Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Na+ and H20 Secretion (2) Plasma Volume (3) Vascular Response To Catecholamines ( Dopamine, Norepinephrine, Epinephrine)
Na+ and H20 Secretion (2) Plasma Volume (3) Vascular Response To Catecholamines ( Dopamine, Norepinephrine, Epinephrine)
Uploaded by
Grace Butler0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
109 views1 pageThis document summarizes different categories of diuretic drugs, their mechanisms of action, effects, side effects, and nursing considerations. It describes:
1) Thiazide diuretics like hydrochlorothiazide which increase sodium and chloride excretion in the urine by blocking their reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. They initially increase extracellular fluid volume and subsequently increase systemic vascular resistance, lowering blood pressure. Side effects include hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
2) Loop diuretics like furosemide which powerfully increase urine output by blocking sodium reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle. They can cause hypokalemia and other electrolyte abnormalities.
3
Original Description:
Table of common diuretic drug types. Used for nursing school.
Original Title
Diuretic Drugs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes different categories of diuretic drugs, their mechanisms of action, effects, side effects, and nursing considerations. It describes:
1) Thiazide diuretics like hydrochlorothiazide which increase sodium and chloride excretion in the urine by blocking their reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. They initially increase extracellular fluid volume and subsequently increase systemic vascular resistance, lowering blood pressure. Side effects include hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
2) Loop diuretics like furosemide which powerfully increase urine output by blocking sodium reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle. They can cause hypokalemia and other electrolyte abnormalities.
3
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
109 views1 pageNa+ and H20 Secretion (2) Plasma Volume (3) Vascular Response To Catecholamines ( Dopamine, Norepinephrine, Epinephrine)
Na+ and H20 Secretion (2) Plasma Volume (3) Vascular Response To Catecholamines ( Dopamine, Norepinephrine, Epinephrine)
Uploaded by
Grace ButlerThis document summarizes different categories of diuretic drugs, their mechanisms of action, effects, side effects, and nursing considerations. It describes:
1) Thiazide diuretics like hydrochlorothiazide which increase sodium and chloride excretion in the urine by blocking their reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. They initially increase extracellular fluid volume and subsequently increase systemic vascular resistance, lowering blood pressure. Side effects include hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
2) Loop diuretics like furosemide which powerfully increase urine output by blocking sodium reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle. They can cause hypokalemia and other electrolyte abnormalities.
3
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
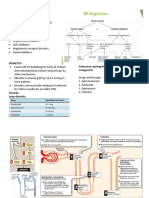
Diuretics = fluids in the body, urine output
(1) Na+ and H20 secretion
(2) plasma volume
(3) vascular response to catecholamines (=dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine)
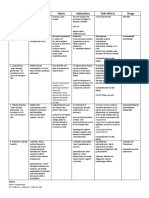
Drug Cat. / MOA Drug Examples Implications Side Effects Nursing Considerations
Thiazides chlorothiazide(Diuril) urine output Orthostatic hypotension SLOW (2-4 wks for effect)
= block NaCl chlorthalidone Na+ and Cl- in urine Hypokalemia Na+ will hypokalemia risk
reabsorption in the hydrochlorothiazide ECF, initially Metabolic alkalosis FIRST line of treatment (HT)
DCT indapamide SVR, sustained
metolazone(Zaroxolyn) Lower BP Contraindications:
Think: Thiazides, DCT Digoxin (cardiotoxicity)
NSAIDs (diuretic effect +
renal impairment risk)
Loop Diuretics bumetanide (Bumex) urine output Orthostatic hypotension MOST potent / FASTEST
= block NaCl furosemide (Lasix) Na+ and Cl- in urine Hypokalemia
reabsorption in the torsemide (Demadex) Other electrolytes But LESS effective for
ascending loop hypertension
SHORT duration of effect
Renal impaired PT is OKAY
K+ Sparing Diuretics amiloride (Midamor) urine output Orthostatic hypotension Contraindications:
= K+ and Na+ triamterene(Dyrenium) Na+ in urine Hyperkalemia Renal impairment
exchange in DCT K+ in body Other electrolytes ACE inhibitors
H+, Ca, Mg in body Angiotensin II blockers
Aldosterone receptor block
K+ supplements
Aldosterone spironolactone(Aldactone) urine output Orthostatic hypotension Contraindications:
Receptor Blockers eplerenone (Inspra) Na+ in urine Hyperkalemia ACE inhibitors
= inhibit action of K+ in body Angiotensin II blockers
aldosterone on DCT K+ sparing diuretics
K+ supplements
You might also like
- Chucks Drug BoxDocument2 pagesChucks Drug BoxKara Dawn MasonNo ratings yet
- Maternity 17 Newborn Transitioning 2019Document51 pagesMaternity 17 Newborn Transitioning 2019Marvin AnciroNo ratings yet
- Easy Hypertension ClassificationDocument1 pageEasy Hypertension ClassificationGirish WaruNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology A ReviewDocument15 pagesPharmacology A ReviewKathrynne MendozaNo ratings yet
- D. Preparing The Medication For Bolus AdministrationDocument17 pagesD. Preparing The Medication For Bolus AdministrationseanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Drugs - Active Stack® Pharmacology Flash Cards - Study Materials - My ATIDocument1 pageCardiovascular System Drugs - Active Stack® Pharmacology Flash Cards - Study Materials - My ATIAntonette Joy SolinapNo ratings yet
- NCMA216.PHARMA Drugs Acting On The Endocrine SystemDocument71 pagesNCMA216.PHARMA Drugs Acting On The Endocrine SystemKhams TolentinoNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesElectrolytesChariza Trompeta100% (1)
- Steroids Drug ListDocument2 pagesSteroids Drug ListJezKagandahanNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions of Antianginal Drugs..Document40 pagesDrug Interactions of Antianginal Drugs..Kamal SikandarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideDocument15 pagesNursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia)Document1 pageMagnesium Hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia)ENo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNDocument36 pagesAcid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNkatrinasdNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Protocol RQHRDocument15 pagesVancomycin Protocol RQHRl1o2stNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesDrugs Acting On Cardiovascular SystemAnwar Ul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Pharm Chapter 2 and 3 Study GuideDocument10 pagesPharm Chapter 2 and 3 Study GuideamkNo ratings yet
- OTC Labels HorizontalDocument1 pageOTC Labels HorizontalTsoojiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders LectureDocument132 pagesCardiovascular Disorders LectureHarper Epps100% (1)
- Drugs To Watch With WARFARINDocument3 pagesDrugs To Watch With WARFARINRajendra RaiNo ratings yet
- MdsMgtModule Calculations FinalDocument35 pagesMdsMgtModule Calculations FinalChrissieNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument6 pagesEndocrine DrugsdiriniumNo ratings yet
- CH 59 Care of Patients With Problems of The Biliary System and PancreasDocument28 pagesCH 59 Care of Patients With Problems of The Biliary System and Pancreasjrflores1284No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Final OutputDocument19 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Final OutputNatasha Alaine E. CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 1Document39 pagesPharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNo ratings yet
- Drugs Med-SurgTest 3Document6 pagesDrugs Med-SurgTest 3Sarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Alpha Adrenergic BlockersDocument7 pagesAlpha Adrenergic BlockersNadine BacalangcoNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument35 pagesPharmacologyJan Michael ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument4 pagesGoutapi-3822433100% (1)
- O Insert Picture Here From Slide: Heart Failure Heart FailureDocument4 pagesO Insert Picture Here From Slide: Heart Failure Heart FailureAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants DrugsDocument6 pagesAnticoagulants DrugsHusam Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsDocument54 pagesAdrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsNel100% (1)
- OTC Pain Relievers Dosage Chart For Adults and Children 12 Years and OlderDocument2 pagesOTC Pain Relievers Dosage Chart For Adults and Children 12 Years and OlderAdocueNo ratings yet
- Antepartum 1Document3 pagesAntepartum 1Emily DavisNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument172 pagesEndocrine DrugsAlvim Tiel FactorNo ratings yet
- Antihyperlipidemic Drugs: Key Terms Chapter ObjectivesDocument9 pagesAntihyperlipidemic Drugs: Key Terms Chapter ObjectivesSasa AbassNo ratings yet
- ACE InhibitorsDocument26 pagesACE Inhibitorsali mohammedNo ratings yet
- LasixDocument1 pageLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Pharmacology 2 NotesDocument14 pagesPharmacology 2 NotesNikko MabbayadNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants: Depression Is One The Most Treatable Mental IllnessDocument40 pagesAntidepressants: Depression Is One The Most Treatable Mental IllnessMohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- N196 GI Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesN196 GI Exam Study Guideaznknight3230% (1)
- Clinical Case Study - Online Discussion Form Fall 2020-1Document14 pagesClinical Case Study - Online Discussion Form Fall 2020-1Sabrina Odies100% (1)
- Drug Card Solu-MEDROLDocument2 pagesDrug Card Solu-MEDROLBenNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Gastrointestinal SystemDocument4 pagesPharmacology of Gastrointestinal SystemZaira KimNo ratings yet
- Module 14 - Drugs-affecting-the-Respiratory-System-3Document48 pagesModule 14 - Drugs-affecting-the-Respiratory-System-3weissNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrineUnclePorkchopNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FreebieDocument3 pagesPharmacology FreebieMohammad Farooq KhanNo ratings yet
- Mishba +pharmacology + Tapan ShahDocument232 pagesMishba +pharmacology + Tapan ShahRaushan BlakeNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument23 pagesEndocrinensvickneswaranNo ratings yet
- 201103-Fkg-Drugs Act On Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pages201103-Fkg-Drugs Act On Cardiovascular SystemEidelen Lovani Sembiring100% (1)
- St. Paul University Dumaguete St. Paul University System College of Nursing ISO 9001Document16 pagesSt. Paul University Dumaguete St. Paul University System College of Nursing ISO 9001Dinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Pharmacology: Shan NanjiDocument24 pagesGastrointestinal Pharmacology: Shan NanjijenniferluzonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine: Common Lab Tests For Endocrine and Hormonal DisordersDocument19 pagesEndocrine: Common Lab Tests For Endocrine and Hormonal DisordersPhilip SimanganNo ratings yet
- N461 - Final Exam Study Guide - RN-BS - Spring 2017Document7 pagesN461 - Final Exam Study Guide - RN-BS - Spring 2017Jeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Types of Diagnosis:: Problem-Focused Nursing Diagnoses Have Three Components: (1) Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesTypes of Diagnosis:: Problem-Focused Nursing Diagnoses Have Three Components: (1) Nursing DiagnosisDaisy MellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08: Injectable Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionDocument13 pagesChapter 08: Injectable Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionadenNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocument5 pagesCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Measuring Household and Individual Dietary DiversityFrom EverandGuidelines for Measuring Household and Individual Dietary DiversityNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument15 pagesDiureticsnk999999No ratings yet
- PCL 302 Lecture DiureticsDocument7 pagesPCL 302 Lecture DiureticsZayyanu AminuNo ratings yet
- DIURETICSDocument55 pagesDIURETICSRAVISH100% (1)
- Generic Brand 2Document6 pagesGeneric Brand 2villafloresramonakristylleNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Sumolly Anak DavidDocument29 pagesDiuretics: Sumolly Anak Davidfarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 160418020107Document21 pagesDiuretics 160418020107P meruguNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: DR Mozna TalpurDocument33 pagesDiuretics: DR Mozna TalpurShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Diuretic DrugsDocument62 pagesDiuretic DrugsAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonDocument28 pagesDiuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonCham PianoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Renal System I. Diuretics II. Parenteral Fluids (Video) III. Electrolytes (Video)Document44 pagesDrugs Affecting The Renal System I. Diuretics II. Parenteral Fluids (Video) III. Electrolytes (Video)Juliene Hannah FloresNo ratings yet
- Principles of Diuretic Therapy: Dr. Rania Magadmi, MBBS, PHDDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Diuretic Therapy: Dr. Rania Magadmi, MBBS, PHDمشاعرمبعثرةNo ratings yet
- Post Test Blok 11Document12 pagesPost Test Blok 11Dina Ayu SavitriNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology and Clinical Use of DiureticsDocument5 pagesPharmacology and Clinical Use of DiureticsvivianNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Renal DiureticsDocument24 pagesPharmacology Renal Diureticskpsuan100% (1)
- 12B) RenalDocument6 pages12B) RenalrbskbjzqrnNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument4 pagesDiureticsNazmul Islam AbirNo ratings yet
- CHF-Diuretics v2.1 Apr-2017Document1 pageCHF-Diuretics v2.1 Apr-2017Robbie WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Professor C. B. Choudhary Department of Pharmacology NMCTH, BiratnagarDocument52 pagesDiuretics: Professor C. B. Choudhary Department of Pharmacology NMCTH, BiratnagarKulgaurav RegmiNo ratings yet
- Health Medical: Enter Text HereDocument15 pagesHealth Medical: Enter Text HereRekaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics MOA Notes Indications Side Effects DrugsDocument1 pageDiuretics MOA Notes Indications Side Effects Drugsmonica leeNo ratings yet
- نسخة Pharma1 diuretics and anti HTN. Manar.BQDocument6 pagesنسخة Pharma1 diuretics and anti HTN. Manar.BQAblah Hamdan ThaherNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Chris Hague, PHDDocument29 pagesDiuretics: Chris Hague, PHDranachamanNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument14 pagesDiureticsZahid MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Pharmacology 79 88Document6 pagesDiuretics Pharmacology 79 88Neha RoyNo ratings yet
- Beige Brown Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20230922 - 184226 - 0000Document25 pagesBeige Brown Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20230922 - 184226 - 0000Mercurio AysonNo ratings yet
- PHA 824 The Pharmacodynamics of Diuretic Drugs Dr. M.T. Piascik ObjectivesDocument12 pagesPHA 824 The Pharmacodynamics of Diuretic Drugs Dr. M.T. Piascik ObjectivespriapisNo ratings yet
- DIURETICSDocument2 pagesDIURETICSLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Methazolamide-Diuretic (Sar)Document11 pagesMethazolamide-Diuretic (Sar)Laras Haryan LNo ratings yet
- Diuretic DrugsDocument16 pagesDiuretic DrugslabillabooNo ratings yet