Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geotechnics Reviewer
Geotechnics Reviewer
Uploaded by
anon_365523868Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geotechnics Reviewer
Geotechnics Reviewer
Uploaded by
anon_365523868Copyright:
Available Formats
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
Etymology Geotechnical engineers can be employed by the following
types of organizations:
GEOTECHNICAL – relating to the application of
technology to engineering problems caused by Colleges and universities
geological factors. Construction contractors
o Geo – gē (Gk.), meaning earth Electrical utility companies
o Technical – tekhnikos (Gk.) Engineering consulting firms
– involving or needing special Mining companies
skills or knowledge. Municipal, regional, and federal government
ENGINEERING - ingenium (L.) – cleverness Oil and gas exploration, production, and
- ingenaire – to contrive; devise transportation companies
Petroleum services companies
Definition Public and private research organizations
branch of civil engineering that deals with the Real estate development companies
behavior of earth materials. History
important to construction activities taking place on
the surface or within the ground. (e.g. mining, 1. The Primitive Era of Soil Usage
coastal, drilling, and other discipline) 2. The Perception of Soil Design as an Art rather than
process of understanding and working with soil and Science
rock, underground water, site and structural 3. Foundation-Related Engineering Issues
conditions, in relation to a construction project. 4. The Emergence of the Principle of Soil Mechanics
(Geotechnical Engineering)
* Geotechnical engineers plan and design the structures for
buildings, roads, embankments, canals, and hundreds of Specialization
construction role. The geotechnical engineer will also deal SOIL MECHANICS
with geological hazards like landslides, soil erosion and, in - a discipline that applies the principles of
some extreme conditions, earthquakes. They study the soil engineering mechanics to soils to predict the
as well as rock layers that make up the earth in order to mechanical behavior of soils.
establish their physical and chemical characteristics. ROCK MECHANICS
What does Geotechnical Engineer do? - theoretical and applied science of the
mechanical behavior of rock and rock masses.
Figure out the impact that geological formations investigate subsurface conditions and materials;
may have on construction projects. determine the relevant physical/mechanical and
Guard and maintain the earth’s physical chemical properties of these materials;
environment during the development of major evaluate the stability of natural slopes and man-
public and private projects. made soil deposits;
Geotechnical engineers perform the following functions assess risks posed by site conditions;
design earthworks and structure foundations;
within the framework of the following jobs:
and monitor site conditions, earthwork and
Geotechnical or Geological Engineers (General) foundation construction.
Geotechnical or Geological Engineers (Oil Sands
Project)
Hydrogeological Engineer
Reservoir Geomechanics Engineer (Oil & Gas
Operations)
Geomechanics Engineers (Marine Operations)
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
Elements
Foundation and Pavement Design
Expansive/Collapsing Soils
Compaction Monitoring & Testing
Vibration Monitoring
Soil and Rock classification and parameters
Settlement and Subsidence Analysis
Field Permeability Tests
Underpinning and Special Foundation
Applications
SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS
o for transferring building loads to underlying
ground.
o mostly for firm soils or light loads
- Foundation Systems
Designing of Shallow
Foundation Systems –
Bearing Capacity Failure
DEEP FOUNDATIONS
o for transferring building loads to underlying
ground
o mostly for weak soils or heavy loads
- Foundation Systems
Deep Foundation Systems:
Driven Piles
Driven timber piles; Pacific
Highway
RETAINING WALLS
o prevent soils from spreading laterally
COFFERDAM
o sheet pile walls enclosing an area, to
prevent water seeping in
*By knowing about geotechnical engineering, the durability
of any civil engineering structures can be improved.
You might also like
- GeologyDocument29 pagesGeologyMonny MOM100% (1)
- Underground Neutral or Undergrounded SystemDocument4 pagesUnderground Neutral or Undergrounded SystemaocalayNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical EngineeringDocument13 pagesGeotechnical Engineeringwdy2ysq8d7No ratings yet
- Ce212 Lecture 1 - Geology For Civil Engineering IntroductionDocument11 pagesCe212 Lecture 1 - Geology For Civil Engineering IntroductionKIM JINHWANNo ratings yet
- 2 Geology IntroductionDocument7 pages2 Geology Introduction22100204No ratings yet
- CE 212 Lec 1. Course Description, Objectives, and IntroductionDocument30 pagesCE 212 Lec 1. Course Description, Objectives, and IntroductionJojo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Finals Topics 5-9Document16 pagesFinals Topics 5-9Pink WandererNo ratings yet
- CET 202 Module 1Document145 pagesCET 202 Module 1KRISHNENDU VRNo ratings yet
- Geo Lecture 1 - IntroDocument37 pagesGeo Lecture 1 - IntroMucaad XalaneNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument130 pagesIlovepdf Mergednik amriNo ratings yet
- What Is Geotechnical EngineeringDocument1 pageWhat Is Geotechnical EngineeringIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology: Prerequisites: None Text BOOKSDocument19 pagesEngineering Geology: Prerequisites: None Text BOOKSMuhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering DefinitionDocument1 pageGeotechnical Engineering DefinitionRamsis Pimentel BayoNo ratings yet
- GeotekDocument1 pageGeotekLabora RaefNo ratings yet
- G EOSYNTHETICSDocument33 pagesG EOSYNTHETICSNitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Geotechnical EngineeringDocument26 pagesLecture 6 Geotechnical EngineeringMichaela BotinNo ratings yet
- Engineering GeologyDocument10 pagesEngineering GeologyKaneezNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics IntroductionDocument82 pagesSoil Mechanics IntroductionShawonNo ratings yet
- Geology For Civil EngineersDocument4 pagesGeology For Civil EngineersMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- What Is Engineering Geology?Document26 pagesWhat Is Engineering Geology?kavya1811No ratings yet
- What Is Engineering GeologyDocument14 pagesWhat Is Engineering Geologyjustine galonNo ratings yet
- Advanced Foundation Engineering - Over ViewDocument96 pagesAdvanced Foundation Engineering - Over Viewofadol830No ratings yet
- Geotechnical EngineeringDocument5 pagesGeotechnical EngineeringNicole ForrosueloNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Unit 1 SE EGDocument15 pagesTopic 1 Unit 1 SE EGShivam G BorlepawarNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Lecture NotesSumalinog G. GelsonNo ratings yet
- Geology For Engineers Module 1 - IntroductionDocument31 pagesGeology For Engineers Module 1 - IntroductionMark GabonNo ratings yet
- The Geosynthetics For Sustainable Construction of Infrastructure ProjectsDocument33 pagesThe Geosynthetics For Sustainable Construction of Infrastructure ProjectsApoorva AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Geology in Civil EngineeringDocument5 pagesGeology in Civil EngineeringLyka Jane Tapia OpeñaNo ratings yet
- Geology For Engineers Module 1 - IntroductionDocument31 pagesGeology For Engineers Module 1 - Introductiontaylor swiftNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 1 - Pengenalan 2022Document25 pagesKuliah 1 - Pengenalan 2022nik amriNo ratings yet
- Eg PPT - 1Document43 pagesEg PPT - 1Rohit PatilNo ratings yet
- Ece 3106 - Engineering Geology - NotesDocument89 pagesEce 3106 - Engineering Geology - NotesBrian MutethiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ch1 and 2 Introduction and Relationship Between Eng Geology and Structures 2022 2023Document19 pages1 Ch1 and 2 Introduction and Relationship Between Eng Geology and Structures 2022 2023Yousif MawloodNo ratings yet
- Rock MechanicsDocument49 pagesRock MechanicsMohamed KessyNo ratings yet
- I. Geology in Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesI. Geology in Civil EngineeringBeau NorNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Engineering Geology To Civil EngineeringDocument9 pagesRelevance of Engineering Geology To Civil EngineeringIfiokobong AkpanNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 2 Importance of Geology in Civil EnggDocument15 pagesLecture No. 2 Importance of Geology in Civil EnggJovin ManarinNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument21 pages1 IntroductionZain KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Geotechnical EngineeringDocument14 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Geotechnical EngineeringkaicaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument7 pagesLecture 1 - Introductionsudeep neupaneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeotehnicalDocument15 pagesIntroduction To GeotehnicalAnna CristinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2 - Soil FormationandCompositionDocument25 pagesChapter 1 and 2 - Soil FormationandCompositionCarjez Love100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Geotechnical EngineeringDocument3 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Geotechnical EngineeringCecille Marcos100% (1)
- Module 5-7 - CeoDocument14 pagesModule 5-7 - CeoAndrei Yuri DiñoNo ratings yet
- CE-312 Engineering Geology and Seismology (Theory) Credit Hours 3Document20 pagesCE-312 Engineering Geology and Seismology (Theory) Credit Hours 3Hammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentJackie ChunNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology UNIT-I Part-IDocument14 pagesEngineering Geology UNIT-I Part-IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION: (Importance To A Civil Engineer) :: Engineering Geology Unit - IDocument13 pagesINTRODUCTION: (Importance To A Civil Engineer) :: Engineering Geology Unit - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Soil & Index PropertiesDocument49 pagesIntroduction of Soil & Index PropertiesShekh Muhsen Uddin Ahmed100% (1)
- Geotechnical EngineeringDocument5 pagesGeotechnical EngineeringAlbasir Tiang Sedik REENo ratings yet
- Geotech 1 I Module 1 I Geotechnical Engineering, Soil Mechanics and Geology Basic PrinicplesDocument2 pagesGeotech 1 I Module 1 I Geotechnical Engineering, Soil Mechanics and Geology Basic PrinicplesJohn Paul Liwaliw100% (1)
- 2 Introduction To Civil Engineering 4 11 2020Document125 pages2 Introduction To Civil Engineering 4 11 2020Yousif MawloodNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology As An Interdisciplinary FieldDocument8 pagesEngineering Geology As An Interdisciplinary FieldSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Geol I CH - 1Document9 pagesGeol I CH - 1Aye Thida NyeinNo ratings yet
- CE 211 Geology For Civil For Civil EngineeringDocument10 pagesCE 211 Geology For Civil For Civil EngineeringJackielou Marmojada DomaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter-i-Introduction To Soil MechanicsDocument27 pagesChapter-i-Introduction To Soil MechanicsVijaykumar Nagnaik100% (2)
- Geotechnical Engineering, Also Known As Geotechnics, Is The Branch ofDocument4 pagesGeotechnical Engineering, Also Known As Geotechnics, Is The Branch ofLester BiñasNo ratings yet
- Geology For Civil Engineers: Course OutlineDocument10 pagesGeology For Civil Engineers: Course OutlineCağdaş AydınNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology 1Document203 pagesEngineering Geology 1B Divya jyothiNo ratings yet
- Rock MechanicsDocument139 pagesRock MechanicsAastha Soni100% (1)
- Soil Investigation and Foundation DesignFrom EverandSoil Investigation and Foundation DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Book 1Document25 pagesBook 1mustha keemNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Fitting - ICE Level 3 - 06 10 14Document6 pagesMechanical Fitting - ICE Level 3 - 06 10 14KingsleyOwunariDokuboNo ratings yet
- Triptico InglesDocument10 pagesTriptico InglesMaria BerrioNo ratings yet
- Students DirDocument39 pagesStudents DirAriane PaquilbareNo ratings yet
- Vibration StandardDocument15 pagesVibration Standardelrajil100% (2)
- Session 13Document27 pagesSession 13etaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Waterfall ModelDocument8 pagesLiterature Review On Waterfall Modelc5pnw26s100% (1)
- Baja Saeindia 2020 - Old Vs New Team StatusDocument4 pagesBaja Saeindia 2020 - Old Vs New Team StatusRamraj SinghNo ratings yet
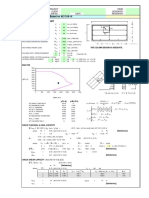
- Concrete Column Design Based On ACI 318-14: Input Data & Design SummaryDocument1 pageConcrete Column Design Based On ACI 318-14: Input Data & Design SummaryJuanAlfaroRodríguezNo ratings yet
- ME491-Ch 1Document42 pagesME491-Ch 1Yazan MannaNo ratings yet
- Night PlanDocument5 pagesNight PlanSyed Ali Hassan100% (1)
- Electrical Safety BookDocument36 pagesElectrical Safety Bookapi-285243890No ratings yet
- Affordable Housing Design BriefDocument3 pagesAffordable Housing Design Briefapi-193079720100% (1)
- D17A - BDA - (Autonomous Header) Index - 23-24Document4 pagesD17A - BDA - (Autonomous Header) Index - 23-24GautiiiNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument75 pagesSoftware EngineeringGolu MishraNo ratings yet
- Various Types of Shear ConnectorsDocument6 pagesVarious Types of Shear Connectorssilverware1No ratings yet
- Automotive Technology Level 6Document10 pagesAutomotive Technology Level 6nathanngari45No ratings yet
- CV - Brendon ChimpunguDocument6 pagesCV - Brendon ChimpunguRoy Marecha100% (1)
- Ajishmon Vs Qatar 8.01 YrsDocument5 pagesAjishmon Vs Qatar 8.01 YrsHR RecruiterNo ratings yet
- Software Sizing UnitsDocument7 pagesSoftware Sizing UnitsMurali ChemuturiNo ratings yet
- 7568-2144 Typical Manhole DetailsDocument1 page7568-2144 Typical Manhole DetailsKhabbab Hussain K-hNo ratings yet
- Michael Campbell's ResumeDocument1 pageMichael Campbell's ResumefrdmrckrNo ratings yet
- 2004 CFRPDocument9 pages2004 CFRPShashikant GaurNo ratings yet
- Presentation 11-16-05Document2 pagesPresentation 11-16-05Srimanthula SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Tensile Testing of Metallic Materials in Engineering MechanicsDocument4 pagesExperimental Study of Tensile Testing of Metallic Materials in Engineering Mechanicsishtiaq raoNo ratings yet
- B.E. EieDocument48 pagesB.E. EieSuganthiVasanNo ratings yet
- 0 - Mohd - Abrar CV PDFDocument3 pages0 - Mohd - Abrar CV PDFHayatul mondalNo ratings yet
- Abtech Stainless Steel and Mild Steel Electrical Enclosures Abtech SXDocument34 pagesAbtech Stainless Steel and Mild Steel Electrical Enclosures Abtech SXrocketvtNo ratings yet
- UAE Sprinkler InstallationDocument24 pagesUAE Sprinkler InstallationDinesh100% (2)