Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition & Pathogenesis (Ngân) : Asthma - Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment 2015
Definition & Pathogenesis (Ngân) : Asthma - Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment 2015
Uploaded by
everydayisagift99990 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesThis document provides an overview of the diagnosis and treatment of asthma. It defines asthma as a chronic inflammatory airway disorder characterized by reversible airflow obstruction. Common symptoms include wheezing, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and coughing, which are often worse at night. Diagnosis involves demonstrating reversible airflow obstruction through lung function tests or bronchodilator response. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and controlling symptoms with medications.
Original Description:
Hen Suyen
Original Title
Asthma
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of the diagnosis and treatment of asthma. It defines asthma as a chronic inflammatory airway disorder characterized by reversible airflow obstruction. Common symptoms include wheezing, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and coughing, which are often worse at night. Diagnosis involves demonstrating reversible airflow obstruction through lung function tests or bronchodilator response. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and controlling symptoms with medications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesDefinition & Pathogenesis (Ngân) : Asthma - Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment 2015
Definition & Pathogenesis (Ngân) : Asthma - Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment 2015
Uploaded by
everydayisagift9999This document provides an overview of the diagnosis and treatment of asthma. It defines asthma as a chronic inflammatory airway disorder characterized by reversible airflow obstruction. Common symptoms include wheezing, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and coughing, which are often worse at night. Diagnosis involves demonstrating reversible airflow obstruction through lung function tests or bronchodilator response. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and controlling symptoms with medications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
ASTHMA – CURRENT MEDICAL rates are consistently highest among
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT blacks aged 15–24 years.
2015
▶▶Definition & Pathogenesis (ngân)
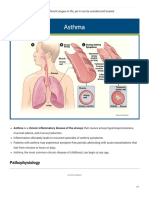
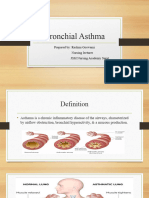
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory
ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS disorder of the airways. No single
(trang) histopathologic feature is pathognomonic
Episodic or chronic symptoms of but common findings include
airflow obstruction. inflammatory cell infiltration with
eosinophils, neutrophils, and
▶▶ Reversibility of airflow lymphocytes (especially T lymphocytes);
obstruction, either spontaneously or goblet cell hyperplasia, sometimes with
following bronchodilator therapy. plugging of small airways with thick
mucus; collagen deposition beneath the
▶▶ Symptoms frequently worse at basement membrane; hypertrophy of
night or in the early morning. bronchial smooth muscle; airway edema;
mast cell activation; and denudation of
▶▶ Prolonged expiration and diffuse airway epithelium. This airway
wheezes on physical examination. inflammation underlies disease chronicity
and contributes to airway hyper-
▶▶ Limitation of airflow on responsiveness and airflow limitation.
pulmonary function testing or positive (hòa)The strongest identifiable
bronchoprovocation challenge. predisposing factor for the development
of asthma is atopy, but obesity is
increasingly recognized as a risk factor.
General Considerations (hoàng) Exposure of sensitive patients to inhaled
Asthma is a common disease, affecting allergens increases airway inflammation,
approximately 7–10% of the population. airway hyper-responsiveness, and
It is slightly more common in male symptoms. Symptoms may develop
children (< 14 years old) and in female immediately (immediate asthmatic
adults. There is a genetic predisposition response) or 4–6 hours after allergen
to asthma. Prevalence, hospitalizations, exposure (late asthmatic response).
and fatal asthma have all increased in the Common allergens include house dust
United States over the past 20 years. Each mites (often found in pillows, mattresses,
year, approximately 500,000 hospital upholstered furniture, carpets, and
admissions and 4500 deaths in the United drapes), cockroaches, cat dander, and
States are attributed to asthma. seasonal pollens. Substantially reducing
Hospitalization rates have been highest exposure reduces pathologic findings and
among blacks and children, and death clinical symptoms.
nguyenthaiduy.med@gmail.com Pulmonary Disorders Mark S. Chesnutt, MD Thomas J. Prendergast, MD
0985 53 53 36 – 0938 057 921 Current medical diagnosis and treatment
(Thanh LA) Nonspecific precipitants Symptoms and signs vary widely between
of asthma include exercise, upper patients as well as individually over time.
respiratory tract infections, rhinosinusitis,
postnasal drip, aspiration, A. Symptoms and Signs (yến)
gastroesophageal reflux, changes in the Asthma is characterized by episodic
weather, and stress. Exposure to products wheezing, difficulty in breathing, chest
tightness, and cough. Excess sputum
of combustion (eg, tobacco smoke, crack
production is common. The frequency of
cocaine, methamphetamines, and other
asthma symptoms is highly variable.
agents) increases asthma symptoms and Some patients have infrequent, brief
the need for medications and reduces lung attacks of asthma while others may suffer
function. Air pollution (increased air nearly continuous symptoms. Asthma
levels of respirable particles, ozone, SO2, symptoms may occur spontaneously or be
and NO2) precipitate asthma symptoms precipitated or exacerbated by many
and increase emergency department visits different triggers as
and hospitalizations. Selected individuals discussed above. Asthma symptoms are
may experience asthma symptoms after frequently worse at night; circadian
exposure to aspirin, nonsteroidal anti- variations in bronchomotor tone and
inflammatory drugs, or tartrazine dyes. bronchial reactivity reach their nadir
Other medications may precipitate between 3 am and 4 am, increasing
symptoms of bronchoconstriction.
asthma symptoms (see Table 9–23).
Châu - Occupational asthma is Some physical examination findings
triggered by various agents in the increase the probability of asthma. Nasal
workplace and may occur weeks to years mucosal swelling, secretion increases,
after initial exposure and sensitization. and polyps are often seen in patients with
allergic
Women may experience catamenial
asthma. Eczema, atopic dermatitis, or
asthma at predictable times during the
other allergic skin disorders may also be
menstrual cycle. Exercise-induced present. Wheezing or a prolonged
bronchoconstriction begins during expiratory phase during normal breathing
exercise or within 3 minutes after its end, correlates well with the presence of
peaks within 10–15 minutes, and then airflow obstruction. (Wheezing during
resolves by 60 minutes. This phenomenon forced expiration does not.) Chest
is thought to be a consequence of the examination may be normal between
airways’ attempt to warm and humidify exacerbations in patients with mild
an increased volume of expired air during asthma. During severe asthma
exercise. “Cardiac asthma” is wheezing exacerbations,
precipitated by decompensated heart airflow may be too limited to produce
failure. wheezing, and the only diagnostic clue on
auscultation may be globally reduced
Clinical Findings breath sounds with prolonged expiration.
Hunched shoulders and use of accessory
nguyenthaiduy.med@gmail.com Pulmonary Disorders Mark S. Chesnutt, MD Thomas J. Prendergast, MD
0985 53 53 36 – 0938 057 921 Current medical diagnosis and treatment
muscles of respiration suggest an obstruction results in significant air
increased work of breathing. trapping, with an increase in residual
volume and consequent reduction in
B. Laboratory Findings FVC, resulting in a pattern that may
Arterial blood gas measurements may be mimic a restrictive ventilatory defect.
normal during a mild asthma
exacerbation, but respiratory alkalosis Bronchial provocation testing with
and an increase in the alveolar-arterial inhaled histamine or methacholine may
oxygen difference (a–a– be useful when asthma is suspected but
Do2) are common. During severe spirometry is nondiagnostic. Bronchial
exacerbations, hypoxemia develops and provocation is not recommended if the
the Paco2 returns to normal. The FEV1 is less than 65% of predicted. A
combination of an increased Paco2 and positive methacholine test is defined as a
respiratory acidosis may indicate ≥ 20% fall in the FEV1 at exposure to a
impending respiratory failure and the concentration of 8 mg/mL or less. A
need for mechanical ventilation. negative test has a negative predictive
value for asthma of 95%. Exercise
C. Pulmonary Function Testing challenge testing may be useful in
Clinicians are able to identify airflow patients with symptoms of exercise-
obstruction on examination, but they have induced bronchospasm.
limited ability to assess its severity or to
predict whether it is reversible. The Peak expiratory flow (PEF) meters are
evaluation for asthma should therefore handheld devices designed as personal
include spirometry (forced expiratory monitoring tools. PEF monitoring can
volume in 1 second [FEV1], forced vital establish peak flow variability, quantify
capacity [FVC], FEV1/FVC) before and asthma severity, and provide both patient
after the administration of a short-acting and clinician with objective
bronchodilator. These measurements help measurements on which to base treatment
determine the presence and extent of decisions. There are conflicting data
airflow obstruction and whether it is about whether measuring PEF improves
immediately reversible. Airflow asthma outcomes, but doing so is
obstruction is indicated by a reduced recommended to help confirm the
FEV1/FVC ratio. Significant reversibility diagnosis of asthma, to improve asthma
of airflow obstruction is defined by an control in patients with poor perception of
increase of ≥ 12% and 200 mL in FEV1 airflow obstruction, and to identify
or ≥ 15% and 200 mL in FVC after environmental and occupational causes of
inhaling a short-acting bronchodilator. A symptoms. Predicted values for PEF vary
positive bronchodilator response strongly with age, height, and gender but are
confirms the diagnosis of asthma but a poorly standardized. Comparison with
lack of responsiveness in the pulmonary reference values is less helpful than
function laboratory does not preclude comparison with the patient’s own
success in a clinical trial of baseline. PEF shows diurnal variation. It
bronchodilator therapy. Severe airflow is generally lowest on first awakening and
nguyenthaiduy.med@gmail.com Pulmonary Disorders Mark S. Chesnutt, MD Thomas J. Prendergast, MD
0985 53 53 36 – 0938 057 921 Current medical diagnosis and treatment
highest several hours before the midpoint
of the waking day. PEF should be
measured in the morning before the ▶▶Differential Diagnosis
administration of a bronchodilator and in Patients who have atypical symptoms or
the afternoon after taking a poor response to therapy may have a
bronchodilator. A 20% change in PEF condition that mimics asthma. These
values from morning to afternoon or from disorders typically fall into one of four
day to day suggests inadequately categories: upper airway disorders, lower
controlled asthma. PEF values less than airway disorders, systemic vasculitides,
200 L/min indicate severe airflow and psychiatric disorders.
obstruction.
Upper airway disorders that mimic
D. Additional Testing asthma include vocal fold paralysis, vocal
Routine chest radiographs in patients with fold dysfunction syndrome, foreign body
asthma are usually normal or show only aspiration, laryngotracheal masses,
hyperinflation. Other findings may tracheal narrowing, tracheomalacia, and
include bronchial wall thickening and airway edema (eg, angioedema or
diminished peripheral lung vascular inhalation injury).
shadows. Chest imaging is indicated
when pneumonia, another disorder Lower airway disorders include
mimicking asthma, or a complication of nonasthmatic chronic obstructive
asthma such as pneumothorax is pulmonary disease (COPD) (chronic
suspected. bronchitis or emphysema),
bronchiectasis, allergic
Skin testing or in vitro testing to assess bronchopulmonary mycosis, cystic
sensitivity to environmental allergens can fibrosis, eosinophilic pneumonia, and
identify atopy in patients with persistent bronchiolitis obliterans.
asthma who may benefit from therapies
directed at their allergic diathesis. Systemic vasculitides with pulmonary
Evaluations for paranasal sinus disease or involvement may have an asthmatic
gastroesophageal reflux should be component, such as Churg-Strauss
considered in patients with pertinent, syndrome.
severe or refractory asthma symptoms.
Psychiatric causes include conversion
▶▶Complications disorders (“functional” asthma),
emotional laryngeal wheezing, vocal fold
Complications of asthma include
dysfunction, or episodic laryngeal
exhaustion, dehydration, airway
dyskinesis. Rarely, Münchausen
infection, and tussive syncope.
syndrome or malingering may explain a
Pneumothorax occurs but is rare. Acute
patient’s complaints.
hypercapnic and hypoxemic respiratory
failure occurs in severe disease.
nguyenthaiduy.med@gmail.com Pulmonary Disorders Mark S. Chesnutt, MD Thomas J. Prendergast, MD
0985 53 53 36 – 0938 057 921 Current medical diagnosis and treatment
You might also like
- Lehne S Pharmacology For Nursing Care by PDFDocument3 pagesLehne S Pharmacology For Nursing Care by PDFeverydayisagift999920% (5)
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation Case StudyDocument43 pagesBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation Case Studyroseanne parkNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Management and Study GuideDocument7 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Management and Study GuideRamakrishna BadeNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument5 pagesASTHMAabdulNo ratings yet
- Asthma PDFDocument7 pagesAsthma PDFAlessandro Jr. ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Asthma and CopdDocument44 pagesAsthma and CopdBeer Dilacshe100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory InfectionDocument28 pagesAcute Respiratory InfectionMazharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Bronchial Asthma: Khaled O Hadeli MD, FCCPDocument19 pagesChapter 9. Bronchial Asthma: Khaled O Hadeli MD, FCCPgireeshsachinNo ratings yet
- Asthmatic Attack: Miriti M.D Masters of Clinical Medicine Accidents and Emergency Facilitator: DR Simba DR MburuguDocument26 pagesAsthmatic Attack: Miriti M.D Masters of Clinical Medicine Accidents and Emergency Facilitator: DR Simba DR MburuguDennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- 03 Asthma FinalDocument50 pages03 Asthma FinalG SNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument17 pagesAsthmaderarataye6No ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument46 pagesAsthmaHafiz Muhammad AeymonNo ratings yet
- Asthma in The Primary Care Setting 2019 Medical Clinics of North AmericaDocument18 pagesAsthma in The Primary Care Setting 2019 Medical Clinics of North AmericaYony Morales LeonNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument45 pagesBronchial Asthmamuluken mulatieNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument95 pagesBronchial AsthmaBrian BrownNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument8 pagesAsthmahusainozelNo ratings yet
- Asthma OpdDocument59 pagesAsthma OpdJb TlntinoNo ratings yet
- Asthma Davidson + Osmosis + Step Up MedicineDocument2 pagesAsthma Davidson + Osmosis + Step Up MedicineElyas MehdarNo ratings yet
- Cap 25 Sibilancia e EstridorDocument32 pagesCap 25 Sibilancia e Estridorroquetv93No ratings yet
- SEMINARSKI RAD EnglDocument10 pagesSEMINARSKI RAD EngljuliNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesDisorders of The Respiratory SystemAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation - FinalDocument17 pagesBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation - Finalmary_sulit_150% (2)
- AsthmaDocument28 pagesAsthmamalekNo ratings yet
- Concept Map AsthmaDocument7 pagesConcept Map Asthmashehada bondad100% (2)
- AsthmaDocument10 pagesAsthmaAbirajanNo ratings yet
- Astm ErsDocument9 pagesAstm ErsAdrian RomanNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Cough and Hemoptysis 15 11 13Document34 pagesApproach To The Patient With Cough and Hemoptysis 15 11 13Sanchit PeriwalNo ratings yet
- Problems in Etiology and Diagnosis of Cough and Chronic CoughDocument38 pagesProblems in Etiology and Diagnosis of Cough and Chronic Coughsszh_No ratings yet
- Asthma DR Moses KazevuDocument25 pagesAsthma DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- English in Nursing Science Assignment Name: Devi SetiawanDocument12 pagesEnglish in Nursing Science Assignment Name: Devi SetiawanDevi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Kinyua Md. MCM - A & E MKU Facilitator: Dr. AyungaDocument28 pagesAsthma: Kinyua Md. MCM - A & E MKU Facilitator: Dr. AyungaDennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- File 18585Document15 pagesFile 18585Mohammed MuthanaNo ratings yet
- Disnea Clinics 2016Document21 pagesDisnea Clinics 2016Nicolás Honores RomeroNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Chronic Inflammation of The Airways. The Hyper-Responsive Airways Typical of AsthmaDocument7 pagesAsthma: Chronic Inflammation of The Airways. The Hyper-Responsive Airways Typical of AsthmaRaj PaulNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasesDocument7 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasesGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Approach To Adult Patients With Acute DyspneaDocument21 pagesApproach To Adult Patients With Acute DyspneaCándida DíazNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument9 pagesASTHMAmildred alidonNo ratings yet
- Asthm ADocument3 pagesAsthm ADebbi YuniseraniNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument34 pagesBronchial AsthmaFabb NelsonNo ratings yet
- Articulo Parcial 1 Urgencias Respiratorias Perros y GatosDocument23 pagesArticulo Parcial 1 Urgencias Respiratorias Perros y GatosYara Valentina Toledo ManriqueNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress in PregnancyDocument12 pagesRespiratory Distress in PregnancySitha MahendrataNo ratings yet
- زياد ٤Document43 pagesزياد ٤Ibrahim RamizNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument19 pagesASTHMARIAH BILLANESNo ratings yet
- Bronchospasm During Anaesthesia Update 2011Document5 pagesBronchospasm During Anaesthesia Update 2011hy3pjb1984No ratings yet
- CoughDocument75 pagesCoughVijayachandar Gettala SundaramurthyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearDocument41 pagesRespiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearNancyNo ratings yet
- DR Ambreen Shams NephrologistDocument58 pagesDR Ambreen Shams NephrologistAamer NaeemNo ratings yet
- MedicationsDocument4 pagesMedicationsJosephine IsonNo ratings yet
- Asthma DX Article 1Document16 pagesAsthma DX Article 1Pat Caz SarNo ratings yet
- Asthma Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument11 pagesAsthma Diagnosis and TreatmentginaNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument79 pagesAsthmaraj patel100% (1)
- 3cough Evaluation and TreatmentDocument3 pages3cough Evaluation and TreatmentdrpmdasNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Signs and SymptomsDocument57 pagesAsthma: Signs and SymptomsAjp Ryuzaki CaesarNo ratings yet
- CHD AsthmaDocument20 pagesCHD AsthmaRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0749070421000889 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S0749070421000889 MainEliseu AmaralNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sana Bashir DPT, MS-CPPTDocument46 pagesDr. Sana Bashir DPT, MS-CPPTbkdfiesefll100% (1)
- Asthma in Children: Dr. Vinia Rusli SpaDocument30 pagesAsthma in Children: Dr. Vinia Rusli SpaOlivia FatrinNo ratings yet
- Thursday Teaching SessionsDocument15 pagesThursday Teaching SessionsSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument5 pagesAsthmaabenezer isayasNo ratings yet
- TII Workbook Mar20 FINAL PDFDocument342 pagesTII Workbook Mar20 FINAL PDFeverydayisagift9999No ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: OsteoporosisDocument2 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Osteoporosiseverydayisagift9999No ratings yet
- How To Learn Medical English Through Textbooks PDFDocument4 pagesHow To Learn Medical English Through Textbooks PDFeverydayisagift9999No ratings yet
- NBKids Foot-Fitting Chart PDFDocument1 pageNBKids Foot-Fitting Chart PDFeverydayisagift9999No ratings yet
- : Phương Pháp Giảng Dạy: Đ ề thi h ọ cph ầ nDocument1 page: Phương Pháp Giảng Dạy: Đ ề thi h ọ cph ầ neverydayisagift9999No ratings yet
- Medicover Hospitals: Sampath Nagar, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh 518003Document2 pagesMedicover Hospitals: Sampath Nagar, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh 518003IKON RESPONSENo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument3 pagesAsthmaAnjana BasilNo ratings yet
- 12.chest Percussion Postural DrainageDocument3 pages12.chest Percussion Postural DrainageDwaipayan100% (1)
- Multistage Fitness Test TableDocument3 pagesMultistage Fitness Test TableMumtaz Maulana HidayatNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach of Noisy Breathing in Infant and ChildrenDocument40 pagesClinical Approach of Noisy Breathing in Infant and ChildrenAndriana SusantiNo ratings yet
- Crup Revision PDFDocument9 pagesCrup Revision PDFEmily Gabriela Caicedo RuedaNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument14 pagesBronchial AsthmaRashmi GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Acute Lung Injury, Pulmonary Edema and Multi Organ System FailureDocument10 pagesChapter 27 Acute Lung Injury, Pulmonary Edema and Multi Organ System FailureShanin SalapuddinNo ratings yet
- Noninvasive Ventilation HandbookDocument88 pagesNoninvasive Ventilation HandbookPablo100% (1)
- Ventilator Modes - WEANINGDocument3 pagesVentilator Modes - WEANINGAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- g1b Asthma PDFDocument75 pagesg1b Asthma PDFAniq Zahran MasomNo ratings yet
- Ambu BagDocument12 pagesAmbu BagAejaz Ahmad100% (1)
- SOMNOcheck MicroDocument2 pagesSOMNOcheck MicroEvangelosNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medicine 151 200Document31 pagesRespiratory Medicine 151 200Ahmed Kh. Abu Warda100% (2)
- 2.health AssessmentDocument7 pages2.health Assessment2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- Role of CPAP in ICUDocument21 pagesRole of CPAP in ICUheriNo ratings yet
- Applied Technologies in Pulmonary Medicine (PDFDrive)Document271 pagesApplied Technologies in Pulmonary Medicine (PDFDrive)Богдана ВацебаNo ratings yet
- Nursing InterventionsDocument2 pagesNursing InterventionsJanine Paola CabangilNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Management in Bronchoscopy Procedure NewDocument29 pagesAnesthesia Management in Bronchoscopy Procedure NewChlara Obisuru100% (1)
- Thoracic Trauma: Dr. Bareera AmjadDocument45 pagesThoracic Trauma: Dr. Bareera AmjadMuhammad MuaazNo ratings yet
- Modes of VentilatorDocument10 pagesModes of VentilatorSatya Biomed100% (2)
- Chapter 10Document4 pagesChapter 10Srinu WestNo ratings yet
- NCP For Rapid Shallow BreathingDocument1 pageNCP For Rapid Shallow Breathingbamboo2dNo ratings yet
- Intermountain Stories - Front Page ArticleDocument20 pagesIntermountain Stories - Front Page ArticleSabina Mueller SuggsNo ratings yet
- HY PulmonaryDocument67 pagesHY PulmonaryJeniNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument12 pagesChest Physiotherapysenthilkumar100% (2)
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledMarceline GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Classification of Respiratory Failure. Tejpreet Singh Lamba. 2016Document9 pagesPathophysiology and Classification of Respiratory Failure. Tejpreet Singh Lamba. 2016Danitza VeraNo ratings yet
- Oxygen AdministrationDocument25 pagesOxygen Administrationkirutheka nithilaaNo ratings yet
- Body PlethysmographyDocument52 pagesBody PlethysmographyppgpcsNo ratings yet