Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Directory Implementation: 1. Linear List
Directory Implementation: 1. Linear List
Uploaded by
Yamani DinakarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Directory Implementation: 1. Linear List
Directory Implementation: 1. Linear List
Uploaded by
Yamani DinakarCopyright:
Available Formats
DIRECTORY IMPLEMENTATION
There is the number of algorithms by using which, the directories can be implemented.
However, the selection of an appropriate directory implementation algorithm may significantly
affect the performance of the system.
The directory implementation can be done by using two algorithms:
1. LINEAR LIST
2. HASH TABLE
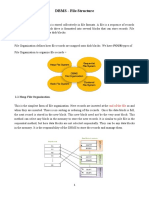
1. Linear List
In this algorithm, all the files in a directory are maintained as singly lined list. Each file contains
the pointers to the data blocks which are assigned to it and the next file in the directory.
Characteristics:
When a new file is created, then the entire list is checked whether the new file name is matching
to a existing file name or not. In case, it doesn't exist, the file can be created at the beginning or
at the end.
Therefore, searching for a unique name is a big concern because traversing the whole list takes
time.
The list needs to be traversed in case of every operation (creation, deletion, updating, etc) on the
files therefore the systems become inefficient.
DISADVANTAGES:
1. Accessing is low
2. Linear search technique is used
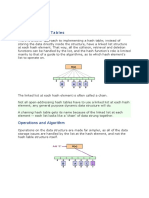
2. Hash Table
To overcome the drawbacks of singly linked list implementation of directories, there is an
alternative approach that is hash table. This approach suggests to use hash table along with the
linked lists.
A key-value pair for each file in the directory gets generated and stored in the hash table. The
key can be determined by applying the hash function on the file name while the key points to
the corresponding file stored in the directory.
Now, searching becomes efficient due to the fact that now, entire list will not be searched on
every operating. Only hash table entries are checked using the key and if an entry found then
the corresponding file will be fetched using the value.
You might also like
- Unit - V - 1Document17 pagesUnit - V - 1Purna Nanda Siva JPNo ratings yet
- 1 Directory: First PartDocument4 pages1 Directory: First PartAnkit GargNo ratings yet
- DBMS - File Organization, Indexing and Hashing NotesDocument19 pagesDBMS - File Organization, Indexing and Hashing NotesKomal RamtekeNo ratings yet
- File Organization in DBMSDocument10 pagesFile Organization in DBMSMani MalaNo ratings yet
- File StructureDocument8 pagesFile StructureNahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chaining Hash TablesDocument2 pagesChaining Hash TablesLaiba MughalNo ratings yet
- File ManagementDocument5 pagesFile ManagementSolomon GodwinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Indexing and HashingDocument31 pagesChapter 12: Indexing and HashingRajvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- 3. Organization of Files - Sequential & MultitableDocument11 pages3. Organization of Files - Sequential & MultitableJerrin SibyNo ratings yet
- Some Applications of Inverted Indexes On The UNIX System - M. E. LeskDocument12 pagesSome Applications of Inverted Indexes On The UNIX System - M. E. LesksungodukNo ratings yet
- A655398144 - 23361 - 19 - 2018 - Database Unit 6Document12 pagesA655398144 - 23361 - 19 - 2018 - Database Unit 6cheppanu dengeyNo ratings yet
- File Organization MethodsDocument22 pagesFile Organization MethodsAastha ChauhanNo ratings yet
- DBMS - R2017 - Anna UniversityDocument20 pagesDBMS - R2017 - Anna UniversityShanmughapriyaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-3 NotesDocument9 pagesDBMS Unit-3 NotesThakur Nishant MoghaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 FDS Relational Database DesignDocument48 pagesGroup 4 FDS Relational Database DesignHannah GaguanNo ratings yet
- Directory StructureDocument27 pagesDirectory StructureSoumya VijoyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 File Organization in DBMSDocument22 pagesUNIT 5 File Organization in DBMSprasadNo ratings yet
- File Organization in DBMSDocument23 pagesFile Organization in DBMSsunny sarwara100% (1)
- 1 File Structure & OrganizationDocument23 pages1 File Structure & OrganizationSufi khanNo ratings yet
- Types of File OrganizationDocument3 pagesTypes of File OrganizationHellenNdegwa100% (1)
- File Organization in DBMSDocument13 pagesFile Organization in DBMSprasadNo ratings yet
- Dotted Background SlidesManiaDocument20 pagesDotted Background SlidesManiaAllen Paulo Vicuña CayaNo ratings yet
- ss2 DPR Second TermDocument5 pagesss2 DPR Second TermTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Indexed Sequential FileDocument2 pagesIndexed Sequential FileStudy MailNo ratings yet
- Hash FilesDocument15 pagesHash FilesMahesh_Umbarka_4467No ratings yet
- File StructureDocument18 pagesFile StructureAbhishek GiriNo ratings yet
- Assignment (DS)Document8 pagesAssignment (DS)Gaurav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Free Space ManagementDocument6 pagesFree Space ManagementlaxmikanthNo ratings yet
- Range of Quiz 2: Database System ImplementationDocument3 pagesRange of Quiz 2: Database System Implementationben8987No ratings yet
- File OrganizationDocument16 pagesFile OrganizationSATHYABAMA MADHANKUMARNo ratings yet
- Internal File Structure: Methods and Design ParadigmDocument6 pagesInternal File Structure: Methods and Design Paradigmdhiraj100No ratings yet
- Ds Mod 5Document17 pagesDs Mod 5afnanazrin123No ratings yet
- E-Note SS Two 2nd Term Data ProcessingDocument17 pagesE-Note SS Two 2nd Term Data ProcessingFaith OzuahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OSDocument13 pagesChapter 5 OSelias ferhanNo ratings yet
- Self Unit 2Document18 pagesSelf Unit 2Ayush NighotNo ratings yet
- Hashing in DBMS: Static & Dynamic With ExamplesDocument8 pagesHashing in DBMS: Static & Dynamic With ExamplesamarNo ratings yet
- Swap Space in Operating SystemDocument4 pagesSwap Space in Operating SystemPrasad DasuvaramNo ratings yet
- Ignou Bca Cs 06 Solved Assignment 2012Document10 pagesIgnou Bca Cs 06 Solved Assignment 2012Vikas SengarNo ratings yet
- L2.2-File Organization TechniquesDocument42 pagesL2.2-File Organization TechniquesEdmunds LarryNo ratings yet
- 8 UnitDocument25 pages8 UnitRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- DS Ut2 QBDocument8 pagesDS Ut2 QBAniruddha ShriwantNo ratings yet
- File System: 1.1 MetadataDocument9 pagesFile System: 1.1 Metadataabebaw ataleleNo ratings yet
- Directory StructureDocument47 pagesDirectory StructureStevenNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Format Name: Rodjean A. Simballa Date: 19/11/21 Grade: Course & Section: BSIT 3D Topic: Lesson 5: File Management Question and AnswerDocument3 pagesProblem Solving Format Name: Rodjean A. Simballa Date: 19/11/21 Grade: Course & Section: BSIT 3D Topic: Lesson 5: File Management Question and AnswerRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- OS - Chapter - 5 - File SystemDocument30 pagesOS - Chapter - 5 - File Systemktesfaneh2No ratings yet
- File System ImplementationDocument38 pagesFile System ImplementationManohar DattNo ratings yet
- Values, Hash Codes, Hash Sums, Checksums or Simply Hashes.: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesValues, Hash Codes, Hash Sums, Checksums or Simply Hashes.: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRuchi Gujarathi100% (1)
- Processes and Processors in Distributed Systems Distributed File SystemsDocument54 pagesProcesses and Processors in Distributed Systems Distributed File SystemsSweta KamatNo ratings yet
- IndexingDocument62 pagesIndexingf20211140No ratings yet
- ABAP Data Dictionary TutorialDocument8 pagesABAP Data Dictionary TutorialCrazycat CrazycatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: File OrganizationDocument13 pagesChapter 5: File OrganizationJaved KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document29 pagesChapter 1swag boysNo ratings yet
- Os-Unit 5-BSCDocument26 pagesOs-Unit 5-BSCsofttech educationNo ratings yet
- Name Synopsis DescriptionDocument22 pagesName Synopsis DescriptionpereczkesNo ratings yet
- File SystemsDocument17 pagesFile SystemsParvinder vidanaNo ratings yet
- File System-1Document11 pagesFile System-1Leslie QwerNo ratings yet
- 1 File Management: 1.1 NamingDocument10 pages1 File Management: 1.1 Namingpaul mulwaNo ratings yet
- MI0034-Database Management System SetDocument17 pagesMI0034-Database Management System SetZameer Ahmed SaitNo ratings yet
- Basic Collection Types: Collection Type Functionality Typical UsesDocument5 pagesBasic Collection Types: Collection Type Functionality Typical Usesisaac_bNo ratings yet
- Data Structures for Beginners: Mastering the Building Blocks of Efficient Data ManagementFrom EverandData Structures for Beginners: Mastering the Building Blocks of Efficient Data ManagementNo ratings yet