Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elastic and Inelastic Collision: Sample Problems
Elastic and Inelastic Collision: Sample Problems
Uploaded by
Anonymous LYUwYGOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elastic and Inelastic Collision: Sample Problems
Elastic and Inelastic Collision: Sample Problems
Uploaded by
Anonymous LYUwYGCopyright:
Available Formats
Elastic and Inelastic Collision
In an elastic collision, the total kinetic energy is conserved i.e. the total kinetic energy of
all the objects of the system after the collision is the same as their kinetic energy before
the collision:
total K after = total K before
𝐾𝑓 = 𝐾𝑏
In an inelastic collision, the total kinetic energy is not conserved. For example, one or
more of the colliding objects may not spring back to its original shape for heat may be
generated.
total K after < total K before
𝐾𝑓 < 𝐾𝑏
For a completely inelastic collision of two objects in which the objects stick together and
have the same velocity after colliding,
𝑚1 𝑣𝑜 = (𝑚1 + 𝑚2 )𝑣
and
𝑚1
𝑣=( )𝑣
𝑚1 + 𝑚2 𝑜
and
𝐾𝑓 𝑚1
=
𝐾𝑖 𝑚1 + 𝑚2
Sample Problems:
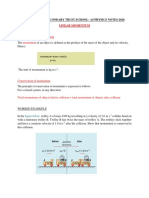
1. A 1.0 kg. ball with a speed of 4.5 m/s strikes a 2.0 kg stationary ball. If the collision
is completely inelastic (a) what are the speeds of the balls after the collision? (b)
What percent of the initial kinetic energy do they have after the collision?
You might also like
- Week-7 1Document41 pagesWeek-7 1christinereponte160No ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions For ch9Document17 pagesProblems and Solutions For ch9yusufyemez1907No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument44 pagesPhysicsAlfred QuintoNo ratings yet
- CollisionDocument15 pagesCollisionFelipe Jr. AdolfoNo ratings yet
- WPE - 8 Mark Questions IPEDocument12 pagesWPE - 8 Mark Questions IPEradhakrishnabuggarapu97No ratings yet
- Momentum, Impulse, and CollisionsDocument2 pagesMomentum, Impulse, and CollisionsDEEPAK TNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 CollisionsDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 9 Collisionsملهم العبدالسلامةNo ratings yet
- CollisionDocument3 pagesCollisionbernardNo ratings yet
- COLLISIONSDocument16 pagesCOLLISIONSfiqih saadahNo ratings yet
- Physics - 61 - Week - 6 - Exercises and Solved Problems PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics - 61 - Week - 6 - Exercises and Solved Problems PDFSebastian SmytheNo ratings yet
- COLLISIONS pptx-2022Document28 pagesCOLLISIONS pptx-2022Nicole Margaret OngNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of MomentumDocument32 pagesLaw of Conservation of MomentumZaira JallorinaNo ratings yet
- Collisions WorksheetDocument3 pagesCollisions WorksheetjessicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Physics For Engineers 1Document77 pagesLesson 7 - Physics For Engineers 1Norman AcainNo ratings yet
- 4515 l3 311 Handout5Document2 pages4515 l3 311 Handout5Steph HunterNo ratings yet
- Momentum LabatoryDocument0 pagesMomentum LabatoryDaniel LiuNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument2 pagesLinear Momentum and CollisionsAlex HuynhNo ratings yet
- Title: Statement of Objectives:: Application: Billiard BallDocument4 pagesTitle: Statement of Objectives:: Application: Billiard BallJia XinNo ratings yet
- KCM Nchaga Secondary Trust School-As Physics Notes-2020: Definition of Linear Momentum MomentumDocument7 pagesKCM Nchaga Secondary Trust School-As Physics Notes-2020: Definition of Linear Momentum MomentumCartwright Ntahandi Nduwa ChipoyaNo ratings yet
- Momentum Conservation PrincipleDocument14 pagesMomentum Conservation PrincipleLaurence Plurad ArizabalNo ratings yet
- (1.6) MomentumDocument3 pages(1.6) MomentumShaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Elastic CollisionDocument10 pagesPresentation - Elastic CollisionPaul Jacob InfanteNo ratings yet
- g484 Module 1 4 1 2 CollisionsDocument8 pagesg484 Module 1 4 1 2 Collisionsapi-236179294No ratings yet
- Units - 1,2,3 Key - 104348Document36 pagesUnits - 1,2,3 Key - 104348KL PHYSICSNo ratings yet
- Class - XI - ch-6, Work Energy Power, Module 5Document14 pagesClass - XI - ch-6, Work Energy Power, Module 5Sayan MajiNo ratings yet
- Day 6 - Newtonian Mechanics PDFDocument31 pagesDay 6 - Newtonian Mechanics PDFJazzverNo ratings yet
- Experiment M3 Collision in One DimensionDocument3 pagesExperiment M3 Collision in One DimensionNqobile KhanyezaNo ratings yet
- Momentum & ImpulseDocument7 pagesMomentum & Impulse333po2024No ratings yet
- MOMENTUMDocument21 pagesMOMENTUMClare Andrea Egalla100% (1)
- Linear Momentum, Impulse, CollisionDocument19 pagesLinear Momentum, Impulse, CollisionrezaewewqewqeNo ratings yet
- Momentum Conservation PrincipleDocument6 pagesMomentum Conservation PrincipleRoda Gayle RañadaNo ratings yet
- Week6 2Document24 pagesWeek6 2KrishnaJaiswalNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesClass 11 - Newton's Laws of MotionDaimani ForresterNo ratings yet
- Momentum Quiz Review Key PDFDocument2 pagesMomentum Quiz Review Key PDFUzi TempoNo ratings yet
- Physics - 2 Momentum, Impulse, and CollisionDocument14 pagesPhysics - 2 Momentum, Impulse, and CollisionMuhammad Grandiv SynNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 - Energy - and - MomentumDocument1 pageWorksheet 6 - Energy - and - MomentumJNZSeriesNo ratings yet
- CollisionsDocument4 pagesCollisionsmadhavi dudaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Impulse and Momentum 1Document10 pagesLecture 6 - Impulse and Momentum 1SujithHarirajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4&5 Review and Chapter 7 IntroductionDocument22 pagesChapter 4&5 Review and Chapter 7 IntroductionJunyi JiNo ratings yet
- General Physics Week 8Document10 pagesGeneral Physics Week 8johnNo ratings yet
- Pyreading Material 8.1 W14 Impulse Momentum and CollisionDocument34 pagesPyreading Material 8.1 W14 Impulse Momentum and CollisionJon Christian L. BobisNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum PPP 1213361160074257 8Document74 pagesConservation of Momentum PPP 1213361160074257 8Mohd Sabri NorNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 1 ResearchDocument8 pagesPhysics Unit 1 ResearchAhmed Mohamed EwisNo ratings yet
- Ch9-Linear Momentum and CollisionDocument28 pagesCh9-Linear Momentum and CollisionLAVA HASSANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document23 pagesChapter 3May FadlNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint - PHY01 - CO4 - Center of Mass Impulse Momentum and CollissionsDocument20 pagesPowerpoint - PHY01 - CO4 - Center of Mass Impulse Momentum and CollissionsAngelika ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Linear MomentumDocument6 pagesLinear Momentummikel artetaNo ratings yet
- Linear MomentumDocument8 pagesLinear Momentummikel artetaNo ratings yet
- 6 CHAPTER 5 The Newtons Laws of MotionDocument29 pages6 CHAPTER 5 The Newtons Laws of Motionملهم العبدالسلامةNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5&6Document24 pagesChapter 5&6Junyi JiNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Mechanics: CollisionsDocument32 pagesModule 4-Mechanics: CollisionsHead LightNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Week 3Document3 pagesWorksheet Week 3Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Collisions 2023Document9 pagesCollisions 2023mrcornis18No ratings yet
- ENGGPHYS Codes: 2671, 2857, 3002, and 3592 Engr. B.R. P. MallareDocument5 pagesENGGPHYS Codes: 2671, 2857, 3002, and 3592 Engr. B.R. P. MallareUploader101No ratings yet
- Momentum Comp LabDocument4 pagesMomentum Comp LabAxel GayondatoNo ratings yet
- Further MechanicsDocument11 pagesFurther MechanicsBecky TenneyNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem FinalDocument12 pagesPractice Problem FinalAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Web Page DesignDocument1 pageRubrics For Web Page DesignAnonymous LYUwYGNo ratings yet
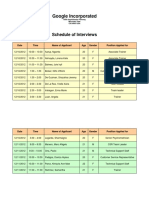
- Google Incorporated: Schedule of InterviewsDocument2 pagesGoogle Incorporated: Schedule of InterviewsAnonymous LYUwYGNo ratings yet
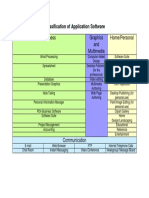
- Business Graphics and Multimedia Home/Personal: Classification of Application SoftwareDocument1 pageBusiness Graphics and Multimedia Home/Personal: Classification of Application SoftwareAnonymous LYUwYGNo ratings yet
- Healthy TipsDocument2 pagesHealthy TipsAnonymous LYUwYGNo ratings yet
- CSDS Lecture Week 7Document6 pagesCSDS Lecture Week 7Anonymous LYUwYGNo ratings yet
- Information Technology PerspectivesDocument64 pagesInformation Technology PerspectivesAnonymous LYUwYGNo ratings yet