Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Decision Making
Decision Making
Uploaded by
Mitali Talukdar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views19 pagesThe document provides an overview of business decision making. It discusses key concepts such as the types of decisions managers make, the decision-making process, models of decision making, and tools that can be used. Some of the main points covered include:
- Managers are responsible for making independent decisions to efficiently execute organizational functions.
- Decision-making involves selecting the best alternative from multiple options to solve problems like crises, opportunities, or routine issues.
- Models of rational decision making assume managers logically choose alternatives to maximize goals, though bounded rationality recognizes limits to rationality.
- Quantitative and qualitative tools can help structure decision making, including techniques like marginal analysis, decision trees, and brainstorming
Original Description:
A PPT on Decision making has been uploaded.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of business decision making. It discusses key concepts such as the types of decisions managers make, the decision-making process, models of decision making, and tools that can be used. Some of the main points covered include:
- Managers are responsible for making independent decisions to efficiently execute organizational functions.
- Decision-making involves selecting the best alternative from multiple options to solve problems like crises, opportunities, or routine issues.
- Models of rational decision making assume managers logically choose alternatives to maximize goals, though bounded rationality recognizes limits to rationality.
- Quantitative and qualitative tools can help structure decision making, including techniques like marginal analysis, decision trees, and brainstorming
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views19 pagesDecision Making
Decision Making
Uploaded by
Mitali TalukdarThe document provides an overview of business decision making. It discusses key concepts such as the types of decisions managers make, the decision-making process, models of decision making, and tools that can be used. Some of the main points covered include:
- Managers are responsible for making independent decisions to efficiently execute organizational functions.
- Decision-making involves selecting the best alternative from multiple options to solve problems like crises, opportunities, or routine issues.
- Models of rational decision making assume managers logically choose alternatives to maximize goals, though bounded rationality recognizes limits to rationality.
- Quantitative and qualitative tools can help structure decision making, including techniques like marginal analysis, decision trees, and brainstorming
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Business Decision
Making
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 1
A Core Function
Managers are responsible for effective and efficient
execution of these organizational functions.
A typical manager performs a number of functions
that are categorized as:
Interpersonal
Informational
Decisional
One of the key traits that distinguish managers from
operatives is the ability to make Independent
Decisions.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 2
What is Decision-Making?
The word decision is defined as:
“A choice between two or more alternatives”.
Thus decision-making can be defined as:
“the selection of a course of action from among
alternatives ”.
The process of choosing the most appropriate
alternative from a given set of alternatives.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 3
Types of problems decision makers face
Managerial decision making typically centers on three
types of problems:
Crisis
A crisis problem is a serious difficulty requiring immediate action.
Non-Crisis
A non-crisis problem is an issue that requires resolution but does not
simultaneously have the importance and immediacy characteristics of a
crisis.
Opportunity Problems
An opportunity problem is a situation that offers strong potential for
significant organizational gain if appropriate actions are taken.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 4
Differences in decision making situations
• There are two situation
Programmed Decision Making
Programmed Decisions are those made in routine, repetitive, well-
structured situations through the use of predetermined decision rules.
Non-Programmed Decision Making
Non-programmed Decisions are those for which predetermined
decision rules are impractical because the situations are novel and/or
relatively ill structured.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 5
Strategic Decisions
• Administrative decisions
• Routine or Operating decisions
Individual and Group decisions
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 6
Decision-Making Process
1) Identifying a problem
2) Identifying decision criteria
3) Allocating weights to criteria
4) Developing alternatives
5) Analyzing alternatives
6) Selecting an alternative
7) Implementing the alternative
8) Evaluation (of decision effectiveness)
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 7
Herbert Simon Model
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 8
Making Rational Decisions
A series of steps that decision makers should consider if their
goal is to maximize the quality of their outcomes.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 9
Rational Economic Man Model
• By Adam Smith, it states that managers are always rational
and choose the alternative which provides maximum gain.
• A rational decision maker has a clear idea of the problem to
be solved and he is fully objective and logical in approach.
Assumptions
1. Decision maker has a clear and well defined goal
2. Is rational and uninfluenced by emotions
3. Can identify the problem clearly and precisely
4. He knows all the alternatives available, with consequences
5. Can rank all consequences according to preferences
6. Has full freedom to choose the best alternative.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 10
Bounded Rationality
A critique of the rational man model. Administrative man he
says is the way decisions are actually made.
He says there are limits on decision making:
1. Bounded rationality: imperfect information about goals
and courses of action and relation of means to ends. Only
perceive a few of the possible decisions, courses of action,
dimly perceive means end relation.
2. Bounded discretion: constraints on optimizing, prior
commitments, moral and ethical standards, laws, and
social standards.
Forced to make decisions that are just good enough.
Called Satisficing. Search for a needle in the haystack.
Optimize is to look for the sharpest. Satisfied is to search
until you find the needle that is just sharp enough to do the
job.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 11
Bounded Rational: Causes
1. Inadequate goal formulation
2. Vaguely defined problems
3. Imperfect knowledge
4. Limited time and resources
5. Human Limitations
6. Power Politics
7. Environmental Dynamics
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 12
Group Decision-making
The group members interact with each other, discuss
the problem and make a collective decision.
The factors requiring group decisions include:
1. Involving sensitive issues
2. High cost alternatives
3. Involving very high risk factor
4. Strategic impact
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 13
Group Decisions: Advantages
1. Acceptance of group members
2. Coordination is easier
3. Communication is easier
4. Existence of large alternatives
5. More information can be processed
6. Diversity of experience and perspectives
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 14
Group Decisions: Disadvantages
1. Take longer time
2. Group can be indecisive
3. Groups can compromise
4. Groups can be dominated
5. Groups can “play games”
6. Victim to Groupthink - group members over look
other available alternatives for the sake of complete
consensus
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 15
Decision Making with Quantitative Tools
1. Marginal Analysis – Comparison of additional revenues from additional
costs to point where the cost resulting MC=MR
2. Cost Effectiveness Analysis – Cost Benefit Analysis
3. Risk Analysis – Determination of the nature and size of risk involved
4. Linear Programming – Technique for determination of optimum
combination of limited resources to minimize cost or to maximise profits.
5. Operations Research- Scientific analysis of decision problems
6. Decision Tree- Graphic method used for identifying the available
alternatives and the risk and outcome associated with each alternative.
7. Network Analysis- Analysis of a project into small interconnected in a
logical order. CPM and PERT
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 16
Decision Making with Qualitative Tools
1. Brainstorming - A group creativity technique by which a group tries to
find a solution for a specific problem by gathering a list of ideas
spontaneously contributed by its members.
2. Delphi Technique - A structured communication technique, originally
developed as a systematic, interactive forecasting method which relies
on a panel of experts. the experts answer questionnaires in two or
more rounds. After each round, a facilitator provides an anonymous
summary of the experts’ forecasts from the previous round as well as
the reasons they provided for their judgments. Thus, experts are
encouraged to revise their earlier answers in light of the replies of other
members of their panel. It is believed that during this process the range
of the answers will decrease and the group will converge towards the
"correct" answer.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 17
3. Nominal Group Technique- A decision making method for use
among groups of many sizes, who want to make their decision quickly, as by
a vote, but want everyone's opinions taken into account (as opposed to
traditional voting, where only the largest group is considered) . Facilitators
will encourage the sharing and discussion of reasons for the choices made
by each group member, thereby identifying common ground, and a plurality
of ideas and approaches. This diversity often allows the creation of a hybrid
idea (combining parts of two or more ideas), often found to be even better
than those ideas being initially considered. The numbers each solution
receives are totalled, and the solution with the lowest (i.e. most favored) total
ranking is selected as the final decision.
4. Simulation – Imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or
process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing
certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract
system.
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 18
?
Free Powerpoint Templates
Page 19
You might also like
- Oral Communication in Context 1st Quarter Week 1Document4 pagesOral Communication in Context 1st Quarter Week 1Valerie Cruz - Ocampo100% (7)
- Decision MakingDocument41 pagesDecision Makingkcirtap7489No ratings yet
- HBO Decision MakingDocument28 pagesHBO Decision MakingKha RenNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Earth Quake Unit Test (1.1)Document2 pagesEarth Science Earth Quake Unit Test (1.1)Julia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- Decision Making New Design FinalDocument25 pagesDecision Making New Design Finalmohamed.aliNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6. Decision MakingDocument65 pagesCHAPTER 6. Decision MakingJerome MogaNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument8 pagesDecision MakingDishuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8. Decision-Making ProcessesDocument47 pagesLecture 8. Decision-Making Processeschiarazando34No ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Human Relations Interpersonal Job-Oriented Skills 12th Edition DuBrin Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument35 pagesInstant Download PDF Human Relations Interpersonal Job-Oriented Skills 12th Edition DuBrin Solutions Manual Full Chaptervicvorpaqize100% (5)
- Prob Solving - Decision MakingDocument26 pagesProb Solving - Decision MakingSonia khanNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and Problem SolvingDocument34 pagesDecision Making and Problem SolvingAnanth AuditorNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lesson 6Document4 pagesModule 3 Lesson 6John Benz SamsonNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument6 pagesDecision MakingHiamsjisbNo ratings yet
- Decision Making (Canvas Upload) - 1Document28 pagesDecision Making (Canvas Upload) - 1Joshua Paro-AnNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Decision MakingDocument35 pages5.0 Decision MakingDaniel NimabwayaNo ratings yet
- 6 Decision MakingDocument28 pages6 Decision MakingMajd MustafaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in ManagementDocument5 pagesDecision Making in ManagementAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Models, Group Decision Making: DR A Jagan Mohan Reddy SIBM, SIU, HyderabadDocument16 pagesDecision Making Models, Group Decision Making: DR A Jagan Mohan Reddy SIBM, SIU, Hyderabadritam chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Butaslac Comilang Cabaluna Camingawan Canque CurachaDocument25 pagesDecision Making Butaslac Comilang Cabaluna Camingawan Canque CurachaGracelyn Abendan CanqueNo ratings yet
- Decision Making1Document20 pagesDecision Making1Kapil KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument4 pagesDecision MakingMousa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument40 pagesDecision MakingBeng Jacob RamoresNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Chapter6Document27 pagesMaintenance Chapter6Milion dugumaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ProcessDocument6 pagesDecision Making ProcessswethashakiNo ratings yet
- Decision - Making: An Essence To Problem SolvingDocument19 pagesDecision - Making: An Essence To Problem SolvingSubhash SoniNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument14 pagesDecision MakingGhanshyamDixitNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - Decision MakingDocument27 pagesMODULE 2 - Decision MakingThejas K JNo ratings yet
- Mgt17 (20 Files Merged)Document446 pagesMgt17 (20 Files Merged)zrdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document4 pagesChapter 12Shahid JugnooNo ratings yet
- LeadingDocument9 pagesLeadingLJ IDANE ARANASNo ratings yet
- Management U 4 NoteDocument18 pagesManagement U 4 Noteyordanosgetahun887No ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document7 pagesChapter 13Jim ThiveosNo ratings yet
- Decisionmaking ManagementDocument25 pagesDecisionmaking Managements a azeemNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Skills and TechniquesDocument17 pagesDecision Making Skills and Techniques212_sarathiNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Ethical Management ParadigmDocument49 pagesModule 7 Ethical Management ParadigmCholo MompilNo ratings yet
- Arthur Haurama Andrew Joshua Christopher Gau: Presented byDocument24 pagesArthur Haurama Andrew Joshua Christopher Gau: Presented byNguyen Dac ThichNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument16 pagesDecision MakingSakshi RelanNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 Making DecisionsDocument9 pagesCHP 2 Making DecisionsNour MoetassemNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Decision-Making PDFDocument10 pagesModule 6 Decision-Making PDFMahua Adak MandalNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Decision MakingDocument14 pagesChapter Three Decision Makingsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: Presented by Rupali SinghDocument36 pagesDecision Making: Presented by Rupali SinghNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report Decision Making ProcessDocument4 pagesNarrative Report Decision Making ProcessMyra GarciaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making SkillsDocument18 pagesDecision Making SkillsJino JohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - Decision MakingDocument33 pagesChapter - 4 - Decision MakingBerhanuTsarikuNo ratings yet
- MGT 316 Assignment Chapter 2 Spring 2017.docx-1Document4 pagesMGT 316 Assignment Chapter 2 Spring 2017.docx-1Hajra FarooqNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 6: Planning and Decision Making (Continuation of Lesson 5)Document4 pagesOrganization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 6: Planning and Decision Making (Continuation of Lesson 5)Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- MGT 501 Tutorial 3Document3 pagesMGT 501 Tutorial 3Caron KumarNo ratings yet
- Decision Making SkillsDocument14 pagesDecision Making Skillssimeon taiwoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document19 pagesChapter 5Fatimah EarhartNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and Problem Solving: LBM MD3Y1-7 Group 1Document30 pagesDecision Making and Problem Solving: LBM MD3Y1-7 Group 1Shubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Decision Making by Individuals & GroupsDocument44 pagesDecision Making by Individuals & Groupsneera SinghNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-Decision MakingDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 3-Decision MakingAngelineNo ratings yet
- Strategic Decision Making ProcessDocument24 pagesStrategic Decision Making ProcessNguyen Dac ThichNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument39 pagesDecision MakingSukirajh RasalingamNo ratings yet
- Module in DECISION MAKING TOOLSDocument24 pagesModule in DECISION MAKING TOOLSAlmira GalloNo ratings yet
- Decision Making SkillsDocument7 pagesDecision Making SkillsAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Reading Material PPM2Document129 pagesSupplementary Reading Material PPM2vishruth karasaniNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ModelsDocument5 pagesDecision Making ModelsAelia HassanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Managment Making DecisionDocument21 pagesFundamental Managment Making DecisionMd AlamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of PlanningDocument30 pagesFundamentals of PlanningTUSHAR RATHINo ratings yet
- 04 Cache MemoryDocument36 pages04 Cache Memorymubarra shabbirNo ratings yet
- HypothesisDocument17 pagesHypothesisRashi TutejaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4: Formalities of Launching A New VentureDocument10 pagesUNIT 4: Formalities of Launching A New VentureSmriti PakkiNo ratings yet
- InvensysCAD - Creo Behavioral Modeling ExtensionDocument3 pagesInvensysCAD - Creo Behavioral Modeling ExtensionanilpagarNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument2 pagesReferencesBrenda Rojas CardozoNo ratings yet
- 2013 ELAand Mathemaitcs Districtand Building Aggregates MediaDocument484 pages2013 ELAand Mathemaitcs Districtand Building Aggregates MediaGothamSchools.orgNo ratings yet
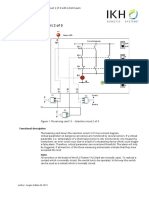
- 15 - Selection Circuit 2 of 3 - Solution - ENGDocument3 pages15 - Selection Circuit 2 of 3 - Solution - ENGhaftu gideyNo ratings yet
- Abstract Program Book International Seminar ISLIVAS 2012Document64 pagesAbstract Program Book International Seminar ISLIVAS 2012SantyindonesiaNo ratings yet
- DictationDocument45 pagesDictationRicky SanjayaNo ratings yet
- DX100 Instruction ManualDocument270 pagesDX100 Instruction Manualalan_smoNo ratings yet
- Identifying: MisinformationDocument25 pagesIdentifying: MisinformationKoala UmiNo ratings yet
- Mapping Diversity in Milan. Historical Approaches To Urban IDocument41 pagesMapping Diversity in Milan. Historical Approaches To Urban IMilica RisticNo ratings yet
- Radified Guide To Norton Ghost: A Tutorial On How To Create & Restore ImagesDocument22 pagesRadified Guide To Norton Ghost: A Tutorial On How To Create & Restore Imagesremush1No ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesEntrepreneurshipMahabub RabbaniNo ratings yet
- The Optimists Daughter Research PaperDocument5 pagesThe Optimists Daughter Research Papersvfziasif100% (1)
- Keysight 16196A/B/C/D Parallel Electrode SMD Test Fixture: Operation and Service ManualDocument81 pagesKeysight 16196A/B/C/D Parallel Electrode SMD Test Fixture: Operation and Service ManualKhang VũNo ratings yet
- Explanation TexrDocument8 pagesExplanation TexrKahlilNo ratings yet
- World Muslim Population: 1950 - 2020Document42 pagesWorld Muslim Population: 1950 - 2020Ouchaoua UcifNo ratings yet
- Rosyida - UTS - Thesis Writing Design ABDocument2 pagesRosyida - UTS - Thesis Writing Design ABYanto SoNo ratings yet
- Science & Technology WritingDocument92 pagesScience & Technology Writingrandy alvaroNo ratings yet
- Quareia Deck PDFDocument160 pagesQuareia Deck PDFzC6MuNiW100% (1)
- Comprehensive List of Excel Keyboard Shortcuts - 97 Shortcuts To Boost Your Productivity - ChandooDocument23 pagesComprehensive List of Excel Keyboard Shortcuts - 97 Shortcuts To Boost Your Productivity - ChandoonrscNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis boilEulerFoam PDFDocument168 pagesPHD Thesis boilEulerFoam PDFSAIKRISHNA NADELLANo ratings yet
- 2501 06 SlidingDocument6 pages2501 06 SlidingKiara Ticangan Argel0% (1)
- Credit Risk ModelingDocument213 pagesCredit Risk Modelinghsk1No ratings yet
- Thời gian làm bài: 90 phút, không kể thời gian phát đề (Đề thi có 07 trang)Document7 pagesThời gian làm bài: 90 phút, không kể thời gian phát đề (Đề thi có 07 trang)haNo ratings yet
- Class9 - Maths - UT1 - Jun2021 NewDocument3 pagesClass9 - Maths - UT1 - Jun2021 NewArhaan JavedNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Single Point Cutting Tool: JournalDocument8 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Single Point Cutting Tool: JournalsasaaNo ratings yet