Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electricity & Magnetism PDF
Electricity & Magnetism PDF
Uploaded by
Jagdish SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electricity & Magnetism PDF
Electricity & Magnetism PDF
Uploaded by
Jagdish SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
downloaded from newtonclasses.
net Page 1
NTSE Question Bank
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
1. An electric charge on a body produces
(A) an magnetic field only (B) an electric field only
(C) both electric and magnetic field (D) neither electric nor magnetic field
2. Number of kilowatt hours=
volt ampere ............
1000
(A) time in seconds (B) time in hours
(C) time in minutes (D) time in days
3. The commonly used safety fuse wire is made of
(A) copper (B) lead
(C) nickel (D) an alloy of tin and lead
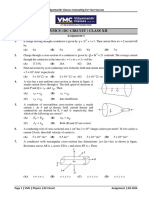
4. What is the current in the circuit
(A) 1.5A (B) 0.5A
(C) 2.5A (D) none of these
5. If the length of wire is doubled and its cross section is also doubled, then the resistance will
(A) increase eight times (B) decrease four times
(C) become four times (D) remain unchanged
6. In the circuit shown in the figure, the reading of the voltmeter V will be
(A) 4 V (B) 2 V
(C) 6 V (D) 3 V
Five identical resistance coils are connected in the network as shown in figure and the resistance
7. measured between A and B is 1 . Then the individual coils must have a resistance of
office : 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom tower , Circular Road Ranchi 1
ph : 0651-2562526,9835508812,8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net
downloaded from newtonclasses.net Page 2
1
(A) 1 (B)
4
7 7
(C) (D)
4 4
8. In figure distance (D) between conductors carrying currents I1 and I2 is varied. Which of the
following graphs correctly represents the variation of force (F) between the conductors and
distance (D)?
9. Which of the following
networks yields maximum
effective resistance between A
and B?
office : 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom tower , Circular Road Ranchi 1
ph : 0651-2562526,9835508812,8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net
downloaded from newtonclasses.net Page 3
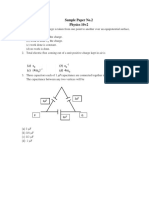
10. What is the resistance between A and B in the given network
3 4
(A) (B)
4 3
1
(C) 2 (D)
2
11. What is the resistance between A and B in the following circuit
(A) 1 (B) 2
1 3
(C) (D)
2 2
12. What is the resistance between P and Q?
3 4
(A) (B)
4 3
16
(C) (D) infinity
3
13. For a metallic conductor, current versus voltage graph is draw at two different temperatures T1 and
T2. From the graph it follows.
(A) T1 = T2 (B) T1 > T2
(C) T1 < T2 (D) nothing can be decided
office : 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom tower , Circular Road Ranchi 1
ph : 0651-2562526,9835508812,8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net
downloaded from newtonclasses.net Page 4
14. How much work is done in moving a charge of two coulombs from a point at 118 volts to a point
at 128 volts?
(A) 10 J (B) 20 J
1
(C) J (D) none of these
10
15. In general, when the temperature of a conductor increases, its resistance
(A) increases (B) decreases
(C) remains the same (D) none of these
16. The fact that current is associated with a magnetic field was discovered by
(A) Oersted (B) Maxwell
(C) Faraday (D) Ohm
17. Ampere rule is used to find the
(A) direction of current
(B) direction of magnetic field
(C) direction of motion of the conductor
(D) magnitude of current
18. The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction was discovered
(A) Lenz (B) Maxwell
(C) Fleming (D) Faraday
19. The intensity of a magnetic field is defined as the force experienced by a
(A) Standard compass
(B) unit positive charge
(C) unit negative charge
(D) unit north pole
20. A certain length of wire carries a steady current. It is bent to from a circular coil of one turn. The
same length is now bent more sharp to give a double loop of smaller radius, as shown in figure.
The magnetic field at the centre caused by the same current is
(A) a quarter of its first value
(B) unaltered
(C) four times its first value
(D) one half its first time
office : 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom tower , Circular Road Ranchi 1
ph : 0651-2562526,9835508812,8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net
downloaded from newtonclasses.net Page 5
21. Two long parallel conductors are placed at right angles to the metre scale, at the 2 cm and 6 cm
marks, as shown
The carry currents of 1 A and 3 A respectively. They will produce zero magnetic field at the
(A) zero mark (B) 10 cm mark
(C) 3 cm mark (D) 6 cm mark
22. Lenz’s law is a consequence of the law of conservation of
(A) energy (B) momentum
(C) angular momentum (D) charge and mass
23. The induced emf due to the motion of conductor in a uniform magnetic field is known as motional
emf. If l is the length of the conductor, V is the speed of conductor and B is the magnetic
induction, then the magnitude of induced emf is given by
Bl BV
(A) (B)
V l
(C) BiV (D) none of these
24. A metallic rod falls under gravity with its ends pointing east and west. Then
(A) an emf is induced in it as it cuts the magnetic lines of force
(B) no emf is induced at all
(C) two emfs of equal but opposite signs are induced, giving no net emf.
(D) its acceleration is equal to the product of g and the radius of the ring
25. A circular coil and a bar magnet recede from each other with the same velocity. Then
(A) there will be no induced emf in the coil
(B) there will be an induced emf in the coil
(C) an emf will be induced in the magnet
(D) none of these
26. Which of the following figures represents the magnetic lines of force due to an isolated north
pole?
office : 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom tower , Circular Road Ranchi 1
ph : 0651-2562526,9835508812,8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net
downloaded from newtonclasses.net Page 6
27. The wire having a black plastic covering is a
(A) live wire (B) neutral wire
(C) earth wire (D) none of these
28. Which of the following is not associated with Fleming’s left hand rule?
(A) Resistance (B) Magnetic field
(C) Force (D) Current
29. If V be the change in potential between two neighbhouring points r apart, the electric field E is
given by
V
(A) E V r (B) E
r
V
2
r
(C) E (D) E
V r
30. A fuse wire is generally made of
(A) silver (B) tin-lead alloy
(C) copper (D) either (A) or (B)
office : 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom tower , Circular Road Ranchi 1
ph : 0651-2562526,9835508812,8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net
You might also like
- MCQ 2nd Year Physics Complete BookDocument49 pagesMCQ 2nd Year Physics Complete BookHaseeb Ahmad92% (24)
- MEC 102 PS 1st Term-2011-2012Document3 pagesMEC 102 PS 1st Term-2011-2012Mond DamascoNo ratings yet
- Physics 40A - Midterm Exam Solutions - Winter 2013: Problem 1 (25 Points)Document7 pagesPhysics 40A - Midterm Exam Solutions - Winter 2013: Problem 1 (25 Points)Mt RushNo ratings yet
- 013 2023 ADocument14 pages013 2023 AAnoop T VNo ratings yet
- Kerala PSC Assistant Professor Question PaperDocument22 pagesKerala PSC Assistant Professor Question Paperageclt.ecNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper - 9 Term-1Document11 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - 9 Term-1JatinNo ratings yet
- CH # 13 (Current Electricity) - Physics 12 (TC)Document4 pagesCH # 13 (Current Electricity) - Physics 12 (TC)Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- 2ND YEAR PHYSICS Full Book Topical MCQS With ANSWERSDocument47 pages2ND YEAR PHYSICS Full Book Topical MCQS With ANSWERSArhamNo ratings yet
- CH # 15 (Electromagnetic Induction) - Physics 12 (TC)Document3 pagesCH # 15 (Electromagnetic Induction) - Physics 12 (TC)Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Physics 2nd Year MCQs ALPDocument23 pagesPhysics 2nd Year MCQs ALPAbu HurairaNo ratings yet
- Test-3 For AMUDocument4 pagesTest-3 For AMUAmmar YasirNo ratings yet
- Most Expected Questions-2023 (Mod2)Document27 pagesMost Expected Questions-2023 (Mod2)Gangambike HKNo ratings yet
- OTQs Physics Class 12th (1 - 14)Document141 pagesOTQs Physics Class 12th (1 - 14)VISALAKSHI ARUNACHALAMNo ratings yet
- XII PhysicsDocument11 pagesXII PhysicsAman SinghNo ratings yet
- DR Flash - Phy124Document7 pagesDR Flash - Phy124baitullahshakaNo ratings yet
- 7.prelim - Physics-2022-QnDocument10 pages7.prelim - Physics-2022-QnEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Class XII PhysicsDocument8 pagesClass XII PhysicsJordan CharlieNo ratings yet
- VIBRANT - Class - 10 - DPPs PhyDocument3 pagesVIBRANT - Class - 10 - DPPs PhyRani PandeyNo ratings yet
- CurrentDocument12 pagesCurrentrajvanshiaditya549No ratings yet
- Grade 12 MCQ Paper 2 18.08.2023Document8 pagesGrade 12 MCQ Paper 2 18.08.2023harkirat3116No ratings yet
- Revision Test 1Document6 pagesRevision Test 1Vansh BhandariNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics EM Half Yearly Exam 2023 Question Paper Madurai District English Medium PDF DownloadDocument2 pages12th Physics EM Half Yearly Exam 2023 Question Paper Madurai District English Medium PDF DownloadPavithra JNo ratings yet
- First Monthly Test MAP PHYSICS XIIDocument4 pagesFirst Monthly Test MAP PHYSICS XIIEr Zuhaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit XII A1Document4 pagesDC Circuit XII A1UJWALNo ratings yet
- Physics QP Ag 2023 PB-1 Set-1Document6 pagesPhysics QP Ag 2023 PB-1 Set-1Rayan SinghNo ratings yet
- All Chapter Mcqs PhysicsDocument11 pagesAll Chapter Mcqs PhysicsMoin YaqoobNo ratings yet
- 6th FNT XII Physics Irfan SanjraniDocument3 pages6th FNT XII Physics Irfan Sanjranipatanineel56No ratings yet
- Chapter #10Document15 pagesChapter #10Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Test#7 Physics Chapter-14+15 GCGDocument2 pagesTest#7 Physics Chapter-14+15 GCGsheikhabaidullah001No ratings yet
- Phy Eng Umeed (Laxman Sir) 3.ODocument52 pagesPhy Eng Umeed (Laxman Sir) 3.Oshivamkumar821101.nNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Summer Vacations Home WorkDocument7 pagesXII Physics Summer Vacations Home WorkVaibhav VermaNo ratings yet
- CH13 MCQDocument4 pagesCH13 MCQvehichlelover22No ratings yet
- 8 Copies 3rd Sem 2k19Document7 pages8 Copies 3rd Sem 2k19Abin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics Holiday Homework (2024-25)Document5 pagesClass Xii Physics Holiday Homework (2024-25)whitedevil0230No ratings yet
- XII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set B 2023Document6 pagesXII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set B 2023Anuradha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Physics - Mock Test - 1 (Obj) - 09.11.2021Document6 pagesClass Xii - Physics - Mock Test - 1 (Obj) - 09.11.2021Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Current Electricity STC VMDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Current Electricity STC VMVeeresh KalkoriNo ratings yet
- Current-Electricity MCQ 2Document9 pagesCurrent-Electricity MCQ 2Anant KumarNo ratings yet
- Section-A (Objective Type Questions) :: Physics by Er. Vinay Kumar 9905428278Document16 pagesSection-A (Objective Type Questions) :: Physics by Er. Vinay Kumar 9905428278PAWAN ROYNo ratings yet
- ouioECTROSTATIC Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFDocument33 pagesouioECTROSTATIC Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFKabilan KabilNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper-2 10+2Document5 pagesSample Paper-2 10+2MANVIRAJ SINGHNo ratings yet
- Marvel Mcq's 3rd PaperDocument5 pagesMarvel Mcq's 3rd Paper384varunjoshiNo ratings yet
- 12 Phy 1Document3 pages12 Phy 1Pathak JiNo ratings yet
- UnitTest - D22 Jun 2024Document21 pagesUnitTest - D22 Jun 2024Lokesh Daga JEE / NEET Chemistry FacultyNo ratings yet
- 8 Copies Ncert Part-1 12th PhyDocument7 pages8 Copies Ncert Part-1 12th PhyAbin VargheseNo ratings yet
- 12 JEE Physics WorksheeetDocument6 pages12 JEE Physics Worksheeetkeystonevp8No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic TechnologyDocument7 pagesElectrical and Electronic TechnologyDanelNo ratings yet
- Bihar Board (BSEB) Physics Class 12 Question Paper 2015Document20 pagesBihar Board (BSEB) Physics Class 12 Question Paper 2015LifeLine5iNo ratings yet
- CLASS 12 PHYSICS CH 1 Electric Charges and Fields MCQDocument47 pagesCLASS 12 PHYSICS CH 1 Electric Charges and Fields MCQPraneel BhattNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 1 MCQ Electric Charges and FieldsDocument33 pagesPhysics XII CH 1 MCQ Electric Charges and Fieldsmanu patankarNo ratings yet
- Tick The Correct Alternative: Monthly Test On Basic Electricity Surya Mitra Skill Development Program 4 Batch, 2018Document5 pagesTick The Correct Alternative: Monthly Test On Basic Electricity Surya Mitra Skill Development Program 4 Batch, 2018Anikendu MaitraNo ratings yet
- Electricity MCQ TestDocument9 pagesElectricity MCQ TestChandra SekarNo ratings yet
- 12th Unit Test Sankalp ObjectiveDocument6 pages12th Unit Test Sankalp ObjectiveJatin ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit and Circuit AnalysisDocument16 pagesElectrical Circuit and Circuit AnalysisGuruKPO100% (1)
- Ziet Bhubaneshwar: - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsDocument16 pagesZiet Bhubaneshwar: - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsI dont have a NameNo ratings yet
- Physics Exclusive Sample PapersDocument6 pagesPhysics Exclusive Sample Papersgauraadi739No ratings yet
- Physics QP Set-2Document13 pagesPhysics QP Set-2J M SUNIL SAIRAJNo ratings yet
- 10th Phy T5Document1 page10th Phy T5Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Set 2 (2.4-4.1)Document2 pagesCBSE Set 2 (2.4-4.1)keystonevp8No ratings yet
- Physics UT-III, calssXIIDocument2 pagesPhysics UT-III, calssXIImohd yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Nas MCQDocument7 pagesNas MCQPankaj KaleNo ratings yet
- NTSE MAT Last Minute Guidelines Quick Revision PDFDocument3 pagesNTSE MAT Last Minute Guidelines Quick Revision PDFJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- NTSE Syllabus For SAT Mathematics PDFDocument13 pagesNTSE Syllabus For SAT Mathematics PDFJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- NTSE Quick Tips MAT SAT What To Know How To Prepare PDFDocument1 pageNTSE Quick Tips MAT SAT What To Know How To Prepare PDFJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Preparation For NTSE: Selection ProcedureDocument1 pagePreparation For NTSE: Selection ProcedureJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Preparation of NTSE: ExamraceDocument1 pageStrategies For Preparation of NTSE: ExamraceJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- NTSE SAT - Important Topics (Download PDF) : ExamraceDocument6 pagesNTSE SAT - Important Topics (Download PDF) : ExamraceJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- 02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EDocument14 pages02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- What Chapter To Study: Tips For NTSE StudentsDocument2 pagesWhat Chapter To Study: Tips For NTSE StudentsJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Optics Assign PDFDocument115 pagesOptics Assign PDFJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Chapter 13Document15 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current Chapter 13Jagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Delhi NTSE Sample Paper SATDocument8 pagesDelhi NTSE Sample Paper SATJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Mat Ntse 2020 Stage 1 Paper Solutions DelhiDocument29 pagesMat Ntse 2020 Stage 1 Paper Solutions DelhiJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- NTSE Stage 1 State Level Model Paper 7Document26 pagesNTSE Stage 1 State Level Model Paper 7Jagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument45 pagesCoulomb's LawLigeon LavelNo ratings yet
- Test Corrections WavesDocument6 pagesTest Corrections WavesDuane TalleyNo ratings yet
- Determining A Bike Wheel's Moment of Inertia (Resistance To Acceleration)Document10 pagesDetermining A Bike Wheel's Moment of Inertia (Resistance To Acceleration)John D Pepin100% (1)
- Cambios de MW A DBmsDocument3 pagesCambios de MW A DBmsramuorNo ratings yet
- Principals of Electrical Engineering: University of Benghazi Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering DepartmentDocument24 pagesPrincipals of Electrical Engineering: University of Benghazi Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering DepartmentRawad SalemNo ratings yet
- Chap12 (3) 3Document65 pagesChap12 (3) 3Vince HarrisNo ratings yet
- 19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)Document4 pages19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)keyur.gala100% (1)
- BuoyancyDocument10 pagesBuoyancyYeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- 5 EmiDocument14 pages5 EmiJatin SonwalNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Formula List Form5Document18 pagesSPM Physics Formula List Form5ShidevNo ratings yet
- Gravitation: PSI AP B PhysicsDocument8 pagesGravitation: PSI AP B PhysicscjNo ratings yet
- "Buoyancy Factor": Mud Weight Lbs/GalDocument2 pages"Buoyancy Factor": Mud Weight Lbs/GalHeris SitompulNo ratings yet
- 7 - Motion in A CircleDocument13 pages7 - Motion in A CircleKamran KhursheedNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-03 Velocity and Graphs PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics 01-03 Velocity and Graphs PDFwade aryanNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument6 pagesMoving Charges and MagnetismRiki BorahNo ratings yet
- Brilliant SeriesDocument18 pagesBrilliant SeriesrayeezNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument80 pagesWork, Energy and PowerJack Lupino100% (1)
- Noor Science Academy Multan: Director: Naveed Noor Cell # 03052440984Document3 pagesNoor Science Academy Multan: Director: Naveed Noor Cell # 03052440984Naveed NoorNo ratings yet
- New 4 HK NewtonDocument20 pagesNew 4 HK Newtonyusuf efendiNo ratings yet
- Ballistic Galvanometer ExperimentDocument3 pagesBallistic Galvanometer ExperimentSurender K Sharma50% (2)
- NMDCAT 2021 Electromagnetism-1Document5 pagesNMDCAT 2021 Electromagnetism-1Umer Ali100% (1)
- Physics1 0608Document18 pagesPhysics1 0608tadruidNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Effects of Magnetic FieldDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Effects of Magnetic FieldSohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Current, Electricity and Its EffectDocument71 pagesCurrent, Electricity and Its EffectParminder singh parmarNo ratings yet
- Explorerof The Mysteries of The Atom: Nuclear Medicine Pioneer: Glenn T. SeaborgDocument2 pagesExplorerof The Mysteries of The Atom: Nuclear Medicine Pioneer: Glenn T. SeaborgtugustraNo ratings yet
- College Physics: Chapter 8: Work and EnergyDocument19 pagesCollege Physics: Chapter 8: Work and Energysheil.cogayNo ratings yet
- Friction: ES 1022y Engineering Statics FrictionDocument16 pagesFriction: ES 1022y Engineering Statics FrictionErikNo ratings yet
- Gauss Law For Dielectric MaterialsDocument3 pagesGauss Law For Dielectric Materialsabhishek secretNo ratings yet