Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 2 - Topic E - Lessons 16-18
Key Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 2 - Topic E - Lessons 16-18
Uploaded by
api-483407220Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 2 - Topic E - Lessons 16-18
Key Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 2 - Topic E - Lessons 16-18
Uploaded by
api-483407220Copyright:
Available Formats
GRADE 5 | MODULE 2 | TOPIC E | LESSONS 16–18
KEY CONCEPT OVERVIEW
Lessons 16 through 18 focus on strategies to help students solve division problems of multi-digit
numbers.
You can expect to see homework that asks your child to do the following:
▪▪ Rewrite division problems as easier problems, and then solve. For example,
12,000 ÷ 300
= 12,000 ÷ 100 ÷ 3
= 120 ÷ 3
= 40
▪▪ Estimate the quotient. For example,
609 ÷ 24
≈ 600 ÷ 20
= 30
▪▪ Solve word problems that involve division of multi-digit numbers.
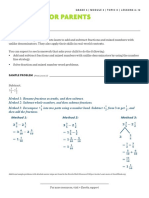
SAMPLE PROBLEM (From Lesson 18)
Estimate the quotient.
5,492 ÷ 72
≈ 5,600 ÷ 70
= 560 ÷ 7
= 80
Additional sample problems with detailed answer steps are found in the Eureka Math Homework Helpers books. Learn more at GreatMinds.org.
For more resources, visit » Eureka.support
GRADE 5 | MODULE 2 | TOPIC E | LESSONS 16–18
HOW YOU CAN HELP AT HOME
▪▪ Play a skip-counting contest with your child. For example, count by 3’s to 30: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, ….
Count by 30’s to 300: 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, …. Count by 300’s to 3,000: 300, 600, 900, 1200, 1500, ….
▪▪ Play the Rounding card game with your child.
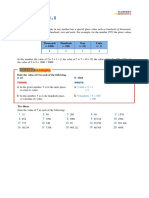
1. Take the jacks, queens, kings, tens, and jokers out of the deck.
2. Put the stack of remaining cards facedown.
3. Flip a set number of cards and have your child practice rounding the number represented
by the flipped cards to different place value units.
For example, you flip a 6, a 1, an 8, and a 2; they represent 6,182. Rounding 6,182 to the nearest
ten is 6,180; rounding 6,182 to the nearest hundred is 6,200; and rounding 6,182 to the nearest
thousand is 6,000.
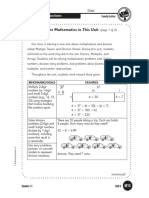
TERMS
Quotient: The answer resulting from the division of two numbers. For example, in 5.4 ÷ 6 = 0.9,
the number 0.9 is the quotient.
For more resources, visit
» Eureka.support © 2016, GREAT MINDS®
You might also like
- Singapore Math Challenge, Grades 5 - 8From EverandSingapore Math Challenge, Grades 5 - 8Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Matematica BasicaDocument93 pagesMatematica Basicavskywokervs100% (2)
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 2 - Topic G - Lessons 24-27Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 2 - Topic G - Lessons 24-27api-483407220No ratings yet
- Parent-Tips g5m2tbDocument2 pagesParent-Tips g5m2tbapi-483407220No ratings yet
- Parent-Tips g5m4tfDocument2 pagesParent-Tips g5m4tfapi-242423137No ratings yet
- Y3 Maths Booster PackDocument29 pagesY3 Maths Booster Packmadhujayan0% (1)
- Unit 9Document4 pagesUnit 9api-260708970No ratings yet
- Yr2 Assessment Cards: The National Strategy inDocument8 pagesYr2 Assessment Cards: The National Strategy ingabio_1No ratings yet
- ELGI Tri candra-5B-A1G018110Document3 pagesELGI Tri candra-5B-A1G018110tiara dwi rizkiNo ratings yet
- Division Lesson 20AJDocument16 pagesDivision Lesson 20AJtai yuanNo ratings yet
- Math TricksDocument14 pagesMath TricksaizaNo ratings yet
- Mondial Primary School Jl. Candi Golf Boulevard No. 2 Semarang - IndonesiaDocument7 pagesMondial Primary School Jl. Candi Golf Boulevard No. 2 Semarang - IndonesiaerikNo ratings yet
- STD 2 Test Maths 1Document5 pagesSTD 2 Test Maths 1Sade J SalvaryNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 3 - Module 3 - Topic A - Lessons 1-3Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 3 - Module 3 - Topic A - Lessons 1-3api-327874233No ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument4 pagesProblem SolvingPriyanka VermaNo ratings yet
- Dunblane Help at Home First LevelDocument2 pagesDunblane Help at Home First LevelDunblane PrimaryNo ratings yet
- 203 Maths TricksDocument50 pages203 Maths TricksSonia Gallegos100% (2)
- Math 5 q1 Week 2 MelcDocument60 pagesMath 5 q1 Week 2 MelcJacqueline AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Parent-Tips g5m3tcDocument2 pagesParent-Tips g5m3tcapi-483407220No ratings yet
- Mod 3 Parent Letter 6Document2 pagesMod 3 Parent Letter 6api-292114962No ratings yet
- Problems of The Week: VisualDocument27 pagesProblems of The Week: VisualRajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- Math Unit 2 Q1 Multiplication of Whole NumbersDocument41 pagesMath Unit 2 Q1 Multiplication of Whole Numberswe.stan.enhypen12345No ratings yet
- Revised Division PolicyDocument11 pagesRevised Division PolicyRandall RhodesNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Mathematics Take Home Pack Term 2 PDFDocument10 pagesGrade 3 Mathematics Take Home Pack Term 2 PDFLoretteNo ratings yet
- Senior Kangaroo 2018: SolutionsDocument11 pagesSenior Kangaroo 2018: SolutionsMmm100% (1)
- Inductive and Deductive ReasoningDocument6 pagesInductive and Deductive ReasoningSheryl BartolayNo ratings yet
- Encode MathDocument30 pagesEncode MathJerome OcampoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Math Grade 4 Deductive MethodDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Math Grade 4 Deductive Methodc76991350No ratings yet
- Mathemagic Teacher GuideDocument14 pagesMathemagic Teacher GuideGajender Singh RauthanNo ratings yet
- (Booklet) KS4 Mastery Foundation 1 - Answers - Single PagesDocument32 pages(Booklet) KS4 Mastery Foundation 1 - Answers - Single PagesJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Math StarsDocument40 pagesGrade 6 Math Starsandrugrasu100% (2)
- VTAMPS Session 2 - Primary 1Document11 pagesVTAMPS Session 2 - Primary 1Mark FoxNo ratings yet
- Math TricksDocument6 pagesMath TricksRoger nocomNo ratings yet
- Y 456 STR 1Document32 pagesY 456 STR 1Rula ShakrahNo ratings yet
- Math Tricks or HacksDocument5 pagesMath Tricks or HacksaizaNo ratings yet
- Cot Math2q3w2Document7 pagesCot Math2q3w2IVY A. GOLONo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry With Modeling and Visualization 6th Edition Rockswold Test BankDocument36 pagesAlgebra and Trigonometry With Modeling and Visualization 6th Edition Rockswold Test Banknotefulaculeate.8kbrvp100% (39)
- Factors Multiples and Prime NumbersDocument5 pagesFactors Multiples and Prime Numbersnalini1501_187919552No ratings yet
- Skill SheetsDocument82 pagesSkill SheetsVincents Genesius EvansNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 2 - Module 1 - Topic A - Lessons 1-2Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 2 - Module 1 - Topic A - Lessons 1-2api-327575446No ratings yet
- Primary Homework Help Games MathDocument5 pagesPrimary Homework Help Games Mathcffge1tw100% (1)
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 2 - Module 3 - Topic D - Lessons 8-10Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 2 - Module 3 - Topic D - Lessons 8-10api-292114962No ratings yet
- Mentally Multiplying by 2, 3, 4, 5 and 10 PDFDocument59 pagesMentally Multiplying by 2, 3, 4, 5 and 10 PDFFERJENNA DELLE TORREDNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 4 - Topic E - Lessons 13-20Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 4 - Topic E - Lessons 13-20api-327441821No ratings yet
- Mental Math Kids Can't ResistDocument80 pagesMental Math Kids Can't ResistImani Balivaja100% (1)
- Day 2 Week 7 q2Document11 pagesDay 2 Week 7 q2GERWIN MARIANONo ratings yet
- Essentials: Week by WeekDocument18 pagesEssentials: Week by WeekHirenkumar ShahNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Snacks: A Collection of Interesting Ideas to Fill Those Spare MomentsFrom EverandMathematical Snacks: A Collection of Interesting Ideas to Fill Those Spare MomentsNo ratings yet
- Impress Your Friends With Mental Math TricksDocument6 pagesImpress Your Friends With Mental Math Tricksray_xNo ratings yet
- Simply Math WRKBKDocument93 pagesSimply Math WRKBKkautiNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document32 pagesCH 01Vincents Genesius EvansNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.1 Coding and Cryptography (Modular Arithmetic and Congruence)Document32 pagesChapter 6.1 Coding and Cryptography (Modular Arithmetic and Congruence)Kyle MartinezNo ratings yet
- Multiple Towers Division Stories Parent LetterDocument2 pagesMultiple Towers Division Stories Parent Letterapi-297079632No ratings yet
- Math Term 1 WK 3Document13 pagesMath Term 1 WK 3Jonelle ColquhounNo ratings yet
- Math Parent Letter-Q1Document1 pageMath Parent Letter-Q1api-261103964No ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 3 Q2 Module 13 1Document30 pagesMATHEMATICS 3 Q2 Module 13 1LEOPOLDO JUNEVIL, JR. PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 6Document8 pagesMathematics 4 6AprilNo ratings yet
- Parent-Tips g5m3tbDocument2 pagesParent-Tips g5m3tbapi-483407220No ratings yet
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 3 - Topic D - Lessons 13-16Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 3 - Topic D - Lessons 13-16api-483407220No ratings yet
- Parent-Tips g5m3tcDocument2 pagesParent-Tips g5m3tcapi-483407220No ratings yet
- Parent-Tips g5m2tdDocument2 pagesParent-Tips g5m2tdapi-483407220No ratings yet
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 2 - Topic G - Lessons 24-27Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 5 - Module 2 - Topic G - Lessons 24-27api-483407220No ratings yet
- Parent-Tips g5m2tbDocument2 pagesParent-Tips g5m2tbapi-483407220No ratings yet