Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing As A Profession Profession Characteristics of Nursing
Nursing As A Profession Profession Characteristics of Nursing
Uploaded by
Aqoh C MayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing As A Profession Profession Characteristics of Nursing
Nursing As A Profession Profession Characteristics of Nursing
Uploaded by
Aqoh C MayCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING AS A PROFESSION Nurse – originated from a Latin word NUTRIX, to
nourish.
Profession
Characteristics of Nursing
Is a calling that requires special knowledge, skill
and preparation. 1. Nursing is caring.
An occupation that requires advanced knowledge 2. Nursing involves close personal contact with the
and skills and that it grows out of society’s needs recipient of care.
for special services. 3. Nursing is concerned with services that take
humans into account as physiological,
psychological, and sociological organisms.
Professional Nursing 4. Nursing is committed to promoting individual,
Is an art and a science, dominated by an ideal of family, community, and national health goals in its
service in which certain principles are applied in best manner possible.
the skillful care of the well and the ill, and through 5. Nursing is committed to personalized services for
relationship with the client/ patient, significant all persons without regard to color, creed, social or
others, and other members of the health team. economic status.
6. Nursing is committed to involvement in ethical,
legal, and political issues in the delivery of health
Criteria of Profession care.
1. To provide a needed service to the society. Personal Qualities of a Nurse
2. To advance knowledge in its field.
3. To protect its members and make it possible to 1. Must have a Bachelor of Science degree in nursing.
practice effectively. 2. Must be physically and mentally fit.
3. Must have a license to practice nursing in the
Characteristics of a Profession country.
1. Education. A profession requires an extended A professional nurse therefore, is a person who
education of its members, as well as basic liberal has completed a basic nursing education
foundation. program and is licensed in his country to
2. Theory. A profession has a theoretical body of practice professional nursing.
knowledge leading to defined skills, abilities and
norms. Roles of a Professional
3. Service. A profession provides basic service.
1. Caregiver/ Care provider
4. Autonomy. Members of a profession have
the traditional and most essential role
autonomy in decision making and in practice.
functions as nurturer, comforter, provider
5. Code of Ethics. The profession as a whole has a
“mothering actions” of the nurse
code of ethics for practice. A profession has
provides direct care and promotes comfort of
sufficient self-impelling power o retain its
client
members throughout life. It must not be a mere
activities involves knowledge and sensitivity to
steppingstone to other occupations.
what matters and what is important to clients
6. Caring. The most unique characteristic of nursing
show concern for client welfare and acceptance of
as a profession is that, it is a CARING profession.
the client as a person
2. Teacher
Nursing
provides information and helps the client to learn
Is a disciplined involved in the delivery of health
or acquire new knowledge and technical skills
care to the society.
Encourages compliance with prescribed therapy.
Is a helping profession
promotes healthy lifestyles
Is service-oriented to maintain health and well-
interprets information to the client
being of people.
3. Counselor
Is an art and a science.
helps client to recognize and cope with stressful
psychologic or social problems; to develop an
improve interpersonal relationships and to teaching and treating minor and self- limiting
promote personal growth illness.
provides emotional, intellectual to and psychologic 3. Nurse-midwife
support A nurse who has completed a program in
Focuses on helping a client to develop new midwifery; provides prenatal and postnatal care
attitudes, feelings and behaviors rather than and delivers babies to woman with uncomplicated
promoting intellectual growth. pregnancies.
Encourages the client to look at alternative 4. Nurse anesthetist
behaviors recognize the choices and develop a A nurse who completed the course of study in an
sense of control. anesthesia school and assess, prescribe, deliver,
4. Change agent and manage care during the preoperative,
Initiate changes or assist clients to make perioperative, and postoperative phases of a
modifications in themselves or in the system of patient’s operative/interventional procedure(s).
care. 5. Nurse Educator
5. Client advocate A nurse usually with advanced degree, who
Involves concern for and actions in behalf of the beaches in clinical or educational settings, teaches
client to bring about a change. theoretical knowledge, clinical skills and conduct
Promotes what is best for the client, ensuring that research.
the client’s needs are met and protecting the 6. Nurse Entrepreneur
client’s right. A nurse who has an advanced degree, and
Provides explanation in client’s language and manages health-related business.
support clients decisions. 7. Nurse administrator
6. Manager A nurse who functions at various levels of
makes decisions, coordinates activities of others, management in health settings; responsible for the
allocate resource management and administration of resources and
evaluate care and personnel personnel involved in giving patient care.
Plans, give direction, develop staff, monitor
operations, give the rewards fairly and represent
both staff and administrations as needed. Fields and Opportunities in Nursing
7. Researcher 1. Hospital/Institutional Nursing
participates in identifying significant researchable A nurse working in an institution with patients
problems Example: rehabilitation, lying-in, etc.
participates in scientific investigation and must be 2. Public Health Nursing/Community Health Nursing
a consumer of research findings Usually deals with families and communities. (no
Must be aware of the research process, language confinement, OPD only)
of research, a sensitive to issues related to Example: Barangay, Health Center
protecting the rights of human subjects. 3. Private Duty/special Duty Nurse
Privately hired
Expanded role as of the nurse 4. Industrial/Occupational Nursing
A nurse working in factories, office, companies
1. Clinical Specialists 5. Nursing Education
Is a nurse who has completed a master’s degree in Nurses working in school, review center and in
specialty and has considerable clinical expertise in hospital as a CI.
that specialty. She provides expert care to 6. Military Nurse
individuals, participates in educating health care Nurses working in a military base.
professionals and ancillary, acts as a clinical 7. Clinic Nurse
consultant and participates in research. Nurses working in a private and public clinic.
2. Nurse Practitioner 8. Independent Nursing Practice
Is a nurse who has completed either as certificate Private practice, BP monitoring, home service.
program or a master’s degree in a specialty and is Independent Nurse Practitioner.
also certified by the appropriate specialty
organization. She is skilled at making nursing
assessments, performing P. E., counseling,
You might also like
- Mental Health Virtual ClinicalsDocument9 pagesMental Health Virtual ClinicalsAdellaine Lois GreyNo ratings yet
- Feu - Teaching-Learning Strategies in The Clinical SettingDocument31 pagesFeu - Teaching-Learning Strategies in The Clinical SettingrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- AMC Obstetrics TopicsDocument29 pagesAMC Obstetrics TopicsMoe Zaw Lin100% (1)
- Nurse As A Profession Part IDocument16 pagesNurse As A Profession Part IRuma Banerjee100% (1)
- Nurse As A Profession-WordDocument6 pagesNurse As A Profession-WordHeide Basing-aNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Nursing As A Profession Lesson 1: Introduction: Intended Learning OutcomesDocument114 pagesUNIT 1: Nursing As A Profession Lesson 1: Introduction: Intended Learning OutcomesGrace Ramos67% (3)
- Leadership Concept & TheoryDocument22 pagesLeadership Concept & TheoryJay PaulNo ratings yet
- Nursing As An ArtDocument9 pagesNursing As An ArtBasti HernandezNo ratings yet
- Nursing As A ProfessionDocument6 pagesNursing As A Professionreyl MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Nursiing Management WR. Whole PackageDocument24 pagesNursiing Management WR. Whole Packageeyna30No ratings yet
- Nursing As A Profession-Nurse's Role DR S FarragDocument28 pagesNursing As A Profession-Nurse's Role DR S FarragAmwaj Mohammed100% (1)
- Prepared By:-Ghada Almukhaini Supervised By: - PROF - DR. ELHAM FAYADHDocument61 pagesPrepared By:-Ghada Almukhaini Supervised By: - PROF - DR. ELHAM FAYADHGhada Almukhaini100% (1)
- Icn Framework PDFDocument84 pagesIcn Framework PDFExOne ThapeLandsNo ratings yet
- DefibrillationDocument11 pagesDefibrillationAli Al-AhmedyNo ratings yet
- Health and IllnessDocument15 pagesHealth and IllnesspauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Nursing As An ArtDocument3 pagesNursing As An Artvivian joy bulosanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Critical CareDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Critical CareANGELICA JANE FLORENDONo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues Faced by Nurses During Nursingpractice in District Layyah PakistanDocument7 pagesEthical Issues Faced by Nurses During Nursingpractice in District Layyah PakistanMawadah Setya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Application of Theory in Nursing ProcessDocument19 pagesApplication of Theory in Nursing ProcessCurly AngehNo ratings yet
- Pulido, Nathaniel T. (Quiz - Activity 6)Document2 pagesPulido, Nathaniel T. (Quiz - Activity 6)Nathaniel PulidoNo ratings yet
- Nursing As A Profession: Agung Setiyadi Middle East UniversityDocument33 pagesNursing As A Profession: Agung Setiyadi Middle East UniversityNise Mon KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Stress and AdaptationDocument56 pagesStress and AdaptationKathleen Frugalidad100% (1)
- OBSTETRICSDocument8 pagesOBSTETRICSAqua LakeNo ratings yet
- Nursing 5 1092 PDFDocument4 pagesNursing 5 1092 PDFDared GesangNo ratings yet
- ANMDocument2 pagesANMShreyas Walvekar100% (1)
- Maternity Nursing and The Role of The Maternity NurseDocument6 pagesMaternity Nursing and The Role of The Maternity NurseMerol Mae C. AdianNo ratings yet
- End of LifeDocument31 pagesEnd of LifeSimran JosanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Nurse Manager RoleDocument8 pagesAnalysis of The Nurse Manager Roleapi-239630424No ratings yet
- Nursing As A ProfessionDocument38 pagesNursing As A ProfessionFranco Razon100% (1)
- Public Health Nursing Community Health NursingDocument23 pagesPublic Health Nursing Community Health NursingJorge Danielle100% (1)
- Lower Limb: Clinicoanatomical ProblemDocument100 pagesLower Limb: Clinicoanatomical ProblemsrisakthiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Nursing Research: Dileep Kumar (R.N, CHN, Post R.N BSC.N) Lecturer, Ilmiya Institute of Nursing, KarachiDocument36 pagesUnit 1: Nursing Research: Dileep Kumar (R.N, CHN, Post R.N BSC.N) Lecturer, Ilmiya Institute of Nursing, KarachiDileep Kumar100% (1)
- An Interventional Skin CareDocument11 pagesAn Interventional Skin CareTatiana SiregarNo ratings yet
- Curriculum For Master of Science (Medical Surgical Nursing) : MGM Institute of Health SciencesDocument266 pagesCurriculum For Master of Science (Medical Surgical Nursing) : MGM Institute of Health Sciencesenam professorNo ratings yet
- 22nd - ROLES AND FUNCTIONS OF NURSESDocument4 pages22nd - ROLES AND FUNCTIONS OF NURSESMercy Anne Ecat100% (1)
- Historical Perspective of Nursing ProcessDocument25 pagesHistorical Perspective of Nursing ProcessJackoleen.kashifNo ratings yet
- Intro To Psychiatric Mental HealthDocument75 pagesIntro To Psychiatric Mental HealthEryl Franz HerreraNo ratings yet
- FUNDA HAND-OUT - Nursing As A ProfessionDocument7 pagesFUNDA HAND-OUT - Nursing As A ProfessionYsabel Francesca AbadNo ratings yet
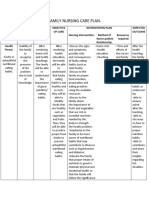
- Community Health Nursing-Family Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesCommunity Health Nursing-Family Nursing Care PlanBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- History of Nursing PDFDocument31 pagesHistory of Nursing PDFbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Electroencephalography: Preparation of Patients and Assisting With EEGDocument15 pagesElectroencephalography: Preparation of Patients and Assisting With EEGPaul MNo ratings yet
- Hall's Core, Care, Cure TheoryDocument36 pagesHall's Core, Care, Cure TheoryKaye Shiela Baybay50% (2)
- Research Unit I Nursing ResearchDocument37 pagesResearch Unit I Nursing ResearchSyed BuRhan Ud-DinNo ratings yet
- PDP KmiuraDocument2 pagesPDP Kmiuraapi-295640482No ratings yet
- Study Guide, Community Health Nursing Science 1Document55 pagesStudy Guide, Community Health Nursing Science 1Enos ErastusNo ratings yet
- Fields in Nursing - FUNDADocument12 pagesFields in Nursing - FUNDADanielle TorresNo ratings yet
- Nurse - Patient RelationshipDocument14 pagesNurse - Patient RelationshipJelly Rose Bajao OtaydeNo ratings yet
- Community As Client PDFDocument2 pagesCommunity As Client PDFNathan0% (1)
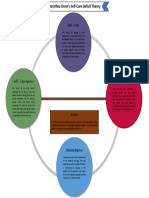
- Dorothea Orem's Self-Care Deficit TheoryDocument1 pageDorothea Orem's Self-Care Deficit TheoryWerlyn Mae GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan 2Document10 pagesTeaching Plan 2Terma JamiriNo ratings yet
- Theory Content WatsonDocument19 pagesTheory Content WatsonSimon JosanNo ratings yet
- Analytical QuestionsDocument29 pagesAnalytical Questionsfujoji92No ratings yet
- Nursing Philosophy UpdatedDocument9 pagesNursing Philosophy Updatedapi-581236671No ratings yet
- Geria Part 1Document16 pagesGeria Part 1Hannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Learning and Teaching in Nursing Practice Analysing The Role of The Nurse As An EducatorDocument5 pagesLearning and Teaching in Nursing Practice Analysing The Role of The Nurse As An Educatorprashanth639No ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To Nursing Theory HandoutDocument4 pages2 Introduction To Nursing Theory HandoutPlacido Edgar MagaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Burden: Global Picture. Number of New Cancer Cases (In Millions)Document5 pagesCancer Burden: Global Picture. Number of New Cancer Cases (In Millions)Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 Endterm NotessssDocument590 pagesNCM 101 Endterm NotessssJude Marie Claire DequiñaNo ratings yet
- Cultural Factor/ethnicity Such As Regard For Elders, Perception of HealthDocument3 pagesCultural Factor/ethnicity Such As Regard For Elders, Perception of HealthQueency Jane Ursulum100% (1)
- Healthcare Reflections, Insights, and Lessons: Proactive/ReactiveFrom EverandHealthcare Reflections, Insights, and Lessons: Proactive/ReactiveNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing ReviewerDocument27 pagesFundamentals of Nursing ReviewerGio AmadorNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument54 pagesPharma NotesAqoh C MayNo ratings yet
- Other Relevant PicturesDocument3 pagesOther Relevant PicturesAqoh C MayNo ratings yet
- Reaction NaguilianDocument4 pagesReaction NaguilianAqoh C MayNo ratings yet
- Leoplods Care of MotherDocument2 pagesLeoplods Care of MotherAqoh C MayNo ratings yet
- Essential Antenatal, Perinatal and Postpartum Care: Training ModulesDocument392 pagesEssential Antenatal, Perinatal and Postpartum Care: Training ModulesReybs -isabella CalubNo ratings yet
- VentiDocument9 pagesVentisri astiniNo ratings yet
- PRC Form Ralph NewaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument13 pagesPRC Form Ralph NewaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaJabez TyNo ratings yet
- Generic Clinical Checklist Area - Labour & DeliveryDocument4 pagesGeneric Clinical Checklist Area - Labour & DeliveryStanley SelvanathanNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka 2Document5 pagesDaftar Pustaka 2Kukuh PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 5 Moments For HHDocument66 pages5 Moments For HHtk100No ratings yet
- Posterior Palatal Seal: DR Muaiyed BuzayanDocument22 pagesPosterior Palatal Seal: DR Muaiyed BuzayanMuhammad Herry SeptianoorNo ratings yet
- Normal Birth As A Cultural PhenomenonDocument8 pagesNormal Birth As A Cultural PhenomenonMaria Johanna SchoutenNo ratings yet
- ObsDocument23 pagesObsRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Complication: Department of Gynaecology and ObstetricsDocument59 pagesPregnancy Complication: Department of Gynaecology and ObstetricssanjivdasNo ratings yet
- (2016.01) 2015 ATA Management Guidelines For Adult Patients With Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer PDFDocument168 pages(2016.01) 2015 ATA Management Guidelines For Adult Patients With Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer PDFfamp_carrijoNo ratings yet
- RetainedDocument2 pagesRetainedSeptian TheaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Critical Care Neurology Part I PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Critical Care Neurology Part I PDFrogelio.dorcy170100% (29)
- Milobar Alexus Resume MayoDocument2 pagesMilobar Alexus Resume Mayoapi-338646789No ratings yet
- Mechanisms and Management of Failed Spinal Anesthesia: Nysora TipsDocument1 pageMechanisms and Management of Failed Spinal Anesthesia: Nysora Tipsnugraha sultanNo ratings yet
- Nurse SpecialistDocument2 pagesNurse SpecialistIman AzrbjNo ratings yet
- Interpleural Block - Part 1: ReviewarticleDocument11 pagesInterpleural Block - Part 1: ReviewarticleAlfredo Salinas CastilloNo ratings yet
- Prenatal and Postpartum Aromatherapy ResourcesDocument2 pagesPrenatal and Postpartum Aromatherapy Resourcescansu sezerNo ratings yet
- Critical Appraisal Safety Data DYDDocument22 pagesCritical Appraisal Safety Data DYDRuth RachmawatyNo ratings yet
- Medical Licensing: An Obstacle To Affordable, Quality Care, Cato Policy Analysis No. 621Document20 pagesMedical Licensing: An Obstacle To Affordable, Quality Care, Cato Policy Analysis No. 621Cato InstituteNo ratings yet
- Notes On Laparoscopic Suturing and Extracorporeal KnotsDocument2 pagesNotes On Laparoscopic Suturing and Extracorporeal KnotsNirav DesaiNo ratings yet
- Guias de Cardiologia Fetal Brasileras 2019Document49 pagesGuias de Cardiologia Fetal Brasileras 2019silvia martinezNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument1 pageAppendicitisMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid UltrasoundDocument62 pagesThyroid Ultrasounddrmoscalin8774No ratings yet
- Shailesh MehtaDocument3 pagesShailesh MehtaThomas ScharrerNo ratings yet
- Breast EngorgementDocument14 pagesBreast EngorgementIvan KurniadiNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument16 pagesUntitled Presentationapi-266407397No ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary TeamworkDocument2 pagesMultidisciplinary Teamworkapi-270308228No ratings yet
- Femto Vs Phaco 2Document6 pagesFemto Vs Phaco 2Bonita AsyigahNo ratings yet