Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 21 - Application of SD (Student)
Unit 21 - Application of SD (Student)
Uploaded by
lllCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- RSL 11+ Comprehension SampleDocument25 pagesRSL 11+ Comprehension Samplenabhan07100% (2)
- The Great Ideas ProgramDocument10 pagesThe Great Ideas ProgramAlysson Nunes SantosNo ratings yet
- DSE 25.2 Applications of DispersionDocument15 pagesDSE 25.2 Applications of DispersionRaphael ChengNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mathematics-ACTIVITY SHEETSDocument144 pagesGrade 8 Mathematics-ACTIVITY SHEETSFlorence Tangkihay77% (13)
- Part VI Module in Problem Solving and Reasoning in Mathematics PDFDocument7 pagesPart VI Module in Problem Solving and Reasoning in Mathematics PDFAngel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual to accompany Introduction to Linear Regression AnalysisFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Introduction to Linear Regression AnalysisRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Course IntroDocument5 pagesCourse IntroMalith De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document90 pagesChapter 4Kaleb MulatuNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesDocument11 pagesSaint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesJimkenneth RanesNo ratings yet
- LP For P&S Normal DistributionDocument6 pagesLP For P&S Normal DistributionRam AndresNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2 - The Normal CurveDocument31 pagesModule 1.2 - The Normal CurveJohn Mark MatibagNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques PDFDocument36 pagesQuantitative Techniques PDFGitsirasNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution LESSON 2Document65 pagesNormal Distribution LESSON 2Chuck DaleNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Variation and Areas Under Normal CurveDocument5 pagesCoefficient of Variation and Areas Under Normal CurvemochiNo ratings yet
- 14 Normal DistributionDocument37 pages14 Normal DistributionJomar Porteros100% (2)
- 84 Percentiles Teacher PDFDocument7 pages84 Percentiles Teacher PDFsidmur321No ratings yet
- Ebook Elementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 7Th Edition Bluman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesEbook Elementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 7Th Edition Bluman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFTraciLewispwng100% (12)
- Answer Sheet in Practical Research 2: Quarter 2-Module 7Document55 pagesAnswer Sheet in Practical Research 2: Quarter 2-Module 7Kenneth Aquino100% (2)
- Instructions: GEN1008 / MED1018 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17Document17 pagesInstructions: GEN1008 / MED1018 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17liNo ratings yet
- NormalWS1 PDFDocument4 pagesNormalWS1 PDFRizza Jane BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Normal DistributionDocument47 pagesLesson 2: Normal DistributionMARITESS COLLADONo ratings yet
- STAT Midterm (Solution)Document14 pagesSTAT Midterm (Solution)L HYNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Calculus 11th Edition by Larson and Edwards ISBN 9781337275347Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Calculus 11th Edition by Larson and Edwards ISBN 9781337275347alyssafloresfnexiwptms100% (34)
- Solution Manual For Calculus 11Th Edition by Larson and Edwards Isbn 9781337275347 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Calculus 11Th Edition by Larson and Edwards Isbn 9781337275347 Full Chapter PDFbenjamin.smith112100% (18)
- Statistics and Probability - Solved Assignments - Semester Spring 2010Document33 pagesStatistics and Probability - Solved Assignments - Semester Spring 2010Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- QTM Cycle 7 Session 4Document79 pagesQTM Cycle 7 Session 4OttilieNo ratings yet
- Math11 SP Q3 M4 PDFDocument16 pagesMath11 SP Q3 M4 PDFJessa Banawan EdulanNo ratings yet
- CH7 - Continuous Probability DistributionDocument50 pagesCH7 - Continuous Probability Distributionlaelafitrya0% (1)
- 2015 OL Maths Past Paper and Answers English Medium PDFDocument60 pages2015 OL Maths Past Paper and Answers English Medium PDFHashan SampathNo ratings yet
- Instructions: GEN1008 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17Document17 pagesInstructions: GEN1008 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17liNo ratings yet
- 1.1 TG For Normal DistributionDocument5 pages1.1 TG For Normal DistributionVincere André AlbayNo ratings yet
- SIMPLEtestofhypothesisDocument35 pagesSIMPLEtestofhypothesisJulius EstrelladoNo ratings yet
- Aga A2 1104 PpsDocument2 pagesAga A2 1104 Pps조윤호No ratings yet
- Estimation of Parameters FinalDocument23 pagesEstimation of Parameters FinalMay Ann MonteroNo ratings yet
- Inferential StatisticsDocument111 pagesInferential StatisticsCameronNo ratings yet
- Independent University, BangladeshDocument20 pagesIndependent University, BangladeshMD. Akif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 Topics: Sampling Distributions and Central Limit TheoremDocument4 pagesProblem Set 2 Topics: Sampling Distributions and Central Limit TheoremSravya Tummala100% (1)
- Instructions: GEN1008 / MED1018 / GED1008 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17Document17 pagesInstructions: GEN1008 / MED1018 / GED1008 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17liNo ratings yet
- SIMPLEtestofhypothesisDocument35 pagesSIMPLEtestofhypothesisJulius EstrelladoNo ratings yet
- ECS7020P Sample Paper SolutionsDocument6 pagesECS7020P Sample Paper SolutionsYen-Kai ChengNo ratings yet
- Worskheet Finals 1Document3 pagesWorskheet Finals 1JENNIFER BALMESNo ratings yet
- Probab Stat Math 311Document26 pagesProbab Stat Math 311Yasuhiro Hinggo EscobilloNo ratings yet
- MATH03-CO4-Lesson2-Sampling Distribution (Proportion and Difference of Two Averages)Document16 pagesMATH03-CO4-Lesson2-Sampling Distribution (Proportion and Difference of Two Averages)Edward SnowdenNo ratings yet
- Practice FinalDocument16 pagesPractice FinalJessica ZhaiNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering and Computer Science Department of Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDocument11 pagesSchool of Engineering and Computer Science Department of Electrical & Electronic EngineeringMD. Akif RahmanNo ratings yet
- 07 - Workbook Part 2 - Business StatisticsDocument158 pages07 - Workbook Part 2 - Business StatisticsvNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variability Lec 7: DR - Nesrin H. Darwesh University of Duhok-College of DentistryDocument48 pagesMeasures of Variability Lec 7: DR - Nesrin H. Darwesh University of Duhok-College of DentistryNivar selevanayNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Practice Problems SOLUTIONSDocument7 pagesModule 7 Practice Problems SOLUTIONSJeff CagleNo ratings yet
- Newbold Sbe8 Tif ch05 PDFDocument58 pagesNewbold Sbe8 Tif ch05 PDFak100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 1ADocument7 pagesMathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 1AEdward Lorenz TabligaNo ratings yet
- GE 4 MMW Reviewer AutosavedDocument12 pagesGE 4 MMW Reviewer AutosavedKyle SarcosNo ratings yet
- Quant 9 - Normal DistDocument19 pagesQuant 9 - Normal DistHieu PhanNo ratings yet
- Practice Set3Document11 pagesPractice Set3JAINAM JAINNo ratings yet
- (FILLED) MCD2080-ETC1000-ETF1100 Exam S1 2018Document10 pages(FILLED) MCD2080-ETC1000-ETF1100 Exam S1 2018michella vegaNo ratings yet
- Stat A01Document6 pagesStat A01Sunny LeNo ratings yet
- Final - Econ3005 - 2022spring - Combined 2Document11 pagesFinal - Econ3005 - 2022spring - Combined 2Swae LeeNo ratings yet
- 24-01-31 Marked SlidesDocument29 pages24-01-31 Marked Slideselyan.dummyaccNo ratings yet
- Questions ch6 PDFDocument5 pagesQuestions ch6 PDFHossam AboomarNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Yong Hwa M. Jeong Grade 11 STEM-B Quarter 4 - Module 1: Test of HypothesisDocument22 pagesStatistics and Probability Yong Hwa M. Jeong Grade 11 STEM-B Quarter 4 - Module 1: Test of HypothesisSarahmae MeñozaNo ratings yet
- Normaldistribution 160627092159 PDFDocument24 pagesNormaldistribution 160627092159 PDFGladzangel LoricabvNo ratings yet
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionlllNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionlllNo ratings yet
- Percubaan Term 1 (2019) JPN KelantanDocument3 pagesPercubaan Term 1 (2019) JPN KelantanlllNo ratings yet
- Section A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxDocument8 pagesSection A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxlllNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006Document18 pagesDokumen - Tips Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006lllNo ratings yet
- Instructions To Candidates:: SECTION A (45 Marks) Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument2 pagesInstructions To Candidates:: SECTION A (45 Marks) Answer All Questions in This Sectionlll0% (1)
- My Hero Project PDFDocument4 pagesMy Hero Project PDFCARLOS NORIEL CABANANo ratings yet
- From Where School You Are From: From University of Makati, Makati Metro Manila Diin Ka Nag Work?Document2 pagesFrom Where School You Are From: From University of Makati, Makati Metro Manila Diin Ka Nag Work?Renzy Myer D. BulahanNo ratings yet
- Math PDFDocument95 pagesMath PDFAnonymous kI39sJC1MNo ratings yet
- Reservation in India - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesReservation in India - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediasreddy_383299No ratings yet
- Clothes Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesClothes Lesson Planapi-314934184No ratings yet
- ABDC Journals List by RatingDocument35 pagesABDC Journals List by RatingstaimoukNo ratings yet
- Yoga Obstacle CourseDocument3 pagesYoga Obstacle Courseapi-313621606No ratings yet
- Catch-Up Friday Action PlanDocument2 pagesCatch-Up Friday Action PlanJim Bryan Wabina Vergara91% (32)
- Institute Name: Aliah University, Kolkata (IR-O-U-0567)Document12 pagesInstitute Name: Aliah University, Kolkata (IR-O-U-0567)saifuddin skNo ratings yet
- Here Is How A Topper Gets 94 Marks in Urdu With Pictures - Top Study WorldDocument10 pagesHere Is How A Topper Gets 94 Marks in Urdu With Pictures - Top Study WorldJulie MerrillNo ratings yet
- Promotin Seniority List For SGT To School Asst in Aug 2011 of All Subjects DT 28.7.11Document82 pagesPromotin Seniority List For SGT To School Asst in Aug 2011 of All Subjects DT 28.7.11Satha SathavishnuNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3-4: English For Academic and Professional Purposes (EAPP)Document4 pagesWEEK 3-4: English For Academic and Professional Purposes (EAPP)Sherri BonquinNo ratings yet
- Module 12 1creating Postive School CultureDocument29 pagesModule 12 1creating Postive School CultureArben EchagueNo ratings yet
- Place Score ReportDocument2 pagesPlace Score Reportapi-280625817No ratings yet
- Sop 27Document1 pageSop 27Atharvä Ravindra HatekařNo ratings yet
- Bar Council of Delhi: Declaration Form To Be Submitted by The Advocates Enrolled After July, 2010Document1 pageBar Council of Delhi: Declaration Form To Be Submitted by The Advocates Enrolled After July, 2010abhikaamNo ratings yet
- English 302 - Final MemoDocument2 pagesEnglish 302 - Final Memoapi-349459678No ratings yet
- Revised Bioethics SyllabusDocument7 pagesRevised Bioethics SyllabuslouradelNo ratings yet
- World Journal On Educational Technology: Current IssuesDocument12 pagesWorld Journal On Educational Technology: Current IssuesBelay HaileNo ratings yet
- 1 DLP Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseDocument7 pages1 DLP Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseJonalene Dulay100% (5)
- The Morning Calm Korea Weekly - Mar. 21, 2008Document24 pagesThe Morning Calm Korea Weekly - Mar. 21, 2008Morning Calm Weekly NewspaperNo ratings yet
- AL 2 PrelimDocument4 pagesAL 2 PrelimJohn Michael Porras HambreNo ratings yet
- Brochure BE 2010 11Document126 pagesBrochure BE 2010 11georgianchailNo ratings yet
- FS 1 PORTFOLIO Episode 1 ENCINA, JULIE JEAN BEED 4B-DAYDocument8 pagesFS 1 PORTFOLIO Episode 1 ENCINA, JULIE JEAN BEED 4B-DAYJulie Jean Restauro EncinaNo ratings yet
- Theories of PersonalityDocument16 pagesTheories of PersonalityLeeYan SaliliNo ratings yet
- Singing ChildrenDocument4 pagesSinging Childrenapi-300652571No ratings yet
- REFLECTION - Q2 - Week 5Document2 pagesREFLECTION - Q2 - Week 5EDITHA PAGUYONo ratings yet
Unit 21 - Application of SD (Student)
Unit 21 - Application of SD (Student)
Uploaded by
lllOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 21 - Application of SD (Student)
Unit 21 - Application of SD (Student)
Uploaded by
lllCopyright:
Available Formats
CMV6120 Mathematics
Unit 21 : Applications of standard deviation
Learning Objectives
The Students should be able to:
Calculate standard score from a given set of data.
Determine, in the case of normal distribution, the percentages of data lying within a certain
number of standard deviations from the mean.
Activities
Teacher demonstration and student hand-on exercise.
Web Reference:
http://www.mste.uiuc.edu/hill/dstate/dstate.html
http://frey.newcastle.edu.au/Stat/stat101.html
Reference
Suen, S.N. “Mathematics for Hong Kong 5A”; rev. ed.; Chapter 5; Canotta
Unit 21: Applications of standard deviation Page 1 of 8
CMV6120 Mathematics
Applications of standard deviation
1. Standard score
Standard scores are used to compare students’ performances in different tests.
For a distribution of marks with mean x and standard deviation ,
The standard score z is
z xx
Example 1
In the final examination, John obtained 70 in Mathematics and 60 in Vocational English.
His results are compared with those for the whole class.
Subject class average class s.d. John’s mark
Mathematics 75 5 70
English 56 2 60
a) Find John’s standard scores in Mathematics and Vocational English.
b) State, for each subject, whether his performance is above or below average.
Solution
a) standard score in Mathematics = (70 – 75) 5 =
standard score in Vocational English =
b) John is below average in Mathematics. (70<75)
John is above average in Vocational English. (60>56)
Although John’s raw mark in Mathematics is higher than that in English (70>60),
he is better in English than Mathematics when compared to other students.
This is reflected by the standard scores (2 > 1).
Remark:
1. Negative standard score means below average.
2. Zero standard score means at the average.
3. Positive standard score means above average.
Unit 21: Applications of standard deviation Page 2 of 8
CMV6120 Mathematics
Example 2
The statistical data of an examination are tabulated below. A student obtained 43 marks and 48
marks in Information Technology Application and Chinese respectively. Calculate the standard
scores that the student obtained in the examination.
Subject mean Standard deviation
Information Technology Application 51.5 13.1
Chinese 63.3 14.5
Solution
Standard score Z = (x – x ) /
Information Technology Application: Z =
Chinese: Z=
Example 3
A student obtained 65 marks in Engineering Science. The mark was equal to a standard score of 3.2.
Calculate the standard deviation of the marks if the mean mark was 45.
Solution
Standard deviation =
Example 4
The mean mark and the standard deviation of the marks in an examination are 58.9 and 19.4
respectively. The standard score of a student is 1.5. What is the actual mark that the student
obtained? .
Solution
Unit 21: Applications of standard deviation Page 3 of 8
CMV6120 Mathematics
2. Percentages of Normal data lying within a certain number of standard
deviations from the mean
A distribution curve for a set of data is basically a frequency or relative frequency curve of the data.
It is found that the distribution curves for a lot of commonly occurring data sets follow a certain
pattern that came to be known as normal distributions.
A normal distribution has a bell-shaped curve as shown.
y 50% 50%
99.7%
95%
68%
34% 34%
13.5% 13.5% 2.35%
2.35%
x
m3 m2 m m m+ m+2 m+3
A normal curve has the following characteristics:
1. It is symmetrical about the mean.
2. Mean = mode = median. They all lie at the centre of the curve.
3. There are fewer data for values further away from the mean.
a) about 68% of the data lie within 1 standard deviation from the mean.
b) about 95% of the data lie within 2 standard deviations from the mean.
c) about 99.7% of the data lie within 3 standard deviations from the mean.
Unit 21: Applications of standard deviation Page 4 of 8
CMV6120 Mathematics
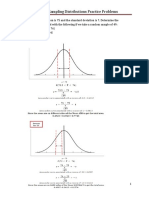
Example 5
John got 70 in a Mathematics examination.
The marks of the examination are normally distributed with mean = 75 and standard deviation = 5.
If there are 100 students, how many students do better than John?
Solution
y Higher than 70
By symmetry, ______% students do better than 75
marks, ______ students do worse.
John’s mark is 70. He has a standard score of –1.
John is at 1 standard deviation below the mean.
There are ______% of students lying within one s.d. 34% 34%
below the mean.
Percentage of students with standard score greater than –
1 is 34% + 50% = _________ 13.5% 13.5%
2.35% 2.35%
Total no. of students doing better than John out of the
x
100 students = 60 65 70 75 80 85 90
Example 6
y
The life hours of 200 sample light bulbs are normally
distributed with a mean of 1000 hours and the standard
deviation is 150 hours. Find the number of light bulbs having
life hours:
a) more than 700 hours;
b) less than 1150 hours.
34% 34%
Solution
a) 700 = 1000 – 2 (150)
= x 2 2.35%
13.5% 13.5% 2.35%
550 700 850 1000 1150 1300 1450 x
Light bulbs with life hours lie greater than x 2
= y
The no. of light bulbs with life hours more than 700 hours
=
b) 1150 = 1000 + 1 (150)
34% 34%
= x
The number of light bulbs with life hours less than 13.5% 13.5%
1150 hours = 2.35% 2.35%
Unit 21: Applications of standard deviation Page 5 of 8
CMV6120 Mathematics
Example 7
The cheesecake made by a cake factory are normally distributed with a mean of 500 gm and a
standard deviation of 12 gm. How many per cent of cheesecake have weigh more than 524 gm?
Solution
Example 8
The length of a sample of 400 conduits are normally distributed with a mean of 2.92 m and a
standard deviation of 2 cm. How many conduits in the sample have length between 2.9 m and 2.96
m?
Solution
Example 9
The resistance of a sample of 100 resistors is normally distributed with a mean of 10k. If all the
resistors have a resistance of 10k 20%, lie within 3 standard deviations from the mean. Find the
standard deviation and the possible resistance lying within x
Solution
The possible highest resistance = 10 k (1 + 20%) = 12 k
12 k = 10 k + 3
= (12 – 10) / 3 = 0.6667 k
Unit 21: Applications of standard deviation Page 6 of 8
CMV6120 Mathematics
Example 10
The movies have a mean playing time of 88 min. and the standard deviation is 5 min. If the playing
times are normally distributed, find the percentage of the movies with playing time
a) less than 78 min;
b) between 83 min. and 103 min..
Solution
a)
Unit 21: Applications of standard deviation Page 7 of 8
CMV6120 Mathematics
Practice
1. Find Peter’s standard scores in English and Chinese
Subject Peter’s mark class mean standard deviation
English 70 55 10
Chinese 66 50 8
2. Keeping the standard score unchanged, find the adjusted marked for the original mark 55.
mean standard deviation
original 40 10
adjusted 50 12
3. Keeping the standard score unchanged, find the mean x of the adjusted marks.
Peter’s mark mean standard deviation
original 38 42 8
adjusted 44 x 12
4. Find the mean m and standard deviation of marks. It is given that:
raw mark standard score
72 -0.6
90 1.2
5. In a Mathematics examination, the marks obtained by 15000 students are normally
distributed with a mean of 52 and a standard deviation of 16. The percentages of marks
lying within 1 and 2 standard deviations from the mean are 68% and 96% respectively.
a) Find the number of students who score less than 68.
b) If the top 2% of students are awarded a distinction, what is the minimum mark a
student must get in order to receive a distinction?
6. The weights of 1000 students are normally distributed with mean 68 kg and standard
deviation 3 kg. If 68% of the students lie within one standard deviation of the mean and 96%
lie within 2 standard deviations of the mean, find
a) number of students who are heavier than 74 kg.
b) number of students whose weight lie between 62 kg and 71 kg.
[Answer 1).1.5, 2; 2) 68 3) 50 4) s = 10, m = 78
5a) 12600, 5b) 84 6a) 20, 6b) 820]
Unit 21: Applications of standard deviation Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- RSL 11+ Comprehension SampleDocument25 pagesRSL 11+ Comprehension Samplenabhan07100% (2)
- The Great Ideas ProgramDocument10 pagesThe Great Ideas ProgramAlysson Nunes SantosNo ratings yet
- DSE 25.2 Applications of DispersionDocument15 pagesDSE 25.2 Applications of DispersionRaphael ChengNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mathematics-ACTIVITY SHEETSDocument144 pagesGrade 8 Mathematics-ACTIVITY SHEETSFlorence Tangkihay77% (13)
- Part VI Module in Problem Solving and Reasoning in Mathematics PDFDocument7 pagesPart VI Module in Problem Solving and Reasoning in Mathematics PDFAngel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual to accompany Introduction to Linear Regression AnalysisFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Introduction to Linear Regression AnalysisRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Course IntroDocument5 pagesCourse IntroMalith De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document90 pagesChapter 4Kaleb MulatuNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesDocument11 pagesSaint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesJimkenneth RanesNo ratings yet
- LP For P&S Normal DistributionDocument6 pagesLP For P&S Normal DistributionRam AndresNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2 - The Normal CurveDocument31 pagesModule 1.2 - The Normal CurveJohn Mark MatibagNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques PDFDocument36 pagesQuantitative Techniques PDFGitsirasNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution LESSON 2Document65 pagesNormal Distribution LESSON 2Chuck DaleNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Variation and Areas Under Normal CurveDocument5 pagesCoefficient of Variation and Areas Under Normal CurvemochiNo ratings yet
- 14 Normal DistributionDocument37 pages14 Normal DistributionJomar Porteros100% (2)
- 84 Percentiles Teacher PDFDocument7 pages84 Percentiles Teacher PDFsidmur321No ratings yet
- Ebook Elementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 7Th Edition Bluman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesEbook Elementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 7Th Edition Bluman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFTraciLewispwng100% (12)
- Answer Sheet in Practical Research 2: Quarter 2-Module 7Document55 pagesAnswer Sheet in Practical Research 2: Quarter 2-Module 7Kenneth Aquino100% (2)
- Instructions: GEN1008 / MED1018 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17Document17 pagesInstructions: GEN1008 / MED1018 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17liNo ratings yet
- NormalWS1 PDFDocument4 pagesNormalWS1 PDFRizza Jane BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Normal DistributionDocument47 pagesLesson 2: Normal DistributionMARITESS COLLADONo ratings yet
- STAT Midterm (Solution)Document14 pagesSTAT Midterm (Solution)L HYNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Calculus 11th Edition by Larson and Edwards ISBN 9781337275347Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Calculus 11th Edition by Larson and Edwards ISBN 9781337275347alyssafloresfnexiwptms100% (34)
- Solution Manual For Calculus 11Th Edition by Larson and Edwards Isbn 9781337275347 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Calculus 11Th Edition by Larson and Edwards Isbn 9781337275347 Full Chapter PDFbenjamin.smith112100% (18)
- Statistics and Probability - Solved Assignments - Semester Spring 2010Document33 pagesStatistics and Probability - Solved Assignments - Semester Spring 2010Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- QTM Cycle 7 Session 4Document79 pagesQTM Cycle 7 Session 4OttilieNo ratings yet
- Math11 SP Q3 M4 PDFDocument16 pagesMath11 SP Q3 M4 PDFJessa Banawan EdulanNo ratings yet
- CH7 - Continuous Probability DistributionDocument50 pagesCH7 - Continuous Probability Distributionlaelafitrya0% (1)
- 2015 OL Maths Past Paper and Answers English Medium PDFDocument60 pages2015 OL Maths Past Paper and Answers English Medium PDFHashan SampathNo ratings yet
- Instructions: GEN1008 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17Document17 pagesInstructions: GEN1008 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17liNo ratings yet
- 1.1 TG For Normal DistributionDocument5 pages1.1 TG For Normal DistributionVincere André AlbayNo ratings yet
- SIMPLEtestofhypothesisDocument35 pagesSIMPLEtestofhypothesisJulius EstrelladoNo ratings yet
- Aga A2 1104 PpsDocument2 pagesAga A2 1104 Pps조윤호No ratings yet
- Estimation of Parameters FinalDocument23 pagesEstimation of Parameters FinalMay Ann MonteroNo ratings yet
- Inferential StatisticsDocument111 pagesInferential StatisticsCameronNo ratings yet
- Independent University, BangladeshDocument20 pagesIndependent University, BangladeshMD. Akif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 Topics: Sampling Distributions and Central Limit TheoremDocument4 pagesProblem Set 2 Topics: Sampling Distributions and Central Limit TheoremSravya Tummala100% (1)
- Instructions: GEN1008 / MED1018 / GED1008 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17Document17 pagesInstructions: GEN1008 / MED1018 / GED1008 Mid-Term Test Page 1 of 17liNo ratings yet
- SIMPLEtestofhypothesisDocument35 pagesSIMPLEtestofhypothesisJulius EstrelladoNo ratings yet
- ECS7020P Sample Paper SolutionsDocument6 pagesECS7020P Sample Paper SolutionsYen-Kai ChengNo ratings yet
- Worskheet Finals 1Document3 pagesWorskheet Finals 1JENNIFER BALMESNo ratings yet
- Probab Stat Math 311Document26 pagesProbab Stat Math 311Yasuhiro Hinggo EscobilloNo ratings yet
- MATH03-CO4-Lesson2-Sampling Distribution (Proportion and Difference of Two Averages)Document16 pagesMATH03-CO4-Lesson2-Sampling Distribution (Proportion and Difference of Two Averages)Edward SnowdenNo ratings yet
- Practice FinalDocument16 pagesPractice FinalJessica ZhaiNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering and Computer Science Department of Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDocument11 pagesSchool of Engineering and Computer Science Department of Electrical & Electronic EngineeringMD. Akif RahmanNo ratings yet
- 07 - Workbook Part 2 - Business StatisticsDocument158 pages07 - Workbook Part 2 - Business StatisticsvNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variability Lec 7: DR - Nesrin H. Darwesh University of Duhok-College of DentistryDocument48 pagesMeasures of Variability Lec 7: DR - Nesrin H. Darwesh University of Duhok-College of DentistryNivar selevanayNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Practice Problems SOLUTIONSDocument7 pagesModule 7 Practice Problems SOLUTIONSJeff CagleNo ratings yet
- Newbold Sbe8 Tif ch05 PDFDocument58 pagesNewbold Sbe8 Tif ch05 PDFak100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 1ADocument7 pagesMathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 1AEdward Lorenz TabligaNo ratings yet
- GE 4 MMW Reviewer AutosavedDocument12 pagesGE 4 MMW Reviewer AutosavedKyle SarcosNo ratings yet
- Quant 9 - Normal DistDocument19 pagesQuant 9 - Normal DistHieu PhanNo ratings yet
- Practice Set3Document11 pagesPractice Set3JAINAM JAINNo ratings yet
- (FILLED) MCD2080-ETC1000-ETF1100 Exam S1 2018Document10 pages(FILLED) MCD2080-ETC1000-ETF1100 Exam S1 2018michella vegaNo ratings yet
- Stat A01Document6 pagesStat A01Sunny LeNo ratings yet
- Final - Econ3005 - 2022spring - Combined 2Document11 pagesFinal - Econ3005 - 2022spring - Combined 2Swae LeeNo ratings yet
- 24-01-31 Marked SlidesDocument29 pages24-01-31 Marked Slideselyan.dummyaccNo ratings yet
- Questions ch6 PDFDocument5 pagesQuestions ch6 PDFHossam AboomarNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Yong Hwa M. Jeong Grade 11 STEM-B Quarter 4 - Module 1: Test of HypothesisDocument22 pagesStatistics and Probability Yong Hwa M. Jeong Grade 11 STEM-B Quarter 4 - Module 1: Test of HypothesisSarahmae MeñozaNo ratings yet
- Normaldistribution 160627092159 PDFDocument24 pagesNormaldistribution 160627092159 PDFGladzangel LoricabvNo ratings yet
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionlllNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionlllNo ratings yet
- Percubaan Term 1 (2019) JPN KelantanDocument3 pagesPercubaan Term 1 (2019) JPN KelantanlllNo ratings yet
- Section A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxDocument8 pagesSection A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxlllNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006Document18 pagesDokumen - Tips Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006lllNo ratings yet
- Instructions To Candidates:: SECTION A (45 Marks) Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument2 pagesInstructions To Candidates:: SECTION A (45 Marks) Answer All Questions in This Sectionlll0% (1)
- My Hero Project PDFDocument4 pagesMy Hero Project PDFCARLOS NORIEL CABANANo ratings yet
- From Where School You Are From: From University of Makati, Makati Metro Manila Diin Ka Nag Work?Document2 pagesFrom Where School You Are From: From University of Makati, Makati Metro Manila Diin Ka Nag Work?Renzy Myer D. BulahanNo ratings yet
- Math PDFDocument95 pagesMath PDFAnonymous kI39sJC1MNo ratings yet
- Reservation in India - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesReservation in India - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediasreddy_383299No ratings yet
- Clothes Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesClothes Lesson Planapi-314934184No ratings yet
- ABDC Journals List by RatingDocument35 pagesABDC Journals List by RatingstaimoukNo ratings yet
- Yoga Obstacle CourseDocument3 pagesYoga Obstacle Courseapi-313621606No ratings yet
- Catch-Up Friday Action PlanDocument2 pagesCatch-Up Friday Action PlanJim Bryan Wabina Vergara91% (32)
- Institute Name: Aliah University, Kolkata (IR-O-U-0567)Document12 pagesInstitute Name: Aliah University, Kolkata (IR-O-U-0567)saifuddin skNo ratings yet
- Here Is How A Topper Gets 94 Marks in Urdu With Pictures - Top Study WorldDocument10 pagesHere Is How A Topper Gets 94 Marks in Urdu With Pictures - Top Study WorldJulie MerrillNo ratings yet
- Promotin Seniority List For SGT To School Asst in Aug 2011 of All Subjects DT 28.7.11Document82 pagesPromotin Seniority List For SGT To School Asst in Aug 2011 of All Subjects DT 28.7.11Satha SathavishnuNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3-4: English For Academic and Professional Purposes (EAPP)Document4 pagesWEEK 3-4: English For Academic and Professional Purposes (EAPP)Sherri BonquinNo ratings yet
- Module 12 1creating Postive School CultureDocument29 pagesModule 12 1creating Postive School CultureArben EchagueNo ratings yet
- Place Score ReportDocument2 pagesPlace Score Reportapi-280625817No ratings yet
- Sop 27Document1 pageSop 27Atharvä Ravindra HatekařNo ratings yet
- Bar Council of Delhi: Declaration Form To Be Submitted by The Advocates Enrolled After July, 2010Document1 pageBar Council of Delhi: Declaration Form To Be Submitted by The Advocates Enrolled After July, 2010abhikaamNo ratings yet
- English 302 - Final MemoDocument2 pagesEnglish 302 - Final Memoapi-349459678No ratings yet
- Revised Bioethics SyllabusDocument7 pagesRevised Bioethics SyllabuslouradelNo ratings yet
- World Journal On Educational Technology: Current IssuesDocument12 pagesWorld Journal On Educational Technology: Current IssuesBelay HaileNo ratings yet
- 1 DLP Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseDocument7 pages1 DLP Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseJonalene Dulay100% (5)
- The Morning Calm Korea Weekly - Mar. 21, 2008Document24 pagesThe Morning Calm Korea Weekly - Mar. 21, 2008Morning Calm Weekly NewspaperNo ratings yet
- AL 2 PrelimDocument4 pagesAL 2 PrelimJohn Michael Porras HambreNo ratings yet
- Brochure BE 2010 11Document126 pagesBrochure BE 2010 11georgianchailNo ratings yet
- FS 1 PORTFOLIO Episode 1 ENCINA, JULIE JEAN BEED 4B-DAYDocument8 pagesFS 1 PORTFOLIO Episode 1 ENCINA, JULIE JEAN BEED 4B-DAYJulie Jean Restauro EncinaNo ratings yet
- Theories of PersonalityDocument16 pagesTheories of PersonalityLeeYan SaliliNo ratings yet
- Singing ChildrenDocument4 pagesSinging Childrenapi-300652571No ratings yet
- REFLECTION - Q2 - Week 5Document2 pagesREFLECTION - Q2 - Week 5EDITHA PAGUYONo ratings yet