Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Astm 3183-84
Astm 3183-84
Uploaded by
Hartojo siahaan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesASTM
Original Title
ASTM 3183-84
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentASTM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesAstm 3183-84
Astm 3183-84
Uploaded by
Hartojo siahaanASTM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 4
iy Designation: D 2240 - 91
Standard Test Method for
Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness"
“This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2240; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
Tea wopion or in ne case of ewsion the year of lst revision A umber in parntheasindicses the year of ast reapproval. A
Sttercriptepilon (indicates an editorial change since the lst revision oF reapprova
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes seven types of durometers
A, B, C, D, DO, O and OO, and the procedure for
determining indentation hardness of substances classified as
rubber, cellular materials, elastomeric materials, thermo-
plastic elastomers and some hard plastics.
1.2 This test method is not applicable to the testing of
fabrics.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. The values given in parentheses are for informa-
tion only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
Insulating Materials for Testing?
D785 Test Method for Rockwell Hardness of Plastics and
Electrical Insulating Materials?
D 1349 Practice for Rubber—Standard Temperatures For
Testing?
14483 Practice for Determining Precision for Test
Method Standards in the Rubber and Carbon Black
Industries?
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 This test method permits hardness measurements
based on either initial indentation or indentation after a
specified period of time, or both.
Note 1—Durometers with maximum reading pointers used to
determine initial hardness values may yield lower hardness when the
‘maximum pointer is used,
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method is based on the penetration of a
specific type of indentor when forced into the material under
specified conditions. The indentation hardness is inversely
related to the penetration and is dependent on the clastic
‘modulus and viscoelastic behavior of the material. The shape
of the indentor and the applied force influence the results
1 This est method is under the juridition of ASTM Commitee D-11 on
‘Rubber and isthe det responsibilty of Subcommittee D110 on Physical Tests,
‘Curren edition approved May 15, 1991. Publshed February 1992. Ongally
published as D 2240 ~ 64. Last previous edition D 2240 ~ 86
* Annual Book af ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01
2 dnmual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01
388,
‘obtained so there may be no simple relationship between the
results obtained with one type of durometer and those
obtained with another type of durometer or other instru-
‘ments for measuring hardness. This test method is an
empirical test intended primarily for control purposes. No
simple relationship is known to exist between indentation
hardness determined by this test method and any funda-
mental property of the material tested. For specification
purposes itis recommended that Test Method D 785 be used
for hard material.
Note 2—Durometer scale comparison chart only. This is not and
cannot be used as a conversion reference
Typed 10 20 3040 $0 60 70 80 90 100
Type 10 20 30 40 $0 60 70 80 80 100
Tye 10. 20-304 $0 60 70 20 90 100
Type D. 1020 30 40 50 60 60 70 $0 90 100
Type DO 10 20 3 4 9 6 70 8 90 100
Tye 0 10 20 30-40 $9 60 70 80 80 100
Type00 10 20 30405060 7080 90 100
5. Apparatus
5.1 Hardness measuring apparatus or durometer con-
sisting of the following components:
S.L.1 Presser Foot, with a hole having a diameter as
specified in Fig. 1(a), 1(5), or 1(¢) with its center 6 mm (0.25
in.) from any edge of the foot.
5.1.2 Indentor, formed from hardened steel rod and
shaped in accordance with Fig. 1(a), 1(b), or 1(c) with full
extension adjustable between 2.46 to 2.54 mm (0,97 t0 0.100
in.)
5.1.3 Indentor Extension Indicating Device (analog or
electronic), having a scale reading from 0 to 100 with equal
divisions throughout the range. The scale reading is an
inverse function of the indentor extension, The device shall
have a pointer that moves on the scale at a rate of one
hardness point for each 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) of indentor
‘movement.
Nore 3—Type A Shore Durometers serial numbers 1 through
16 300 and 16 351 through 16900 and Type A-2 Shore Durometers
numbers I through 8077 do not meet the requirement of 2.46 to 2.54
‘mm (0.097 to 0,100 in, extension of the indentor at zero reading. These
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Step by Step Tutorial Civil 3DDocument32 pagesStep by Step Tutorial Civil 3DHartojo siahaan100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
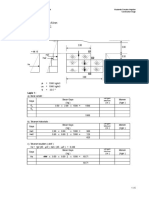
- Stabilitas Bronjong Pengarah Aliran DI. Welamosa (Mautenda III)Document5 pagesStabilitas Bronjong Pengarah Aliran DI. Welamosa (Mautenda III)Hartojo siahaan100% (2)
- Jabker Daring - 28 - 12Document1 pageJabker Daring - 28 - 12Hartojo siahaanNo ratings yet
- Haki Presentation ShamsulDocument33 pagesHaki Presentation ShamsulHartojo siahaanNo ratings yet
- Widjojo Adi PrakosoDocument6 pagesWidjojo Adi PrakosoHartojo siahaanNo ratings yet
- Downfile PDFDocument11 pagesDownfile PDFHartojo siahaanNo ratings yet
- Methods For Quantitative Assessment of Passenger Flow Influence On Train Dwell Time v2 PDFDocument24 pagesMethods For Quantitative Assessment of Passenger Flow Influence On Train Dwell Time v2 PDFHartojo siahaanNo ratings yet