Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment # 04 PDF
Experiment # 04 PDF
Uploaded by
kaleem ullahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment # 04 PDF
Experiment # 04 PDF
Uploaded by
kaleem ullahCopyright:
Available Formats
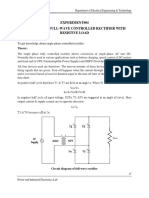
University of Sargodha Department of Electrical Engineering & Technology
EXPERIMENT#04
SINGLE PHASE FULL-WAVE CONTROLLED RECTIFIER WITH
RESISTIVE LOAD
Objective:
To get knowledge about single phase-controlled rectifier.
Theory:
The single phase fully controlled rectifier allows conversion of single-phase AC into DC.
Normally this is used in various applications such as battery charging, speed control of DC motors
and front end of UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) and SMPS (Switched Mode Power Supply).
All four devices used are thyristors. The turn-on instants of these devices are dependent on the
firing signals that are given. Turn-off happens when the current through the device reaches zero
and it is reverse biased at least for duration equal to the turn-off time of the device specified in the
data sheet.
In positive half cycle thyristors T1 & T2 are fired at an angle α. When T1 & T2 conducts
Vo=Vs
IO=Is=Vo/R=Vs/R
In negative half cycle of input voltage, SCR's T3 &T4 are triggered at an angle of (π+α). Here
output current & supply current are in opposite direction
Is=-Io
T3 & T4 becomes off at 2π.
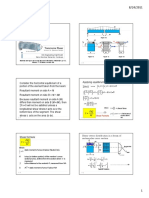
Circuit diagram of full-wave rectifier
17
Power and Industrial Electronics Lab
University of Sargodha Department of Electrical Engineering & Technology
Output waveforms for fully controlled rectifier with R load
Output waveforms with center taped fully controlled rectifier
18
Power and Industrial Electronics Lab
University of Sargodha Department of Electrical Engineering & Technology
Observations:
Using above equations, note down your findings at different angles
At =30 V0 =…………. I0=…………
At =60 V0 =…………. I0=…………
At =90 V0 =…………. I0=…………
At =120 V0 =…………. I0=…………
At =150 V0 =…………. I0=…………
At =180 V0 =…………. I0=…………
CONCLUSION & COMMENTS:
19
Power and Industrial Electronics Lab
You might also like
- TM 5-2410-241-24PDocument640 pagesTM 5-2410-241-24P"Rufus"100% (2)
- 4.circle Diagram of Three Phase Induction Motor From No Load & Blocked Rotor TestsDocument4 pages4.circle Diagram of Three Phase Induction Motor From No Load & Blocked Rotor Testsmandadi_sailesh67% (3)
- Whirlpool SchemaDocument11 pagesWhirlpool SchemanicoletasoceanuNo ratings yet
- Self Healing Concrete - PpsDocument17 pagesSelf Healing Concrete - PpsShubham Agarwal0% (1)
- Algorithm Analysis Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesAlgorithm Analysis Cheat Sheet PDFGabriele Gatti0% (1)
- Experiment#04 Single Phase Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier With Resistive LoadDocument3 pagesExperiment#04 Single Phase Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier With Resistive Loadkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Experiment#03 Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier With Resistive LoadDocument4 pagesExperiment#03 Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier With Resistive Loadkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Experiment#05 Single Phase Controlled Rectifier With Inductive LoadDocument4 pagesExperiment#05 Single Phase Controlled Rectifier With Inductive Loadkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab 2019Document38 pagesElectronics Lab 2019Gopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & Drivesshashi kumarNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesVK DNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument79 pagesLIC Lab ManualSakthikumar Balasundaram67% (3)
- Op AmpDocument16 pagesOp AmpChandan SasamalNo ratings yet
- Single Phase ControlledDocument39 pagesSingle Phase Controlledchandan Goswami50% (2)
- Beee Lab ManualDocument36 pagesBeee Lab ManualChanduVarmaKalidindiNo ratings yet
- To Construct A Square Wave GeneratorDocument4 pagesTo Construct A Square Wave GeneratorMozammel HossainNo ratings yet
- DEPT Lab Question2Document10 pagesDEPT Lab Question2Mostofa Al MuradNo ratings yet
- Op Amp ManualDocument12 pagesOp Amp ManualbndianonymousNo ratings yet
- FINAL IE Lab ManualDocument34 pagesFINAL IE Lab ManualAnudeex ShettyNo ratings yet
- O.C & S.C Test On Single Phase Transformer.: Siddhartha Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDocument6 pagesO.C & S.C Test On Single Phase Transformer.: Siddhartha Institute of Engineering & Technologyal imranNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Experiment-No. 6 Single-Phase Full and Half Wave Controlled SCR Rectifier Aim: To Study and Analyze The Properties and The Characteristics of A Single-PhaseDocument6 pagesPower Electronics Lab Experiment-No. 6 Single-Phase Full and Half Wave Controlled SCR Rectifier Aim: To Study and Analyze The Properties and The Characteristics of A Single-Phaseحسن علي جاسمNo ratings yet
- S6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFDocument27 pagesS6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFhariNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Demo NADocument155 pagesPower Electronics Lab Demo NAsoumyaNo ratings yet
- Ic Applications Lab NewDocument12 pagesIc Applications Lab NewSandy RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Exp-9 11Document4 pagesExp-9 11Dave Pooja DilipkumarNo ratings yet
- EM Observation - Expts-Back To Back 45Document102 pagesEM Observation - Expts-Back To Back 45Y RohitNo ratings yet
- PEL Lab ManualDocument127 pagesPEL Lab Manualmksamy2021No ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Cluster 4Document67 pagesUNIT 3 Cluster 4SandyNo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital Integrated Circuits: Uni T - 1 Operati Onal Ampli FierDocument116 pagesLinear and Digital Integrated Circuits: Uni T - 1 Operati Onal Ampli FierBOGGULA SURENDAR REDDYNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report REVISEDDocument21 pagesSeminar Report REVISEDayash mohantyNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic Lab 11Document2 pagesPower Electronic Lab 11Muhammed Rafay LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document32 pagesLab 1Adhithyan KzhlmNo ratings yet
- Bs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Document13 pagesBs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Bushra IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument53 pagesPe Lab ManualKada JashNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 10Document7 pagesExperiment - 10sanjuNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii Single Phase and Three Phase Controlled RectifiersDocument36 pagesUnit - Ii Single Phase and Three Phase Controlled RectifiersSukhpal Singh100% (2)
- 1 Half-Wave Rectifier With R LoadDocument18 pages1 Half-Wave Rectifier With R LoadKARMUGHILLAAN MANIMARAN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- EET1016 Lab SheetDocument14 pagesEET1016 Lab SheetNatasha92No ratings yet
- 10 InvertersDocument136 pages10 InverterszapzahtNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesExperiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierWaqas MughalNo ratings yet
- Isolators and CirculatorsDocument5 pagesIsolators and CirculatorsKavi KNo ratings yet
- Plugin-TE0221 - Analog & Digital System LabDocument53 pagesPlugin-TE0221 - Analog & Digital System Labnainesh goteNo ratings yet
- EE 306 ManualDocument55 pagesEE 306 Manualzain khuramNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - 18ec36 - Power Electronics - Module 2 - Raja GVDocument33 pagesLecture Notes - 18ec36 - Power Electronics - Module 2 - Raja GVRaja G VNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Power ElectronicsDocument23 pagesLab Manual: Power Electronicsprakhar yadavNo ratings yet
- RESISTANCEDocument50 pagesRESISTANCECdqdpNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: DC, Ac Power Systems Electrical Machines Drives SystemsDocument36 pagesElectric Circuits: DC, Ac Power Systems Electrical Machines Drives SystemsMatthew 'moka' BlandNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier As Differentiator: o Ip Op IpDocument5 pagesOperational Amplifier As Differentiator: o Ip Op IpEdward Raja KumarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory E-Sources - Second Year B - Tech IV SEM (ECE)Document142 pagesLaboratory E-Sources - Second Year B - Tech IV SEM (ECE)Chen-Wei LiangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document41 pagesChapter 4Anil ParmarNo ratings yet
- Swinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)Document24 pagesSwinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 (1903069)Document8 pagesLab 6 (1903069)Tahsin Zaman TalhaNo ratings yet
- CHP 6Document34 pagesCHP 6Kelvin LiewNo ratings yet
- IC Lab MaualDocument59 pagesIC Lab MaualKumar Goud.K100% (2)
- Lic Lab ManuelDocument51 pagesLic Lab Manuelgayathriarmstrong2No ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument20 pagesDC MachinesRaeniel SoritaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Laboratory Nitt B.Tech EeeDocument11 pagesPower Electronics Laboratory Nitt B.Tech EeeHahahNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument42 pagesBasic Electrical Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical EngineeringSourav SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document38 pagesChapter 5Markos NiguseNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Switchgear & Protection: Prepared By: MD - Foyez Ahammad Dept:EEE ID:13205100Document54 pagesSwitchgear & Protection: Prepared By: MD - Foyez Ahammad Dept:EEE ID:13205100kaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Amplitude: ModulationDocument19 pagesAmplitude: Modulationkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Experiment#05 Single Phase Controlled Rectifier With Inductive LoadDocument4 pagesExperiment#05 Single Phase Controlled Rectifier With Inductive Loadkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Experiment#03 Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier With Resistive LoadDocument4 pagesExperiment#03 Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier With Resistive Loadkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Preparing For The InterviewDocument8 pagesPreparing For The Interviewkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Experiment#04 Single Phase Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier With Resistive LoadDocument3 pagesExperiment#04 Single Phase Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier With Resistive Loadkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Islam and The Modern Nation StatesDocument1 pageIslam and The Modern Nation Stateskaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- 2 Purchase Planning 2.1 General 2.1.1 The Importance of Purchase PlanningDocument11 pages2 Purchase Planning 2.1 General 2.1.1 The Importance of Purchase Planningkaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:: M.Shahid Iqbal BSETF17-MOO9 M.Kaleem Ulllah BSETF17-M014Document25 pagesSubmitted By:: M.Shahid Iqbal BSETF17-MOO9 M.Kaleem Ulllah BSETF17-M014kaleem ullahNo ratings yet
- The Secrets of ManifestationDocument38 pagesThe Secrets of ManifestationPasupuleti KalaPriyaNo ratings yet
- CARTOON OF AN IMAGE DocumentationDocument38 pagesCARTOON OF AN IMAGE DocumentationDead poolNo ratings yet
- Comunications FundamentalsDocument271 pagesComunications FundamentalsDiego100% (1)
- Math Review Exercise: Problems From The Whole CourseDocument2 pagesMath Review Exercise: Problems From The Whole CourseKrista BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Measurement, Instrumentation and Control ME2400 Assignment 2Document13 pagesMeasurement, Instrumentation and Control ME2400 Assignment 2Chinmay TambatNo ratings yet
- Siemens Simatic S 7 300 - 400 - System and Standard Functions For S7-300 and S7-400Document486 pagesSiemens Simatic S 7 300 - 400 - System and Standard Functions For S7-300 and S7-400duniaengineering8666100% (7)
- Thermal Overload ProtectionDocument5 pagesThermal Overload ProtectionJigme TamangNo ratings yet
- NFC Technology: Assessment Effective of Security Towards Protecting NFC Devices & ServicesDocument5 pagesNFC Technology: Assessment Effective of Security Towards Protecting NFC Devices & Servicesfifa playNo ratings yet
- Essco CatalogueDocument80 pagesEssco CatalogueDarjeelingNo ratings yet
- Activity in KinematicsDocument7 pagesActivity in KinematicsMark Vincent OrdizNo ratings yet
- tl02 DatasheetDocument3 pagestl02 DatasheetadryanfahriNo ratings yet
- Terapi Seft Spiritual Emotional Freedom TechniqueDocument7 pagesTerapi Seft Spiritual Emotional Freedom TechniqueWiwik AristianiNo ratings yet
- MachineDocument13 pagesMachineashu0990% (2)
- Survey Ppt.1Document14 pagesSurvey Ppt.1priyanka sharmaNo ratings yet
- SJ-20140314093122-002-ZXA10 C300M&C350M (V4.0.1) Multi-Service Access Equipment Hardware DescriptionDocument96 pagesSJ-20140314093122-002-ZXA10 C300M&C350M (V4.0.1) Multi-Service Access Equipment Hardware Descriptionardi.noczteNo ratings yet
- GE G60 ManualDocument616 pagesGE G60 ManualZigor Larrabe UribeNo ratings yet
- PST Solides3dDocument193 pagesPST Solides3djithinaravind007No ratings yet
- Differential Housing ReconditioningDocument10 pagesDifferential Housing ReconditioningPetrus Kanisius WiratnoNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Simple DC MotorDocument1 pageHow To Make A Simple DC MotorQuen AñanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Growth & DevelopmentDocument4 pagesChapter 14 - Growth & DevelopmentGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Physics 20 21Document23 pagesPhysics 20 21CarolusBorromeusWisnuNo ratings yet
- 4 MB Transverse ShearDocument4 pages4 MB Transverse Shearkenny lieNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Questions: 3. What Is Starvation in Operating System?Document4 pagesUnit 1 Questions: 3. What Is Starvation in Operating System?Mohan PatelNo ratings yet
- Photo Luminescence of Surfaces and InterfacesDocument25 pagesPhoto Luminescence of Surfaces and InterfacesNick KellerNo ratings yet
- Using Some of Microsoft Office Excel FunDocument79 pagesUsing Some of Microsoft Office Excel FunPal RichardNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics: Sangeun Jin, Gary A. MirkaDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Industrial Ergonomics: Sangeun Jin, Gary A. MirkaAlexiNo ratings yet