Professional Documents
Culture Documents
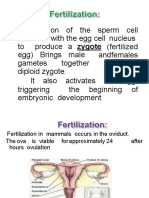
Fertilization: Interstitial Implantation: Adhesion Supported
Fertilization: Interstitial Implantation: Adhesion Supported
Uploaded by
Larraine LopezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fertilization: Interstitial Implantation: Adhesion Supported
Fertilization: Interstitial Implantation: Adhesion Supported
Uploaded by
Larraine LopezCopyright:
Available Formats
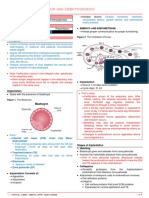
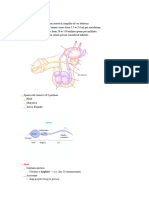
FERTILIZATION: Disintegrates: flagellum and mitochondria
Interstitial implantation: adhesion supported (most of the DNA is from the mother LOL)
migration of syncytiotrophoblasts into the endometrium Decondensation of sperm DNA
along breakdown of ECM by secretion of matrix Pronucleus around sperm DNA
metalloproteinases and other hydrolytic enzymes Egg completes 2nd meiotic division
Occurs in the ampulla Same: 2nd meiotic division, pronucleus
Involves Centrosome: organize the chromosomes for replication to
o Chemoattraction of the sperm to the ovum further develop the forming zygote
o Adherence to the zona pellucida Berne and Levy (6th ed); Ganong (24th ed)
o Penetration of the zona pellucida and acrosome
rxn
o Adherence of the sperm head to the cell
membrane of the ovum (with breakdown of the
area of fusion and release of sperm nucleus into
cytoplasm of the ovum)
Overview:
o Sperm binds to a receptor in the zona
o Acrosomal reaction: breakdown of the acrosome
Enzymes release: trypsin like acrosin
o When one membrane reaches the membrane of
the ovum, fusion of ovum membrane is mediated
by FERTILIN
o This fusion:
signal that initiates development
reduction of in the membrane potential of
the ovum that prevents polyspermy
structural change in zona pellucida that
provides protection against polyspermy on
a long term basis
o Blastocyst uterus : 3 days
o When the blastocyst is in contact with the
endometrium surrounded by
syncytriotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast
o Syncytiotrophoblast invdates the endometrium
and blastocyst implants
USUAL SITE OF IMPLANTATION: dorsal wall of uterus
Progesterone:
o Inhibts myometrial contrxn and prevents release
of paracrine factors that lead to menstruation
o Induces window of receptivity (Day 20 – Day 24)
Inc adhesivity of the endometrial ep
Formation of pinopodes (cellular
extensions)
Increased adhesive proteins
Dec antiadhesive proteins
Endometrium during implantation: full thickness, actively
secreting, tightly adhering
Steps (PCFCED – Pare, can Father Count Eggs Daw)
o STEP 1:
Penetration of expanded cumulus by sperm
Digestion of ECM of the cumulus by
hyaluronidase, PH – 20
o STEP 2: CAPACITATION
Penetration of zona pellucida by sperm
Binding of sperm to ZP3 release of
acrosomal enzymes : acrosomal rxn
Secondary binding: ZP2 digestion of
zona pellucida
o STEP 3:
Fusion of sperm and egg
o STEP 4:
A Ca2+ signaling cascade
o STEP 5:
Exocytosis of cortical granules enzymes
are released to the outside of the egg upon
exocytosis modify both ZP2 and ZP3
ZP2: can no longer bind acrosome
reacted sperm
ZP3: can no longer bind capacitated,
acrosome-intact sperm
This ensures that only ONE sperm
enters the egg
o STEP 6:
Entire sperm fuses with egg
You might also like
- PCR Troubleshooting and Optimization: The Essential GuideDocument2 pagesPCR Troubleshooting and Optimization: The Essential Guidewinter wineNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Square Dance Lyrics Your Description Picture of PhaseDocument3 pagesMeiosis Square Dance Lyrics Your Description Picture of PhaseKatNo ratings yet
- Conception 2021Document15 pagesConception 2021Dhinesh ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Fertilization PDFDocument36 pagesFertilization PDFFarhan AliNo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Çiğdem ElmasDocument49 pagesProf. Dr. Çiğdem ElmasMuhammet Fatih CantepeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 MouseDocument6 pagesChapter 10 MouseCarlo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization ClassDocument41 pagesFertilization ClassredoxtrpNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ravichandran Doraiswamy Professor of AnatomyDocument70 pagesDr. Ravichandran Doraiswamy Professor of AnatomySiva SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- A BeginningDocument12 pagesA BeginningAmey JatharNo ratings yet
- SAQ Unit 2Document9 pagesSAQ Unit 2Shilpa DuttaNo ratings yet
- Human FertilizationDocument3 pagesHuman Fertilizationtamalbio7No ratings yet
- (ObstetricsA) Implantation and Formation of Placenta and Fetal Membranes - Dr. Marinas (Lea Pacis) PDFDocument6 pages(ObstetricsA) Implantation and Formation of Placenta and Fetal Membranes - Dr. Marinas (Lea Pacis) PDFCristina Marie BarrugaNo ratings yet
- Gyne. FertilizationDocument10 pagesGyne. FertilizationdorquinloveNo ratings yet
- Capacitation: Acrosome ReactionDocument13 pagesCapacitation: Acrosome Reaction尤淳敏No ratings yet
- Fertilization Overview: Sperm PenetrationDocument13 pagesFertilization Overview: Sperm PenetrationAmira FahruddinNo ratings yet
- Fertilization PDFDocument25 pagesFertilization PDFgeovani humpireNo ratings yet
- Biol 216 2020 Topic 2 Development - Powerpoint 2.0 Fertilization - TaggedDocument24 pagesBiol 216 2020 Topic 2 Development - Powerpoint 2.0 Fertilization - TaggedMichael HamoudiNo ratings yet
- Only The Capacitated Spermatozoa Undergo Acrosomal ReactionDocument7 pagesOnly The Capacitated Spermatozoa Undergo Acrosomal ReactionbarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- 4 FertilizationDocument59 pages4 FertilizationQaiser InayatNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Gametogenesis and FertilizationDocument43 pagesLec 3 Gametogenesis and FertilizationDacks WangNo ratings yet
- Embryology - Fertilization: Paper 1 - Part BDocument5 pagesEmbryology - Fertilization: Paper 1 - Part BViswa GiriNo ratings yet
- GA&E 13 - Fertilization & ImplantationDocument49 pagesGA&E 13 - Fertilization & ImplantationSu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Local Media8080976868035007820Document19 pagesLocal Media8080976868035007820Kin elladoNo ratings yet
- Fertilization - ImplantationDocument4 pagesFertilization - ImplantationEzeoke ChristabelNo ratings yet
- (OB) 1.05 Implantation and Embryogenesis - Dr. AttabanDocument8 pages(OB) 1.05 Implantation and Embryogenesis - Dr. AttabanMarlon BauagNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument17 pagesFertilizationJahanvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy by DR - Jalal (Embryo)Document25 pagesAnatomy by DR - Jalal (Embryo)lorenoh21No ratings yet
- 02 FertilizationDocument6 pages02 Fertilizationhiba jasimNo ratings yet
- PDF - Curs 5a An 1 Sem 1 ENG - Fertilization and First WeekDocument26 pagesPDF - Curs 5a An 1 Sem 1 ENG - Fertilization and First Weekachraf rabadiNo ratings yet
- Fertilizacion RevisionDocument8 pagesFertilizacion RevisionAsistente IRP RESTREPONo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology - Fertilization (Reviewer)Document2 pagesDevelopmental Biology - Fertilization (Reviewer)shizuNo ratings yet
- HumanDocument18 pagesHumanDavidson VishalNo ratings yet
- Fertilization: Beginning A New Organism: Lee Kui SoonDocument31 pagesFertilization: Beginning A New Organism: Lee Kui SoonSayapPutihNo ratings yet
- Topic: Mechanisms of Fertilization:: Presented byDocument16 pagesTopic: Mechanisms of Fertilization:: Presented byMajani RajbonshiNo ratings yet
- Alakeshbarman Zoology PG 2nd FertilizationDocument28 pagesAlakeshbarman Zoology PG 2nd Fertilizationouafia liiamaniNo ratings yet
- Biology: Find and Fuse: Unsolved Mysteries in Sperm - Egg RecognitionDocument11 pagesBiology: Find and Fuse: Unsolved Mysteries in Sperm - Egg RecognitionFlavio NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation-1Document9 pagesFertilization and Implantation-1hussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- 1st WeekDocument25 pages1st WeekNamra NoorNo ratings yet
- Devlopment Plasm GerminalDocument81 pagesDevlopment Plasm GerminalRian AbendaniNo ratings yet
- 1ST WK EmbryoDocument29 pages1ST WK EmbryoHamilton SebastineNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation: Dr. Madhan KumarDocument47 pagesFertilization and Implantation: Dr. Madhan KumarTan DesmondNo ratings yet
- 14 - Fertilization To Implantation-MbbsDocument52 pages14 - Fertilization To Implantation-MbbsRaoulSusanto SusantoNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentDocument23 pagesFertilization & Fetal DevelopmentDimple CosNo ratings yet
- AlakeshBarman Zoology PG 2ND FERTILIZATIONDocument28 pagesAlakeshBarman Zoology PG 2ND FERTILIZATIONTrueAlpha 16No ratings yet
- Embryology Made Ridiculously Simple Handout PDFDocument15 pagesEmbryology Made Ridiculously Simple Handout PDFAsma SaleemNo ratings yet
- Human Development Days 1-4Document43 pagesHuman Development Days 1-4Kriztine Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 8673-2 Doc2Document13 pages8673-2 Doc2Imaan Khan ImaanNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument11 pagesFertilization137 - ShubhamNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument10 pagesFertilizationdeepakshi rajputNo ratings yet
- اجنه الاخصابDocument12 pagesاجنه الاخصابFatimaAmmarNo ratings yet
- Fertilization by Rahmat Sarkani ADocument10 pagesFertilization by Rahmat Sarkani ARahmat Sarkani AipamaNo ratings yet
- Act 1.1 SintesisDocument13 pagesAct 1.1 SintesisDulce DozalNo ratings yet
- Cellular Mechanism of Sexual ReproductionDocument20 pagesCellular Mechanism of Sexual ReproductionJessa BelleNo ratings yet
- Human Embryology: Dr. Anushri MukhopadhyayDocument61 pagesHuman Embryology: Dr. Anushri MukhopadhyaySabyasachi MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Getting To The Right SiteDocument17 pagesGetting To The Right SiteYunifianti ViviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part 3 FertilizationDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Part 3 FertilizationSyeda Fizza BatoolNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction-IiDocument11 pagesHuman Reproduction-IiSuryansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization &implantationDocument30 pagesFertilization &implantationAzza100% (1)
- C.Fetal DevelopmentDocument5 pagesC.Fetal DevelopmentJulio NazarethNo ratings yet
- Embriologie 2017Document100 pagesEmbriologie 2017Irina LutcanNo ratings yet
- Boundary Exon Prediction Using External InformationDocument5 pagesBoundary Exon Prediction Using External InformationInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- IFU Gram StainDocument5 pagesIFU Gram StainChandra MohanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Pharmacology & Therapeutics Pharmacological Targets and Emerging Treatments For Respiratory Syncytial Virus BronchiolitisDocument18 pages2020 Pharmacology & Therapeutics Pharmacological Targets and Emerging Treatments For Respiratory Syncytial Virus BronchiolitisMayra Concha OstosNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Review WSDocument3 pagesMeiosis Review WSKaelen S. ByrdNo ratings yet
- Improved Downstream Processing of Plasmid DNADocument9 pagesImproved Downstream Processing of Plasmid DNAavisankarNo ratings yet
- Shell Vial CulturesDocument1 pageShell Vial CultureskipilNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesSCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 Biomoleculesizi iordeinNo ratings yet
- Chevon Christie AP Biology Chap 12Document4 pagesChevon Christie AP Biology Chap 12amoney3No ratings yet
- Lesson1: Cell, The Basic Unit of LifeDocument4 pagesLesson1: Cell, The Basic Unit of Lifedream kingNo ratings yet
- The Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) As Biomedical Models: Feature ArticleDocument10 pagesThe Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) As Biomedical Models: Feature ArticleJuniClaudia13No ratings yet
- Cell Lines in Core CollectionDocument5 pagesCell Lines in Core CollectionAmihanNo ratings yet
- Variation and Classification Unit: 5Document19 pagesVariation and Classification Unit: 5MarkhorNo ratings yet
- 1 Extemporaneous Compounding - HPREDocument2 pages1 Extemporaneous Compounding - HPREKianna Marie MuyotNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Genomic DNA From Mammalian TissuesDocument3 pagesPreparation of Genomic DNA From Mammalian Tissuesraffaelec123No ratings yet
- Signature Assignment 6 Pedigree 1Document4 pagesSignature Assignment 6 Pedigree 1api-724481252No ratings yet
- English Final CoursDocument223 pagesEnglish Final CourspopeataNo ratings yet
- Advanced Science Kit Genetics: BiologyDocument2 pagesAdvanced Science Kit Genetics: BiologyUditha MuthumalaNo ratings yet
- Foundation - One CDXDocument43 pagesFoundation - One CDXWenju QianNo ratings yet
- (PHA6129 LAB) PrescriptionDocument5 pages(PHA6129 LAB) PrescriptionNotfor TaoNo ratings yet
- Buffalo Clone - NDRI, KarnalDocument2 pagesBuffalo Clone - NDRI, KarnalMayank Tandon100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S1477893921000375 MainDocument3 pages1 s2.0 S1477893921000375 MainjimiNo ratings yet
- The Use of Protecting Groups in Oxidizing A Specific Hydroxyl Group in RiboseDocument19 pagesThe Use of Protecting Groups in Oxidizing A Specific Hydroxyl Group in RiboseYardley MartinezNo ratings yet
- MASS Pharmacy Law 2014Document313 pagesMASS Pharmacy Law 20147bostondrNo ratings yet
- Lim Et Al 2017 PDFDocument37 pagesLim Et Al 2017 PDFkirshNo ratings yet
- Cord Blood BankingDocument1 pageCord Blood BankingBlue PasNo ratings yet
- Precision Nutrition Ebook Genetics The Universe WithinDocument390 pagesPrecision Nutrition Ebook Genetics The Universe WithinYeoh Shen Horng100% (1)
- Theories of Aging - Biologic Type STOCHASTICDocument12 pagesTheories of Aging - Biologic Type STOCHASTICApril Mae Magos LabradorNo ratings yet
- CourseInfo BookletDocument48 pagesCourseInfo BookletArindam MohantaNo ratings yet