Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SHEET7
SHEET7
Uploaded by
AmrAli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views1 pageThis document contains 6 practice problems related to buckling analysis of structural members. The problems involve determining critical buckling loads and forces for beams, rods, and struts made of various materials like steel and aluminum alloy. Buckling safety factors and minimum member diameters are also calculated based on given member properties, end conditions, loads and geometries.
Original Description:
buckling
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 6 practice problems related to buckling analysis of structural members. The problems involve determining critical buckling loads and forces for beams, rods, and struts made of various materials like steel and aluminum alloy. Buckling safety factors and minimum member diameters are also calculated based on given member properties, end conditions, loads and geometries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views1 pageSHEET7
SHEET7
Uploaded by
AmrAliThis document contains 6 practice problems related to buckling analysis of structural members. The problems involve determining critical buckling loads and forces for beams, rods, and struts made of various materials like steel and aluminum alloy. Buckling safety factors and minimum member diameters are also calculated based on given member properties, end conditions, loads and geometries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
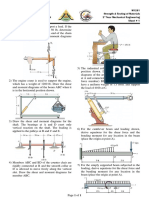
Benha University M1261
Benha Faculty of Engineering Strength & Testing of Materials
Mechanical Engineering Department 2nd Year Mechanical Engineering
Dr. Abdalla M. Abdalla Sheet # 7
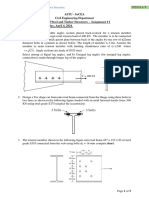
1) Determine the maximum force P that can be 4) If the torsional springs attached to ends A and C
applied to the handle so that the A-36 steel of the rigid members AB and BC have a
control rod BC does not buckle. The rod has a stiffness k, determine the critical load Pcr.
diameter of 25 mm.
2) Determine the maximum allowable intensity w
of the distributed load that can be applied to
member BC without causing member AB to
buckle. Assume that AB is made of steel and is
pinned at its ends for x–x axis buckling and
fixed at its ends for y–y axis buckling. Use a
factor of safety with respect to buckling of 3. Est
= 200 GPa, σy = 360 MPa.
5) Determine the maximum intensity w of the
uniform distributed load that can be applied on
the beam without causing the compressive
members of the supporting truss to buckle. The
members of the truss are made from A-36-steel
rods having a 60-mm diameter. Use F.S. = 2
against buckling.
3) If load C has a mass of 500 kg, determine the
required minimum diameter of the solid L2-steel
rod AB to the nearest mm so that it will not
buckle. Use against buckling. 6) Determine the maximum eccentric load P the
2014-T6-aluminum-alloy strut can support
without causing it either to buckle or yield. The
ends of the strut are pin-connected.
Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- Sheet (3) Chain DriveDocument1 pageSheet (3) Chain DriveAmrAliNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1-1Document3 pagesAssignment # 1-1getachew kassaNo ratings yet
- Composite Deck Technical Manual: 3WH-36 Hi FormDocument33 pagesComposite Deck Technical Manual: 3WH-36 Hi FormVinod Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- 01 Unit I Class Room Problems 2017-18Document6 pages01 Unit I Class Room Problems 2017-18Pavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Shear DesignDocument5 pagesShear DesignScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Final Exam-2021 Steel Design (In English)Document3 pagesFinal Exam-2021 Steel Design (In English)s.amir.hosseinieNo ratings yet
- Dss OrganizedDocument9 pagesDss OrganizedDevanth H CNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Tension MemberDocument29 pagesDesign and Analysis of Tension MemberJhianne Dulpina RoqueNo ratings yet
- Strema 101Document4 pagesStrema 101Hazel VidallonNo ratings yet
- Question TypesDocument1 pageQuestion TypesRSNNo ratings yet
- R13 Jntua Mechanical Engineer Question PaperDocument2 pagesR13 Jntua Mechanical Engineer Question PaperChandrika ReddyNo ratings yet
- 11 ThpaperDocument10 pages11 Thpapertoma97No ratings yet
- 2nd Lacture of Composite BeamsDocument32 pages2nd Lacture of Composite Beamsaa230086enNo ratings yet
- Strength 5 May 2021Document2 pagesStrength 5 May 2021Jon SnowNo ratings yet
- Connection AnalysisDocument13 pagesConnection Analysispavan kumar tNo ratings yet
- HLN On Overhead Line EquipmentDocument11 pagesHLN On Overhead Line EquipmentJayden BarnesNo ratings yet
- Revised - 2nd Lacture of Composite BeamsDocument42 pagesRevised - 2nd Lacture of Composite Beamsaa230086enNo ratings yet
- 2160607-Elementary Structural Design 09012017 040945AMDocument16 pages2160607-Elementary Structural Design 09012017 040945AMAydinAkhtarpour100% (1)
- Concrete 2 November 2022Document2 pagesConcrete 2 November 2022ronnelNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Tension Members PDFDocument26 pagesModule 2 Tension Members PDFjomarie apolinarioNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Analysis & FEA Simulation For Effect of Throat Thickness On Mig Welded Joint StrengthDocument6 pagesMathematical Analysis & FEA Simulation For Effect of Throat Thickness On Mig Welded Joint StrengthARUN VNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1محمد معوضNo ratings yet
- CE 1354 Design of RC ElementsDocument32 pagesCE 1354 Design of RC ElementsSyed Yousuf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Questions (Topic 3)Document2 pagesSelf Assessment Questions (Topic 3)Are FiqNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 1Document2 pagesIndividual Assignment 1Tsedey bereketNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of Steel StructuresDocument43 pagesStructural Design of Steel Structureskiran sreekumarNo ratings yet
- Steel ProblemsDocument8 pagesSteel Problemsiris coleenNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document16 pagesModule 3Hyurinshiro TetsuyaNo ratings yet
- Design of Compression MembersDocument16 pagesDesign of Compression MembersRoselle AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Fuad AhmedinNo ratings yet
- CE (PE) 702A Assignment CA2Document1 pageCE (PE) 702A Assignment CA2shoaib akhterNo ratings yet
- FINAL ExamDocument3 pagesFINAL ExamNahzgie GabzLac FloresNo ratings yet
- Mahalakshmi: Engineering CollegeDocument30 pagesMahalakshmi: Engineering CollegeSawan HussainNo ratings yet
- Densing (CVE163 Lab 2)Document9 pagesDensing (CVE163 Lab 2)Angela Christine DensingNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Element ProblemsDocument2 pagesDesign of Machine Element Problemsmaxpayne5550% (1)
- Enhancemnetof Seismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Columns With BucklingDocument6 pagesEnhancemnetof Seismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Columns With BucklingdestaNo ratings yet
- 7th Sem Prestressed Concrete StructuresDocument9 pages7th Sem Prestressed Concrete StructuresSubhikshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Bolted Connections: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction ManualDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Bolted Connections: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manualedn_mj1645No ratings yet
- Structural Steel: Beam: Types of BeamsDocument7 pagesStructural Steel: Beam: Types of BeamsRafael CuaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - STRESS Sem 2 2023-2024Document8 pagesPractice Problems - STRESS Sem 2 2023-2024Xavier LervineNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDocument5 pagesUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunNo ratings yet
- Beams Structural Design Using Bs 8110Document6 pagesBeams Structural Design Using Bs 8110Okareme PeaceNo ratings yet
- Contact Problems and StressDocument13 pagesContact Problems and Stressdf_campos3353No ratings yet
- Test With StrainDocument20 pagesTest With StrainPhạm Tiến ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Butt Weld StrengthDocument1 pageButt Weld Strengthmanivel.maruthamuthuNo ratings yet
- Corbon Content Steel 1Document75 pagesCorbon Content Steel 1Aditya GadhaviNo ratings yet
- Wachemo University College of Engineering and Technology Department of Civil Engineering Concrete Structures - CENG 6504 Due Date: May 30, 2022Document4 pagesWachemo University College of Engineering and Technology Department of Civil Engineering Concrete Structures - CENG 6504 Due Date: May 30, 2022Daniel TagesseNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Degree Examination Civil Engineering: (Nov-16) (Eur - 503A)Document3 pagesB.Tech. Degree Examination Civil Engineering: (Nov-16) (Eur - 503A)mgrreddyNo ratings yet
- ALCSM1 s2.0 S0141029616301596 MainDocument11 pagesALCSM1 s2.0 S0141029616301596 MainaykutartacNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Cağdaş AydınNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 F23Document3 pagesAssignment 1 F23hakehoustraNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV DSR Answer AssignmentDocument3 pagesUnit-IV DSR Answer Assignmenttejasgujar15No ratings yet
- 3Document6 pages3k2org.seoNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Discussion: Section A-ADocument4 pages5.4 Discussion: Section A-AAJBAJBNo ratings yet
- Tension Members: Tension Member Analysis StressDocument1 pageTension Members: Tension Member Analysis StresssereNo ratings yet
- Week 8 RC ColumnsDocument2 pagesWeek 8 RC ColumnsOmar ElerakyNo ratings yet
- Me6503 Dme Unit 3 Study Notes 2015Document21 pagesMe6503 Dme Unit 3 Study Notes 2015Bala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Steel TutorialsDocument7 pagesSteel Tutorialscuckoomodi1527No ratings yet
- Triangular LoadsDocument4 pagesTriangular LoadsMark SyNo ratings yet
- Shear Connection in Composite Bridge Beams - SteelconstructionDocument12 pagesShear Connection in Composite Bridge Beams - Steelconstructionpatricklim1982No ratings yet
- XGNPR Graphene Nanoplatelets Grade M en WHMIS OSHA GHS SDS 2015-11-26Document5 pagesXGNPR Graphene Nanoplatelets Grade M en WHMIS OSHA GHS SDS 2015-11-26AmrAliNo ratings yet
- SHEET6Document1 pageSHEET6AmrAliNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Chemtech Research: J.G. ManjunathaDocument11 pagesInternational Journal of Chemtech Research: J.G. ManjunathaAmrAliNo ratings yet
- Function (W) Angular - Velocity (F) % Calculate The Angular Velocity W (2 Pi F )Document1 pageFunction (W) Angular - Velocity (F) % Calculate The Angular Velocity W (2 Pi F )AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Torqe - Eq 3Document1 pageTorqe - Eq 3AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Torqe - Eq 3Document1 pageTorqe - Eq 3AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Variables Calculatting Variable The Check On The Twist and Make It Safe The Required DiameterDocument3 pagesVariables Calculatting Variable The Check On The Twist and Make It Safe The Required DiameterAmrAliNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) Belt Drive: Standard)Document2 pagesSheet (2) Belt Drive: Standard)AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Angular-Velocity 10Document1 pageAngular-Velocity 10AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) Revision: You Are Required ToDocument3 pagesSheet (1) Revision: You Are Required ToAmrAliNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) Belt Drive: Standard)Document2 pagesSheet (2) Belt Drive: Standard)AmrAliNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document1 pageSheet 1AmrAli0% (1)
- Impulse and MomentumDocument0 pagesImpulse and MomentumStone WangNo ratings yet