Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PT CH6
PT CH6
Uploaded by
Nabin ShresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 30days English Learning PlanDocument32 pages30days English Learning Planbruce lee100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- SK Year 6 Cefr Unit 7 - Music and SongDocument25 pagesSK Year 6 Cefr Unit 7 - Music and SongMAJJI ATHI LAKSHMY A/P SURYANARAYANAN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Activity Sheet English 6 Quarter 1 Week 4 Day 3Document10 pagesActivity Sheet English 6 Quarter 1 Week 4 Day 3IamCcj67% (3)
- Java Server Pages (JSP) /servlet Technology 10.1. Applets, Servlets, and Java Server PagesDocument22 pagesJava Server Pages (JSP) /servlet Technology 10.1. Applets, Servlets, and Java Server PagesNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Programming Architecture 2.1 Model View Controller (MVC)Document7 pagesChapter 2: Programming Architecture 2.1 Model View Controller (MVC)Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- File and File Structure: Overview of Storage DeviceDocument29 pagesFile and File Structure: Overview of Storage DeviceNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- InterviewDocument2 pagesInterviewNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Pramod Parajuli Simulation and Modeling, CS-331: CsitnepalDocument12 pagesPramod Parajuli Simulation and Modeling, CS-331: CsitnepalNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nabin Shrestha: Thankot, Kathmandu Nepal + 9 7 7 9 8 4 3 4 1 2 4 0 5Document1 pageNabin Shrestha: Thankot, Kathmandu Nepal + 9 7 7 9 8 4 3 4 1 2 4 0 5Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Chapter 7Document5 pagesDBMS Chapter 7Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Chapter 4Document39 pagesDBMS Chapter 4Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management System: 1.1 DataDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Database Management System: 1.1 DataNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transact-SQLDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Transact-SQLPatoRetamozoNo ratings yet
- CDocument93 pagesCAanchal TyagiNo ratings yet
- Ar-Raheeq Al Makhtum SindhiDocument612 pagesAr-Raheeq Al Makhtum SindhiInder KishanNo ratings yet
- Teaching Assignments For English 2nd Sem 15-16Document5 pagesTeaching Assignments For English 2nd Sem 15-16AlyssaBetoFernandezNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Program Term 3Document14 pagesMathematics Program Term 3api-208000806100% (1)
- Spanish 1 - Lessons 1-40Document1 pageSpanish 1 - Lessons 1-40Lacs100% (1)
- g12 Sem1 q1 Literature Final ReviewerDocument5 pagesg12 Sem1 q1 Literature Final ReviewerNadine Victoria DizonNo ratings yet
- IBPS PO Mock Test 3Document6 pagesIBPS PO Mock Test 3GOPAL SINo ratings yet
- 4as Lesson PlanDocument3 pages4as Lesson Planjerwin arcaNo ratings yet
- Writing A Thesis Statement in Third PersonDocument6 pagesWriting A Thesis Statement in Third Personygsyoeikd100% (2)
- Worksheet 1 9th Grade II Term - Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesWorksheet 1 9th Grade II Term - Passive Voicewilliamces507100% (1)
- Marc Reibert Legged RobotsDocument16 pagesMarc Reibert Legged RobotsChris LatanNo ratings yet
- 996 English Year 9 Sample ChapterDocument25 pages996 English Year 9 Sample ChapterBranka ArrivéNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 3 English Practice Worksheets (12) - Kinds of NounsDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 3 English Practice Worksheets (12) - Kinds of NounsAarna RewariNo ratings yet
- UsingDocument57 pagesUsingdomielNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Direct Method and Translation Method in The Teaching of English Grammar: Unit 'Preposition'.Document7 pagesEffectiveness of Direct Method and Translation Method in The Teaching of English Grammar: Unit 'Preposition'.Mohit Goswami100% (2)
- Objectives:: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Expected ToDocument21 pagesObjectives:: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Expected ToRomyross JavierNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Tricks For Delphi and C++Builder VCL Database Developers by Cary JensenDocument25 pagesTop 10 Tricks For Delphi and C++Builder VCL Database Developers by Cary JensenIP ManNo ratings yet
- Korean Phrases Dating&RelationshipsDocument12 pagesKorean Phrases Dating&RelationshipsDragomir DavidNo ratings yet
- Sentence Concept, Coordination and Interrogative Forms. English Language IVDocument7 pagesSentence Concept, Coordination and Interrogative Forms. English Language IVRicardo MarquesNo ratings yet
- PAHC Talking Stories BrochureDocument84 pagesPAHC Talking Stories BrochureHARTSONLINENo ratings yet
- C# NetcDocument22 pagesC# Netcprakash_net4_0100% (1)
- Verb Patterns in EnglishDocument5 pagesVerb Patterns in Englishpedroarana100% (1)
- Defintion of Learning StylesDocument23 pagesDefintion of Learning StylesNasr-edineOuahaniNo ratings yet
- Spanish Irregular VerbsDocument9 pagesSpanish Irregular VerbsNadia LIbNo ratings yet
- Transitional Words LessonDocument3 pagesTransitional Words Lessonapi-2738740990% (1)
- So Some of Us Are Afraid of AI - What AIDocument5 pagesSo Some of Us Are Afraid of AI - What AIdawudhNo ratings yet
PT CH6
PT CH6
Uploaded by
Nabin ShresthaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PT CH6
PT CH6
Uploaded by
Nabin ShresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
Programming
Technology
BECE
IV
Semester
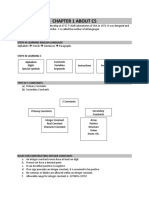
Chapter 6: Java Framework
The Java programming language was originally created in 1995 by James Gosling from Sun
Microsystems (currently a subsidiary of Oracle Corporation).
The goal was to provide a simpler and platform-independent alternative to C++.
Java is a general-purpose programming language that’s used in all industries for almost any
type of application.
The Life Cycle of a Java Program
Java requires the source code of our program to be compiled first.
It gets converted to either machine-specific code or a bytecode that is understood by some
run-time engine or a virtual machine.
Not only will the program be checked for syntax errors by a Java compiler, but also some
other libraries of Java code can be added (linked) to our program after the compilation is
complete (deployment stage).
Technically we can write the source code of our Java program in any plain text editor that
we prefer (Notepad, TextEdit, vi, etc.), but to compile our program we’ll need additional
tools and code libraries that are included in the Java Development Kit (JDK).
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
Java Runtime Environment (JRE) contains JVM, class libraries, and other supporting files. It does
not contain any development tools such as compiler, debugger, etc. Actually JVM runs the
program, and it uses the class libraries, and other supporting files provided in JRE. If we want to
run any java program, we need to have JRE installed in the system.
Java Development Kit (JDK)
Java Developer Kit contains tools needed to develop the Java programs, and JRE to run the
programs. The tools include compiler (javac.exe), Java application launcher (java.exe),
Appletviewer, etc. Compiler converts java code into byte code. Java application launcher opens a
JRE, loads the class, and invokes its main method. We need JDK, if at all we want to write our own
programs, and to compile the program. For running java programs, JRE is sufficient. JRE is
targeted for execution of Java files i.e. JRE = JVM + Java Packages Classes (like util, math, lang,
awt,swing etc)+runtime libraries. JDK is mainly targeted for java development. i.e. we can create a
Java file (with the help of Java packages), compile a Java file and run a java file.
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
The Java Virtual Machine provides a platform-independent way of executing code; programmers
can concentrate on writing software, without having to be concerned with how or where it will
run. But, note that JVM itself not a platform independent. It only helps Java to be executed on the
platform-independent way. When JVM has to interpret the byte codes to machine language, then it
has to use some native or operating system specific language to interact with the system. One has to
be very clear on platform independent concept. Even there are many JVMs written on Java,
however they too have little bit of code specific to the operating systems.
As we all aware when we compile a Java file, output is not an ‘exe’ but it’s a ‘.class’ file. ‘.class’
file consists of Java byte codes which are understandable by JVM. Java Virtual Machine interprets
the byte code into the machine code depending upon the underlying operating system and hardware
combination. It is responsible for all the things like garbage collection, array bounds checking,
etc.JVM is platform dependent.
Prepared By: Madan Kadariya
Nepal College of Information Technology
Programming Technology
BECE IV Semester
The JVM is called “virtual” because it provides a machine interface that does not depend on the
underlying operating system and machine hardware architecture. This independence from hardware
and operating system is a cornerstone of the write-once run-anywhere value of Java programs.
There are different JVM implementations are there. These may differ in things like performance,
reliability, speed, etc. These implementations will differ in those areas where Java specification
doesn’t mention how to implement the features, like how the garbage collection process works is
JVM dependent, Java spec doesn’t define any specific way to do this.
Difference between JRE, JDK and JVM
In short here are few differences between JRE, JDK and JVM:
1) JRE and JDK come as installer while JVM are bundled with them.
2) JRE only contain environment to execute java program but doesn’t contain other tool for
compiling java program.
3) JVM comes along with both JDK and JRE and created when we execute Java program by giving
“java” command.
Just in Time Compiler (JIT)
Initially Java has been accused of poor performance because it’s both compiles and interprets
instruction. Since compilation or Java file to class file is independent of execution of Java program.
Here compilation word is used for byte code to machine instruction translation. JIT are advanced
part of Java Virtual machine which optimize byte code to machine instruction conversion part by
compiling similar byte codes at same time and thus reducing overall execution time. JIT is part of
Java Virtual Machine and also performs several other optimizations such as in-lining function.
Prepared By: Madan Kadariya
Nepal College of Information Technology
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 30days English Learning PlanDocument32 pages30days English Learning Planbruce lee100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- SK Year 6 Cefr Unit 7 - Music and SongDocument25 pagesSK Year 6 Cefr Unit 7 - Music and SongMAJJI ATHI LAKSHMY A/P SURYANARAYANAN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Activity Sheet English 6 Quarter 1 Week 4 Day 3Document10 pagesActivity Sheet English 6 Quarter 1 Week 4 Day 3IamCcj67% (3)
- Java Server Pages (JSP) /servlet Technology 10.1. Applets, Servlets, and Java Server PagesDocument22 pagesJava Server Pages (JSP) /servlet Technology 10.1. Applets, Servlets, and Java Server PagesNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Programming Architecture 2.1 Model View Controller (MVC)Document7 pagesChapter 2: Programming Architecture 2.1 Model View Controller (MVC)Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- File and File Structure: Overview of Storage DeviceDocument29 pagesFile and File Structure: Overview of Storage DeviceNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- InterviewDocument2 pagesInterviewNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Pramod Parajuli Simulation and Modeling, CS-331: CsitnepalDocument12 pagesPramod Parajuli Simulation and Modeling, CS-331: CsitnepalNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nabin Shrestha: Thankot, Kathmandu Nepal + 9 7 7 9 8 4 3 4 1 2 4 0 5Document1 pageNabin Shrestha: Thankot, Kathmandu Nepal + 9 7 7 9 8 4 3 4 1 2 4 0 5Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Chapter 7Document5 pagesDBMS Chapter 7Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Chapter 4Document39 pagesDBMS Chapter 4Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management System: 1.1 DataDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Database Management System: 1.1 DataNabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transact-SQLDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Transact-SQLPatoRetamozoNo ratings yet
- CDocument93 pagesCAanchal TyagiNo ratings yet
- Ar-Raheeq Al Makhtum SindhiDocument612 pagesAr-Raheeq Al Makhtum SindhiInder KishanNo ratings yet
- Teaching Assignments For English 2nd Sem 15-16Document5 pagesTeaching Assignments For English 2nd Sem 15-16AlyssaBetoFernandezNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Program Term 3Document14 pagesMathematics Program Term 3api-208000806100% (1)
- Spanish 1 - Lessons 1-40Document1 pageSpanish 1 - Lessons 1-40Lacs100% (1)
- g12 Sem1 q1 Literature Final ReviewerDocument5 pagesg12 Sem1 q1 Literature Final ReviewerNadine Victoria DizonNo ratings yet
- IBPS PO Mock Test 3Document6 pagesIBPS PO Mock Test 3GOPAL SINo ratings yet
- 4as Lesson PlanDocument3 pages4as Lesson Planjerwin arcaNo ratings yet
- Writing A Thesis Statement in Third PersonDocument6 pagesWriting A Thesis Statement in Third Personygsyoeikd100% (2)
- Worksheet 1 9th Grade II Term - Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesWorksheet 1 9th Grade II Term - Passive Voicewilliamces507100% (1)
- Marc Reibert Legged RobotsDocument16 pagesMarc Reibert Legged RobotsChris LatanNo ratings yet
- 996 English Year 9 Sample ChapterDocument25 pages996 English Year 9 Sample ChapterBranka ArrivéNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 3 English Practice Worksheets (12) - Kinds of NounsDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 3 English Practice Worksheets (12) - Kinds of NounsAarna RewariNo ratings yet
- UsingDocument57 pagesUsingdomielNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Direct Method and Translation Method in The Teaching of English Grammar: Unit 'Preposition'.Document7 pagesEffectiveness of Direct Method and Translation Method in The Teaching of English Grammar: Unit 'Preposition'.Mohit Goswami100% (2)
- Objectives:: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Expected ToDocument21 pagesObjectives:: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Expected ToRomyross JavierNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Tricks For Delphi and C++Builder VCL Database Developers by Cary JensenDocument25 pagesTop 10 Tricks For Delphi and C++Builder VCL Database Developers by Cary JensenIP ManNo ratings yet
- Korean Phrases Dating&RelationshipsDocument12 pagesKorean Phrases Dating&RelationshipsDragomir DavidNo ratings yet
- Sentence Concept, Coordination and Interrogative Forms. English Language IVDocument7 pagesSentence Concept, Coordination and Interrogative Forms. English Language IVRicardo MarquesNo ratings yet
- PAHC Talking Stories BrochureDocument84 pagesPAHC Talking Stories BrochureHARTSONLINENo ratings yet
- C# NetcDocument22 pagesC# Netcprakash_net4_0100% (1)
- Verb Patterns in EnglishDocument5 pagesVerb Patterns in Englishpedroarana100% (1)
- Defintion of Learning StylesDocument23 pagesDefintion of Learning StylesNasr-edineOuahaniNo ratings yet
- Spanish Irregular VerbsDocument9 pagesSpanish Irregular VerbsNadia LIbNo ratings yet
- Transitional Words LessonDocument3 pagesTransitional Words Lessonapi-2738740990% (1)
- So Some of Us Are Afraid of AI - What AIDocument5 pagesSo Some of Us Are Afraid of AI - What AIdawudhNo ratings yet