNo ratings yet
- Specifications Battery Chargers For Rail VehiclesDocument2 pagesSpecifications Battery Chargers For Rail VehiclesPirata ScribNo ratings yet
- LS10 6clozeDocument1 pageLS10 6clozesinned68No ratings yet
- SC14-07 01-02 Hospital Preventive Maintenance Memo-AttachDocument16 pagesSC14-07 01-02 Hospital Preventive Maintenance Memo-AttachRaydoon SadeqNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Length Calculator - RevADocument10 pagesEquivalent Length Calculator - RevArkrajan1502No ratings yet
- Perform-3d-V5 0 0Document15 pagesPerform-3d-V5 0 0Darley MauricioNo ratings yet
- Martha RogersDocument2 pagesMartha RogersMary Angel VelascoNo ratings yet
- From The Perspective of Battery Production: Energy-Environment-Economy (3E) Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries in ChinaDocument12 pagesFrom The Perspective of Battery Production: Energy-Environment-Economy (3E) Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Chinazoran cukovicNo ratings yet
- Wizard 2 BPUNIR2 PDFDocument16 pagesWizard 2 BPUNIR2 PDFalpdrNo ratings yet
- Chap 11Document3 pagesChap 11Flia Diaz ZunigaNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To HydraulicsDocument32 pages1.introduction To HydraulicsJet Espejon JavierNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionAhinurNo ratings yet
- Drinks Menu - Community Food & JuiceDocument1 pageDrinks Menu - Community Food & JuiceDyske SuematsuNo ratings yet
- Human Nutritional RequirementsDocument3 pagesHuman Nutritional RequirementsAgnesMagadiaNo ratings yet
- 7TH Grade Health Unit 3 Study Guide AnswersDocument8 pages7TH Grade Health Unit 3 Study Guide AnswersBader AlmshariNo ratings yet
- Anode InfoDocument5 pagesAnode InfoEberg NlnoNo ratings yet
Literature Review Table: Bacillus Subtilis As A
Literature Review Table: Bacillus Subtilis As A
Uploaded by
anon_8844424020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThis literature review table summarizes two studies on using bacteria to improve concrete properties. The first study by M.V Seshagiri Rao, et al. investigated using Bacillus subtilis bacteria and found it led to a 16-17% increase in compressive strength, 14-13% increase in split tensile strength, and 30-26% increase in flexural strength for M20 and M40 concrete grades. The second study by C.C Gavimath, et al. examined using B.sphaericus bacteria and found a 30.76-32.21% increase in compressive strength and 13.75-18.35% increase in split tensile strength compared to conventional concrete without
Original Description:
LR
Original Title
Literature Review Table
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis literature review table summarizes two studies on using bacteria to improve concrete properties. The first study by M.V Seshagiri Rao, et al. investigated using Bacillus subtilis bacteria and found it led to a 16-17% increase in compressive strength, 14-13% increase in split tensile strength, and 30-26% increase in flexural strength for M20 and M40 concrete grades. The second study by C.C Gavimath, et al. examined using B.sphaericus bacteria and found a 30.76-32.21% increase in compressive strength and 13.75-18.35% increase in split tensile strength compared to conventional concrete without
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesLiterature Review Table: Bacillus Subtilis As A
Literature Review Table: Bacillus Subtilis As A
Uploaded by
anon_884442402This literature review table summarizes two studies on using bacteria to improve concrete properties. The first study by M.V Seshagiri Rao, et al. investigated using Bacillus subtilis bacteria and found it led to a 16-17% increase in compressive strength, 14-13% increase in split tensile strength, and 30-26% increase in flexural strength for M20 and M40 concrete grades. The second study by C.C Gavimath, et al. examined using B.sphaericus bacteria and found a 30.76-32.21% increase in compressive strength and 13.75-18.35% increase in split tensile strength compared to conventional concrete without
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
LITERATURE REVIEW TABLE
AUTHOR/YEAR OBJECTIVES THEORIES VARIABLES METHODOLOGY FINDING/RESULT REMARK
M.V Seshagiri Rao, et Studies on the possibility Bacterial concrete has Micro-crack is the Compressive test at For controlled concrete:
al. (2013) of using specific bacteria i.e. better acid resistance in main cause to 28 days for concrete M20 = 28.18 MPa
Bacillus subtilis as a aggressive environment structural failure grade M20 and M40 M40 = 52.01 MPa
sustainable and concrete
embedded self-healing For bio concrete:
agent M20 = 32.74 MPa
(16% increase)
M40 = 61.06 MPa
(17% increase)
Split tensile test at For controlled concrete:
28 days for concrete M20 = 3.26 MPa
grade M20 and M40 M40 = 4.51 MPa
For bio concrete:
M20 = 3.73 MPa
(14% increase)
M40 = 5.13 MPa
(13% increase)
Flexural test at For controlled concrete:
28 days for concrete M20 = 4.68 MPa
grade M20 and M40 M40 = 6.11 MPa
For bio concrete:
M20 = 6.11 MPa
(30% increase)
M40 = 7.73 MPa
(26% increase)
C.C Gavimath, et al. To study the potential B.spharicus bacteria The crack in concrete Compressive tests There is an increase in
(2018) Application of bacterial increase the strength of create ploblem with and without compressive strength of
species i.e. B.sphaericus to the concrete addition of 30.76%, 46.15% and 32.21%
improve the strength of B.sphaericus at 3rd, 7th and 28th day
cement concrete respectively while using
B.sphaericus bacteria
compared to
conventional concrete
Split tensile test with There is an increase in
and without addition split tensile strength
of B.spharicus. of 13.75%, 14.28% and
18.35% at 3rd, 7th
and 28 th day respectively
when B.sphaericus bacteria
are used and compared with
conventional concrete
You might also like
- Through The Eyes of The Masters - David AnriasDocument93 pagesThrough The Eyes of The Masters - David Anriasmalazza95% (21)
- Practica Asist Socialeintre Religios Si SecularDocument12 pagesPractica Asist Socialeintre Religios Si Seculargabriela100% (2)
- Chippewa Park Master Plan ReportDocument28 pagesChippewa Park Master Plan ReportinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Isrm 11congress 2007 155 PDFDocument4 pagesIsrm 11congress 2007 155 PDFCyrillus Arthur SaputraNo ratings yet
- Extended Abstract - Nypa FruiticanDocument3 pagesExtended Abstract - Nypa FruiticanRevilo SilecNo ratings yet
- Fly Ash Concrete PDFDocument5 pagesFly Ash Concrete PDFVishal PanchalNo ratings yet
- Analisis Diameter Gelembung Pada Kerugian Tekanan Aliran Fluida Rachmat Subagyo, I.N.G. Wardana, Agung Widodo., Eko SiswantoDocument4 pagesAnalisis Diameter Gelembung Pada Kerugian Tekanan Aliran Fluida Rachmat Subagyo, I.N.G. Wardana, Agung Widodo., Eko SiswantoLara Aisya ZaharahNo ratings yet
- Simplified Interaction Diagrams: For Single and Bi-Axial MomentsDocument11 pagesSimplified Interaction Diagrams: For Single and Bi-Axial MomentsAhmed EwisNo ratings yet
- Box Culvert Design: Title: Units: KN, M Materials: ConcreteDocument1 pageBox Culvert Design: Title: Units: KN, M Materials: ConcreteDelahan AbatyoughNo ratings yet
- J JMMM 2019 165719Document13 pagesJ JMMM 2019 165719brandt.nickNo ratings yet
- Resistencia de ProbetasDocument11 pagesResistencia de ProbetasAlcides Emerson Cerda GomezNo ratings yet
- BEHAVIOUR AND STRENGTH ASSESSMENT OF Masonry PrismsDocument42 pagesBEHAVIOUR AND STRENGTH ASSESSMENT OF Masonry Prismsmanish_shashikantNo ratings yet
- (IJETA-V11I3P6) :binit Gopal, Hemant Kumar SainDocument4 pages(IJETA-V11I3P6) :binit Gopal, Hemant Kumar SaineditorijetaNo ratings yet
- The Background of The Selected MixturesDocument1 pageThe Background of The Selected MixturesAayu GargNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Micro-Stresses and Interfacial Tractions in Boron Carbide/AA5050 Alloy Metal Matrix CompositesDocument3 pagesEstimation of Micro-Stresses and Interfacial Tractions in Boron Carbide/AA5050 Alloy Metal Matrix CompositesA. Chennakesava ReddyNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Multiscale Quantum Mechanics Modeling of The Mechanical PropertiesDocument16 pagesExperimental and Multiscale Quantum Mechanics Modeling of The Mechanical PropertiesMaribel VirreyraNo ratings yet
- Example TopographyDocument1 pageExample TopographyredhoardianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Week 5 - Updated17.10Document61 pagesChapter 5 - Week 5 - Updated17.10anon_884442402No ratings yet
- ECG426 - Week 3a - I - Soil Classification - Problematic Soil PDFDocument82 pagesECG426 - Week 3a - I - Soil Classification - Problematic Soil PDFanon_884442402No ratings yet
- ECG426 - Week 1a - I - OBE & Intro PDFDocument56 pagesECG426 - Week 1a - I - OBE & Intro PDFanon_884442402No ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument2 pagesApparatusanon_884442402No ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Bendable Concrete Using Natural and Artificial Fibres (Jute and Nylon)Document5 pagesExperimental Investigation On Bendable Concrete Using Natural and Artificial Fibres (Jute and Nylon)anon_884442402No ratings yet
- JACOB ThirdDocument16 pagesJACOB ThirdWendell ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dơnload A Simple Secret 2nd Edition M Brereton Full ChapterDocument24 pagesDơnload A Simple Secret 2nd Edition M Brereton Full Chapterjsfjarbin100% (4)
- Chapter 10b Kinetic Theory For Ideal GasesDocument3 pagesChapter 10b Kinetic Theory For Ideal GasesPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Agribusiness: ExamplesDocument4 pagesAgribusiness: ExamplesAngelo AristizabalNo ratings yet
- Polyphenol Oxidase Activity and Browning of Three Avocado VarietiesDocument6 pagesPolyphenol Oxidase Activity and Browning of Three Avocado VarietiesMiguelArceMonroyNo ratings yet
- Benign Ovarian TumorsDocument16 pagesBenign Ovarian TumorsPatNo ratings yet
- Initial Newborn AssessmentDocument14 pagesInitial Newborn Assessmentaclark831No ratings yet
- Beyond Risk - Bacterial Biofilms and Their Regulating ApproachesDocument20 pagesBeyond Risk - Bacterial Biofilms and Their Regulating ApproachesVictor HugoNo ratings yet
- Star Holman 210HX Conveyor OvenDocument2 pagesStar Holman 210HX Conveyor Ovenwsfc-ebayNo ratings yet
- Biology Q & A Booklet: (English Medium)Document76 pagesBiology Q & A Booklet: (English Medium)La EscenaNo ratings yet
- Quail Farming Business Plan PDF OverviewDocument5 pagesQuail Farming Business Plan PDF OverviewhenrymcdoNo ratings yet
- Specifications Battery Chargers For Rail VehiclesDocument2 pagesSpecifications Battery Chargers For Rail VehiclesPirata ScribNo ratings yet
- LS10 6clozeDocument1 pageLS10 6clozesinned68No ratings yet
- SC14-07 01-02 Hospital Preventive Maintenance Memo-AttachDocument16 pagesSC14-07 01-02 Hospital Preventive Maintenance Memo-AttachRaydoon SadeqNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Length Calculator - RevADocument10 pagesEquivalent Length Calculator - RevArkrajan1502No ratings yet
- Perform-3d-V5 0 0Document15 pagesPerform-3d-V5 0 0Darley MauricioNo ratings yet
- Martha RogersDocument2 pagesMartha RogersMary Angel VelascoNo ratings yet
- From The Perspective of Battery Production: Energy-Environment-Economy (3E) Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries in ChinaDocument12 pagesFrom The Perspective of Battery Production: Energy-Environment-Economy (3E) Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Chinazoran cukovicNo ratings yet
- Wizard 2 BPUNIR2 PDFDocument16 pagesWizard 2 BPUNIR2 PDFalpdrNo ratings yet
- Chap 11Document3 pagesChap 11Flia Diaz ZunigaNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To HydraulicsDocument32 pages1.introduction To HydraulicsJet Espejon JavierNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionAhinurNo ratings yet
- Drinks Menu - Community Food & JuiceDocument1 pageDrinks Menu - Community Food & JuiceDyske SuematsuNo ratings yet
- Human Nutritional RequirementsDocument3 pagesHuman Nutritional RequirementsAgnesMagadiaNo ratings yet
- 7TH Grade Health Unit 3 Study Guide AnswersDocument8 pages7TH Grade Health Unit 3 Study Guide AnswersBader AlmshariNo ratings yet
- Anode InfoDocument5 pagesAnode InfoEberg NlnoNo ratings yet