Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Reviewer 9
Chemistry Reviewer 9
Uploaded by
Jade Ronquillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pages1) The mole concept defines 1 mole as containing 6.022 x 1023 constituent particles, whether atoms, molecules, ions, etc.
2) Molar mass is calculated by adding the atomic masses of each element in a compound and represents grams/mole.
3) Percent composition by mass of an element in a compound is calculated by taking the molar mass of that element divided by the molar mass of the whole compound.
Original Description:
goodluck to your exam
Original Title
CHEMISTRY REVIEWER 9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The mole concept defines 1 mole as containing 6.022 x 1023 constituent particles, whether atoms, molecules, ions, etc.
2) Molar mass is calculated by adding the atomic masses of each element in a compound and represents grams/mole.
3) Percent composition by mass of an element in a compound is calculated by taking the molar mass of that element divided by the molar mass of the whole compound.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesChemistry Reviewer 9
Chemistry Reviewer 9
Uploaded by
Jade Ronquillo1) The mole concept defines 1 mole as containing 6.022 x 1023 constituent particles, whether atoms, molecules, ions, etc.
2) Molar mass is calculated by adding the atomic masses of each element in a compound and represents grams/mole.
3) Percent composition by mass of an element in a compound is calculated by taking the molar mass of that element divided by the molar mass of the whole compound.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
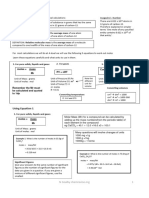
Mole Concept Atoms to moles
If one dozen is equals to 12 pieces, 1 mole is equals 6.022𝑥10!"
to 6.022 x 1023 (Avogadro’s number) given ×
1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
1 mole of a molecule, atom or ion will always be Percent Composition and Molar Mass
equal to 6.022 x 1023
How to compute for the molar mass?
23
1 mole of Carbon 6.022 x 10 atoms of
Add all the atomic weight of the element in a
Carbon compound.
1 mole of CO2 6.022 x 1023 molecule
of CO2 Example:
+
1 mole of Na 6.022 x 1023 atoms of CO2 = 12.01 (Atomic weight of Carbon) + 15.99x2
Na= (atomic weight of oxygen multiplied to how many
oxygens is in the molecule) = 43.99 (molar mass)
Note: 1 mole of a molecule contains 6.022 x 1023 Percent composition by mass use this formula
entities, but the moles of the elements involved
𝑛 × 𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑚𝑖𝑐 𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡
may be different. × 100
𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑑
Example: 1 mole of CO2 contains 6.022 x 1023
Example:
molecules of CO2 but it would contain twice the
number of oxygen in order to form the compound. CO2
This statement can be expressed using this Molar mass: 43.99
equation:
1(12.01)
%𝐶 = × 100 = 27.30%
2 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑂 6.022𝑥10TU 43.99
1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝐶𝑂T × × = 1.2044𝑥10TV
1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝐶𝑂T 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝑂 2(15.99)
%𝑂 = × 100 = 72.70%
43.99
Formulas
Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Mass to atoms/molecules
Ionic Bonds
1 mole 6.022x10!" Caused by the attraction of a metal cation to a non-
given × ×
atomic weight 1 mole metal anion. The ions are formed from the donation
of the electrons from metals which the non-metals
Atoms/molecules to Mass receive.
1 mole atomic weight Covalent Bonds
given × !" ×
6.022x10 1 mole
Covalent bonds exist due to the sharing of electrons
Mass to moles between non-metal.
1 mole Property Ionic Covalent
given ×
atomic weight Formed from Transferred Shared
electrons electrons
Moles to Mass Conductivity High Low
Solubility in Soluble Insoluble
#$%&'( *+',-$
given × Water
. &%/+
Boiling and High Low
Atoms to moles Melting Point
Phase in Solid Solid, Liquid
1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 Room and Gas
given × Temperature
6.022𝑥10!"
Variety of Carbon Compounds
What makes carbon special?
• Carbon can make four covalent bonds
• Can bond to another carbon to form long
chains
• Able to form single, double and triple bonds
Hydrocarbons (Hydrogen and Carbon)
Alkane – single bond C-C.
Alkene – at least one carbon double bond C=C.
Alkyne – at least one triple bond C≡C.
Some Common Uses of the Functional Groups
Alcohol – disinfectant, present in alcoholic drinks.
Ether – anesthetics
Aldehyde – reservation (formalin)
Ketone – nail polish remover (acetone).
Carboxylic Acid – vitamin C, present in various
citrus fruits.
Ester – artificial flavoring and aroma.
Amine – amino acids which is a building block of
protein.
Amide – used for making Kevlar and strong ropes.
You might also like
- Moles Gizmo by ADocument9 pagesMoles Gizmo by Apeepee poopooNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Nclex High YieldDocument32 pagesMental Health Nclex High Yieldnene lewis100% (1)
- Ark700a 1Document84 pagesArk700a 1Ana LauraNo ratings yet
- Personal Affidavit of Non-EmploymentDocument23 pagesPersonal Affidavit of Non-Employmentrussell apura galvezNo ratings yet
- (SciNotes) ChemistryDocument6 pages(SciNotes) ChemistrydxrksxxllNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry-Complete and UpdatedDocument109 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry-Complete and UpdatedSaadNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument58 pagesFinalJayson DoceNo ratings yet
- TrishaDocument73 pagesTrishaJayson DoceNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 Summary General Chemistry The Essential Concepts 7th EditionDocument50 pagesCHP 3 Summary General Chemistry The Essential Concepts 7th Editionyerturk2477No ratings yet
- 1 2 Revision Guide Calculations Aqa PDFDocument14 pages1 2 Revision Guide Calculations Aqa PDFAlisha ShahidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. The Mole Concept and The Molar Mass of ElementsDocument4 pagesLesson 3. The Mole Concept and The Molar Mass of ElementsJamelle SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - The MoleDocument28 pagesChapter 3 - The MoleNajma AqilahNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 EOY Revision PackageDocument67 pagesSec 3 EOY Revision Packagecharlotteyap0307No ratings yet
- C T: C C F E Part One: Mass and Moles of Substance: Hapter Hree Alculations With Hemical Ormulas and QuationsDocument16 pagesC T: C C F E Part One: Mass and Moles of Substance: Hapter Hree Alculations With Hemical Ormulas and QuationsAbdelfattah Mohamed OufNo ratings yet
- Physics NoDocument14 pagesPhysics NosofiajameNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviseDocument206 pagesChem ReviseAmir ArifNo ratings yet
- XI Study FullDocument89 pagesXI Study FullpradeepvcpNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Abul FazalDocument51 pagesChemistry: Abul FazalRania ZahidNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Revision Guide CalculationsDocument14 pages1 2 Revision Guide CalculationsHamid HarunaNo ratings yet
- MoleDocument2 pagesMoleحنين حنينNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mole?: Calculate How Many Molecules Are in 5.5 Moles of Glucose (C H O) ?Document5 pagesWhat Is A Mole?: Calculate How Many Molecules Are in 5.5 Moles of Glucose (C H O) ?Bea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Notes - Stoichiometry and The Mole ConceptDocument1 pageIB Chemistry Notes - Stoichiometry and The Mole ConceptKefin TajebNo ratings yet
- The Mole IntroductionDocument15 pagesThe Mole IntroductionJov Vito Jr.No ratings yet
- MCAT Gen Chem NotesDocument8 pagesMCAT Gen Chem NotesViviana PerezNo ratings yet
- Numbers and Molecules: Masses of Molecules Mass Not WeightDocument3 pagesNumbers and Molecules: Masses of Molecules Mass Not WeightShivani ArchuletaNo ratings yet
- Che - Lesson3 - Crystalline SolidDocument5 pagesChe - Lesson3 - Crystalline SolidBren Jousef BayhonNo ratings yet
- Neo Neet 12 p1 Phy e Nuclei 5 211Document87 pagesNeo Neet 12 p1 Phy e Nuclei 5 211Yashraj NarwariyaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd Edition Steven S Zumdahl Susan A ZumdahlDocument51 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd Edition Steven S Zumdahl Susan A ZumdahlChristianGonzalezsrybm100% (80)
- Adv Chem Week 3Document13 pagesAdv Chem Week 3Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- mbm362 5aDocument17 pagesmbm362 5aMert ÜnalNo ratings yet
- mbm362 5aDocument17 pagesmbm362 5aMert ÜnalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Calculations With Chemical Formulas and Equations PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 4 Calculations With Chemical Formulas and Equations PDFHani TamimiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Revision Guide Calculations AqaDocument14 pages1.2 Revision Guide Calculations AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- C15 Notes CH2 StoichiometryDocument5 pagesC15 Notes CH2 StoichiometryArnieNo ratings yet
- (B) The Components of MatterDocument52 pages(B) The Components of MatterJoe NasalitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three:: StoichiometryDocument67 pagesChapter Three:: StoichiometryBiagio CastronovoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Stoichiometry Part-1Document30 pagesChapter 3 Stoichiometry Part-1eyadismail40No ratings yet
- HGC1101 Recorded Lec On Mole ConceptDocument24 pagesHGC1101 Recorded Lec On Mole Concepto livNo ratings yet
- 1 The Mole ConceptDocument20 pages1 The Mole ConceptAlliyah Cecilio AndreaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2 Practice MSDocument3 pagesChemistry Paper 2 Practice MSQidaliNo ratings yet
- MolesDocument11 pagesMolesAiram Ailicec Ojepse ValesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula and Percent CompositionDocument73 pagesChemical Formula and Percent Compositiontupasrowen65No ratings yet
- Oxo ACheQ 0201 cs01 XxaannDocument3 pagesOxo ACheQ 0201 cs01 XxaannAs6870No ratings yet
- Mole and Stoichiometry PIDocument38 pagesMole and Stoichiometry PIvinuns18No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Atoms Molecules StoichiometryDocument25 pagesChapter - 1 - Atoms Molecules StoichiometrylidiaepNo ratings yet
- Math ReviewDocument3 pagesMath ReviewmasamocmarquishaNo ratings yet
- Aspire Mole Concept (17!4!21)Document44 pagesAspire Mole Concept (17!4!21)sourav gargNo ratings yet
- Mass and Moles: General Chemistry I: CHEM 1111 Alberto L. Vivoni AlonsoDocument15 pagesMass and Moles: General Chemistry I: CHEM 1111 Alberto L. Vivoni AlonsoBryan BerriosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Moles 2021Document35 pagesChapter 3 - Moles 2021dyron francoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Student Post-Lecture1Document25 pagesChapter 2 Student Post-Lecture1Taha Alper ŞenNo ratings yet
- Moleconcept NotesDocument53 pagesMoleconcept Notesajay gudlaNo ratings yet
- Unhh TitledDocument39 pagesUnhh Titledraza anandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - StoichiometryDocument42 pagesChapter 3 - StoichiometrymachungwachishimbaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - June 2015Document1 pageChemistry - June 2015Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry - Chemical CalculationsDocument81 pagesStoichiometry - Chemical CalculationsZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Inorganic and Analytical Chem Module 78 1Document14 pagesInorganic and Analytical Chem Module 78 1Donita Rose AdtoNo ratings yet
- 03 - Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument31 pages03 - Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsMorales, Jerome R.No ratings yet
- ExplainerrrrrDocument12 pagesExplainerrrrrbruhstfuxdNo ratings yet
- 1-Why The Concept of Mole Was InventedDocument5 pages1-Why The Concept of Mole Was InventedMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Chemistry (2021-22)Document15 pagesBasic Concept of Chemistry (2021-22)ritvikpradeepNo ratings yet
- Colour and the Optical Properties of Materials: An Exploration of the Relationship Between Light, the Optical Properties of Materials and ColourFrom EverandColour and the Optical Properties of Materials: An Exploration of the Relationship Between Light, the Optical Properties of Materials and ColourNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Sales Rep. / Sales ManagerDocument3 pagesSales Rep. / Sales Managerapi-121455688No ratings yet
- Cl3 Eng Chapter 2Document9 pagesCl3 Eng Chapter 2smruti sangitaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solutions Manual To Accompany Statistics and Data Analysis 9780137444267 PDFDocument34 pagesFull Download Solutions Manual To Accompany Statistics and Data Analysis 9780137444267 PDFdonna.duke560100% (33)
- Engine Dynamic Properties-3Document5 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties-3Gthulasi78No ratings yet
- Wicking Suggestion Chart P SDocument2 pagesWicking Suggestion Chart P Ssusan_alexander_77No ratings yet
- Agung Podomoro Land: 2H10 Earnings Preview and Focus AreasDocument9 pagesAgung Podomoro Land: 2H10 Earnings Preview and Focus AreaserlanggaherpNo ratings yet
- Prayer LetterDocument9 pagesPrayer LetterJohnNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses WorksheetDocument1 pagePast Tenses WorksheetAyşe KadirNo ratings yet
- User Manual Smart Eather Ensors: A Passion For Precision Passion Pour La PrécDocument169 pagesUser Manual Smart Eather Ensors: A Passion For Precision Passion Pour La PrécJose MorenoNo ratings yet
- Cisco - Two Mds San Switches After Connecting With Isl or EislDocument11 pagesCisco - Two Mds San Switches After Connecting With Isl or EislbahugunaharishNo ratings yet
- METHODS OF TEACHING Lesson 1Document19 pagesMETHODS OF TEACHING Lesson 1Joey Bojo Tromes BolinasNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Syllabus DeclassifiedDocument4 pagesApplied Economics Syllabus DeclassifiedAl Jay MejosNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms Relating To Signs and Symptoms: DictionaryDocument9 pagesGlossary of Terms Relating To Signs and Symptoms: DictionaryMishael Octaviany JirehNo ratings yet
- 【拉图尔】临界区域:关键区域Critical ZonesDocument472 pages【拉图尔】临界区域:关键区域Critical Zoneszhang yanNo ratings yet
- Business Research ReportDocument16 pagesBusiness Research Reportapi-454197312No ratings yet
- WeaknessesDocument4 pagesWeaknessesshyamiliNo ratings yet
- 08 Investmentquestfinal PDFDocument13 pages08 Investmentquestfinal PDFralphalonzo0% (1)
- Compuware DCRUM Intro 2012 Version 12.00Document142 pagesCompuware DCRUM Intro 2012 Version 12.00JanNo ratings yet
- 12cheat Sheet - IntegersDocument2 pages12cheat Sheet - IntegersshagogalNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument17 pagesStringsnikhil kumarNo ratings yet
- Activity STSDocument1 pageActivity STSRalph ZeusNo ratings yet
- Joseph Kyle Neibert v. Computer Sciences Corporation, 11th Cir. (2015)Document20 pagesJoseph Kyle Neibert v. Computer Sciences Corporation, 11th Cir. (2015)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Object Detection and Trackinfg in Videos: N. RasathiDocument8 pagesObject Detection and Trackinfg in Videos: N. RasathiIJITJournalsNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLesson PlanAyameeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 2a: Visualizing Fractions Equal To One and Greater Than OneDocument16 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 2a: Visualizing Fractions Equal To One and Greater Than OneVanessa NaveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Marketing Research MalhotraDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Marketing Research MalhotraFoveero link100% (1)
- Billy Elliot EssayDocument2 pagesBilly Elliot Essayafabkgddu100% (1)