Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Test Parameters Descriptions
Blood Test Parameters Descriptions
Uploaded by
Sachin JainCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Drugs and Substance Abuse PDFDocument8 pagesDrugs and Substance Abuse PDFMaria Aminta CacerecesNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Pump Selection and Application: Date Assigned: 6 December 2020 Date Due: 14 December 2020 Instructions To CandidatesDocument4 pagesPump Selection and Application: Date Assigned: 6 December 2020 Date Due: 14 December 2020 Instructions To CandidatesSelesteNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Cardiovasular DiseaseDocument62 pagesNutrition in Cardiovasular DiseaseMalisa Fitri UmarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Metabolic SyndromeDocument59 pagesNutrition in Metabolic SyndromeRadya AgnaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Result and InterpretationDocument11 pagesLaboratory Result and Interpretationtzuquino Emz100% (1)
- Anti Hyper Lip I de MicsDocument7 pagesAnti Hyper Lip I de MicsAravinthNo ratings yet
- Screening and Management of DyslipidemiaDocument16 pagesScreening and Management of DyslipidemiaSakina GhaziNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Lipid MetabolismDocument41 pagesInborn Errors of Lipid MetabolismWalterNo ratings yet
- Alanine Aminotransferase Alt, GPT, SGPT: Iu/L Kat/lDocument8 pagesAlanine Aminotransferase Alt, GPT, SGPT: Iu/L Kat/lLuis Ferdinand Dacera-Gabronino Gamponia-NonanNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Cardiovascular Disease 2013Document30 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Cardiovascular Disease 2013ashry909100% (1)
- Heart FailureDocument24 pagesHeart Failureapi-435424684No ratings yet
- Nutrition of Liver Disease in Pediatric: Hvck1: Lê TânDocument30 pagesNutrition of Liver Disease in Pediatric: Hvck1: Lê TânLê TânNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseases and Hyperlipidemias: Continuing.Document19 pagesCardiovascular Diseases and Hyperlipidemias: Continuing.Zai ZaiNo ratings yet
- Diet and Diabetes MellitusDocument17 pagesDiet and Diabetes MellitusBumanghat ElviraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Atherosclerosis N Fatty LiverDocument24 pagesLecture 11 Atherosclerosis N Fatty Livernironkushbhuyan2002No ratings yet
- Background: PTH-mediated HypercalcemiaDocument3 pagesBackground: PTH-mediated HypercalcemiaDiana TardecillaNo ratings yet
- Equilíbrio Veterinary Product KnowledgeDocument141 pagesEquilíbrio Veterinary Product KnowledgeDerlin NahariNo ratings yet
- Independent Work Topic: AnemiaDocument23 pagesIndependent Work Topic: AnemiaFizzahNo ratings yet
- Group 1 HypokalemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 1 HypokalemiaAdegboye AdedayoNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeDocument19 pagesHepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeRacha MougharbelNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis and Vitamin D Deficiency: Muhammad Asif Shaheen Lecturer Pathology KEMU, LahoreDocument21 pagesPancreatitis and Vitamin D Deficiency: Muhammad Asif Shaheen Lecturer Pathology KEMU, LahoreSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- DyslipidemiaDocument20 pagesDyslipidemiaapi-261438047No ratings yet
- HypocalcemiaDocument2 pagesHypocalcemiaRachel Frances SorillaNo ratings yet
- Group CDocument39 pagesGroup CKhushboo IkramNo ratings yet
- Hyperlipidemia: Revised: October 4, 2019Document7 pagesHyperlipidemia: Revised: October 4, 2019HannaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For HyperlipidemiaDocument29 pagesDrugs For Hyperlipidemiasultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Carbohydrate 1Document39 pagesLecture 1 Carbohydrate 1mer12sswNo ratings yet
- GERIADocument8 pagesGERIAmoncalshareen3No ratings yet
- Presentation On CHEMICALDocument12 pagesPresentation On CHEMICALOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Patients With Cardiovascular Disorders Lec 6Document14 pagesNutrition For Patients With Cardiovascular Disorders Lec 6Youssif MenamNo ratings yet
- Hyproliferative Anemias: What Is Anemia?Document15 pagesHyproliferative Anemias: What Is Anemia?yamie sulongNo ratings yet
- Uworld Notes CK PDFDocument123 pagesUworld Notes CK PDFNik KalairNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Phase 2Document65 pagesSession 4 Phase 2ayoub shams mohamedNo ratings yet
- Metabolic SyndromeDocument55 pagesMetabolic SyndromeAakash BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- 13 Antihyperlipidemic Drugs 7Document8 pages13 Antihyperlipidemic Drugs 7Md MurtazaNo ratings yet
- DR Pravin Final Paper UploadDocument5 pagesDR Pravin Final Paper Uploadrahumics256No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykymsh_kimNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of Hyperlipidemia: Philip Marcus, MD MPHDocument56 pagesDrug Treatment of Hyperlipidemia: Philip Marcus, MD MPHVictor EkutaNo ratings yet
- Lab Data InterpretationDocument38 pagesLab Data Interpretationraziajaffery14No ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureJashine DajayNo ratings yet
- ATI Med Surg TipsDocument17 pagesATI Med Surg Tipsmike Gee100% (5)
- Laboratory Values: Serum SodiumDocument3 pagesLaboratory Values: Serum SodiumVincentNo ratings yet
- Lecture Anti Hyperlipidemic DrugsDocument21 pagesLecture Anti Hyperlipidemic DrugsNowfal Hasan SiamNo ratings yet
- LipoproteinemiaDocument50 pagesLipoproteinemiaShajeer Salim67% (6)
- CVD HTN Case Study AssignmentDocument7 pagesCVD HTN Case Study Assignmentapi-353723892No ratings yet
- Asuhan Gizi Pada CVDDocument38 pagesAsuhan Gizi Pada CVDEva MutiarasariNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Blood TestsDocument6 pagesDictionary of Blood Teststvland1098No ratings yet
- Lipid Lowering AngentDocument22 pagesLipid Lowering AngentDave BraveNo ratings yet
- Renal MNTDocument58 pagesRenal MNTMARIA TARIQNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyHomework Ping100% (2)
- Nutrition 409 - Case 12Document2 pagesNutrition 409 - Case 12api-252471038No ratings yet
- LO 1 HematoDocument6 pagesLO 1 HematobeatriceNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION For Renal Diseases 1Document15 pagesNUTRITION For Renal Diseases 1Cristina AdolfoNo ratings yet
- HypercalcemiaDocument39 pagesHypercalcemiaPrajina KansakarNo ratings yet
- Metabolic DR - RehabDocument24 pagesMetabolic DR - RehabMohammed Saad NabhanNo ratings yet
- LC HyperlipidemiaDocument11 pagesLC Hyperlipidemiaabdul basithNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret Your Blood Test ResultsDocument23 pagesHow To Interpret Your Blood Test Resultstin1625100% (1)
- Health Disorders & DietDocument120 pagesHealth Disorders & DietHannaniah Gabriel AmanteNo ratings yet
- Ald & MasldDocument19 pagesAld & MasldAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- 340 Final StudyDocument21 pages340 Final StudyLeah ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- ASSOCHAM - Upcoming Events List Week 27th July To 2nd Aug 2020 - CirculationDocument2 pagesASSOCHAM - Upcoming Events List Week 27th July To 2nd Aug 2020 - CirculationSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Getting Started Oracle CloudDocument77 pagesGetting Started Oracle CloudSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Functional Testing Suite Advanced Pack For Oracle E-Business Suite - Property ManagerDocument34 pagesOracle® Functional Testing Suite Advanced Pack For Oracle E-Business Suite - Property ManagerSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Your Dob Today Your Age: Years Months and DaysDocument13 pagesYour Dob Today Your Age: Years Months and DaysSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Burn Down Chart: Burned Down Balance Day Planned Actual Planned Actual Done TodayDocument2 pagesBurn Down Chart: Burned Down Balance Day Planned Actual Planned Actual Done TodaySachin JainNo ratings yet
- Cond Format Icon Set LogicDocument2 pagesCond Format Icon Set LogicSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Employees' Pension Scheme - 95 Calculator: Particulars Date MonthDocument2 pagesEmployees' Pension Scheme - 95 Calculator: Particulars Date MonthSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Aged Accounts Receivable: (Enter UW Department Name) (Enter Date)Document5 pagesAged Accounts Receivable: (Enter UW Department Name) (Enter Date)Sachin JainNo ratings yet
- Retirement PlanningDocument2 pagesRetirement PlanningSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Sprint Burndown Chart TemplateDocument9 pagesSprint Burndown Chart TemplateSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Sample DocumentationDocument44 pagesSample DocumentationSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Unix Shell Programming WorkshopDocument35 pagesUnix Shell Programming WorkshopSachin JainNo ratings yet
- DNA Book 12 Cover PDFDocument1 pageDNA Book 12 Cover PDFSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Payment Details Report: Orders Under This TransactionDocument1 pagePayment Details Report: Orders Under This TransactionSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Poster Sample BookDocument1 pagePoster Sample BookSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Elasticsearch, Logstash and KibanaDocument11 pagesElasticsearch, Logstash and KibanaSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Operating System VirtualizationDocument13 pagesOperating System VirtualizationSachin JainNo ratings yet
- SQL Loader1Document4 pagesSQL Loader1Sachin JainNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Edge TestDocument11 pagesBig Bang Edge TestAman VimayuNo ratings yet
- John Blue - DP 139 Diaphragm Pump - Parts and Instruction Manual - 7 M 17 - 0622Document12 pagesJohn Blue - DP 139 Diaphragm Pump - Parts and Instruction Manual - 7 M 17 - 0622Dung PhamNo ratings yet
- Quick Test 2 - LEVEL 7Document3 pagesQuick Test 2 - LEVEL 7Matías MocilnikarNo ratings yet
- Im12a01f01 03enDocument95 pagesIm12a01f01 03enkjonasamNo ratings yet
- Synergy Shuttle ConveyorDocument5 pagesSynergy Shuttle ConveyorTamal Tanu RoyNo ratings yet
- Beermom Ism c10Document164 pagesBeermom Ism c10joão victor carvalho100% (1)
- 02.1-WCDMA Basic Principle of Radio Propagation - 20051214Document20 pages02.1-WCDMA Basic Principle of Radio Propagation - 20051214kltowerNo ratings yet
- Catalog 2019 Jyhy DieselDocument10 pagesCatalog 2019 Jyhy DieselAndre vatar andreNo ratings yet
- The Berkeley Review: MCAT Chemistry Atomic Theory PracticeDocument37 pagesThe Berkeley Review: MCAT Chemistry Atomic Theory Practicerenjade1516No ratings yet
- Hick's Law Lab 1Document6 pagesHick's Law Lab 1Merna SamieNo ratings yet
- Webhunt Conor FoleyDocument3 pagesWebhunt Conor Foleyapi-367746310No ratings yet
- Flow in Pipe: Characteristic LengthDocument9 pagesFlow in Pipe: Characteristic Lengthguapo93No ratings yet
- Learning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Document18 pagesLearning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Zyke NovenoNo ratings yet
- NBRK0200 Installation Configuration ManualDocument32 pagesNBRK0200 Installation Configuration ManualGoran JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Glossary CambridgeDocument14 pagesGlossary CambridgeAlexey PetrovNo ratings yet
- Terreal Facing Brick BrochureDocument32 pagesTerreal Facing Brick BrochuresmdiviNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts ManagementDocument19 pagesSpare Parts ManagementdaveferalNo ratings yet
- Gabisan Let Scheck1 PDFDocument3 pagesGabisan Let Scheck1 PDFEdrick Paras100% (1)
- Text 1 (A & B)Document2 pagesText 1 (A & B)ifx leeNo ratings yet
- Learn Astrology PDFDocument45 pagesLearn Astrology PDFRajagopal Rao85% (20)
- Colour BalanceDocument2 pagesColour Balancenghi100% (1)
- Bhel Training ReportDocument32 pagesBhel Training ReportVivek PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sustainability PackagingDocument3 pagesSustainability Packagingdong.quan.1705No ratings yet
- Selina Concise Physics Solutions Class 6 Chapter 1 MatterDocument22 pagesSelina Concise Physics Solutions Class 6 Chapter 1 MatterAltaf TalpurNo ratings yet
- Acustica Ruby EbonyDocument1 pageAcustica Ruby EbonyZizja TurtleNo ratings yet
- Math10 - Q4 - Weeks 1 - 2Document30 pagesMath10 - Q4 - Weeks 1 - 2Rogelio Canuel Jr.No ratings yet
- Mates Orals SyllabusDocument3 pagesMates Orals SyllabusmahmutNo ratings yet
- Intel System Management Specification - Rev2p0Document63 pagesIntel System Management Specification - Rev2p0Nisarg UpadhyayNo ratings yet
Blood Test Parameters Descriptions
Blood Test Parameters Descriptions
Uploaded by
Sachin JainOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Test Parameters Descriptions
Blood Test Parameters Descriptions
Uploaded by
Sachin JainCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Test Parameter Descriptions
Serum Uric Acid
Uric acid is by-product of purine metabolism and its excess quantity is excreted in urine. Uric acid can
crystallize in the urinary tract in acidic urine. Its level varies day to day should be repeated over several
days or weeks. Serum accumulation of uric acid can lead to a type of arthritis known as gout. Acute attacks
of gout can occur even when serum urate level is normal. Saturation levels of uric acid in blood may result
in one form of kidney stones when the urate crystallizes in the kidney.
Conditions associated with increased Uric Acid Level: Diminished renal excretion of uric acid (as in
renal impairment), certain drugs (diuretics, low doses of aspirin, pyrazinamide), gout, myxedema,
hyperparathyroidism, lactic acidosis, high intake of purine-rich foods or fructose intake, cancers, diabetes
(severe), hemolytic anemia etc.
Conditions associated with decreased Uric Acid Level: Wilsons Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Folic Acid
Deficiency anemia Burn, Pregnancy, decreased intake of purine-rich food etc.
Opinion & Advice
Uric acid level should be repeated at multiple occasion to derive a conclusive diagnosis.
People with increased Uric acid level are advised to undergo: KFT at regular intervals. Such people should
avoid foods rich in purine.
Decreased uric acid level is of little significance.
Calcium
Calcium is found most abundantly in bones and teeth. Calcium is necessary for the transmission of nerve
impulses and contraction of the myocardium & skeletal muscles. it causes blood clotting. Long-term calcium
deficiency can lead to rickets and poor blood clotting and in case of a menopausal woman, it can lead to
osteoporosis. The purpose of this test is to check for serum calcium excess or deficit, to monitor calcium
levels & to detect calcium imbalance
Conditions associated with increased calcium levels: Hypervitaminosis D, hyperparathyroidism ,
malignant neoplasm of the bone, multiple myeloma etc.
Conditions associated with decreased calcium levels: Diarrhoea, malabsorption of calcium from the
gastrointestinal tract, extensive infections, burns, lack of calcium and vitamin D intake, hypoparathyroidism,
chronic renal failure caused by phosphorus retention, alcoholism, pancreatitis etc.
People with deranged serum calcium levels are advised to undergo: ionic calcium, phosphorus and serum
PTH.
Cholestrol
The purpose of this test is to check/monitor blood cholesterol level. Serum cholesterol is used as an
indicator of atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease and is an important screening test for heart disease.
Condition associated with increased cholesterol levels : Familial (hereditary) tendency, abnormal dietary
intake, alcoholism, hypothyroidism, Acute MI, nephrotic syndrome, pancreatectomy, biliary obstruction,
pregnancy (third trimester), dru influence such as aspirin, corticosteroids, steroids, oral contraceptives,
vitamin A & D, etc
Condition associated with decreased cholesterol levels: Hypo-alpha lipoproteinemia, Hyperthyroidism,
Malabsorption syndrome, starvation, chronic anemia etc.
People with increased cholesterol levels are advised to undergo: Lipid Profile and Apolipoprotein A &
B at regular intervals.
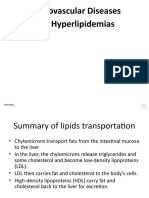
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are blood lipids formed by esterification of glycerol and three fatty acids and are carried by
the serum lipoproteins. The intestine processes the triglycerides from dietary fatty acid and they are
transported in the blood stream as chylomicrones. A function of triglycerides is to provide energy to heart
and skeletal muscles. Triglycerides are major contributor to arterial diseases. As the concentration of
triglycerides increases, so will the VLDL increases. A peak concentration of chylomicron associated
triglycerides occurs within 3-6 hrs. after ingestion of fat rich meal. Alcohol intake also causes transient
increase of serum TG level. If TG is more than 400 mg/dl, VLDL cannot be calculated. Conditions
associated with increased TG levels: Hypolipoproteinemia, stress, high carbohydrate or fatty diet, acute MI,
hypertension, cerebral thrombosis, hypothyroidism, uncontrolled diabetes, pancreatitis, pregnancy etc.
Conditions associated with decreased TG levels: Hyperthyroidism, Hyperparathyroidism, Lipoproteinemia,
protein malnutrition, exercise etc. People with increased levels are advised to undergo Lipid Profile at
regular intervals, Apolipoprotein A & B metabolism of the other lipoproteins and transport of cholesterol
from peripheral tissues to the liver.
High Density Lipoprotein Good Cholesterol
HDL can remove cholesterol from within vascular system and transport it back to liver from excretion or re-
utilization which is why HDL-bound cholesterol is called "Good Cholesterol". Low HDL cholesterol leads to
increased risk for heart disease. High HDL level is an optimal condition considered to be protective against
heart disease. Certain changes in lifestyle can have a positive impact on raising HDL levels, like - Aerobic
exercise, Weight loss, Smoking cessation, removing trans-fatty acids from the diet, adding soluble fiber to
diet, using supplement such as omega 3 fish oil.
HDL detect Hypolipoproteinemia & to monitor Lipid Counts for people with hyerlipoproteinemia.
Conditions associated with increased HDL level: Familial hyper alpha lipoproteinemia, cirrhosis,
alcoholism, hepatitis, Long term aerobic or vigorous exercise. Conditions associated with decreased HDL
level: Familial hypo alpha lipoprotrinemia, Familial hyper triglyceridemia, poorly controlled diabetes mellitus,
chronic renal failure.
Opinion & Advice:
People with decreased levels are advised to undergo Lipid Profile at regular intervals, Apolipoprotein A &
B.
Low HDL level can be raised by diet management, exercise, weight loss & smoking cessation
Low Density Lipoprotein Bad Cholesterol
LDL is a type of lipoprotein that transports cholesterol and triglycerides from the liver to peripheral tissues.
LDL also regulates cholesterol synthesis at these sites. Since high level of LDL cholesterol can cause
problem like cardio vascular disease, it is called "Bad Cholesterol"(as opposed to HDL, the "good
Cholesterol"). It is the largest contributor of atherosclerosis & coronary artery disease.
Conditions associated with increased LDL level: Hypolipoproteinemia, acute MI, hypothyroidism,
diabetes, nephrotic syndrome, multiple myeloma, eclampsia etc.
Conditions associated with decreased LDL level: Chronic obstructive Lung disease, Tangier disease
etc.
Opinion & Advice:
People with increased levels are advised to undergo Lipid Profile at regular intervals, Apolipoprotein A & B
People with increased LDL levels are advised to follow diet management, exercise, weight loss & smoking
cessation
EOSINOPHIL
Respond to parasitic infection and allergic conditions.
ABSOLUTE MONOCYTE COUNT (AMC)
Second line of defense in bacterial infections, respond late during acute phase of infection and inflammatory
process, continue to function till chronic phase of infection.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) is an important water-soluble vitamin. In contrast to other water-soluble vitamins
it is not excreted quickly in the urine, but rather accumulates and is stored in the liver, kidney and other
body tissues. Humans obtain Vitamin B12 exclusively from animal dietary sources, such as meat, eggs and
milk. As a result, a vitamin B12 deficiency may not manifest itself until after 5 or 6 years of a diet supplying
inadequate amounts. Vitamin B12 functions as a methyl donor and works with folic acid in the synthesis of
DNA and red blood cells and is vitally important in maintaining the health of the insulation sheath (myelin
sheath) that surrounds nerve cells.
You might also like
- Drugs and Substance Abuse PDFDocument8 pagesDrugs and Substance Abuse PDFMaria Aminta CacerecesNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Pump Selection and Application: Date Assigned: 6 December 2020 Date Due: 14 December 2020 Instructions To CandidatesDocument4 pagesPump Selection and Application: Date Assigned: 6 December 2020 Date Due: 14 December 2020 Instructions To CandidatesSelesteNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Cardiovasular DiseaseDocument62 pagesNutrition in Cardiovasular DiseaseMalisa Fitri UmarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Metabolic SyndromeDocument59 pagesNutrition in Metabolic SyndromeRadya AgnaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Result and InterpretationDocument11 pagesLaboratory Result and Interpretationtzuquino Emz100% (1)
- Anti Hyper Lip I de MicsDocument7 pagesAnti Hyper Lip I de MicsAravinthNo ratings yet
- Screening and Management of DyslipidemiaDocument16 pagesScreening and Management of DyslipidemiaSakina GhaziNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Lipid MetabolismDocument41 pagesInborn Errors of Lipid MetabolismWalterNo ratings yet
- Alanine Aminotransferase Alt, GPT, SGPT: Iu/L Kat/lDocument8 pagesAlanine Aminotransferase Alt, GPT, SGPT: Iu/L Kat/lLuis Ferdinand Dacera-Gabronino Gamponia-NonanNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Cardiovascular Disease 2013Document30 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Cardiovascular Disease 2013ashry909100% (1)
- Heart FailureDocument24 pagesHeart Failureapi-435424684No ratings yet
- Nutrition of Liver Disease in Pediatric: Hvck1: Lê TânDocument30 pagesNutrition of Liver Disease in Pediatric: Hvck1: Lê TânLê TânNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseases and Hyperlipidemias: Continuing.Document19 pagesCardiovascular Diseases and Hyperlipidemias: Continuing.Zai ZaiNo ratings yet
- Diet and Diabetes MellitusDocument17 pagesDiet and Diabetes MellitusBumanghat ElviraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Atherosclerosis N Fatty LiverDocument24 pagesLecture 11 Atherosclerosis N Fatty Livernironkushbhuyan2002No ratings yet
- Background: PTH-mediated HypercalcemiaDocument3 pagesBackground: PTH-mediated HypercalcemiaDiana TardecillaNo ratings yet
- Equilíbrio Veterinary Product KnowledgeDocument141 pagesEquilíbrio Veterinary Product KnowledgeDerlin NahariNo ratings yet
- Independent Work Topic: AnemiaDocument23 pagesIndependent Work Topic: AnemiaFizzahNo ratings yet
- Group 1 HypokalemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 1 HypokalemiaAdegboye AdedayoNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeDocument19 pagesHepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeRacha MougharbelNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis and Vitamin D Deficiency: Muhammad Asif Shaheen Lecturer Pathology KEMU, LahoreDocument21 pagesPancreatitis and Vitamin D Deficiency: Muhammad Asif Shaheen Lecturer Pathology KEMU, LahoreSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- DyslipidemiaDocument20 pagesDyslipidemiaapi-261438047No ratings yet
- HypocalcemiaDocument2 pagesHypocalcemiaRachel Frances SorillaNo ratings yet
- Group CDocument39 pagesGroup CKhushboo IkramNo ratings yet
- Hyperlipidemia: Revised: October 4, 2019Document7 pagesHyperlipidemia: Revised: October 4, 2019HannaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For HyperlipidemiaDocument29 pagesDrugs For Hyperlipidemiasultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Carbohydrate 1Document39 pagesLecture 1 Carbohydrate 1mer12sswNo ratings yet
- GERIADocument8 pagesGERIAmoncalshareen3No ratings yet
- Presentation On CHEMICALDocument12 pagesPresentation On CHEMICALOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Patients With Cardiovascular Disorders Lec 6Document14 pagesNutrition For Patients With Cardiovascular Disorders Lec 6Youssif MenamNo ratings yet
- Hyproliferative Anemias: What Is Anemia?Document15 pagesHyproliferative Anemias: What Is Anemia?yamie sulongNo ratings yet
- Uworld Notes CK PDFDocument123 pagesUworld Notes CK PDFNik KalairNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Phase 2Document65 pagesSession 4 Phase 2ayoub shams mohamedNo ratings yet
- Metabolic SyndromeDocument55 pagesMetabolic SyndromeAakash BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- 13 Antihyperlipidemic Drugs 7Document8 pages13 Antihyperlipidemic Drugs 7Md MurtazaNo ratings yet
- DR Pravin Final Paper UploadDocument5 pagesDR Pravin Final Paper Uploadrahumics256No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykymsh_kimNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of Hyperlipidemia: Philip Marcus, MD MPHDocument56 pagesDrug Treatment of Hyperlipidemia: Philip Marcus, MD MPHVictor EkutaNo ratings yet
- Lab Data InterpretationDocument38 pagesLab Data Interpretationraziajaffery14No ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureJashine DajayNo ratings yet
- ATI Med Surg TipsDocument17 pagesATI Med Surg Tipsmike Gee100% (5)
- Laboratory Values: Serum SodiumDocument3 pagesLaboratory Values: Serum SodiumVincentNo ratings yet
- Lecture Anti Hyperlipidemic DrugsDocument21 pagesLecture Anti Hyperlipidemic DrugsNowfal Hasan SiamNo ratings yet
- LipoproteinemiaDocument50 pagesLipoproteinemiaShajeer Salim67% (6)
- CVD HTN Case Study AssignmentDocument7 pagesCVD HTN Case Study Assignmentapi-353723892No ratings yet
- Asuhan Gizi Pada CVDDocument38 pagesAsuhan Gizi Pada CVDEva MutiarasariNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Blood TestsDocument6 pagesDictionary of Blood Teststvland1098No ratings yet
- Lipid Lowering AngentDocument22 pagesLipid Lowering AngentDave BraveNo ratings yet
- Renal MNTDocument58 pagesRenal MNTMARIA TARIQNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyHomework Ping100% (2)
- Nutrition 409 - Case 12Document2 pagesNutrition 409 - Case 12api-252471038No ratings yet
- LO 1 HematoDocument6 pagesLO 1 HematobeatriceNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION For Renal Diseases 1Document15 pagesNUTRITION For Renal Diseases 1Cristina AdolfoNo ratings yet
- HypercalcemiaDocument39 pagesHypercalcemiaPrajina KansakarNo ratings yet
- Metabolic DR - RehabDocument24 pagesMetabolic DR - RehabMohammed Saad NabhanNo ratings yet
- LC HyperlipidemiaDocument11 pagesLC Hyperlipidemiaabdul basithNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret Your Blood Test ResultsDocument23 pagesHow To Interpret Your Blood Test Resultstin1625100% (1)
- Health Disorders & DietDocument120 pagesHealth Disorders & DietHannaniah Gabriel AmanteNo ratings yet
- Ald & MasldDocument19 pagesAld & MasldAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- 340 Final StudyDocument21 pages340 Final StudyLeah ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- ASSOCHAM - Upcoming Events List Week 27th July To 2nd Aug 2020 - CirculationDocument2 pagesASSOCHAM - Upcoming Events List Week 27th July To 2nd Aug 2020 - CirculationSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Getting Started Oracle CloudDocument77 pagesGetting Started Oracle CloudSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Functional Testing Suite Advanced Pack For Oracle E-Business Suite - Property ManagerDocument34 pagesOracle® Functional Testing Suite Advanced Pack For Oracle E-Business Suite - Property ManagerSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Your Dob Today Your Age: Years Months and DaysDocument13 pagesYour Dob Today Your Age: Years Months and DaysSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Burn Down Chart: Burned Down Balance Day Planned Actual Planned Actual Done TodayDocument2 pagesBurn Down Chart: Burned Down Balance Day Planned Actual Planned Actual Done TodaySachin JainNo ratings yet
- Cond Format Icon Set LogicDocument2 pagesCond Format Icon Set LogicSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Employees' Pension Scheme - 95 Calculator: Particulars Date MonthDocument2 pagesEmployees' Pension Scheme - 95 Calculator: Particulars Date MonthSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Aged Accounts Receivable: (Enter UW Department Name) (Enter Date)Document5 pagesAged Accounts Receivable: (Enter UW Department Name) (Enter Date)Sachin JainNo ratings yet
- Retirement PlanningDocument2 pagesRetirement PlanningSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Sprint Burndown Chart TemplateDocument9 pagesSprint Burndown Chart TemplateSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Sample DocumentationDocument44 pagesSample DocumentationSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Unix Shell Programming WorkshopDocument35 pagesUnix Shell Programming WorkshopSachin JainNo ratings yet
- DNA Book 12 Cover PDFDocument1 pageDNA Book 12 Cover PDFSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Payment Details Report: Orders Under This TransactionDocument1 pagePayment Details Report: Orders Under This TransactionSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Poster Sample BookDocument1 pagePoster Sample BookSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Elasticsearch, Logstash and KibanaDocument11 pagesElasticsearch, Logstash and KibanaSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Operating System VirtualizationDocument13 pagesOperating System VirtualizationSachin JainNo ratings yet
- SQL Loader1Document4 pagesSQL Loader1Sachin JainNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Edge TestDocument11 pagesBig Bang Edge TestAman VimayuNo ratings yet
- John Blue - DP 139 Diaphragm Pump - Parts and Instruction Manual - 7 M 17 - 0622Document12 pagesJohn Blue - DP 139 Diaphragm Pump - Parts and Instruction Manual - 7 M 17 - 0622Dung PhamNo ratings yet
- Quick Test 2 - LEVEL 7Document3 pagesQuick Test 2 - LEVEL 7Matías MocilnikarNo ratings yet
- Im12a01f01 03enDocument95 pagesIm12a01f01 03enkjonasamNo ratings yet
- Synergy Shuttle ConveyorDocument5 pagesSynergy Shuttle ConveyorTamal Tanu RoyNo ratings yet
- Beermom Ism c10Document164 pagesBeermom Ism c10joão victor carvalho100% (1)
- 02.1-WCDMA Basic Principle of Radio Propagation - 20051214Document20 pages02.1-WCDMA Basic Principle of Radio Propagation - 20051214kltowerNo ratings yet
- Catalog 2019 Jyhy DieselDocument10 pagesCatalog 2019 Jyhy DieselAndre vatar andreNo ratings yet
- The Berkeley Review: MCAT Chemistry Atomic Theory PracticeDocument37 pagesThe Berkeley Review: MCAT Chemistry Atomic Theory Practicerenjade1516No ratings yet
- Hick's Law Lab 1Document6 pagesHick's Law Lab 1Merna SamieNo ratings yet
- Webhunt Conor FoleyDocument3 pagesWebhunt Conor Foleyapi-367746310No ratings yet
- Flow in Pipe: Characteristic LengthDocument9 pagesFlow in Pipe: Characteristic Lengthguapo93No ratings yet
- Learning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Document18 pagesLearning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Zyke NovenoNo ratings yet
- NBRK0200 Installation Configuration ManualDocument32 pagesNBRK0200 Installation Configuration ManualGoran JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Glossary CambridgeDocument14 pagesGlossary CambridgeAlexey PetrovNo ratings yet
- Terreal Facing Brick BrochureDocument32 pagesTerreal Facing Brick BrochuresmdiviNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts ManagementDocument19 pagesSpare Parts ManagementdaveferalNo ratings yet
- Gabisan Let Scheck1 PDFDocument3 pagesGabisan Let Scheck1 PDFEdrick Paras100% (1)
- Text 1 (A & B)Document2 pagesText 1 (A & B)ifx leeNo ratings yet
- Learn Astrology PDFDocument45 pagesLearn Astrology PDFRajagopal Rao85% (20)
- Colour BalanceDocument2 pagesColour Balancenghi100% (1)
- Bhel Training ReportDocument32 pagesBhel Training ReportVivek PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sustainability PackagingDocument3 pagesSustainability Packagingdong.quan.1705No ratings yet
- Selina Concise Physics Solutions Class 6 Chapter 1 MatterDocument22 pagesSelina Concise Physics Solutions Class 6 Chapter 1 MatterAltaf TalpurNo ratings yet
- Acustica Ruby EbonyDocument1 pageAcustica Ruby EbonyZizja TurtleNo ratings yet
- Math10 - Q4 - Weeks 1 - 2Document30 pagesMath10 - Q4 - Weeks 1 - 2Rogelio Canuel Jr.No ratings yet
- Mates Orals SyllabusDocument3 pagesMates Orals SyllabusmahmutNo ratings yet
- Intel System Management Specification - Rev2p0Document63 pagesIntel System Management Specification - Rev2p0Nisarg UpadhyayNo ratings yet