Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
557 viewsTle (2) 1
Tle (2) 1
Uploaded by
Earl KennethTools such as mixing bowls, sifters, spoons, and pots are needed to prepare starch and cereal dishes. Starches are found in seeds, roots, and tubers and are the main components of many foods. Starch is made of amylose and amylopectin molecules packed into granules. As starch is heated in water, it undergoes gelatinization where the granules swell and burst. Starch provides thickness and structure to foods through viscosity and gel formation. It plays important roles as a thickener, stabilizer, moisture retainer, and binder in foods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Anaemia in PregnancyDocument81 pagesAnaemia in PregnancyEmmanuel Kings80% (5)
- WTR Grade 10Document9 pagesWTR Grade 10Danilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Prepare Cereals and StarchDocument59 pagesLesson 2 Prepare Cereals and StarchMarry Jane Lustre CanabalNo ratings yet
- Prepare Cereals and StarchDocument30 pagesPrepare Cereals and StarchLucille PaglingayenNo ratings yet
- Cereals and StarchDocument31 pagesCereals and StarchSheryl Borromeo100% (1)
- Cookery 10 Cereals and StarchDocument62 pagesCookery 10 Cereals and StarchHANNA CLAIRE ROSAL100% (1)
- Cookery Grade 10 - Quarter-I-Module 2Document39 pagesCookery Grade 10 - Quarter-I-Module 2Van ImperialNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Q3 Week 2Document13 pagesCookery 10 Q3 Week 2Samantha MusniNo ratings yet
- Q3W5 TleDocument12 pagesQ3W5 TlePauli Ann BumanlagNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2JonardNadelaNo ratings yet
- Cookery9 Q3 W6 Prepare SauceDocument9 pagesCookery9 Q3 W6 Prepare SauceRomnick CosteloNo ratings yet
- Written Work in Cookery Part of Fish Second GradingDocument1 pageWritten Work in Cookery Part of Fish Second GradingVincent LibreaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Week 5 8 Cookery Final 2Document32 pagesQ3 - Week 5 8 Cookery Final 2It's Me JohnNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 3 Las 3Document4 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 3 Las 3Michole Godwin RegalaNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 - Mod - 4.1-4.2Document7 pagesCOOKERY 10 - Mod - 4.1-4.2Charmaigne GalvezNo ratings yet
- FINAL Module Grade 10 1st Quarter 2021 2022Document74 pagesFINAL Module Grade 10 1st Quarter 2021 2022Alfon John BoadillaNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Cook Meat: Cookery 10 School Year 2019 - 2020Document43 pagesPrepare and Cook Meat: Cookery 10 School Year 2019 - 2020Alodie Dela Raiz AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Prepare Soups Required For Menu Items 4TH Q WEEK2Document18 pagesPrepare Soups Required For Menu Items 4TH Q WEEK2De ShangNo ratings yet
- Cookery9 Q3 W8 Prepare SauceDocument11 pagesCookery9 Q3 W8 Prepare SauceRomnick CosteloNo ratings yet
- 04 LO 1 POULTRY Miseen PlaceDocument31 pages04 LO 1 POULTRY Miseen PlaceCanals MaxermelaNo ratings yet
- Physical Structure of An Egg Grade 10Document15 pagesPhysical Structure of An Egg Grade 10Jessa Brigole TorresNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics-Cookery Performing Mise' en PlaceDocument10 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics-Cookery Performing Mise' en PlaceConstancia PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan q3 Week 6 g10 CookeryDocument4 pagesLesson Plan q3 Week 6 g10 CookeryJohnnexter GubatNo ratings yet
- Final Cookery10 q4 Module 4Document16 pagesFinal Cookery10 q4 Module 4eda gadoyNo ratings yet
- TLE-10 Cookery Module2 Week2Document6 pagesTLE-10 Cookery Module2 Week2arjeangrace delosreyesNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Quarter 1Document6 pagesWeek 5 - Quarter 1Teddy RaquelNo ratings yet
- Store and ReconstituteDocument20 pagesStore and ReconstituteDiane Vill100% (1)
- Final Cookery 12 q3 Module 5Document22 pagesFinal Cookery 12 q3 Module 5Elle GatchNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Observation 23Document19 pagesCookery 10 Observation 23Shery Cantago100% (1)
- 3rdquarter 10 CookeryDocument76 pages3rdquarter 10 CookeryJeah Asilum DalogdogNo ratings yet
- Tle q2 Cookery Weeek 5 8Document16 pagesTle q2 Cookery Weeek 5 8Chasie Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 3 Las Number 8Document7 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 3 Las Number 8Zhen Reas AmpoNo ratings yet
- Tle 1o q4 ModuleDocument22 pagesTle 1o q4 ModuleRhea AnselmoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Cookery 10Document93 pagesReviewer in Cookery 10Arneil RealizaNo ratings yet
- TLE 10 Q2 Cokery-Seafood AS#1Document6 pagesTLE 10 Q2 Cokery-Seafood AS#1CYRIL DOMENS0% (1)
- Cookery-10 LAS-Q3 Week6Document6 pagesCookery-10 LAS-Q3 Week6Angeline CortezNo ratings yet
- Cookery - 10-Quarter 4-Week-1Document12 pagesCookery - 10-Quarter 4-Week-1Ereca Mae Papong100% (1)
- Tle Cookery-10 - 4TH QuarterDocument34 pagesTle Cookery-10 - 4TH QuarterPatrick Dave San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Quarter IVTLE - M1-5 - wk1-5Document32 pagesQuarter IVTLE - M1-5 - wk1-5Villa WengzyNo ratings yet
- 10 Cookery 10 Q1 M1Document42 pages10 Cookery 10 Q1 M1Sheryn Mae Purisima De VeraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Preparing Fish and Seafood Dishes A. Seafood: Definition, Types, and CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesLesson 1: Preparing Fish and Seafood Dishes A. Seafood: Definition, Types, and CharacteristicsReygina Mae Sibayan Palaganas100% (2)
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics - COOKERYDocument25 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics - COOKERYCristy MonjeNo ratings yet
- Glak Tle-Cookery-10 Q-3 WK 5-6Document14 pagesGlak Tle-Cookery-10 Q-3 WK 5-6adadNo ratings yet
- Lo 2 .... 3rd QuarterDocument24 pagesLo 2 .... 3rd QuarterMarcelina MedranoNo ratings yet
- Lx49l0a7r - Weeks 26 and 27 - TLE 10.docx - Approved - JCC - Docx - Office Copy - JCCDocument8 pagesLx49l0a7r - Weeks 26 and 27 - TLE 10.docx - Approved - JCC - Docx - Office Copy - JCCDI ANNo ratings yet
- Storing & ReconstituteDocument1 pageStoring & ReconstituteRochelle Jossanah OsalNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Cookery LAS Week 1-8 2nd QuarterDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Cookery LAS Week 1-8 2nd Quarteradad100% (1)
- Final Cookery12 q3 Module 6Document24 pagesFinal Cookery12 q3 Module 6Elle GatchNo ratings yet
- Market Forms of EggDocument2 pagesMarket Forms of EggBrix Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Selecting Good Quality Poultry and GameDocument11 pagesSelecting Good Quality Poultry and GameCheriel Alcala Calledo100% (1)
- Tle 1o No. 7Document15 pagesTle 1o No. 7Juvelyn MundoyNo ratings yet
- TLE9 COOKERY Q3 M2 Different-Sandwich-Ingredients FVDocument10 pagesTLE9 COOKERY Q3 M2 Different-Sandwich-Ingredients FVgwenNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 CookeryDocument18 pagesMODULE 1 CookeryMaribel B GarciaNo ratings yet
- TLE10 Module 3Document14 pagesTLE10 Module 3Leyzyl Nieves MaravillasNo ratings yet
- Learning OUTCOME 3 PlatingDocument10 pagesLearning OUTCOME 3 PlatingrichardNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 3 LAS Number 3Document11 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 3 LAS Number 3Constancia PerezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10: Tle - He (Cookery 10) Quarter 1 - Prepare Egg Dishes Module 2-Prepare and Cook Egg DishesDocument12 pagesGrade 10: Tle - He (Cookery 10) Quarter 1 - Prepare Egg Dishes Module 2-Prepare and Cook Egg DishesTIPAY, EMELIE L.No ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education Home Economics-Cookery: Storing MeatDocument13 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education Home Economics-Cookery: Storing MeatConstancia PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Lo#2Document28 pagesLesson 2 Lo#2Marcelina Medrano100% (1)
- Cereals PastaDocument17 pagesCereals PastaSarah Jean Erika SebastianNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Prepare Cereals and Starch: Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise'en Place (Week 5)Document19 pagesLesson 2 Prepare Cereals and Starch: Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise'en Place (Week 5)BERNARDO VIZARRANo ratings yet
- MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin)Document7 pagesMCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin)U WidNo ratings yet
- A Review On Effects of Metformin On Vitamin B12status PDFDocument9 pagesA Review On Effects of Metformin On Vitamin B12status PDFJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- The Relevance of Nutrition To Pediatric Oncology - A Cancer Control Perspective - PEDIATRIC BLOODDocument8 pagesThe Relevance of Nutrition To Pediatric Oncology - A Cancer Control Perspective - PEDIATRIC BLOODGUSTAVO BELLONo ratings yet
- CHN Rationalization 9 16Document22 pagesCHN Rationalization 9 16joyNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University Nursing ThesisDocument8 pagesRajiv Gandhi University Nursing Thesistracyaldridgejackson100% (2)
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument5 pagesVitamins and Mineralsdheeptha sundar100% (1)
- Mapeh 10Document5 pagesMapeh 10Flora MacaougasNo ratings yet
- Anaemia in PregnancyDocument15 pagesAnaemia in PregnancyNorshahidah Ieda100% (1)
- FinalDocument101 pagesFinalVimal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- All Case Studies Blood Student Copy FINAL 2019Document14 pagesAll Case Studies Blood Student Copy FINAL 2019saud rehmanNo ratings yet
- Cookery10vegetables 190117235613Document43 pagesCookery10vegetables 190117235613Meach CallejoNo ratings yet
- Diapositivas Del Dr. Walsh - Nutrient TherapyDocument90 pagesDiapositivas Del Dr. Walsh - Nutrient TherapyLucasNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document80 pagesVitamin B12Anand Veeranan100% (1)
- Prevention and Tratment of Iron-Deficiency AnaemiaDocument12 pagesPrevention and Tratment of Iron-Deficiency Anaemiaطارق رشيد100% (1)
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur: Presentation On Anemia and Nutritional DeficiencyDocument7 pagesGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur: Presentation On Anemia and Nutritional Deficiencypriyanka100% (2)
- Anemias of Abnormal Nuclear DEVELOPMENT: Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument24 pagesAnemias of Abnormal Nuclear DEVELOPMENT: Megaloblastic AnemiaSukhrian MuhdaNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition: Dr. Radhika KapurDocument15 pagesFood and Nutrition: Dr. Radhika Kapurthat's my dream to workNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Healthy PregnancyDocument13 pagesPractice Paper Healthy Pregnancytimea_gheneaNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients Vitamins Report 3Document53 pagesMicronutrients Vitamins Report 3XanderNo ratings yet
- Ept 6Document16 pagesEpt 6dianela fionaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument120 pagesAnemiagaddam narasimhaNo ratings yet
- Anemia Saranya Ranjith PresentationDocument23 pagesAnemia Saranya Ranjith PresentationSaranya DeviNo ratings yet
- g10 Quarter 2 Module 3 and Module 4Document41 pagesg10 Quarter 2 Module 3 and Module 4KieshaNo ratings yet
- RFP FRK 9800 NMEL 28dec22Document45 pagesRFP FRK 9800 NMEL 28dec22durgaprasadNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12: Harsha Vardhini.SDocument17 pagesVitamin B12: Harsha Vardhini.SScindiaaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics Rajiv Gandhi UniversityDocument8 pagesDissertation Topics Rajiv Gandhi UniversityHelpWriteMyPaperUK100% (1)
- Prenatal SuppsDocument14 pagesPrenatal SuppsJessNo ratings yet
- Vitamin ChatDocument9 pagesVitamin Chatnusdar20No ratings yet
- UNIT II SulfonamidesDocument12 pagesUNIT II SulfonamidesTasya MadifaNo ratings yet
Tle (2) 1
Tle (2) 1
Uploaded by
Earl Kenneth0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
557 views12 pagesTools such as mixing bowls, sifters, spoons, and pots are needed to prepare starch and cereal dishes. Starches are found in seeds, roots, and tubers and are the main components of many foods. Starch is made of amylose and amylopectin molecules packed into granules. As starch is heated in water, it undergoes gelatinization where the granules swell and burst. Starch provides thickness and structure to foods through viscosity and gel formation. It plays important roles as a thickener, stabilizer, moisture retainer, and binder in foods.
Original Description:
Original Title
TLE (2)1.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTools such as mixing bowls, sifters, spoons, and pots are needed to prepare starch and cereal dishes. Starches are found in seeds, roots, and tubers and are the main components of many foods. Starch is made of amylose and amylopectin molecules packed into granules. As starch is heated in water, it undergoes gelatinization where the granules swell and burst. Starch provides thickness and structure to foods through viscosity and gel formation. It plays important roles as a thickener, stabilizer, moisture retainer, and binder in foods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
557 views12 pagesTle (2) 1
Tle (2) 1
Uploaded by
Earl KennethTools such as mixing bowls, sifters, spoons, and pots are needed to prepare starch and cereal dishes. Starches are found in seeds, roots, and tubers and are the main components of many foods. Starch is made of amylose and amylopectin molecules packed into granules. As starch is heated in water, it undergoes gelatinization where the granules swell and burst. Starch provides thickness and structure to foods through viscosity and gel formation. It plays important roles as a thickener, stabilizer, moisture retainer, and binder in foods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
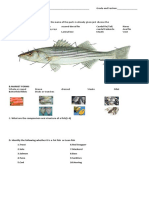
Tools and Equipment Needed 11.
Measuring spoon – used for measuring dry and liquid
ingredients which require a little amount
The success of cooking starch and cereal dishes depends on 12. Sauce pan and pots – used for cooking meat and fish
the proper tools and equipment used in the preparation of dishes with gravy and sauce.
food. The preparation of starch and cereal dishes requires 13. Kettle and rice cooker – used for cooking rice and other
the various tools and equipment below. Each tool must be foods.
used according to its function. 14. Pressure cooker – used for tenderizing or cooking meat,
1. Mixing bowl – used when preparing cake mixture, salads, chicken, and other grains or legumes, such as mongo and
creams, and sauces. white beans in lesser time..
2. Sifter – used for separating coarse particles of flour, 15. Double boiler – used for preparing sauces which easily
sugar, baking powder, and powdered ingredients to retain get scorched when cooked directly on the stove.
finer textures. 16. Steamer – used for cooking food by steaming.
3. Wire whip – used for beating egg whites, egg yolk, 17. Colander - a perforated bowl of varying sizes made of
creams and mayonnaise. stainless steel, aluminum or plastic, used to drain, wash, or
4. Wooden spoon – used for mixing creams, butter, and for cook ingredients from liquid
tossing salads. 18. Canister - a plastic or metal container with a lid that is
5. Slotted spoon – used to separate solid particles from used for keeping dry products
soup; also for stirring purposes, such as making egg white 19. Butcher knife – used for cutting, sectioning, and
fine in texture for bird‘s nest soup and mock nido soup. trimming raw meats
6. Blending fork – used for testing the tenderness of meat, 20. Channel knife – a small hand tool used generally in
combining big cuts and particles of meat and vegetables, decorative works such as making garnishes.
and for blending other ingredients with flour. Cereals are usually starchy pods or grains. Cereal grains are
7. Rubber scraper – used for scraping off mixtures of butter, the most important group of food crops in the world. The
sugar, and egg from the sides of the mixing bowl. main components of human diets.
8. Strainer – used for separating liquids from fine or solid
food particles, such as coco cream from coconut and Starch is the second most abundant organic substance on
tamarind extract. earth. It is found in all forms of leafy green plants, located
9. Tongs – used for handling hot foods. in the roots, fruits or grains. Many of the food staples of
10. Measuring Cups – used for measuring dry and liquid man throughout the world are basically starchy foods, such
ingredients as rice, corn, cassava, wheat, potato and others.
The parts of plants that store most starch are: Amylose is a long chain-like molecule, sometimes called the
Seeds roots, and tubers. linear fraction, and is produced by linking together 500 to 2,
The most common sources of food starch are: 000 glucose molecules. The amylose fraction of starch
cereal grains, including corn, wheat, rice, grain, sorghum, contributes gelling characteristics to cooked and cooled
and oats; starch mixtures.
legumes; and A gel is rigid to a certain degree and holds a shape when
roots or tubers, including potato, sweet potato, molded.
arrowroot, and the tropical cassava plant (marketed as Amylopectin has a highly branched, bushy type of structure,
tapioca) very different from the long, string-like molecules of
Common Source of Manufactured Food Starch amylose. In both, amylose and amylopectin, however, the
1. corn basic building unit is glucose. Cohesion or thickening
2. potato properties are contributed by amylopectin when a starch
3. Tapioca (cassava) mixture is cooked in the presence of water, but this fraction
Starches are named after its plant sources does not produce a gel.
corn starch from corn
rice starch from rice Most natural starches are mixtures of the two fractions.
tapioca from cassava Corn, wheat, rice, potato,
Classification of Starch Tapioca starches contains 24 to 16 percent amylose, with
1. Native or Natural Starch refers to the starches as the remainder being amylopectin.
originally derived from its plant source. The root starches of tapioca and potato are lower in
2. Modified Starches are starches that have been altered amylose content than the cereal starches of corn, wheat,
physically or chemically, to modify one or more of its key and rice.
chemicals and/or physical property. The Starch Granule
3. Purified starch may be separated from grains and tubers Granules – is a tiny unit storage area of plants, notably the
by a process called wet milling. seeds and roots molecules of starch.
Starch Composition and Structure Hilum - placed of amylose and amylopectin molecules
The Starch Molecule tightly packed stratified layers formed around a central spot
Starch is polysaccharide made up of hundreds or even in the granules
thousands of glucose molecules joined together. The starch molecules are systematically structured in the
Two General Types of Molecules of Starch granule to form crystalline-like patterns.
Birefringence - the highly oriented structure causes light to 3. Retrogradation - is the process in which starch molecules,
be rotated so that a Maltese cross pattern on each granule particularly the amylose fraction, re-associate or bond
is observed together in an ordered structure after disruption by
Starch Properties and Reactions gelatinization; ultimately a crystalline order appears.
1. Gelatinization. The sum of changes that occur in the first 4. Syneresis. Oozing of liquid from gel when cut and
stages of heating starch granules in a moist environment allowed to stand (e.g. jelly or baked custard). The oozing of
which includes swelling of granules as water is absorbed liquid from a rigid gel; sometimes called weeping.
and disruption of the organized granule structure. This reaction occurs in all kinds of gels:
2. Viscosity. The resistance to flow; increase in thickness or puddings
consistency. When the newly gelatinized starch is stirred, jellies
more swollen granules break and more starch molecules custards
spill causing increase in viscosity or thickness. gelatin
Changes in Gelatinization of Starch agar
hydration and swelling to several times original size 5. Dextrinization. It is the process of forming dextrin.
loss of birefringence Dextrins – are partially hydrolyzed starches that are
increase in clarity prepared by dry roasting. In home kitchens, dextrinization is
marked, rapid increase in consistency and attainment of achieved by toasting flour for polvoron, rice flour for kare-
peak kare sauce, and bread slices for breakfast.
"dissolution" of linear molecules and diffusion from 6. Hydrolysis Starches undergo hydrolysis during cooking or
ruptured granules. processing and during storage of food where a chemical
with heat removal, retro gradation of mixture to a paste- reaction in which a molecular linkage is broken and a
like mass of gel. molecule of water is utilized.
The type of sugar influences the temperature and rate of a. Prolonged heating of starches with acid will promote
gelatinization. The effect of sugar is attributed to hydrolysis. This can happen when cooking an acidic food,
competition for water. It was observed that sugar actually such as: Pineapple pie resulting in reduced viscosity or
interacts with the amorphous areas of the starch granules. firmness of the pie filling.
Different Sweeteners Added to Starch Gel Preparation. Starch plays various roles in food, a typical multi-tasker
honey 1. Thickeners in gravies, sauces and pudding. It absorbs
molasses water and become a gel when cooked.
panutsa or granulated sugar 2. Colloidal stabilizers
3. Moisture retainer
4. Gel forming agents
5. Binders The physiological function of noodles and pasta will depend
6. Package on its starch and other constituents. Since it is basically a
7. Flavor carriers– its ability to trap oils and fats, which starchy food, the nutritional significance discussed for
absorb flavoring substances more efficiently. starches also applies. In addition to starches, including
resistant fat as well.
Starches – are added to processed meats (luncheon meats, Cereals provide the body with:
hot dogs, sausages, etc.) as a filler, binder, moisture, Carbohydrates
retainer, and fat substitute. The quality characteristics of Protein
the starch itself depends upon which role or function it was Fat
used. Vitamins
Cereal. Cereal is any grain that is used for food. Grains Minerals
especially whole grain are not just empty calories. These Water
are very valuable and can contribute a great deal to our Cellulose or roughage
health. You should include at least four servings from this Nutritive value:
food group each day. Water
Cereal-processed food: Protein
A whole grain cereal is a grain product that has retained Fat
the specific nutrients of the whole, unprocessed grain and Carbon
contains natural proportions of bran, germ and endosperm. Calcium
Enriched cereals are excellent sources of thiamine, niacin, Phosphorous
riboflavin, and iron. Iron
A restored cereal is one made from either the entire grain Thiamin
or portions of one or more grains to which there have been Riboflavin
added sufficient amounts of thiamine, niacin, and iron to Niacin
attain the accepted whole grain levels of these three
nutrients found in the original grain from which the cereal Learning Outcome 2: Prepare and Cook Starch and Cereal
is prepared. Dishes
2.1: Methods of Cooking Starch and
Nutritional Significance of Noodles and Pasta or Alimentary Cereal Dishes
Paste Introduction:
One of the properties of starch is viscosity which is the If cooled too slowly, the amylase fractions will have a
resistance to flow of starch and modified starch paste. In chance to align too much and become too close together
the preparation and cooking of starch and cereal dishes, and the liquid portion will not be trapped in the micelles. In
factors affecting starch paste viscosity and starch gel both instances there will be weeping and syneresis (the
strength should be considered. contraction of a gel accompanied by the separating out of
Factors Affecting Starch Paste Viscosity and Starch Gel liquid.).
Strength Ingredients added (acid, enzyme, sugar, fat and emulsifiers
Stress or other factor. Stirring Amount and Type. This is a a. Addition of acid or enzyme can also cause dextrinization
gelatinized cornstarch dispersion that is likely to break; the (the process of forming dextrins).
granules broke apart due to stirring. Dextrin – a pale powder obtained from starch, used
Kind and Amount of Starch. Certain type of starch will mainly as an adhesive.
influence the characteristics of the starch paste viscosity In making kalamansi pudding or pie, if the juice is added
and gel strength. Generally speaking, with "native starches" early in the gelatinization process, dextrinization of the
the greater the amount of amylopectin the more viscous starch will occur resulting in decreased viscosity and gel
the starch paste, whereas, the greater the amount of strength.
amylase, the firmer the gel is (greater the gel strength). Sugar will delay or inhibit gelatinization of starch.
Heating rate. The faster starch-water dispersion is heated; Starch pudding with excess sugar will be less viscous or
the thicker it will be at the identical endpoint temperature. form less firm gel.
Endpoint Temperature A cake may collapse as the structural contribution of
Each type of starch has a specific endpoint temperature at starch is delayed or inhibited.
which it will undergo optimum gelatinization. Decreased starch paste viscosity and gel strength because
Incompletely gelatinized starch will not attain optimum the sugar added to water won‘t be available for
starch paste viscosity or gel strength. gelatinization. The kind of sugar used also affect viscosity.
Over gelatinization results in decreased starch paste Fat and surfactants, will serve to ―waterproof‖ the starch
viscosity and gel strength because the swollen granules granules so that water will not penetrate as readily during
fragmented with stirring and/or imploded due to the the gelatinization process.
extensive loss of amylase from the granule. Function of Starch
Cooling and storage conditions Type of Food Preparation
If cooled too fast, the amylase will not have time to form Recipes
the vital micelles necessary for the three dimensional Thickening
structure. Sauces, Gravies, Pie fillings and soups
Sauces: Sweet sour, lechon, lumpia, kare-kare, 1. Thinning of Gel. This problem is usually encountered
palabok when using acid or acid ingredients such as lemon or
Pie filling: mango, buko, apple, pineapple vinegar.
Soups: Arrozcaldo, cream soups. 2. Weak Gel. Weak gel results if there is too much liquid in
Gelling relation to the starch
Puddings, kakanin 3. Skin Formation. Skin formation is due to loss of water
Bread pudding, Maja Blanca, sapin-sapin, kutchinta, from the starch and protein molecules near the surface of
cassava bibingka the mixture. To reduce this problem, cover container of the
Binding and filling starch gel with a waterproof cover.
Meat loaves and meat emulsions 4. Scorching. This can be avoided by temperature control
Luncheon meat, hot dogs, Vienna Sausage, chicken and constant stirring so the starch granules do not settle at
nuggets, chicken balls, Ukoy, tempura the bottom of the cooking pan.
Stabilizing 5. Raw Starch Flavor. This is due to ungelatinized starch.
Beverage, syrup, salad dressing Principles in Cooking Cereals
Chocolate drinks, fruits drinks, yogurt drinks, cooked In cooking all cereal products, the following points should
dressings be observed:
Moisture retaining 1. Use a double boiler.
Cake fillings, candies 2. Observe carefully the correct proportions of cereal,
Cake rolls, cream fillings water and salt.
Coating or ducting 3. Cook at boiling temperature (212° F.).
Breads, confectionery, pastries 4. Watch the time by the clock, and always cook the full
Pandesal, Biscuits, candies, espasol time prescribed, preferably longer.
Diluent 5. Serve attractively.
Baking powder, 6. Improper cooking and poor serving are largely
Cupcake responsible for unpopularity of cereal foods.
Coloring Cooking Pasta
Toasts, bread crumbs Noted: Pasta should be cooked al dente, or ―to the tooth.
Polvoron, Lechon sauce, Kare-kare sauce, breading Al dente - is an Italian phrase that means ―to the tooth. ‖
Common Problems in Starch Cookery This means the cooking should be stopped when the pasta
still feels firm to the bite, not soft and mushy.
Tips in Cooking Pasta
The pleasure of cooking pasta is its texture, and this is lost if Noted: Flavored pasta is available in a variety of shapes in
it is overcooked. both the dried and fresh forms. Vegetable ingredients are
To test for doneness, break pasta into small piece and taste added to pasta to provide both color and flavor. An
it. As soon as pasta is al dente, cooking must be stopped at example of flavored pasta is spinach noodles that are
once. green.
Half a minute extra is enough to overcook it. Follow the package directions for cooking flavored pastas.
Cooking times differ for every shape and size of pasta. Cooking Time Depends on the Shape
Timing also depends on the kind of flour used, and the It is important to be familiar with different shapes of pasta
moisture content. so cooking times can be adjusted.
Fresh egg pasta, if it has not been allowed to dry, takes only The larger and fuller the pasta shape, the longer the
1 to 1 ½ minutes to cook after the water has returned to a cooking time.
boil. Most pasta recipes specify cooking times for pasta cooked
Italian practice is to toss the pasta with the sauce the al dente, tender but firm.
minute it is drained, the sauce immediately coats all Some of the pasta shapes and cooking times are shown in
surfaces of the pasta, and the cheese, melts in the heat of the ―Cooking Chart for Various Pasta Shapes. ‖ Just seeing
the boiling hot noodles. this chart helps to emphasize how important it is to follow
the recipe and cook pasta the right way.
Basic Principles in Preparing Pasta Pasta Gets Bigger and Heavier when Cooked
Pasta Shapes Generally, pasta doubles or triples in weight when it is
There are hundreds of shapes and sizes of pasta with each cooked. Likewise, the volume increases 2 to 2 ½ times
shape used for different preparations based on how the during cooking.
sauce will cling, the texture desired, or how the product will Follow the Recipe
be used. For example: The general rule for cooking pasta in boiling water
• Pasta shapes with holes or ridges, such as wagon wheels 1 pound of pasta, use 1 gallon of water, 1 teaspoon of salt,
or rotini, are perfect for chunkier sauces. and 1 teaspoon of oil.
• Thin, delicate pastas, such as angel hair or vermicelli, are For 100 servings of spaghetti, 6 gallons of water, 2
better served with light, thin sauces. tablespoons of salt, and 2 tablespoons of oil are needed to
• Thicker pasta shapes, such as fettuccine, work well with cook 6 pounds of dried spaghetti.
heavier sauces. When pasta is to be used as an ingredient in a recipe that
• Very small pasta shapes, like alphabet shapes and acini di will be cooked more, like macaroni and cheese, it should be
pepe, are good for soups. slightly undercooked.
This means reducing the cooking time by about 2 minutes. Use separate equipment and utensils for handling raw
Pasta that is not cooked enough is tough and chewy. foods
Pasta that is overcooked is soft and pasty. Sanitize all surfaces and equipment used for food
When overcooked pasta is combined with a sauce, it often preparation
breaks apart. Clean thoroughly the cutting-boards and work areas after
Handle pasta the right way after it is cooked. each use
Like most foods, pasta is best when it is cooked and served Protect the kitchen areas and food from insects, pests and
right away. other animals
However, it is sometimes necessary to cook it ahead and Maintain the highest standards of sanitation in the
hold it until time for service. kitchen at all times
Repair immediately broken but still serviceable kitchen
Learning Outcome 2.2: Food Safety tools, utensils and equipment to be ready for next use
Risk in the preparation and cooking of starch and cereal Sanitize completely all kitchen utensils especially cups,
dishes and other food saucers, flatware after each use
Food handlers; Provide for adequate space, proper ventilation and
Kitchen facilities; window screens in the area
Food selection and preparation; and Provide garbage receptacle for proper waste disposal
Safe temperatures. 3. Food Preparation and Cooking
Check expiry dates of food commodities bought and those
Guidelines on proper and safe handling of food in stock
1. Food handlers Use iodized salt as a must in salt-seasoned preparations
Undergo training on food safety and obtain medical Cover the food properly.
certificates from the local/provincial/city/municipal health Practice segregation of materials
office. Store food properly
Observe proper hand washing technique 4. Safe temperature
Wear complete cooking outfit and use disposable gloves Do not leave cooked food at room temperature for more
for direct food contact. than two hours
Observe personal hygiene at all times. Refrigerate promptly all cooked and perishable food
Avoid handling food if you are sick. preferably below 50C within four hours
2. Kitchen facilities Do not store food too long even in the refrigerator.
Thaw food inside the refrigerator, not at room 5. Measure portions into mounds on trays. Cover with
temperature. plastic film and refrigerate until service time.
Check internal temperature during cooking to assure 6. To serve, place the desired number of portions in a china
proper end-point time and temperature has been met to at cap and immerse in simmering water to reheat. Drain,
least 700C/1650F plate, and add sauce.
Reheat cooked food thoroughly to 700C/1650F within two
hours. Learning Outcome 4: Store Starch and Cereal Dishes
4.1: Storing Starch and Cereal Dishes
Learning Outcome 3: Present Starch and Cereal Dishes
3.1: Presentation of Starch and Cereal Dishes Introduction
Proper storage of food is very crucial in keeping food safe
Plating food- refers to placing food on a plate in as because the manner and temperature of storage will affect
appealing manners as possible. the food ‘s susceptibility to bacterial growth, other
contaminants, and infestation. Storing food will not
Presentation – is the very important part of dining improve its quality, it will only delay the rate of
experience because we eat with our eyes first. deterioration, and thus, the proper period of storage should
also be observed.
Garnishing – is simply an attempt to add color and /or
flavor so as to accent or dress up cereals dishes you are FIFO (First In, First Out) in storing food is very important.
serving. Though it is a long-time method in store-keeping where the
first food stored should be the first food to be out from the
Techniques in Preparing Pasta before Plating storage it is high time to make it a habit or put into practice.
1. Pasta is best if cooked and served immediately. Try to Write the expiry date, date received and date of storage to
cook pasta upon order. the food package and regularly check the expiration date.
2. If pasta is to be served immediately, just drain and do not How to Store Pasta Noodles
rinse in cold water. Pasta is stored in airtight containers.
3. If pasta is to be used cold in salad, it is ready to be Pasta noodles are usually sold dry at the grocery store,
incorporated in the recipe as soon as it has cooled. allowing you to store them with other staples in your
4. If pasta is to be held, toss gently with a small amount of pantry.
oil to keep it from sticking. Dry noodles have a long storage life when properly
packaged.
Improper storage causes the pasta to become moist, which Place the pasta in a tight-sealed container. Store in the
leads to mildew. Even without moisture, pasta can become refrigerator for three to five days.
stale if it's not stored correctly. Cooked pasta can be stored unsauced in an airtight
Proper storage ensures your pasta to always taste its best. container and refrigerated for 4 or 5 days.
1. Dry Pasta The sauce should be refrigerated separate from the pasta
Remove the pasta from the store packaging if the noodles and can be stored for 6 or 7 days. This prevents the pasta
come in a box or other non-airtight container. from soaking up too much flavor and oil from the sauce,
Place the noodles in a sealable plastic bag or other which causes the taste of the pasta to be drowned out.
container that closes tightly. For long noodles, such as If the pasta is stored together with the sauce, it should be
spaghetti, use a tall plastic storage container. eaten within 1 or 2 days to limit the amount of sauce that is
Seal the bag or screw the lid on tightly. Store the pasta in a absorbed.
cool, dry place. Dry pasta stores indefinitely, but should be If cooked pasta is not going to be used within the suggested
used within two years to prevent loss of flavor. Store dried time period, it should be frozen and then it can be stored
egg noodles for up to six months. for approximately 3 months.
Dried pasta need not to be refrigerated. It can be stored on Frozen cooked pasta should be thawed in the refrigerator
the shelf in an airtight container in a dry area that is not and not on the kitchen counter.
exposed to extreme temperature. The sauce should be refrigerated separate from the pasta
Dried pasta can be stored indefinitely and still be safe to and can be stored for 6 or 7 days. This prevents the pasta
eat but the USDA recommends storing dried pasta for no from soaking up too much flavor and oil from the sauce,
more than two years to obtain the best quality. which causes the taste of the pasta to be drowned out.
Some manufacturers will stamp their packages with a "best If the pasta is stored together with the sauce, it should be
if used by" date, which indicates that the flavor, color and eaten within 1 or 2 days to limit the amount of sauce that is
nutritional value may be affected if used beyond that date. absorbed.
2. Cooked Pasta If cooked pasta is not going to be used within the suggested
Pour the noodles into a colander. Allow as much moisture time period, it should be frozen and then it can be stored
as possible to drain. Noodles left in standing water become for approximately 3 months.
overly soft and mushy. Frozen cooked pasta should be thawed in the refrigerator
Sprinkle 1 tsp. salad oil over the noodles. Toss the pasta so and not on the kitchen counter.
the noodles are evenly coated in the oil. Salad oil prevents When refrigerating or freezing cooked pasta, be sure it is
the pasta from sticking together. stored in a well-sealed container so that it does not absorb
any odor.
Cooked lasagna and baked pasta dishes can be refrigerated If you are going to use the pasta on the same day as it is
or frozen in the same manner as plain cooked pasta. made, you can allow it to dry on a clean towel for a couple
The lasagna and casseroles should be first cut into of hours before you cook it unless it is stuffed pasta. Stuffed
individual servings before placing them in a sealed bag or pasta, such as ravioli, should be cooked within half an hour,
container. This will make it easier when reheating. otherwise it will begin to discolor and become damp.
The lasagna and baked pasta dishes can be refrigerated for 4. Frozen pasta does not have to be thawed before it is
3 or 4 days or they can be placed in a freezer and kept for cooked. Just place the frozen pasta into boiling water and
approximately 3 months. If frozen, the pasta dish should be reheat it. It will need to cook a little longer than unfrozen
thawed in the refrigerator and not on the kitchen counter. pasta.
3. Fresh Pasta Tips & Warnings
Fresh pasta should ideally be used on the same day as • Store pasta sauce separate from the noodles, otherwise
manufactured. the noodles will become mushy.
This is not always possible, but if it is used within the next • You can freeze cooked pasta but it may be too soft once
two days it will give adequate results. After this it tends to thawed. Use frozen pasta in baked dishes so the softer
crack through excess drying. texture is not noticeable.
It must be stored, keep it well-covered in the fridge, to QUARTER II
minimize the risk of this happening. PREPARE VEGETABLE AND SEAFOOD DISHES
Frozen filled pastas will keep for up to three months if held Overview
at -18oC or lower. This quarter will guide you, learners to acquire the essential
Fresh pasta can be stored in the refrigerator for 2 or 3 days. knowledge and competencies and develop your skills with
If the pasta will not be used within that time, it can be understanding in the preparation, cooking, presentation,
frozen and stored in the freezer for 2 to 3 months. and storing vegetables and seafood dishes.
Homemade pasta can be stored in the refrigerator for 1 or Products/performances required in every activity will help
2 days or frozen for 2 to 3 months. you to practice gained understanding.
Homemade pasta can also be allowed to dry thoroughly
and then placed in a plastic bag or airtight container. LESSON 1: PREPARE VEGETABLE DISHES
The length of time it will take to dry will vary depending on Learning Outcome 1: Characteristics of Vegetables
the type of pasta and its size, shape and thickness. 1.1. Different Classification of Vegetables
If dried completely, the pasta can then be stored in a cool
dry place for a couple of months. Vegetables
Are plants or parts of plants like leaves, fruits, tubers, important for proper bowel function. It helps reduce
roots, bulbs, stems, shoots, and flower used in a dish constipation and diverticulosis. Fiber-containing
either raw or cooked. foods such as vegetables help provide a feeling of
Give color, texture and flavor to our meals. fullness with fewer calories.
They also give vitamins and minerals. Folate (folic acid) helps the body form red blood cells.
Provide nutrients vital for health and maintenance of Women of childbearing age who may become
your body. pregnant should consume adequate folate from
Eating vegetables provides health benefits to people foods, and in addition, 400 mcg of synthetic folic acid
like reduced risk of some chronic diseases including from fortified foods or supplements. This reduces the
heart attack and stroke, protect them against certain risk of neural tube defects, spinal bifida, and
types of cancers, reduce obesity and type two anencephaly during fetal development.
diabetes, lower blood pressures, reduce the risk of 2. According to Chemical Composition
developing kidney stones and help decrease bone Carbohydrates-rich vegetables – seeds, roots, tubers
loss. Protein-rich vegetables –legumes, peas, beans
Are important sources of many nutrients, including Fat-rich vegetables – nuts, olives, avocado
potassium, dietary fiber, folate (folic acid), vitamin A, High moisture content – mushroom, tomatoes, radish,
and vitamin C. green leafy vegetables
Diets rich in potassium may help maintain normal
blood pressure. Vegetable sources of potassium
include sweet potatoes, white potatoes, white beans,
tomato products (paste, sauce, and juice), beet
greens, soybeans, lima beans, spinach, lentils, and
kidney beans.
Vitamin A keeps eyes and skin healthy and helps to
protect against infections.
Vitamin C helps heal cuts and wounds, and keeps
teeth and gums healthy. Vitamin C aids in iron
absorption.
Dietary fiber from vegetables, as part of an overall
healthy diet, helps reduce blood cholesterol levels
and may lower risk of heart disease. Fiber is
You might also like
- Anaemia in PregnancyDocument81 pagesAnaemia in PregnancyEmmanuel Kings80% (5)
- WTR Grade 10Document9 pagesWTR Grade 10Danilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Prepare Cereals and StarchDocument59 pagesLesson 2 Prepare Cereals and StarchMarry Jane Lustre CanabalNo ratings yet
- Prepare Cereals and StarchDocument30 pagesPrepare Cereals and StarchLucille PaglingayenNo ratings yet
- Cereals and StarchDocument31 pagesCereals and StarchSheryl Borromeo100% (1)
- Cookery 10 Cereals and StarchDocument62 pagesCookery 10 Cereals and StarchHANNA CLAIRE ROSAL100% (1)
- Cookery Grade 10 - Quarter-I-Module 2Document39 pagesCookery Grade 10 - Quarter-I-Module 2Van ImperialNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Q3 Week 2Document13 pagesCookery 10 Q3 Week 2Samantha MusniNo ratings yet
- Q3W5 TleDocument12 pagesQ3W5 TlePauli Ann BumanlagNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2JonardNadelaNo ratings yet
- Cookery9 Q3 W6 Prepare SauceDocument9 pagesCookery9 Q3 W6 Prepare SauceRomnick CosteloNo ratings yet
- Written Work in Cookery Part of Fish Second GradingDocument1 pageWritten Work in Cookery Part of Fish Second GradingVincent LibreaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Week 5 8 Cookery Final 2Document32 pagesQ3 - Week 5 8 Cookery Final 2It's Me JohnNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 3 Las 3Document4 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 3 Las 3Michole Godwin RegalaNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 - Mod - 4.1-4.2Document7 pagesCOOKERY 10 - Mod - 4.1-4.2Charmaigne GalvezNo ratings yet
- FINAL Module Grade 10 1st Quarter 2021 2022Document74 pagesFINAL Module Grade 10 1st Quarter 2021 2022Alfon John BoadillaNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Cook Meat: Cookery 10 School Year 2019 - 2020Document43 pagesPrepare and Cook Meat: Cookery 10 School Year 2019 - 2020Alodie Dela Raiz AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Prepare Soups Required For Menu Items 4TH Q WEEK2Document18 pagesPrepare Soups Required For Menu Items 4TH Q WEEK2De ShangNo ratings yet
- Cookery9 Q3 W8 Prepare SauceDocument11 pagesCookery9 Q3 W8 Prepare SauceRomnick CosteloNo ratings yet
- 04 LO 1 POULTRY Miseen PlaceDocument31 pages04 LO 1 POULTRY Miseen PlaceCanals MaxermelaNo ratings yet
- Physical Structure of An Egg Grade 10Document15 pagesPhysical Structure of An Egg Grade 10Jessa Brigole TorresNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics-Cookery Performing Mise' en PlaceDocument10 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics-Cookery Performing Mise' en PlaceConstancia PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan q3 Week 6 g10 CookeryDocument4 pagesLesson Plan q3 Week 6 g10 CookeryJohnnexter GubatNo ratings yet
- Final Cookery10 q4 Module 4Document16 pagesFinal Cookery10 q4 Module 4eda gadoyNo ratings yet
- TLE-10 Cookery Module2 Week2Document6 pagesTLE-10 Cookery Module2 Week2arjeangrace delosreyesNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Quarter 1Document6 pagesWeek 5 - Quarter 1Teddy RaquelNo ratings yet
- Store and ReconstituteDocument20 pagesStore and ReconstituteDiane Vill100% (1)
- Final Cookery 12 q3 Module 5Document22 pagesFinal Cookery 12 q3 Module 5Elle GatchNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Observation 23Document19 pagesCookery 10 Observation 23Shery Cantago100% (1)
- 3rdquarter 10 CookeryDocument76 pages3rdquarter 10 CookeryJeah Asilum DalogdogNo ratings yet
- Tle q2 Cookery Weeek 5 8Document16 pagesTle q2 Cookery Weeek 5 8Chasie Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 3 Las Number 8Document7 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 3 Las Number 8Zhen Reas AmpoNo ratings yet
- Tle 1o q4 ModuleDocument22 pagesTle 1o q4 ModuleRhea AnselmoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Cookery 10Document93 pagesReviewer in Cookery 10Arneil RealizaNo ratings yet
- TLE 10 Q2 Cokery-Seafood AS#1Document6 pagesTLE 10 Q2 Cokery-Seafood AS#1CYRIL DOMENS0% (1)
- Cookery-10 LAS-Q3 Week6Document6 pagesCookery-10 LAS-Q3 Week6Angeline CortezNo ratings yet
- Cookery - 10-Quarter 4-Week-1Document12 pagesCookery - 10-Quarter 4-Week-1Ereca Mae Papong100% (1)
- Tle Cookery-10 - 4TH QuarterDocument34 pagesTle Cookery-10 - 4TH QuarterPatrick Dave San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Quarter IVTLE - M1-5 - wk1-5Document32 pagesQuarter IVTLE - M1-5 - wk1-5Villa WengzyNo ratings yet
- 10 Cookery 10 Q1 M1Document42 pages10 Cookery 10 Q1 M1Sheryn Mae Purisima De VeraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Preparing Fish and Seafood Dishes A. Seafood: Definition, Types, and CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesLesson 1: Preparing Fish and Seafood Dishes A. Seafood: Definition, Types, and CharacteristicsReygina Mae Sibayan Palaganas100% (2)
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics - COOKERYDocument25 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics - COOKERYCristy MonjeNo ratings yet
- Glak Tle-Cookery-10 Q-3 WK 5-6Document14 pagesGlak Tle-Cookery-10 Q-3 WK 5-6adadNo ratings yet
- Lo 2 .... 3rd QuarterDocument24 pagesLo 2 .... 3rd QuarterMarcelina MedranoNo ratings yet
- Lx49l0a7r - Weeks 26 and 27 - TLE 10.docx - Approved - JCC - Docx - Office Copy - JCCDocument8 pagesLx49l0a7r - Weeks 26 and 27 - TLE 10.docx - Approved - JCC - Docx - Office Copy - JCCDI ANNo ratings yet
- Storing & ReconstituteDocument1 pageStoring & ReconstituteRochelle Jossanah OsalNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Cookery LAS Week 1-8 2nd QuarterDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Cookery LAS Week 1-8 2nd Quarteradad100% (1)
- Final Cookery12 q3 Module 6Document24 pagesFinal Cookery12 q3 Module 6Elle GatchNo ratings yet
- Market Forms of EggDocument2 pagesMarket Forms of EggBrix Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Selecting Good Quality Poultry and GameDocument11 pagesSelecting Good Quality Poultry and GameCheriel Alcala Calledo100% (1)
- Tle 1o No. 7Document15 pagesTle 1o No. 7Juvelyn MundoyNo ratings yet
- TLE9 COOKERY Q3 M2 Different-Sandwich-Ingredients FVDocument10 pagesTLE9 COOKERY Q3 M2 Different-Sandwich-Ingredients FVgwenNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 CookeryDocument18 pagesMODULE 1 CookeryMaribel B GarciaNo ratings yet
- TLE10 Module 3Document14 pagesTLE10 Module 3Leyzyl Nieves MaravillasNo ratings yet
- Learning OUTCOME 3 PlatingDocument10 pagesLearning OUTCOME 3 PlatingrichardNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 3 LAS Number 3Document11 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 3 LAS Number 3Constancia PerezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10: Tle - He (Cookery 10) Quarter 1 - Prepare Egg Dishes Module 2-Prepare and Cook Egg DishesDocument12 pagesGrade 10: Tle - He (Cookery 10) Quarter 1 - Prepare Egg Dishes Module 2-Prepare and Cook Egg DishesTIPAY, EMELIE L.No ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education Home Economics-Cookery: Storing MeatDocument13 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education Home Economics-Cookery: Storing MeatConstancia PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Lo#2Document28 pagesLesson 2 Lo#2Marcelina Medrano100% (1)
- Cereals PastaDocument17 pagesCereals PastaSarah Jean Erika SebastianNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Prepare Cereals and Starch: Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise'en Place (Week 5)Document19 pagesLesson 2 Prepare Cereals and Starch: Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise'en Place (Week 5)BERNARDO VIZARRANo ratings yet
- MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin)Document7 pagesMCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin)U WidNo ratings yet
- A Review On Effects of Metformin On Vitamin B12status PDFDocument9 pagesA Review On Effects of Metformin On Vitamin B12status PDFJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- The Relevance of Nutrition To Pediatric Oncology - A Cancer Control Perspective - PEDIATRIC BLOODDocument8 pagesThe Relevance of Nutrition To Pediatric Oncology - A Cancer Control Perspective - PEDIATRIC BLOODGUSTAVO BELLONo ratings yet
- CHN Rationalization 9 16Document22 pagesCHN Rationalization 9 16joyNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University Nursing ThesisDocument8 pagesRajiv Gandhi University Nursing Thesistracyaldridgejackson100% (2)
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument5 pagesVitamins and Mineralsdheeptha sundar100% (1)
- Mapeh 10Document5 pagesMapeh 10Flora MacaougasNo ratings yet
- Anaemia in PregnancyDocument15 pagesAnaemia in PregnancyNorshahidah Ieda100% (1)
- FinalDocument101 pagesFinalVimal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- All Case Studies Blood Student Copy FINAL 2019Document14 pagesAll Case Studies Blood Student Copy FINAL 2019saud rehmanNo ratings yet
- Cookery10vegetables 190117235613Document43 pagesCookery10vegetables 190117235613Meach CallejoNo ratings yet
- Diapositivas Del Dr. Walsh - Nutrient TherapyDocument90 pagesDiapositivas Del Dr. Walsh - Nutrient TherapyLucasNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document80 pagesVitamin B12Anand Veeranan100% (1)
- Prevention and Tratment of Iron-Deficiency AnaemiaDocument12 pagesPrevention and Tratment of Iron-Deficiency Anaemiaطارق رشيد100% (1)
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur: Presentation On Anemia and Nutritional DeficiencyDocument7 pagesGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur: Presentation On Anemia and Nutritional Deficiencypriyanka100% (2)
- Anemias of Abnormal Nuclear DEVELOPMENT: Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument24 pagesAnemias of Abnormal Nuclear DEVELOPMENT: Megaloblastic AnemiaSukhrian MuhdaNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition: Dr. Radhika KapurDocument15 pagesFood and Nutrition: Dr. Radhika Kapurthat's my dream to workNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Healthy PregnancyDocument13 pagesPractice Paper Healthy Pregnancytimea_gheneaNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients Vitamins Report 3Document53 pagesMicronutrients Vitamins Report 3XanderNo ratings yet
- Ept 6Document16 pagesEpt 6dianela fionaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument120 pagesAnemiagaddam narasimhaNo ratings yet
- Anemia Saranya Ranjith PresentationDocument23 pagesAnemia Saranya Ranjith PresentationSaranya DeviNo ratings yet
- g10 Quarter 2 Module 3 and Module 4Document41 pagesg10 Quarter 2 Module 3 and Module 4KieshaNo ratings yet
- RFP FRK 9800 NMEL 28dec22Document45 pagesRFP FRK 9800 NMEL 28dec22durgaprasadNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12: Harsha Vardhini.SDocument17 pagesVitamin B12: Harsha Vardhini.SScindiaaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics Rajiv Gandhi UniversityDocument8 pagesDissertation Topics Rajiv Gandhi UniversityHelpWriteMyPaperUK100% (1)
- Prenatal SuppsDocument14 pagesPrenatal SuppsJessNo ratings yet
- Vitamin ChatDocument9 pagesVitamin Chatnusdar20No ratings yet
- UNIT II SulfonamidesDocument12 pagesUNIT II SulfonamidesTasya MadifaNo ratings yet