Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anaerobes - Are Bacteria The Require Zero O2 Cooked Meat Medium)
Anaerobes - Are Bacteria The Require Zero O2 Cooked Meat Medium)
Uploaded by
Marianette Ginulos CainongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anaerobes - Are Bacteria The Require Zero O2 Cooked Meat Medium)
Anaerobes - Are Bacteria The Require Zero O2 Cooked Meat Medium)
Uploaded by
Marianette Ginulos CainongCopyright:
Available Formats
Anaerobes – are bacteria the require zero O2 -Culture – anaerobes are very fastidious as they
tension for their growth(they don’t need it at require to be in an Enriched Medium (ex.
all). The presence of O2 is either inhibitory or Cooked Meat Medium)
toxic to these organisms.
Sporeforming Anaerobes – Clostidrium Family
- The amount of anaerobic normal
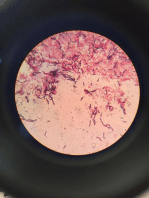
: C. tetani(tetanus) , C. perfringens(gas
bacteria outnumber the amount of
gangrene), C. defficile(pseudonmembranous
aerobic bacteria. Ex. Bacteroides
entereocolitis), C. botulinum(food poisoning)
anaerobes outnumber the facultative
anaerobic bacteria (E.coli) by a ratio of Clostridium tetani(tetanus bacilli)
1:1000
Characteristics:
- Two major divisions of anaerobes:
Sporeforming and Non-sporeforming - Gram (+) because they are
sporeforming bacilli, terminal spore
Generally, most of the anaerobes are
with a characteristic of drumstick or
destructive, these lesions may be produced by:
tennis racket appearance
- tissue necrosis – is the form of cell - Most possess peritrichous flagella
injury which results to the premature therefore motile
death of cells in the living tissue - Best method to destroy this bacteria is
- foul-smelling discharges and purulent autoclave
drainage - Normally found in soil, intestine of
- manifestation of gas in soft tissues ; lower animals and humans
resulting into crepitus ( cracking
Pathogenecity:
sounds)
- They release a powerful exotoxin and
Laboratory Diagnosis:
an neurotoxin known as tetanospasmin
Normally for diagnosis the specimen is taken which specifically targets the tissues of
directly from the site normally sterile the Central Nervous System, also
responsible for the signs and symptoms
Specimens that you cannot use: Voided urine,
of tetanus. Note: This bacteria does not
feces and sputum
invade the bloodstream
Recommended collection technique: Needle
Clinical infection: lockjaw or tetanus or trismus
aspiration
Mode of transmission:
Used for transportation: special transport or
collection tube(gassed-out tube) - Punctured wood contained with C.
tetani
Incubate: using gas pack jars
- Tetanus neonatorum- infected
Procedures for examination: umbilicus (for the newborn)
-Gram staining Incubation period:
- Short IP – 3-21 days
- Long IP – 4-5 weeks
Clinical manifestations: necrosis with the accumulation of fluid and
gas. This can occur in extremities, intestines
- Neuromuscular spasms – lockjaw
and uterus.
- Risus sardonicus (sardonic grin) –
clenching of jaw - Food poisoning:
- Hyperextension of neck and body – This is due to the production of
opisthotonus ; painful muscle spasms enterotoxins (entero meaning inside
often provoked by the slightest “enter”)
stimulation Caused by the ingestion of
contaminated meat
Immunity- non existent
Manifestations appear at 8-24 hours
Prevention and control: after the ingestion, symptoms occur as
abdominal pain and diarrhea that will
- Through the cleansing of wound;
last 12-18 hours.
debridement or removement of
necrotic areas Clostidrium difficile
- Active immunization:
: causes diarrhea or a more severe
Diptheria vaccine- per schedule
pesudomembrane enterocolitis associated with
Tetanus toxoid- immunization of
administration of certain antibiotics (including
pregnant mothers (IgG)
penicillin and ampicillin)
- Passive immunization
ATS; anti-tetanus serum ( horse serum) : this is normal flora to some individuals
Hyperimmune tetanus serum
:Enterotoxin A – promotes fluid secretion
Clostridium perfringens (Clostridial
: Cytotoxin B- damages mucosal membranes
mynecrosis)
Clostidrium Botolinum
Characteristics:
: produces the most potent(powerful) exotoxin
- Causes gas gangrenes
known, a neurotoxin which is responsible for
- Also causes food poisoning
the signs and symptoms of botulism which is a
- Central/subterminal spore (box-car or
fatal neuroparalytic disease.
matchbox shaped)
- Found in soil, intestines of humans and Botulism
animals
- Results from the ingestion of preformed
Clinical Infections: botulinum toxin in contaminated food(
caused by improperly canning or failure
- Wound and soft tissue infections:
to preserve food)
C. perfringens is responsible for 60-90% of - Heating of food destroys toxin
clostridial mynecrosis - Incubation Period is 18-36 hours
- Earliest manifestation:
It is brought by the release of exotoxin
: weakness,dizziness and severe dryness
called a-toxin which is cytotoxic -> then
of mouth
attacks the muscles -> resulting into
:paralysis of muscles of vision and
swallowing and respiration
(dysfunctional respiratory system =
death)
:Death occurs within 3-7 days
Non-sporeforming Anaerobes
- Consists mainly of Gram(+) and Gram (-)
on cocci and bacilli
Bacteroides fragilis
- The most important organism
- Gram (-)
- Important because of foul-smelling
abscesses and ulcers( found especially
in bedridden patients)
Treatment : Cleaning of wound or antibiotic
therapy
You might also like
- MCNDocument23 pagesMCNJASTINE NICOLE SABORNIDONo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases USMLE NotesDocument1 pageInfectious Diseases USMLE NotesDhanoush Mşđ33% (3)
- An Introduction To Applied Epidemiology and BiostatisticsDocument511 pagesAn Introduction To Applied Epidemiology and BiostatisticsMelissa Sindiong100% (7)
- Causative Agents of Anaerobe Infections. (NXPowerLite)Document70 pagesCausative Agents of Anaerobe Infections. (NXPowerLite)ashishanandaakNo ratings yet
- Lec4 Clostridium 2Document6 pagesLec4 Clostridium 2hindaoda90100% (1)
- Swine Infectious Gastrointestinal DiseasesDocument6 pagesSwine Infectious Gastrointestinal DiseasesnessimmounirNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1. Gram Positive Rods - ClostridiaDocument58 pages3.2.1. Gram Positive Rods - Clostridiaahmed mohammed100% (1)
- Micro Chapter 17Document8 pagesMicro Chapter 17Ana AbuladzeNo ratings yet
- 5B - Spore Forming Gram Positive Bacteria - CLOSTRIDIUMDocument5 pages5B - Spore Forming Gram Positive Bacteria - CLOSTRIDIUMRaunaq Singh RatraNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology (Heba)Document176 pagesBacteriology (Heba)irs531997No ratings yet
- Disaster Caused BY Biological AgentsDocument25 pagesDisaster Caused BY Biological AgentsKaren Mae Dacoco MamuyacNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Nervous SystemAnaNo ratings yet
- Micro by DR - Hesham (GIT)Document65 pagesMicro by DR - Hesham (GIT)abcde990075No ratings yet
- Lec. 8 Bacillus Clostridium1193786926542Document18 pagesLec. 8 Bacillus Clostridium1193786926542تجربة أولىNo ratings yet
- Clostridium TetaniDocument4 pagesClostridium Tetanitummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Perinatal Infection - Infeksi NeonatusDocument51 pagesPerinatal Infection - Infeksi NeonatusRiska PriyaniNo ratings yet
- Brucellosis: The Short Textbook of PediatricsDocument3 pagesBrucellosis: The Short Textbook of PediatricsHosny M IsseNo ratings yet
- Clostrdia: G Positive Spore Forming Anaerobic Toxin Producing RodsDocument36 pagesClostrdia: G Positive Spore Forming Anaerobic Toxin Producing Rodsjamal nasirNo ratings yet
- (Powerpoint) CHAPTER 16 AND 22 - BACILLUS, CLOSTRIDIUM, ANAEROBIC BACTERIOLOGYDocument59 pages(Powerpoint) CHAPTER 16 AND 22 - BACILLUS, CLOSTRIDIUM, ANAEROBIC BACTERIOLOGYNel TinduganiNo ratings yet
- UII Gram Pos Spore-FormfefefeDocument30 pagesUII Gram Pos Spore-FormfefefeDito TrunogatiNo ratings yet
- 13anaerobic BacteriaDocument25 pages13anaerobic BacteriaClarence SantosNo ratings yet
- Microbiology of Clostridium Tetani and Wound ClassificationDocument3 pagesMicrobiology of Clostridium Tetani and Wound ClassificationAZIZAH ARDINALNo ratings yet
- Tetanus and BotulismDocument40 pagesTetanus and BotulismPatriceNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument2 pagesTetanusmai_serpicNo ratings yet
- Group 2 TetanusDocument43 pagesGroup 2 TetanusDaymon, Ma. TeresaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive BacilliDocument7 pagesGram Positive Bacillieros18No ratings yet
- Tetanu S: By: Reno WaisyahDocument18 pagesTetanu S: By: Reno WaisyahReno WaisyahNo ratings yet
- K6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICDocument23 pagesK6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICbanuperiahNo ratings yet
- Bordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andDocument38 pagesBordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andkrstnkyslNo ratings yet
- BacillusDocument25 pagesBacillusyousfinadjah5No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document20 pagesUnit 3jjumlaboratoryNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Mrs.G.Manibharathi, MSC (N), Associate ProfessorDocument26 pagesTetanus: Mrs.G.Manibharathi, MSC (N), Associate ProfessormanibharathiNo ratings yet
- Strangles: Distemper, Infectious Adenitis Strept ThroatDocument21 pagesStrangles: Distemper, Infectious Adenitis Strept ThroatMuhammad Hamza AlviNo ratings yet
- Clostridia Lec 6Document1 pageClostridia Lec 6markmuiruri581No ratings yet
- Bacteriology by Dhshan Hassan DhshanDocument48 pagesBacteriology by Dhshan Hassan Dhshanعلي الكوافي100% (1)
- Streptococcus Pyogens Handout G2Document3 pagesStreptococcus Pyogens Handout G2Raiden EiNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Anthracis PowerpointDocument32 pagesBacillus Anthracis PowerpointEnerose MagnoNo ratings yet
- Tetanus ADocument3 pagesTetanus ASadaqat KhanNo ratings yet
- Tetanus (Harrison's Principle of Internal Medicine)Document4 pagesTetanus (Harrison's Principle of Internal Medicine)Renz Mervin Rivera100% (1)
- Lovely Professional University: Term Paper of Advanced MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesLovely Professional University: Term Paper of Advanced Microbiology27AlokKumarNo ratings yet
- ClostridiumDocument20 pagesClostridiumNuura jeylani KasimNo ratings yet
- Clostridium Tetani: Tejpratap S.P. Tiwari, MD Pedro L. Moro, MD, MPH and Anna M. Acosta, MDDocument14 pagesClostridium Tetani: Tejpratap S.P. Tiwari, MD Pedro L. Moro, MD, MPH and Anna M. Acosta, MDClaudia FreyonaNo ratings yet
- 5A - Spore Forming Gram Positive Bacteria - BACILLUSDocument2 pages5A - Spore Forming Gram Positive Bacteria - BACILLUSRaunaq Singh RatraNo ratings yet
- Dm-Lecture 4-11-23Document28 pagesDm-Lecture 4-11-23s.zainabtanweerNo ratings yet
- Dairy Cattle DiseasesDocument14 pagesDairy Cattle DiseasesLaddi SandhuNo ratings yet
- Kepaniteraan Klinik RSD Mardi Waluyo Blitar - FK Unisma: Pembimbing: Dr. Utchu Tedja Mulya SP.BDocument35 pagesKepaniteraan Klinik RSD Mardi Waluyo Blitar - FK Unisma: Pembimbing: Dr. Utchu Tedja Mulya SP.BDada DoniNo ratings yet
- 10 Bacillus & ClostridiumDocument11 pages10 Bacillus & ClostridiumASECO LISHNo ratings yet
- ECHINOCOCCUSDocument5 pagesECHINOCOCCUSGhina RizwanNo ratings yet
- Enterotoxemia, Anaerobic Dysentery, Bradsot, Botulism and NecrobacteriosisDocument17 pagesEnterotoxemia, Anaerobic Dysentery, Bradsot, Botulism and NecrobacteriosisNajafova SuadaNo ratings yet
- تَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٣?Document10 pagesتَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٣?سلطان محمد فوزي سلمانNo ratings yet
- Meningitis, Tetanus, LeprosyDocument39 pagesMeningitis, Tetanus, LeprosyKhemz Dalde LimNo ratings yet
- Final BactroDocument6 pagesFinal Bactronida akramNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Genesis of Bacterial InfectionsDocument4 pagesPa Tho Genesis of Bacterial InfectionssgelidoNo ratings yet
- Soil Transmitted HelminthiasesDocument6 pagesSoil Transmitted HelminthiasesJemimah MejiaNo ratings yet
- Comm DiseasesDocument5 pagesComm DiseasesZaireXandraReyesNo ratings yet
- Clostridium TetaniDocument15 pagesClostridium TetaniAishwarya Prabhakaran100% (1)
- (MIKROBIOLOGI) IT 15 - Basil Gram Positif - YONDocument47 pages(MIKROBIOLOGI) IT 15 - Basil Gram Positif - YONAnonymous rzPX6lUNo ratings yet
- 1 Bacterial DeseaseDocument108 pages1 Bacterial DeseasechachaNo ratings yet
- ClostridumDocument30 pagesClostridumFrancesca VargasNo ratings yet
- K6 - ParasitologiDocument56 pagesK6 - Parasitologisilakan_isiNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic BacteriaDocument65 pagesAnaerobic BacteriaJames TorresNo ratings yet
- Medical History Physical FormDocument2 pagesMedical History Physical Formapi-69208402No ratings yet
- Ultimate Ceramic Veneers A Laboratory-Guided Ultraconservative PreparationDocument15 pagesUltimate Ceramic Veneers A Laboratory-Guided Ultraconservative PreparationEvelina HaddadienNo ratings yet
- ScrapbookDocument12 pagesScrapbookKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- Draft CPG Diabetes in PregnancyDocument55 pagesDraft CPG Diabetes in PregnancyAyuni Salleh100% (2)
- DATA - ChemistsDocument7 pagesDATA - Chemistsgrissalkwilson90No ratings yet
- Improving Bedside Shift-To-shift Nursing Report ProcessDocument34 pagesImproving Bedside Shift-To-shift Nursing Report ProcessJaypee Fabros Edra100% (2)
- Morbidity and Mortality Weekly ReportDocument32 pagesMorbidity and Mortality Weekly Reporthimanshu7188No ratings yet
- Divya ResumeDocument3 pagesDivya Resumeapi-516676990No ratings yet
- EBook Krause and Mahans Food and The Nutrition Care Process E Book Krauses Food Nutrition Therapy PDF Docx Kindle Full ChapterDocument62 pagesEBook Krause and Mahans Food and The Nutrition Care Process E Book Krauses Food Nutrition Therapy PDF Docx Kindle Full Chapterdanielle.greene745100% (32)
- Powerful Answer Key of Board QuestionsDocument59 pagesPowerful Answer Key of Board QuestionsKaren khaye AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guideline: Enteral Feeding - Iron Supplementation: Neonatal Clinical Oversight GroupDocument12 pagesClinical Guideline: Enteral Feeding - Iron Supplementation: Neonatal Clinical Oversight GroupStphn WllngtnNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cervical Cancer InterviewDocument4 pagesCase Study Cervical Cancer InterviewLYNDON MENDIOLANo ratings yet
- MPhil Thesis Defence - Schedule of Presentation - October 2021Document1 pageMPhil Thesis Defence - Schedule of Presentation - October 2021Saheed AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Newborn Umbilical Cord Care - An Evidence Based Quality ImprovemenDocument45 pagesNewborn Umbilical Cord Care - An Evidence Based Quality ImprovemenNuridha FauziyahNo ratings yet
- Arieu, A. - Defines A Leader As "A Person Capable of Inspiring and Associate Others With ADocument7 pagesArieu, A. - Defines A Leader As "A Person Capable of Inspiring and Associate Others With ALorraine JuanNo ratings yet
- VIVA - TarrifDocument1 pageVIVA - TarrifSrinivas VadtheNo ratings yet
- Biotecnology McqsDocument5 pagesBiotecnology McqsSaba RiazNo ratings yet
- Monthly Records - NewDocument4 pagesMonthly Records - NewGrace NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Feig 2017Document13 pagesFeig 2017Lembaga Pendidikan dan PelayananNo ratings yet
- Assisted Delivery In: University of Iloilo Rizal Street, Iloilo City Tel No. (033) 338-1071 Loc. 146Document3 pagesAssisted Delivery In: University of Iloilo Rizal Street, Iloilo City Tel No. (033) 338-1071 Loc. 146Khyara Marie Estante DemiarNo ratings yet
- Cleaning+Standards+2021 v1.0+ (Revised+final)Document48 pagesCleaning+Standards+2021 v1.0+ (Revised+final)ابراهيم الحربيNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Temperature Using An Overhead Radiant WarmerDocument1 pageMonitoring Temperature Using An Overhead Radiant WarmerydtrgnNo ratings yet
- FUNDA - Health & IllnessDocument3 pagesFUNDA - Health & IllnessRICVANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlanJess Fernandez BorgaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Ethics and Qawaid FiqhiyyahDocument12 pagesBiomedical Ethics and Qawaid FiqhiyyahSurgeon AsimNo ratings yet
- Invention Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document9 pagesInvention Electrocardiogram (ECG)Xyz XyzNo ratings yet
- CHN1 Course Outline 20 - 21Document14 pagesCHN1 Course Outline 20 - 21Edna Uneta RoblesNo ratings yet
- Legal Considerations of Maternal and Child PracticeDocument22 pagesLegal Considerations of Maternal and Child PracticeChari RivoNo ratings yet