Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Derivatives and Integrals Formula
Derivatives and Integrals Formula
Uploaded by
Paul Daryl CutamoraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Derivatives and Integrals Formula
Derivatives and Integrals Formula
Uploaded by
Paul Daryl CutamoraCopyright:
Available Formats
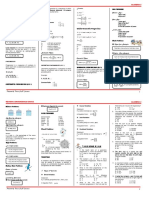
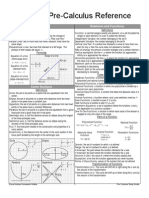
Basic Derivatives Basic Integrals
y=c 𝑦=0 ′
y = cx 𝑦=c
′ ∫ 𝐶 𝑑𝑥 = Cx + C
𝑥 𝑛+1
y = 𝑥𝑛 𝑦 ′ = n 𝑥 𝑛−1 y = 𝑢𝑛 𝑦 ′ = n 𝑢𝑛−1 du ∫ 𝑥 𝑛 dx = 𝑛+1
+C
𝑢 𝑣 𝑑𝑢− 𝑢 𝑑𝑣 ∫ 𝐶 𝑥 𝑛 dx = C ∫ 𝑥 𝑛 dx + C
y = uv 𝑦 ′ = u dv + v du y= 𝑦 ′=
𝑣 𝑣2
𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑢 Integral of Exponential Functions and Logarithmic Functions
y = √𝑢 𝑦′ = y = 3√𝑢 𝑦′ = 3
2√𝑢 3 √𝑢 𝑎𝑢
∫ 𝑎𝑢 𝑑𝑢 = +𝑐 ∫ 𝑒 𝑢 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑒 𝑢 + 𝑐
Chain Rule 𝑙𝑛 𝑎
𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑢 𝑎𝑏𝑥
𝑑𝑥
= 𝑑𝑢
∙ 𝑑𝑥 ∫ 𝑎𝑏𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑏 𝑙𝑛 𝑎
+𝑐 ∫ 𝑒 −𝑢 𝑑𝑢 = −𝑒 −𝑢 + 𝑐
Derivatives of logarithmic functions: 𝑒 𝑏𝑥
𝑑𝑢 ∫ 𝑒 𝑏𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = +𝑐
y = 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑎 𝑢 𝑦 = ′ 𝑏
𝑢𝑙𝑛 𝑎
𝑑𝑢 1 𝑑𝑢
y = ln u 𝑦′ = ∫ 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = ln|𝑥 | + 𝑐 ∫ 𝑢
= ln |𝑢| + 𝑐
𝑙𝑛 𝑎
Integral of Trigo Functions
Derivatives of exponential functions: ∫ cos 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = sin x + C
y=𝑎 𝑢
𝑦 = 𝑎 lna du
′ 𝑢
∫ sin 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = - cos x + C
y=𝑒 , 𝑢
𝑦 ′ = 𝑒 𝑢 du ∫ 𝑠𝑒𝑐 2 x dx = tan x + C
∫ 𝑐𝑠𝑐 2 x dx = -cot x + C
Derivatives of trigo functions: ∫ sec 𝑥 tan 𝑥 dx = sec x + C
y = sin u 𝑦 ′ = (cos u) du ∫ csc 𝑥 cot 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = -csc x + C
y = cos u 𝑦 ′ = (- sin u) du
y = tan u 𝑦 ′ = (𝑠𝑒𝑐 2 u) du ∫ tan 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = ln |sec x | + C
y = cot u 𝑦 ′ = (- 𝑐𝑠𝑐 2 u) du ∫ cot 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = ln |sin x | + C
y = sec u 𝑦 ′ = (sec u tan u) du ∫ sec 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = ln |sec x + tan x| + C
y = csc u 𝑦 ′ = (- csc u cot u) du ∫ csc 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = ln | csc x - cot x| + C
Integral of Inverse Trigo Functions
𝑑𝑢 𝑢
Derivatives of inverse trigo functions: ∫ √𝑎2 −𝑢2 = sin−1 𝑎 + C
𝑑𝑢
y = (𝑠𝑖𝑛−1 𝑢) 𝑦′ = 𝑑𝑢 1 𝑢
√1−𝑢 2
∫ 𝑎2 + 𝑢2 = 𝑎 tan−1 𝑎 + C where a ≠ 0
−𝑑𝑢
y = (𝑐𝑜𝑠 −1 𝑢) 𝑦′ =
√1−𝑢 2
𝑑𝑢 1 |𝑢|
y = (𝑡𝑎𝑛−1 𝑢) 𝑦′ =
𝑑𝑢 ∫ 𝑢√𝑢2−𝑎2 = sec −1 +C
1+𝑢 2 𝑎 𝑎
−𝑑𝑢
y = (𝑐𝑜𝑡 −1 𝑢) 𝑦′ = 1+𝑢 2 Chain Rule for Integration
𝑑𝑢
y = (𝑠𝑒𝑐 −1
𝑢) 𝑦 =
′
𝑢 √𝑢 2 −1
−𝑑𝑢
∫ 𝑓[𝑔(𝑥)]𝑔′ (𝑥)𝑑𝑥 = 𝐹(𝑔(𝑥)) + 𝑐
y = (𝑐𝑠𝑐 −1
𝑢) 𝑦 =
′
𝑢 √𝑢 2 −1
-JeeaaReeS
You might also like
- Wall Street Mastermind S Investment Banking Technical Interview Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesWall Street Mastermind S Investment Banking Technical Interview Cheat Sheetxandar198No ratings yet
- Math102 Equation SheetDocument0 pagesMath102 Equation SheetMaureen LaiNo ratings yet
- Algebra I Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAlgebra I Cheat SheetgolfwomannNo ratings yet
- 151 Exam 1 Review AU10Document3 pages151 Exam 1 Review AU10Nathan W. SerafiniNo ratings yet
- Solving Equation Foldable Multi Step KeyDocument1 pageSolving Equation Foldable Multi Step Keyapi-293260026No ratings yet
- Area and Perimeter With Polynomials WorksheetDocument5 pagesArea and Perimeter With Polynomials WorksheetArdaniel, Alpha Dayne CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Exponential FormsDocument4 pagesExponential FormsWella Wella WellaNo ratings yet
- Algebra IDocument5 pagesAlgebra IMatthew SteinNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Derivatives and IntegralsDocument1 pageFormulas For Derivatives and IntegralsAcapSuiNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Studies Formula BooketDocument7 pagesMathematical Studies Formula BooketsaloniNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic and Exponential FunctionsDocument22 pagesLogarithmic and Exponential FunctionsAshley MorganNo ratings yet
- Final Notes For AB and BCDocument16 pagesFinal Notes For AB and BCsapabapjava2012No ratings yet
- 1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsDocument58 pages1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsMiy ChanNo ratings yet
- Gases and Atmospheric ChemistryDocument10 pagesGases and Atmospheric ChemistryKatheeja MusatheekNo ratings yet
- Boolean Algebra & Logic GatesDocument45 pagesBoolean Algebra & Logic Gateszeeshan jamilNo ratings yet
- Sub Folder Contents2012-13Document7 pagesSub Folder Contents2012-13Lee Ann SpillaneNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document4 pagesAlgebra 2Kim OrtuosteNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields and Waves HW1 Solution - IskanderDocument6 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and Waves HW1 Solution - Iskanderamacombe100% (1)
- Plane Trigonometry PArt 2Document12 pagesPlane Trigonometry PArt 2Maria Lourven AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lesson 1 Notes Angle Relationships in TrianglesDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Lesson 1 Notes Angle Relationships in Trianglesapi-264764674No ratings yet
- Math FomulasDocument13 pagesMath FomulasChristine GomezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields and Waves HW3 Solution - IskanderDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and Waves HW3 Solution - IskanderamacombeNo ratings yet
- A2 Reference Sheet 01Document5 pagesA2 Reference Sheet 01rajbmohanNo ratings yet
- Boolean Algebra and Logic GatesDocument57 pagesBoolean Algebra and Logic GatesABDULLAH AAMIRNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Formula Sheet CondensedDocument1 pageDerivatives Formula Sheet CondensedintegralCALCNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Maths XIIDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Maths XIIrohitsrohit75% (4)
- DALTON'S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES (Answers)Document1 pageDALTON'S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES (Answers)Brianna WilsonNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC IntegrationDocument1 pageAP Calculus BC IntegrationteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C EquationsDocument3 pagesAP Physics C EquationsJoe ReiniNo ratings yet
- (Answer) Assignment For Physics 1 PDFDocument8 pages(Answer) Assignment For Physics 1 PDFTake IchiruNo ratings yet
- D - Solving A Triangle With The Law of CosinesDocument3 pagesD - Solving A Triangle With The Law of Cosinescitisolo0% (1)
- First Quarter DLL June 26 29Document3 pagesFirst Quarter DLL June 26 29BabyrrechBalilu100% (1)
- Number Systems and Conversion: This Chapter in The Book IncludesDocument34 pagesNumber Systems and Conversion: This Chapter in The Book Includes최재원No ratings yet
- AIST Math Practice TestDocument21 pagesAIST Math Practice TestnourNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Chapter 19 Thermodynamics - Spontaneity and Entropy KeyDocument3 pagesAP Chemistry Chapter 19 Thermodynamics - Spontaneity and Entropy Keyphuonglehuuyen100% (1)
- 3.3 Rational Root TheoremDocument15 pages3.3 Rational Root TheoremJoseph S. Palileo Jr.No ratings yet
- MM-Limits and ContinuityDocument22 pagesMM-Limits and ContinuityKim Say Chun / Sc.KIMNo ratings yet
- Pre CalcDocument2 pagesPre Calcapi-213604106No ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet ReducedPhirak KhimNo ratings yet
- Fall Prep Session Materials 2014-15 DraftDocument216 pagesFall Prep Session Materials 2014-15 Draftapi-283319039No ratings yet
- 8-1 Measurement of Arcs (Presentation)Document13 pages8-1 Measurement of Arcs (Presentation)Sandra Miller100% (1)
- Number Theory TutorialDocument46 pagesNumber Theory TutorialNiranjan Prasad67% (3)
- Calculus Formula Sheet:: Sin X Cos XDocument4 pagesCalculus Formula Sheet:: Sin X Cos X17090 Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- CSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Differential CalculusDocument8 pagesCSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Differential CalculusCinderella WhiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 DifferenciationDocument37 pagesChapter 15 DifferenciationminhazNo ratings yet
- Exponential LogarithmicDocument54 pagesExponential LogarithmicShella M LuarNo ratings yet
- cc3 PG FullDocument97 pagescc3 PG Fullapi-262082485No ratings yet
- Polar CoordinatesDocument11 pagesPolar Coordinates918goodyNo ratings yet
- 1 AlgebraDocument48 pages1 AlgebraDiana Perez100% (1)
- Partial DifferentiationDocument11 pagesPartial DifferentiationwewillburythemtooNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IntegrationDocument4 pagesIntroduction To IntegrationwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Logic Gates and ExercisesDocument17 pagesLogic Gates and Exercises4gen_1No ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives Reduced PDFDocument2 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives Reduced PDFzeinamakNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean TheoremDocument34 pagesPythagorean Theoremales8806No ratings yet
- FormulaDocument7 pagesFormulaMàddìRèxxShìrshírNo ratings yet
- Problem of The WeekDocument13 pagesProblem of The WeekviterickNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC Quiz 3: The DerivativeDocument1 pageAP Calculus BC Quiz 3: The DerivativeteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas de DerivadasDocument3 pagesFórmulas de DerivadasNicolas OvalleNo ratings yet
- Integration FormulasDocument2 pagesIntegration FormulasJohn Gemre Taruc PanemNo ratings yet
- Formula. Basic CalculusDocument1 pageFormula. Basic Calculusjarenhndsm.placiegoNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Maths Nov 2018 Questio Papaer8874Document9 pagesGrade 5 Maths Nov 2018 Questio Papaer8874Shane KalakgosiNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Gen Maths Test 02 Answer SheetDocument3 pagesGR 12 Gen Maths Test 02 Answer SheetDokta UrameNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Kumon ReviewDocument13 pagesThe Ultimate Kumon ReviewRichie BallyearsNo ratings yet
- Alpha Mathematics Homework BookDocument5 pagesAlpha Mathematics Homework Bookcfdxd0qz100% (1)
- Delhi Public School Faridabad Viii Aryabhatta Hand Out-57: Topic: Mixed QuestionsDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School Faridabad Viii Aryabhatta Hand Out-57: Topic: Mixed Questionsrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Maths Books ListDocument4 pagesMaths Books ListKiransinh D RathodNo ratings yet
- Physics - Basic General Relativity (Benjamin McKay, U of Utah, 2001) PDFDocument24 pagesPhysics - Basic General Relativity (Benjamin McKay, U of Utah, 2001) PDFAmitanshu PandaNo ratings yet
- Online Portfolio Ashley Fitzpatrick ResumeDocument2 pagesOnline Portfolio Ashley Fitzpatrick Resumeapi-250147675No ratings yet
- U6l1t Similar TrianglesDocument3 pagesU6l1t Similar TrianglesShabina KhalidNo ratings yet
- Nama: Etik Eliza NIM: B1A020107 Kelas: C Biologi Praktikum Statistika DeskriptifDocument23 pagesNama: Etik Eliza NIM: B1A020107 Kelas: C Biologi Praktikum Statistika DeskriptifEtik ElizaNo ratings yet
- Hilbert Space For Random ProcessesDocument11 pagesHilbert Space For Random ProcessesSafa ÇelikNo ratings yet
- KPM - Soal Seleksi - JBMO 2020 PDFDocument5 pagesKPM - Soal Seleksi - JBMO 2020 PDFBIMBEL GG SAHABAT AFGHANNo ratings yet
- Ass 8 F 11 SolDocument8 pagesAss 8 F 11 SolOmonda NiiNo ratings yet
- A. Introduciton: MethodDocument19 pagesA. Introduciton: MethodStrag ChrisNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola: Special Rectangular Hyperbola and Properties of HyperbolaDocument15 pagesHyperbola: Special Rectangular Hyperbola and Properties of HyperbolaJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- XRD Data PointsDocument70 pagesXRD Data PointsKhoniz NingthoujaNo ratings yet
- Boosting Mathematics Achievement With Game-Based LearningDocument1 pageBoosting Mathematics Achievement With Game-Based LearningMika AndersonNo ratings yet
- Goertzel Algorithm For Complex InputDocument3 pagesGoertzel Algorithm For Complex InputCarlosNo ratings yet
- L4 MRASeightDocument11 pagesL4 MRASeightJens RydNo ratings yet
- sEMIDETAILED LESSON PLAN (Hubby)Document5 pagessEMIDETAILED LESSON PLAN (Hubby)Joem'z Burlasa-Amoto Esler-DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Study GuideDocument9 pagesAlgebra 1 Study Guideyousefbattah126No ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - 1Document10 pagesChapter 15 - 1feryawan 21No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 StudentDocument15 pagesChapter 4 Studentshalini arivalaganNo ratings yet
- Geometry Enrichment Packet - Answer Key PDFDocument30 pagesGeometry Enrichment Packet - Answer Key PDFlesNo ratings yet
- G10 Mathematics - 1st Periodic Test Oct 2022Document3 pagesG10 Mathematics - 1st Periodic Test Oct 2022Joy Marie Claire JumliNo ratings yet
- CAD Answers DimensionsDocument22 pagesCAD Answers DimensionsBreuk PeziNo ratings yet
- Math 5Document4 pagesMath 5Jake AbragarNo ratings yet
- LQG/LQR Controller Design: Undergraduate Lecture Notes OnDocument37 pagesLQG/LQR Controller Design: Undergraduate Lecture Notes OnJován MéridaNo ratings yet
- Maths Text (Form 1 & 2)Document162 pagesMaths Text (Form 1 & 2)Kareema MohammedNo ratings yet