Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 7 Motion in A Circle
Topic 7 Motion in A Circle
Uploaded by
Muhammad AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 7 Motion in A Circle
Topic 7 Motion in A Circle
Uploaded by
Muhammad AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 7 Motion in a circle
Summary
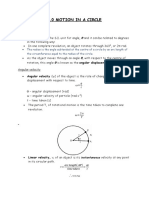
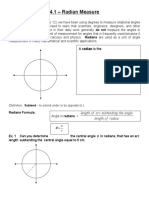
• Angles may be measured in radians (rad). One radian is the angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc
of the circle equal in length to its radius.
• Angular speed ω is the angle swept out per unit time by a line rotating about a point.
• A particle moving along a circle of radius r with linear speed v has angular velocity ω given by v = rω.
• A resultant force acting towards the centre of the circle, called the centripetal force, is required to make an
object move in a circle.
• An object moving along a circle of radius r with linear speed v and angular speed ω has an
acceleration a towards the centre (the centripetal acceleration) given by a = v /r = rω .
2 2
• For an object of mass m moving along a circle of radius r with linear speed v and angular speed ω, the
centripetal force F is given by F = mv /r = mrω .
2 2
Definitions and formulae
• One radian is defined as the angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius.
• θ (in radians) = arc distance ÷ radius of circle (i.e. 2π radians = 360° for 1 complete circle)
• Angular speed = Δθ/Δt
• Recall and use v = rω
• Centripetal acceleration = = rω
2
• A constant force acting perpendicular to the direction of motion is required for circular motion
Time period
centripetal force F = = mrω in circular motion.
2
You might also like
- Physics Week 8 9 Rotational Motion and The Law of GravityDocument44 pagesPhysics Week 8 9 Rotational Motion and The Law of GravityMark Lorens Staana100% (1)
- Section 6.2 Applications of Radian Measure: Objective 1: Determining The Area of A Sector of A CircleDocument3 pagesSection 6.2 Applications of Radian Measure: Objective 1: Determining The Area of A Sector of A CircleKhen Mehko OjedaNo ratings yet
- 52 Pu94 Circular Motion PDFDocument29 pages52 Pu94 Circular Motion PDFAdivaNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument12 pagesCircular Motionමේනුක සූවින්දNo ratings yet
- 4.2.1 Circular MotionDocument8 pages4.2.1 Circular MotionshakiraNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics - Circular MotionDocument23 pagesGrade 12 Physics - Circular MotionJabez CabahugNo ratings yet
- Circular MeasureDocument14 pagesCircular MeasureShadman BhuiyaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry ActivityDocument9 pagesCoordinate Geometry ActivityFernanda FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Motion IcDocument8 pagesMotion IcRaraNo ratings yet
- Motion in A CircleDocument4 pagesMotion in A CircleLaud FumhandaNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument34 pagesCircular MotionMustafa Hatim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Week 7 LectureDocument45 pagesWeek 7 LectureshakcodproNo ratings yet
- File 68244Document25 pagesFile 68244Atul SinghNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion CieDocument2 pagesCircular Motion CiePeterMwagweNo ratings yet
- OCR ALevel H556 Circular MotionDocument12 pagesOCR ALevel H556 Circular MotionlollolNo ratings yet
- Circular Frames PresentationDocument12 pagesCircular Frames PresentationADIBAR AHMAD RUDAWANNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion notesDocument6 pagesCircular Motion notesCatherine DayagNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Circle Part 1Document5 pagesMotion in A Circle Part 1Adam ChiangNo ratings yet
- Phy Sem 1 CHP 1Document9 pagesPhy Sem 1 CHP 1TAN YAN YAN MoeNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 1 Describing Rotational Motion StudentDocument11 pagesCA Lesson 1 Describing Rotational Motion StudentMunaNo ratings yet
- 04 RotationDocument11 pages04 RotationmanalaysayedelwaysNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 Rotational MotionDocument35 pagesWEEK 7 Rotational MotionsyafiqahizzatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Circular MotionDocument43 pagesChapter 7 Circular MotionMuhammad ZuhilmiNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion2Document7 pagesCircular Motion2333po2024No ratings yet
- Slides Motion (Contd) Uniform CircularDocument17 pagesSlides Motion (Contd) Uniform CircularOsahon IsaacNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Circular MotionDocument50 pages6.1 Circular MotionJiwoo SeoNo ratings yet
- 04 rotationDocument11 pages04 rotationCONIX- TVNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 A2 Motion in A Circle NotesDocument6 pagesTopic 12 A2 Motion in A Circle NotesIffahNo ratings yet
- Rotation of A Rigid Object About A Fixed AxisDocument71 pagesRotation of A Rigid Object About A Fixed Axisholman22494No ratings yet
- AP CH 7 PP - TeacherDocument91 pagesAP CH 7 PP - TeacherDianeNo ratings yet
- PHY 101 Lecture 3Document43 pagesPHY 101 Lecture 3johnbello1357No ratings yet
- Circular Motion 1 2022Document28 pagesCircular Motion 1 2022Harper IrwinNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion and The Law of GravityDocument47 pagesRotational Motion and The Law of Gravitymahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- 13 - Trigonometric FunctionsDocument63 pages13 - Trigonometric FunctionsjohnronnfernandezNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument26 pagesCircular Motionmalonesdave4No ratings yet
- G11 - Motion in CircleDocument34 pagesG11 - Motion in CircleNi Luh Divanian Darsana PutriNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument30 pagesCircular Motiondreambiggere22No ratings yet
- Motion in A CircleDocument11 pagesMotion in A CircleabdulrahmanibnfayyazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Circular MotionDocument19 pagesChapter 6: Circular MotionMary IdrusNo ratings yet
- g484 Module 2 4 2 1circular MotionDocument8 pagesg484 Module 2 4 2 1circular Motionapi-236179294No ratings yet
- 4.1 - Radian Measure: Degrees. There Is Another Unit of Measurement For Angles That Is Frequently Used Because ItDocument4 pages4.1 - Radian Measure: Degrees. There Is Another Unit of Measurement For Angles That Is Frequently Used Because ItBetty WangNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument4 pagesCircular Motionryan valerioNo ratings yet
- 5.2. Circular Motion PDFDocument3 pages5.2. Circular Motion PDFjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Motion in A CircleDocument10 pagesLecture 3-Motion in A CircleRichard SaputuNo ratings yet
- Notes On Rotational MotionDocument41 pagesNotes On Rotational Motionnagito komaedaNo ratings yet
- Rahadian N - Mechanics - Rotational Motion OnlyDocument25 pagesRahadian N - Mechanics - Rotational Motion OnlyBagus RizalNo ratings yet
- Uniform Rotary MotionDocument26 pagesUniform Rotary MotionMark RamosNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument6 pagesCircular MotionRasoolKhadibiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Circular MotionDocument2 pagesTopic 2 - Circular Motionmariam hNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (Part 1.1) - WEEK 1Document20 pagesCHAPTER 1 (Part 1.1) - WEEK 1Nadhirah NizarNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument28 pagesCircular MotionShapnil FinneyNo ratings yet
- Phy 111 DDocument22 pagesPhy 111 DCharisse StevensNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 8: Rotational MotionDocument9 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 8: Rotational MotionSenica Caydil Jay D.No ratings yet
- Circular Motion 2019Document40 pagesCircular Motion 2019Ali KasimNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion Notes ElectDocument11 pagesUniform Circular Motion Notes ElectProxima YusNo ratings yet
- Physics of Rotational Motion University of Applied Sciences Lippe Und Höxter, GermanyDocument16 pagesPhysics of Rotational Motion University of Applied Sciences Lippe Und Höxter, GermanyMartin CardozoNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument14 pagesCircular Motionwww.gulraizsaadiNo ratings yet
- Circular Notes 2023Document28 pagesCircular Notes 2023tingtong3141No ratings yet
- Circular Motion: 4.1b Further MechanicsDocument38 pagesCircular Motion: 4.1b Further MechanicsJeffreyNo ratings yet