Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Egao, Vanessa Jones C. Section: Block 260
Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Egao, Vanessa Jones C. Section: Block 260
Uploaded by
Vanessa EgaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Egao, Vanessa Jones C. Section: Block 260
Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Egao, Vanessa Jones C. Section: Block 260
Uploaded by
Vanessa EgaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Mindanao State University – Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Egao, Vanessa Jones C.
Section: Block 260
PHARMACOLOGY
DRUG STUDY
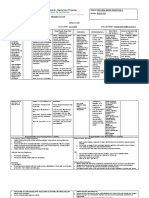
Brand Name: Lanoxin_______________________________Generic Name: Digoxin_______________________ Drug Classification: Cardiac Glycoside
Dosage, Route & Frequency Drug-Drug & Drug-Food Side Effects Adverse Reactions (By
Drug Action Indications Contraindications
Recommended Prescribed Interactions (By System) System)
Digitalizing Dose HF: Inhibits sodium/potassium ATPase DRUG: Amiodarone may Rapid digitalization Hypersensitivity to digoxin. Dizziness, headache, CNS: Fatigue, muscle weakness,
Adult: PO 10–15 mcg/kg (1 mg) in pump in myocardial cells. Promotes increase concentration/toxicity. and for maintenance Ventricular fibrillation. diarrhea, rash, visual headache, facial neuralgia,
divided doses over 24–48 h IV 10– calcium influx. Supraventricular Beta blockers (e.g., metoprolol), therapy in CHF, atrial disturbances mental depression, paresthesias,
hallucinations, confusion,
15 mcg/kg (1 mg) in divided Arrhythmias: Suppresses AV node calcium channel blockers (e.g., fibrillation, atrial flutter, Cautions: Renal
drowsiness, agitation,
doses over 24 h conduction. Therapeutic Effect: diltiaZEM) may have additive effect paroxysmal atrial impairment, sinus nodal dizziness. CV: Arrhythmias,
Child: PO/IV <2 y, 40–60 on slowing AV nodal conduction. tachycardia. disease, acute MI (within 6 hypotension, AV block. Special
mcg/kg; 2–10 y, 20–40 mcg/kg; HF: Increases contractility. Potassium-depleting diuretics (e.g., mos), second-or third- Senses: Visual
>10 y, 10–15 mcg/kg (1.5–2 mg) Supraventricular Arrhythmias: Increases furosemide) may increase toxicity degree heart block (unless disturbances. GI: Anorexia, naus
Neonate: PO/IV 30–50 mcg/kg effective refractory period/decreases due to hypokalemia. functioning pacemaker), ea, vomiting,
Premature neonate: PO/IV 20 conduction velocity, decreases heart Sympathomimetics (e.g., concurrent use of strong diarrhea. Other: Diaphoresis,
recurrent malaise, dysphagia
mcg/kg rate. norepinephrine) may increase risk of inducers or inhibitors of P-
arrhythmias. HERBAL: Ephedra may glycoprotein
Maintenance Dose Absorption: 70% PO tablets; 90% PO liquid increase risk of arrhythmias. Licorice (e.g.,cyclosporine),
Adult: PO/IV 0.1–0.375 mg/d and capsules. may cause sodium and water hyperthyroidism,
Child: PO/IV <2 y, 7.5–9 Onset: 1–2 h PO; 5–30 min IV. retention, loss of potassium. FOOD: hypothyroidism,
Peak: 6–8 h PO; 1–5 h IV.
mcg/kg/d; 2–10 y, 6–7.5 Meals with increased fiber (bran) or hypokalemia,
Duration: 3–4 d in fully digitalized patient.
mcg/kg/d; >10 y, 0.125–0.25 mg/d high in pectin may decrease hypocalcemia.
Distribution: Widely distributed; tissue
Neonate: 6–7.5 mcg/kg/d levels significantly higher than plasma absorption.
Premature neonate: 3.75 levels; crosses placenta.
mcg/kg/d Metabolism: Approximately 14% in liver.
Elimination: 80–90% excreted by kidneys;
may appear in breast milk.
Half-Life: 34–44 h.
Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE) Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE)
Assessment & Drug Effects Intervention/ Health Education
Take apical pulse for 1 full min, noting rate, rhythm, and quality before administering drug. Report to physician if pulse falls below 60 or rises above 110 or if you detect skipped beats or other changes in rhythm, when digoxin
Be familiar with patient's baseline data (e.g., quality of peripheral pulses, blood pressure, clinical symptoms, serum electrolytes, creatinine is prescribed for atrial fibrillation.
clearance) as a foundation for making assessments. Suspect toxicity and report to physician if any of the following occur: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or visual disturbances.
Lab tests: Baseline and periodic serum digoxin, potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Draw blood samples for determining plasma digoxin Weigh each day under standard conditions. Report weight gain >1 kg (2 lb)/d.
levels at least 6 h after daily dose and preferably just before next scheduled daily dose. Take digoxin PRECISELY as prescribed, do not skip or double a dose or change dose intervals, and take it at same time each day.
Monitor for S&S of drug toxicity: In children, cardiac arrhythmias are usually reliable signs of early toxicity. Early indicators in adults (anorexia, Do not to take OTC medications, especially those for coughs, colds, allergy, GI upset, or obesity, without prior approval of physician.
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, visual disturbances) are rarely initial signs in children. Continue with brand originally prescribed unless otherwise directed by physician.
Monitor I&O ratio during digitalization, particularly in patients with impaired renal function. Also monitor for edema daily and auscultate Encourage periods of rest and assist with all activities.
chest for rales.
Observe patients closely when being transferred from one preparation (tablet, elixir, or parenteral) to another; when tablet is replaced by
Assist the patient in assuming a high Fowler’s position.
elixir potential for toxicity increases since 30% of drug is absorbed. Provide quiet environment: explain therapeutic management, help patient avoid stressful situations, listen and respond to expressions
Nursing Diagnosis: of feelings.
Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output
Planning: Evaluation:
After 16 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will demonstrate adequate cardiac output as evidenced by vital signs within acceptable After 16 hours of nursing interventions, the patient demonstrated adequate cardiac output as evidenced by vital signs within
limits, dysrhythmias absent/controlled, and no symptoms of failure (e.g., hemodynamic parameters within acceptable limits, urinary output acceptable limits, dysrhythmias absent/controlled, and no symptoms of failure (e.g., hemodynamic parameters within acceptable
adequate) limits, urinary output adequate)
You might also like
- Mark Klimek Yellow BookDocument5 pagesMark Klimek Yellow Bookmaniz44295% (19)
- Board Stiff ThreeDocument440 pagesBoard Stiff Threewin co100% (1)
- FlecainideDocument3 pagesFlecainideAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Easy ECG GuideDocument17 pagesEasy ECG GuideDr.Chinmay Kulkarni83% (12)
- Advanced EKG RefresherDocument181 pagesAdvanced EKG Refreshersimi100% (4)
- Pharma Drug StudyDocument56 pagesPharma Drug StudyGrace Pikit Bacsan100% (1)
- LanoxinDocument2 pagesLanoxinJOHN PAUL ORTIZNo ratings yet
- Sotalol HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesSotalol HydrochlorideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Carvedilol - Drug StudyDocument1 pageCarvedilol - Drug StudyAcads useNo ratings yet
- AmloDocument1 pageAmloamy navajaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DigoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DigoxinKian Herrera50% (2)
- Drug Name WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesDrug Name WPS OfficeCAMILLE GAIL HADJIRANINo ratings yet
- Drug Study DigoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study DigoxinEzra CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Amiodarone)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Amiodarone)Justine Conui100% (1)
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Final Drug Study-12-25Document41 pagesFinal Drug Study-12-25Poinsithia OrlandaNo ratings yet
- PCU Medication ListDocument11 pagesPCU Medication ListreneecolemanNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Salimbagat, Christine. P Section: 262Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Salimbagat, Christine. P Section: 262Christine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263AkiraMamo100% (1)
- Dalidig - Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDalidig - Drug StudyRaf DalidigNo ratings yet
- Cilostazol (Pletal)Document4 pagesCilostazol (Pletal)Maria Leonie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Course TaskDocument96 pagesCourse TaskJoelynMacalintalNo ratings yet
- AtropineDocument3 pagesAtropineChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument25 pagesDrug StudyshakiraNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Ma'am D)Document3 pagesDRUG STUDY (Ma'am D)Angelica Mercado SirotNo ratings yet
- Digoxin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDigoxin Drug StudyHarline GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DopamineDocument1 pageDrug Study Dopaminejulesubayubay542880% (5)
- Med LopressorDocument2 pagesMed LopressorDeanna Lang ThibodauxNo ratings yet
- Medicationrecords - Shortness of BreathingDocument1 pageMedicationrecords - Shortness of BreathingHero StoreNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document3 pagesDrug Study 1G4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Brand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Brand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DigoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DigoxinDanielle AglusolosNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQuetiapine Drug StudyEula Angelica Oco100% (1)
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument1 pageMetformin Drug StudyRose Echevarria67% (3)
- Drug Study For Losartan PotassiumDocument2 pagesDrug Study For Losartan PotassiumChryst Louise SaavedraNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument4 pagesAmiodaroneChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam 2 Drug Chart Pharm Exam 2 Drug ChartDocument20 pagesPharm Exam 2 Drug Chart Pharm Exam 2 Drug Chartminhmap90_635122804No ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Advserse Effects (Specify) Nursing InterventionsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Advserse Effects (Specify) Nursing InterventionsKaterina Petrova100% (1)
- Drug Study (Duty2)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Duty2)Robert َMirandaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- LisinoprilDocument3 pagesLisinoprilLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideYanejoulce SacanleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyApril Sarol67% (3)
- Drug AnalysisDocument9 pagesDrug AnalysisKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsDocument7 pagesDiuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Medication Class Mechanism of Action Dosage Range Side Effects Nursing Implications/ Teaching Generic NameDocument19 pagesMedication Class Mechanism of Action Dosage Range Side Effects Nursing Implications/ Teaching Generic NameindyaphdNo ratings yet
- Generic Name T Rade Name Lanoxin DigoxinDocument1 pageGeneric Name T Rade Name Lanoxin DigoxinChristopher LeeNo ratings yet
- 25 Ethical 24 OTCDocument42 pages25 Ethical 24 OTCBagus KafiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document9 pagesDrug Study 2John Michael M. RosalesNo ratings yet
- Albuterol (Ventolin, Salbutamol)Document1 pageAlbuterol (Ventolin, Salbutamol)Jocelyn Rivera100% (1)
- Dosage & RouteDocument1 pageDosage & RouteinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IcuDocument6 pagesDrug Study IcuJenny Juniora AjocNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- VaccinesDocument27 pagesVaccinesVanessa EgaoNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: EGAO, Vanessa Jones C. - Section:260Document1 pageMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: EGAO, Vanessa Jones C. - Section:260Vanessa EgaoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPVanessa EgaoNo ratings yet
- TigecyclineDocument2 pagesTigecyclineVanessa Egao100% (1)
- Epidemiology, Mechanisms, and Lifelong Effect. Lancet 2016 387: 475-90Document1 pageEpidemiology, Mechanisms, and Lifelong Effect. Lancet 2016 387: 475-90Vanessa EgaoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document24 pagesClinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)soniya josephNo ratings yet
- CLIX ECG Tutorial Part 3 Ischaemia EtcDocument97 pagesCLIX ECG Tutorial Part 3 Ischaemia Etcdragon66No ratings yet
- Ehz 467Document65 pagesEhz 467Coy Calapatia-TorresNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi CHFDocument7 pagesPatofisiologi CHFHafiz Idul FitranulNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Adult Patient With Syncope in The Emergency DepartmentDocument26 pagesApproach To The Adult Patient With Syncope in The Emergency DepartmentVinicius DumontNo ratings yet
- Kroll CV 26 March 2018Document92 pagesKroll CV 26 March 2018wolf woodNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhythmiaDocument5 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmiahoney_eytNo ratings yet
- KULIAH ECG Dinkes PurworejoDocument69 pagesKULIAH ECG Dinkes PurworejoSofian PalupiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway-Pacemaker InsertionDocument2 pagesClinical Pathway-Pacemaker InsertionJanua Navarette100% (1)
- Handbook of Critical Care Drug Therapy PDFDocument382 pagesHandbook of Critical Care Drug Therapy PDFntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Little Book of CardioDocument62 pagesLittle Book of CardioRichardNo ratings yet
- (Pharma) Cardio QuestionnaireDocument38 pages(Pharma) Cardio QuestionnaireMarqxczNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology For Medical Transcription TraineesDocument74 pagesMedical Terminology For Medical Transcription TraineesRangothri Sreenivasa SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- GP Emergency Manual PDFDocument72 pagesGP Emergency Manual PDFRumana Ali100% (2)
- EKGDocument137 pagesEKGGbariel100% (3)
- Design of Telemonitoring Medical Record of Cardiac Arrhythmia Patients Based On RFID and WEBDocument4 pagesDesign of Telemonitoring Medical Record of Cardiac Arrhythmia Patients Based On RFID and WEBRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Presented By: Layan S. Barqawi & Yasmin N. NassarDocument73 pagesCardiovascular Diseases: Presented By: Layan S. Barqawi & Yasmin N. Nassarasop06No ratings yet
- Definition, Classification, Etiology, and Pathophysiology of Shock in Adults - UpToDateDocument16 pagesDefinition, Classification, Etiology, and Pathophysiology of Shock in Adults - UpToDatevara prasadNo ratings yet
- Oct 2018 - YogaDocument56 pagesOct 2018 - Yogamjoseyoga100% (1)
- Ekg PrehospitalarioDocument6 pagesEkg PrehospitalarioLudwinNo ratings yet
- 9 - Dental Treatment For High-Risk Patients With Refractory Heart Failure A Retrospective Observational Comparison StudyDocument10 pages9 - Dental Treatment For High-Risk Patients With Refractory Heart Failure A Retrospective Observational Comparison StudykochikaghochiNo ratings yet
- Medical Equipment - DefibrillatorDocument25 pagesMedical Equipment - DefibrillatorLem PaneloNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmia PowerpointDocument10 pagesDysrhythmia PowerpointWynton De JesusNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Fetal Cardiovascular Disease (Dec 19, 2018) - (9811019916) - (Springer)Document225 pagesMaternal and Fetal Cardiovascular Disease (Dec 19, 2018) - (9811019916) - (Springer)taher100% (1)
- Syncope: Emergency Evaluation and Risk StratificationDocument34 pagesSyncope: Emergency Evaluation and Risk StratificationAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument24 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptRahul NNo ratings yet