Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Entrepreneurship: Marketing
Entrepreneurship: Marketing
Uploaded by
Shielah Marie RequizCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Entrep Module 3Document3 pagesEntrep Module 3Mariam Gamos100% (8)
- Prayer For Moving UpDocument1 pagePrayer For Moving UpShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- 11b Subiect+baremDocument5 pages11b Subiect+baremprobulinaNo ratings yet
- S3 Seizing The OpportunityDocument12 pagesS3 Seizing The OpportunityMylene Santiago0% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Quarter 2: Module10Document19 pagesEntrepreneurship Quarter 2: Module10Primosebastian Tarrobago0% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Quarter 2: Module 3Document16 pagesEntrepreneurship Quarter 2: Module 3Karyl Dianne B. Laurel75% (4)
- Quiz ConjDocument1 pageQuiz ConjShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Finding Your FlowDocument29 pagesFinding Your Flowmarianaluca100% (1)
- Lipura Ts Module6EntrepDocument8 pagesLipura Ts Module6EntrepGeniza Fatima Lipura100% (1)
- LAS 3, Week 4Document13 pagesLAS 3, Week 4Marife CulabaNo ratings yet
- Entrepneurship Module 3 Performance TaskDocument2 pagesEntrepneurship Module 3 Performance TaskIvanah Mae Guaro Aclo100% (1)
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 3 Week 4Document9 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 3 Week 4michelleNo ratings yet
- Jas Module 1-3Document9 pagesJas Module 1-3Juanita Cabigon50% (2)
- Entrep Module 8Document8 pagesEntrep Module 8Trisha BantingNo ratings yet
- Entrepneurship Module 4 Performance TasksDocument11 pagesEntrepneurship Module 4 Performance TasksIvanah Mae Guaro Aclo100% (1)
- Entrep q1 - Week3 GiecelDocument15 pagesEntrep q1 - Week3 Giecelmarjun catanNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Entrep (April 26-30)Document7 pagesWeek 8 Entrep (April 26-30)LouisseNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship (Q1 - M1) LOLO - GATESDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurship (Q1 - M1) LOLO - GATESCriestefiel LoloNo ratings yet
- ENTREPR. Q1-M3, Ladrido JJDocument4 pagesENTREPR. Q1-M3, Ladrido JJAdiel SeraphimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Strategic and Tactical MarketingDocument12 pagesChapter 4 - Strategic and Tactical MarketingHerbert Kim Dator NacarioNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 8: Computation of Gross Profit What I KnowDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 8: Computation of Gross Profit What I KnowDos Dos67% (6)
- MODULE 2 Entrepreneurship Quarter 1Document14 pagesMODULE 2 Entrepreneurship Quarter 1Justine Teasacam78% (9)
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 1 - Module 7: 1. Branding 2. The Business PlanDocument27 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 1 - Module 7: 1. Branding 2. The Business PlanSheyn RanayNo ratings yet
- Chelsea Ann V. Albarece October 8, 2020 Grade 12-Simplicity Entrepreneur Module # 1 Lesson 1 Post-AssessmentDocument1 pageChelsea Ann V. Albarece October 8, 2020 Grade 12-Simplicity Entrepreneur Module # 1 Lesson 1 Post-AssessmentChelsea Albarece100% (2)
- Module 1 EnterpreneurshipDocument6 pagesModule 1 EnterpreneurshipJanna GunioNo ratings yet
- Week 6 EntrepreneurshipDocument10 pagesWeek 6 EntrepreneurshipSuperHero ForFun70% (10)
- Entrep Q1 WK3Document17 pagesEntrep Q1 WK3Dos Dos100% (2)
- SomethingDocument4 pagesSomethingJereson palacioNo ratings yet
- Entrep12 Q1 Mod3 Recognize-and-Understand-the-Market v2Document13 pagesEntrep12 Q1 Mod3 Recognize-and-Understand-the-Market v2MrBigbozz21No ratings yet
- QTR 4 - Performance Task 1Document2 pagesQTR 4 - Performance Task 1Ginevieve Gibertas100% (2)
- Business PlanDocument22 pagesBusiness PlanRekka Joy SantillanNo ratings yet
- EAPP FINAL Module 1... Grade 12 BezosDocument2 pagesEAPP FINAL Module 1... Grade 12 Bezosadrian lozano100% (1)
- Application (The Road Trip) Using The Road Trip Signs Write Your Answer On The FollowingDocument2 pagesApplication (The Road Trip) Using The Road Trip Signs Write Your Answer On The FollowingPam Maglalang SolanoNo ratings yet
- Activity I: Warming Up Directions: "RECALLING FACTS" Read Each Item Carefully. Then, Answer Each byDocument8 pagesActivity I: Warming Up Directions: "RECALLING FACTS" Read Each Item Carefully. Then, Answer Each byKristine Joy Palayad Marinay100% (1)
- Contemporary Module 4 DoneDocument5 pagesContemporary Module 4 DoneYaokhen SingaliboNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Lesson, The Learners Will Be Able ToDocument7 pagesAt The End of The Lesson, The Learners Will Be Able ToKENJ ABELLANo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 4Document19 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 4Nicole Peña TercianoNo ratings yet
- Choco Balls FinalDocument8 pagesChoco Balls Finalrhys_jaya100% (2)
- Media and Information Literacy Core Subject: - 1 Quarter - SY 2020-2021Document1 pageMedia and Information Literacy Core Subject: - 1 Quarter - SY 2020-2021アーロンクリスチャンNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From Different Regions: Week 4Document10 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From Different Regions: Week 4Aoi Miyu Shino100% (10)
- Entrepreneurship Q1 MOD-6Document23 pagesEntrepreneurship Q1 MOD-6LOUIE MARK FANGON100% (3)
- Lemon Juice and ShakeDocument15 pagesLemon Juice and ShakeGemaris Laurenaria MercadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Week 1-2 PerdevDocument54 pagesLesson Week 1-2 PerdevElaineVidalRodriguez100% (1)
- Activity 4 Pauline Anne R. Grana 12-ABM-A Mr. Jayson SantelicesDocument4 pagesActivity 4 Pauline Anne R. Grana 12-ABM-A Mr. Jayson SantelicesPark Eunbi100% (1)
- Inquiries, Investigation, and Immersion: Understanding Data and Ways To Collect Data (Population and Sampling Method)Document20 pagesInquiries, Investigation, and Immersion: Understanding Data and Ways To Collect Data (Population and Sampling Method)Rhiza Marie Monares67% (3)
- Entrepreneuship 9Document3 pagesEntrepreneuship 9Alex Myner79% (14)
- MM 01 Handout 4 Marketing OpportunityDocument19 pagesMM 01 Handout 4 Marketing OpportunityAsset Dy100% (1)
- Lipura Ts Module5EappDocument7 pagesLipura Ts Module5EappGeniza Fatima LipuraNo ratings yet
- Fruity Graham Mission and VisionDocument2 pagesFruity Graham Mission and VisionJohn Danielle Cerdan100% (2)
- What'S In: Visual Arts Literacy Arts Audio - Visual Arts Contemporary ArtDocument5 pagesWhat'S In: Visual Arts Literacy Arts Audio - Visual Arts Contemporary ArtRon Adrianne AsedillaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Right StepsDocument63 pagesActivity 1: Right StepsGem N AquarianNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 6 10Document97 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 6 10Jocet GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- Directions: Write 2-3 Sentence Reflection On What Significant Learning You Get Out of The Following ActivitiesDocument3 pagesDirections: Write 2-3 Sentence Reflection On What Significant Learning You Get Out of The Following ActivitiesCHARLENE SAGUINHONNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Entrep ModuleDocument12 pagesWeek 4 Entrep ModuleSuperHero ForFun100% (3)
- Implications of Media and Information: Amando A. Fabio Memorial National High SchoolDocument4 pagesImplications of Media and Information: Amando A. Fabio Memorial National High SchoolLorenzo Cagula Jr.No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 1 Week 3 Module 3Document13 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 1 Week 3 Module 3Johny Johnsons33% (3)
- Entrepreneurship: 1St Generation Modules - Version 2.0Document18 pagesEntrepreneurship: 1St Generation Modules - Version 2.0mhaiibreakerNo ratings yet
- Module 9: Business ImplementationDocument27 pagesModule 9: Business ImplementationPrincess Enrian Quintana Polinar100% (1)
- Wrigley's Chewing GumDocument1 pageWrigley's Chewing GumEver After Beautique29% (7)
- Lesson 4 Market Key Concepts Competitors Products and ServicesDocument2 pagesLesson 4 Market Key Concepts Competitors Products and ServicesLiam Flores100% (1)
- Market ResearchDocument16 pagesMarket ResearchKimberly Anne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EM Reports CompiledDocument10 pagesEM Reports CompiledgutierrezyoofclaridethNo ratings yet
- D1 - U1 - HW (Concept + Extra Reading)Document2 pagesD1 - U1 - HW (Concept + Extra Reading)k61.2215215059No ratings yet
- Term Paper-Unit 1 Nature of Business Research and Its SignificanceDocument4 pagesTerm Paper-Unit 1 Nature of Business Research and Its SignificancemickeyNo ratings yet
- Types of PlayDocument5 pagesTypes of PlayShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Quiz ConjDocument1 pageQuiz ConjShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Types of PlayDocument5 pagesTypes of PlayShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Observation ChecklistDocument2 pagesObservation ChecklistShielah Marie Requiz100% (1)
- SSG Constitutions and by LawsDocument14 pagesSSG Constitutions and by LawsShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Unit Activity Map: Western Aklan Academy Nabas, AklanDocument9 pagesUnit Activity Map: Western Aklan Academy Nabas, AklanShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- LETTER of The Correct Answer On The Space Provided Before The NumberDocument1 pageLETTER of The Correct Answer On The Space Provided Before The NumberShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Prayer For Moving UpDocument1 pagePrayer For Moving UpShielah Marie Requiz86% (7)
- IntramsDocument3 pagesIntramsShielah Marie Requiz100% (1)
- B. FACT OR BLUFF. Write Fact If The Sentence Is Correct in Ideas and Bluff If You Think TheDocument1 pageB. FACT OR BLUFF. Write Fact If The Sentence Is Correct in Ideas and Bluff If You Think TheShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Vision of A SchoolDocument177 pagesVision of A SchoolGgy VictorNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organizational Behavior Emerging Knowledge Global Reality 9th Edition Steven Mcshane Mary Von Glinow Full DownloadDocument47 pagesTest Bank For Organizational Behavior Emerging Knowledge Global Reality 9th Edition Steven Mcshane Mary Von Glinow Full Downloadricardochangzbdwaqfyj100% (21)
- Management (Final) (Management Concepts and Organizational Behaviour (Dr. Karam Pal) )Document2 pagesManagement (Final) (Management Concepts and Organizational Behaviour (Dr. Karam Pal) )Ghulam Mustafa GM100% (3)
- Eidetic-Therapy BookDocument8 pagesEidetic-Therapy Bookmagasara123100% (1)
- Ge6100 Understanding SelfDocument100 pagesGe6100 Understanding SelfRalph Chowsen Bati-onNo ratings yet
- of Health Belief ModelDocument25 pagesof Health Belief ModelShailja Sharma100% (6)
- Innovations in Career CounselingDocument10 pagesInnovations in Career CounselingtrinoaparicioNo ratings yet
- Eced260-Reflective Analysis of Portfolio Artifact Standard 4Document1 pageEced260-Reflective Analysis of Portfolio Artifact Standard 4api-140794817No ratings yet
- Research G5Document14 pagesResearch G5reuben tanglaoNo ratings yet
- Combining Dictogloss and Cooperative Learning To Promote Language LearningDocument15 pagesCombining Dictogloss and Cooperative Learning To Promote Language LearningEmily JamesNo ratings yet
- Problem Framing CanvasDocument2 pagesProblem Framing CanvasKPNo ratings yet
- Individuals in An Organization Form Its Vital Resource and Must Be ValuedDocument6 pagesIndividuals in An Organization Form Its Vital Resource and Must Be ValuedNikhil AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Three Facets To CurriculumDocument2 pagesThree Facets To CurriculumAaron Jed100% (2)
- What Makes A Goood Teacher GreatDocument1 pageWhat Makes A Goood Teacher GreatKamaladharanii Ragu NathanNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal, Bias & Feedback - ManagersDocument27 pagesPerformance Appraisal, Bias & Feedback - ManagersMrigakshi SarmahNo ratings yet
- Mpu 3401 Muhammad Danish Adam Bin Azaman 1191201250Document5 pagesMpu 3401 Muhammad Danish Adam Bin Azaman 1191201250Danish AdamNo ratings yet
- Xyz Presentation of ManagementDocument31 pagesXyz Presentation of ManagementvysrilekhaNo ratings yet
- Developing The Teaching Profession Factors InfluenDocument6 pagesDeveloping The Teaching Profession Factors InfluenJudy Aljecera AvilaNo ratings yet
- Caffolding Eading Omprehension: Ffice of Pecial RogramsDocument47 pagesCaffolding Eading Omprehension: Ffice of Pecial RogramsmarleneNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision Making: Organizational BehaviorDocument23 pagesPerception and Individual Decision Making: Organizational BehaviorNiraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- By Eva Broch Pierrakos 2000 The Pathwork FoundationDocument4 pagesBy Eva Broch Pierrakos 2000 The Pathwork FoundationcrisbretzNo ratings yet
- Challenges of TrainingDocument9 pagesChallenges of TrainingHimanshu BansalNo ratings yet
- Report Card GR KDocument1 pageReport Card GR Kapi-520282910No ratings yet
- SKM - Jadwal 2021Document227 pagesSKM - Jadwal 2021bagas waraNo ratings yet
- Management Notes and Discussion QuestionsDocument4 pagesManagement Notes and Discussion Questionsapi-308919474No ratings yet
- What Is Research OnionDocument9 pagesWhat Is Research Onionahsan121100% (2)
- Expectancy Theory Predictions of Salesmen's Performance: Richard L. OliverDocument12 pagesExpectancy Theory Predictions of Salesmen's Performance: Richard L. OliverWaseem JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Quiz Power and PolitcsDocument6 pagesChapter Quiz Power and PolitcsMubasher7100% (3)
Entrepreneurship: Marketing
Entrepreneurship: Marketing
Uploaded by
Shielah Marie RequizOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Entrepreneurship: Marketing
Entrepreneurship: Marketing
Uploaded by
Shielah Marie RequizCopyright:
Available Formats
Entrepreneurship
MARKETING
Market Research
It is the process of gathering information which will make the company more aware of how the people,
the company hopes to sell to, will react to the company’s current or potential products or services.
It is undertaken so that an entrepreneur can have information needed to make informed business
decisions about start-up, innovation, growth and the 7Ps.
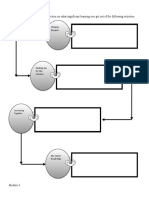
Reasons Why Business Owners
1. Identify 3. Set realistic
potential 2. Understand targets
customers existing
customers
4. Develop 5. Examine and
effective solve business
strategies problems
6. Prepare for
7. Identify
business
business
expansion
opportunities
According to the Guide to Market Research and Analysis (2015), to conduct market research, it is important to
set clear goals for the market research activity and define what are needed to be known and why.
MARKET RESEARCH TYPE
A. Primary Research- is information gathered directly from the respondents who answered set of questions.
This information is usually collected through surveys, observation, focused group discussion or experimentation.
*Surveys- are the most common way to gather primary research with the use of questionnaire or
interview schedule.
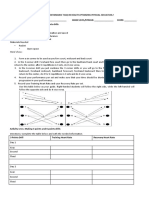
Guidelines in designing or constructing your own research questionnaire:
Keep it short as simple as possible
Make sure it is visually appealing and easy to read
Move from general questions to specific questions
Make sure questions are brief and easy to understood
*Focused Group Discussions (FGDs) – These can be moderated group interviews and brainstorming
sessions that provide information on user’s needs and behaviors. These are now gaining wider usage in
market research due to substantial information gathered given a time limit.
FGDs can be useful for the following type of discussions:
1) Exploratory- Obtain information on general attitudes, understand the circumstances under which
customers might require your product or service, understand their desired outcomes.
2) Feature Prioritization- If trade-offs have to be made among various customer needs, focus groups
can be helpful in prioritizing them.
3) Comparative Analysis- Understand where else customers go to get similar information, services or
products and what attract them to source sources.
4) Trend explanation- If you notice a trend in the way that customers use your website( for example,
they always use the search function rather than navigating through the structured product list),
then focus groups can be used to better understand why this is happening.
Prepared by: Ms. Sherly May M. Polido
Entrepreneurship
Following considerations in the use of FGDs in market research by the Canada Business Network:
Limit the length of the session to between 90 and 120 minutes.
Generally, conduct focus groups with 8 to 10 participants per group (recruit 10 to 12 participants to
ensure the 8 to 10 show up).
Use a semi-structured or open-format discussion.
Strive for uniformity in the group’s composition. For example, it may not be advisable to have
business customers and retail customers in the same focus group, if their needs are very different.
If you feel that group influence is likely to be a strong factor (participants will be influenced
greatly by what others are saying), the personal interviews or smaller groups may be an option to
consider than FGD.
*Personal Interviews- are traditional method of data collection which is normally done on a face-to-face
manner with the respondents.
Personal Interview can be used in the following situations:
The topic is too personal or sensitive to be discussed in a group, or confidentiality of the
participant is required.
A person’s opinion may easily be influenced by others in a group.
The interview respondents are executives from competing firms who would be reluctant to open
up in a group situation.
The interview respondents are busy and it is difficult to schedule group sessions, or it is
important to visit interview respondents individually at their convenience.
Following considerations in the use of personal interview in market research:
It can be helpful to use a list of mostly open- ended questions to be in person or by telephone.
An in-depth interview gives participants the opportunity to express their views.
Interviews typically last from 15 to 40 minutes, but they can last longer depending on the
participant’s interest in the topic.
This technique allows the interviewer to get detailed descriptions of individual experiences.
B. Secondary Research- It gathers data from existing available resources like company records, data bases,
research reports published in the media, internet search engines, libraries, and books which answer the question
at hand. It is normally less time consuming than primary research, and can be less expensive as well. Existing
company records such as sales invoices, receipts and formal complaints are important secondary resources that
business can utilize.
Another key secondary resource is statistical data from official statistics providers (like National Statistics
Office; NEDA; Department of Trade and Industry) and other organizations (Marketing Associations; Chambers
of Commerce; Industry Associations). These statistics in turn can feed into analytical papers and market profiles
that can help to put the numbers in context.
BRANDING
It is the use of a name, term, symbol, or design—or a combination of these—to identify a product.
It encompasses the use of brand names, trademarks and practically all other means of product
identification.
* Brand Name
Is a word, letter, or a group of words or letters.
It connects a product with the benefits a customer can expect. The connection may learned from past
consumer experience, from the company’s promotion, or other advertising strategies.
*Brand Logos
Are graphic marks or symbols commonly used by commercial enterprises, organizations and even
individuals to aid and promote instant public recognition.
*Trademark
Includes only those words, symbols, or marks that are legally registered for use by a single company.
Prepared by: Ms. Sherly May M. Polido
Entrepreneurship
*Service Mark
It is the same as a trademark except that it refers to a service offering.
Prepared by: Ms. Sherly May M. Polido
You might also like
- Entrep Module 3Document3 pagesEntrep Module 3Mariam Gamos100% (8)
- Prayer For Moving UpDocument1 pagePrayer For Moving UpShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- 11b Subiect+baremDocument5 pages11b Subiect+baremprobulinaNo ratings yet
- S3 Seizing The OpportunityDocument12 pagesS3 Seizing The OpportunityMylene Santiago0% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Quarter 2: Module10Document19 pagesEntrepreneurship Quarter 2: Module10Primosebastian Tarrobago0% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Quarter 2: Module 3Document16 pagesEntrepreneurship Quarter 2: Module 3Karyl Dianne B. Laurel75% (4)
- Quiz ConjDocument1 pageQuiz ConjShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Finding Your FlowDocument29 pagesFinding Your Flowmarianaluca100% (1)
- Lipura Ts Module6EntrepDocument8 pagesLipura Ts Module6EntrepGeniza Fatima Lipura100% (1)
- LAS 3, Week 4Document13 pagesLAS 3, Week 4Marife CulabaNo ratings yet
- Entrepneurship Module 3 Performance TaskDocument2 pagesEntrepneurship Module 3 Performance TaskIvanah Mae Guaro Aclo100% (1)
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 3 Week 4Document9 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 3 Week 4michelleNo ratings yet
- Jas Module 1-3Document9 pagesJas Module 1-3Juanita Cabigon50% (2)
- Entrep Module 8Document8 pagesEntrep Module 8Trisha BantingNo ratings yet
- Entrepneurship Module 4 Performance TasksDocument11 pagesEntrepneurship Module 4 Performance TasksIvanah Mae Guaro Aclo100% (1)
- Entrep q1 - Week3 GiecelDocument15 pagesEntrep q1 - Week3 Giecelmarjun catanNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Entrep (April 26-30)Document7 pagesWeek 8 Entrep (April 26-30)LouisseNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship (Q1 - M1) LOLO - GATESDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurship (Q1 - M1) LOLO - GATESCriestefiel LoloNo ratings yet
- ENTREPR. Q1-M3, Ladrido JJDocument4 pagesENTREPR. Q1-M3, Ladrido JJAdiel SeraphimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Strategic and Tactical MarketingDocument12 pagesChapter 4 - Strategic and Tactical MarketingHerbert Kim Dator NacarioNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 8: Computation of Gross Profit What I KnowDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 8: Computation of Gross Profit What I KnowDos Dos67% (6)
- MODULE 2 Entrepreneurship Quarter 1Document14 pagesMODULE 2 Entrepreneurship Quarter 1Justine Teasacam78% (9)
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 1 - Module 7: 1. Branding 2. The Business PlanDocument27 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 1 - Module 7: 1. Branding 2. The Business PlanSheyn RanayNo ratings yet
- Chelsea Ann V. Albarece October 8, 2020 Grade 12-Simplicity Entrepreneur Module # 1 Lesson 1 Post-AssessmentDocument1 pageChelsea Ann V. Albarece October 8, 2020 Grade 12-Simplicity Entrepreneur Module # 1 Lesson 1 Post-AssessmentChelsea Albarece100% (2)
- Module 1 EnterpreneurshipDocument6 pagesModule 1 EnterpreneurshipJanna GunioNo ratings yet
- Week 6 EntrepreneurshipDocument10 pagesWeek 6 EntrepreneurshipSuperHero ForFun70% (10)
- Entrep Q1 WK3Document17 pagesEntrep Q1 WK3Dos Dos100% (2)
- SomethingDocument4 pagesSomethingJereson palacioNo ratings yet
- Entrep12 Q1 Mod3 Recognize-and-Understand-the-Market v2Document13 pagesEntrep12 Q1 Mod3 Recognize-and-Understand-the-Market v2MrBigbozz21No ratings yet
- QTR 4 - Performance Task 1Document2 pagesQTR 4 - Performance Task 1Ginevieve Gibertas100% (2)
- Business PlanDocument22 pagesBusiness PlanRekka Joy SantillanNo ratings yet
- EAPP FINAL Module 1... Grade 12 BezosDocument2 pagesEAPP FINAL Module 1... Grade 12 Bezosadrian lozano100% (1)
- Application (The Road Trip) Using The Road Trip Signs Write Your Answer On The FollowingDocument2 pagesApplication (The Road Trip) Using The Road Trip Signs Write Your Answer On The FollowingPam Maglalang SolanoNo ratings yet
- Activity I: Warming Up Directions: "RECALLING FACTS" Read Each Item Carefully. Then, Answer Each byDocument8 pagesActivity I: Warming Up Directions: "RECALLING FACTS" Read Each Item Carefully. Then, Answer Each byKristine Joy Palayad Marinay100% (1)
- Contemporary Module 4 DoneDocument5 pagesContemporary Module 4 DoneYaokhen SingaliboNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Lesson, The Learners Will Be Able ToDocument7 pagesAt The End of The Lesson, The Learners Will Be Able ToKENJ ABELLANo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 4Document19 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 4Nicole Peña TercianoNo ratings yet
- Choco Balls FinalDocument8 pagesChoco Balls Finalrhys_jaya100% (2)
- Media and Information Literacy Core Subject: - 1 Quarter - SY 2020-2021Document1 pageMedia and Information Literacy Core Subject: - 1 Quarter - SY 2020-2021アーロンクリスチャンNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From Different Regions: Week 4Document10 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From Different Regions: Week 4Aoi Miyu Shino100% (10)
- Entrepreneurship Q1 MOD-6Document23 pagesEntrepreneurship Q1 MOD-6LOUIE MARK FANGON100% (3)
- Lemon Juice and ShakeDocument15 pagesLemon Juice and ShakeGemaris Laurenaria MercadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Week 1-2 PerdevDocument54 pagesLesson Week 1-2 PerdevElaineVidalRodriguez100% (1)
- Activity 4 Pauline Anne R. Grana 12-ABM-A Mr. Jayson SantelicesDocument4 pagesActivity 4 Pauline Anne R. Grana 12-ABM-A Mr. Jayson SantelicesPark Eunbi100% (1)
- Inquiries, Investigation, and Immersion: Understanding Data and Ways To Collect Data (Population and Sampling Method)Document20 pagesInquiries, Investigation, and Immersion: Understanding Data and Ways To Collect Data (Population and Sampling Method)Rhiza Marie Monares67% (3)
- Entrepreneuship 9Document3 pagesEntrepreneuship 9Alex Myner79% (14)
- MM 01 Handout 4 Marketing OpportunityDocument19 pagesMM 01 Handout 4 Marketing OpportunityAsset Dy100% (1)
- Lipura Ts Module5EappDocument7 pagesLipura Ts Module5EappGeniza Fatima LipuraNo ratings yet
- Fruity Graham Mission and VisionDocument2 pagesFruity Graham Mission and VisionJohn Danielle Cerdan100% (2)
- What'S In: Visual Arts Literacy Arts Audio - Visual Arts Contemporary ArtDocument5 pagesWhat'S In: Visual Arts Literacy Arts Audio - Visual Arts Contemporary ArtRon Adrianne AsedillaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Right StepsDocument63 pagesActivity 1: Right StepsGem N AquarianNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 6 10Document97 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 6 10Jocet GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- Directions: Write 2-3 Sentence Reflection On What Significant Learning You Get Out of The Following ActivitiesDocument3 pagesDirections: Write 2-3 Sentence Reflection On What Significant Learning You Get Out of The Following ActivitiesCHARLENE SAGUINHONNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Entrep ModuleDocument12 pagesWeek 4 Entrep ModuleSuperHero ForFun100% (3)
- Implications of Media and Information: Amando A. Fabio Memorial National High SchoolDocument4 pagesImplications of Media and Information: Amando A. Fabio Memorial National High SchoolLorenzo Cagula Jr.No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 1 Week 3 Module 3Document13 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 1 Week 3 Module 3Johny Johnsons33% (3)
- Entrepreneurship: 1St Generation Modules - Version 2.0Document18 pagesEntrepreneurship: 1St Generation Modules - Version 2.0mhaiibreakerNo ratings yet
- Module 9: Business ImplementationDocument27 pagesModule 9: Business ImplementationPrincess Enrian Quintana Polinar100% (1)
- Wrigley's Chewing GumDocument1 pageWrigley's Chewing GumEver After Beautique29% (7)
- Lesson 4 Market Key Concepts Competitors Products and ServicesDocument2 pagesLesson 4 Market Key Concepts Competitors Products and ServicesLiam Flores100% (1)
- Market ResearchDocument16 pagesMarket ResearchKimberly Anne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EM Reports CompiledDocument10 pagesEM Reports CompiledgutierrezyoofclaridethNo ratings yet
- D1 - U1 - HW (Concept + Extra Reading)Document2 pagesD1 - U1 - HW (Concept + Extra Reading)k61.2215215059No ratings yet
- Term Paper-Unit 1 Nature of Business Research and Its SignificanceDocument4 pagesTerm Paper-Unit 1 Nature of Business Research and Its SignificancemickeyNo ratings yet
- Types of PlayDocument5 pagesTypes of PlayShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Quiz ConjDocument1 pageQuiz ConjShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Types of PlayDocument5 pagesTypes of PlayShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Observation ChecklistDocument2 pagesObservation ChecklistShielah Marie Requiz100% (1)
- SSG Constitutions and by LawsDocument14 pagesSSG Constitutions and by LawsShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Unit Activity Map: Western Aklan Academy Nabas, AklanDocument9 pagesUnit Activity Map: Western Aklan Academy Nabas, AklanShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- LETTER of The Correct Answer On The Space Provided Before The NumberDocument1 pageLETTER of The Correct Answer On The Space Provided Before The NumberShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Prayer For Moving UpDocument1 pagePrayer For Moving UpShielah Marie Requiz86% (7)
- IntramsDocument3 pagesIntramsShielah Marie Requiz100% (1)
- B. FACT OR BLUFF. Write Fact If The Sentence Is Correct in Ideas and Bluff If You Think TheDocument1 pageB. FACT OR BLUFF. Write Fact If The Sentence Is Correct in Ideas and Bluff If You Think TheShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Vision of A SchoolDocument177 pagesVision of A SchoolGgy VictorNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organizational Behavior Emerging Knowledge Global Reality 9th Edition Steven Mcshane Mary Von Glinow Full DownloadDocument47 pagesTest Bank For Organizational Behavior Emerging Knowledge Global Reality 9th Edition Steven Mcshane Mary Von Glinow Full Downloadricardochangzbdwaqfyj100% (21)
- Management (Final) (Management Concepts and Organizational Behaviour (Dr. Karam Pal) )Document2 pagesManagement (Final) (Management Concepts and Organizational Behaviour (Dr. Karam Pal) )Ghulam Mustafa GM100% (3)
- Eidetic-Therapy BookDocument8 pagesEidetic-Therapy Bookmagasara123100% (1)
- Ge6100 Understanding SelfDocument100 pagesGe6100 Understanding SelfRalph Chowsen Bati-onNo ratings yet
- of Health Belief ModelDocument25 pagesof Health Belief ModelShailja Sharma100% (6)
- Innovations in Career CounselingDocument10 pagesInnovations in Career CounselingtrinoaparicioNo ratings yet
- Eced260-Reflective Analysis of Portfolio Artifact Standard 4Document1 pageEced260-Reflective Analysis of Portfolio Artifact Standard 4api-140794817No ratings yet
- Research G5Document14 pagesResearch G5reuben tanglaoNo ratings yet
- Combining Dictogloss and Cooperative Learning To Promote Language LearningDocument15 pagesCombining Dictogloss and Cooperative Learning To Promote Language LearningEmily JamesNo ratings yet
- Problem Framing CanvasDocument2 pagesProblem Framing CanvasKPNo ratings yet
- Individuals in An Organization Form Its Vital Resource and Must Be ValuedDocument6 pagesIndividuals in An Organization Form Its Vital Resource and Must Be ValuedNikhil AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Three Facets To CurriculumDocument2 pagesThree Facets To CurriculumAaron Jed100% (2)
- What Makes A Goood Teacher GreatDocument1 pageWhat Makes A Goood Teacher GreatKamaladharanii Ragu NathanNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal, Bias & Feedback - ManagersDocument27 pagesPerformance Appraisal, Bias & Feedback - ManagersMrigakshi SarmahNo ratings yet
- Mpu 3401 Muhammad Danish Adam Bin Azaman 1191201250Document5 pagesMpu 3401 Muhammad Danish Adam Bin Azaman 1191201250Danish AdamNo ratings yet
- Xyz Presentation of ManagementDocument31 pagesXyz Presentation of ManagementvysrilekhaNo ratings yet
- Developing The Teaching Profession Factors InfluenDocument6 pagesDeveloping The Teaching Profession Factors InfluenJudy Aljecera AvilaNo ratings yet
- Caffolding Eading Omprehension: Ffice of Pecial RogramsDocument47 pagesCaffolding Eading Omprehension: Ffice of Pecial RogramsmarleneNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision Making: Organizational BehaviorDocument23 pagesPerception and Individual Decision Making: Organizational BehaviorNiraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- By Eva Broch Pierrakos 2000 The Pathwork FoundationDocument4 pagesBy Eva Broch Pierrakos 2000 The Pathwork FoundationcrisbretzNo ratings yet
- Challenges of TrainingDocument9 pagesChallenges of TrainingHimanshu BansalNo ratings yet
- Report Card GR KDocument1 pageReport Card GR Kapi-520282910No ratings yet
- SKM - Jadwal 2021Document227 pagesSKM - Jadwal 2021bagas waraNo ratings yet
- Management Notes and Discussion QuestionsDocument4 pagesManagement Notes and Discussion Questionsapi-308919474No ratings yet
- What Is Research OnionDocument9 pagesWhat Is Research Onionahsan121100% (2)
- Expectancy Theory Predictions of Salesmen's Performance: Richard L. OliverDocument12 pagesExpectancy Theory Predictions of Salesmen's Performance: Richard L. OliverWaseem JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Quiz Power and PolitcsDocument6 pagesChapter Quiz Power and PolitcsMubasher7100% (3)