Professional Documents
Culture Documents
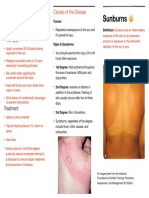
Sunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and Stings
Sunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and Stings
Uploaded by
Jaz Mn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views5 pagesThe document summarizes information about sunburn and insect bites and stings. It discusses causes, symptoms, and non-prescription treatments for both. Sunburn is caused by UV radiation from the sun damaging skin. Symptoms range from mild redness and pain to severe blistering. Insect bites and stings are caused by mosquitoes, flies, fleas, and other insects. Symptoms include swelling, pain, itching, and potentially severe allergic reactions. Non-prescription treatments for sunburn include sunscreen and pain relief. For insect bites, insect repellent and first aid measures can help provide relief.
Original Description:
microbes
Original Title
C Sunburn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes information about sunburn and insect bites and stings. It discusses causes, symptoms, and non-prescription treatments for both. Sunburn is caused by UV radiation from the sun damaging skin. Symptoms range from mild redness and pain to severe blistering. Insect bites and stings are caused by mosquitoes, flies, fleas, and other insects. Symptoms include swelling, pain, itching, and potentially severe allergic reactions. Non-prescription treatments for sunburn include sunscreen and pain relief. For insect bites, insect repellent and first aid measures can help provide relief.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views5 pagesSunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and Stings
Sunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and Stings
Uploaded by
Jaz MnThe document summarizes information about sunburn and insect bites and stings. It discusses causes, symptoms, and non-prescription treatments for both. Sunburn is caused by UV radiation from the sun damaging skin. Symptoms range from mild redness and pain to severe blistering. Insect bites and stings are caused by mosquitoes, flies, fleas, and other insects. Symptoms include swelling, pain, itching, and potentially severe allergic reactions. Non-prescription treatments for sunburn include sunscreen and pain relief. For insect bites, insect repellent and first aid measures can help provide relief.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
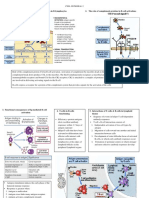
Sunburn (suntan) & insect bites and stings
Sunburn Bites and Stings
Causes Any time our skin is not protected by sunscreen or Although an insect bite and an insect sting
clothes and gets too much sun, it can burn or tan. are both
Melanin painful, there is a big difference between
▪A complex polymer derived from the amino acid the types of
tyrosine. insects that bite and those that sting
▪Melanin is responsible for determining skin and
hair colour and is present in the skin to varying Common
degrees; depending on how much a population has type of
been exposed to the sun historically. insects
▪Basically, people who have dark skin have more that bites Business
melanin. People who have light skin have less. Finance
Leader Economy
Melanin related to mutation (resulting in various Risk
skin colour link to melanin level) Profit
Depending on the amount of UV radiation received, Rise
population group gained different skin colour in Idea
different part of world. 1. Mosquito
2. Fly
How melanin relates to the skin burn or tan: 3. Flea
Our body normally makes melanin to try to 4. Chigger
protect the deeper layers of our skin from 5. Tick
damage. 6. Spider
When our skin gets damaged by the sun's rays, it 7. Fire ant
makes even more melanin to try to protect our 8. Scabies mite
skin from being damaged even more. That 9. Bed bugs
causes the skin to change colour when we go in 10. Lice
the sun:
Dark-skinned people usually turn darker brown,
or tan.
Light-skinned people usually turn more red, or
burn.
Besides tanning or burning, a lot of people also
get uneven patches of colour, or freckles.
NOTE: Even if we have naturally dark skin or never
burn and always tan, that still means the sun is
damaging our skin. And we can still get skin cancer
and wrinkles some day.
sun gives off three wavelengths of ultraviolet (UV)
light:
▪ UVA
▪ UVB
(Both can penetrate our skin and cause damage)
▪ UVC (light does not reach the Earth's surface)
UV rays can alter our DNA, prematurely aging our
skin.
▪Over time, DNA damage can contribute to skin
cancers, including deadly melanoma.
symptoms CLASSIFICATION: Common symptoms of
Mild, moderate, or severe depending on several reactions to bites and
factors: stings
▪The skin complexion of an individual (fair-skinned 1. Swelling, which may be concentrated
complexion has the highest risk of burning). in the affected area or may spread
▪The time of day, duration, and altitude of exposure throughout the body redness or rash
to the sun 2. Pain in the affected area or in the
▪Certain medications or chemicals in some skin muscles.
preparations can make an individual more 3. Itching.
susceptible to sunburn if proper precautions are not 4. Heat on and around the site of the bite
taken. or sting.
5. Numbness or tingling in the affected
Mild: The first signs of sunburn may not appear for area.
up to 4 hours after exposure and may peak between
12 and 24 hours following exposure. Symptoms of a severe reaction
Mild to moderate sunburn typically presents with requiring immediate medical
symptoms that can include red erythematous skin, treatment include:
tenderness, pain, and peeling of skin. • High fever
Severe reactions can occur as well and can cause the • Difficulty breathing
development of blisters and sometimes fever, chills, • Nausea or vomiting
and weakness. In these instances, the individual • Muscle spasms
should always be referred to a physician for further • Rapid heartbeat
evaluation. • Swelling of the lips and throat
• Confusion
• Loss of consciousness
symptoms CLASSIFICATION: Common symptoms of
Mild, moderate, or severe depending on several reactions to bites and
factors: stings
▪The skin complexion of an individual (fair-skinned 6. Swelling, which may be concentrated
complexion has the highest risk of burning). in the affected area or may spread
▪The time of day, duration, and altitude of exposure throughout the body redness or rash
to the sun 7. Pain in the affected area or in the
▪Certain medications or chemicals in some skin muscles.
preparations can make an individual more 8. Itching.
susceptible to sunburn if proper precautions are not 9. Heat on and around the site of the bite
taken. or sting.
10. Numbness or tingling in the affected
Mild: The first signs of sunburn may not appear for area.
up to 4 hours after exposure and may peak between
12 and 24 hours following exposure. Symptoms of a severe reaction
Mild to moderate sunburn typically presents with requiring immediate medical
symptoms that can include red erythematous skin, treatment include:
tenderness, pain, and peeling of skin. • High fever
Severe reactions can occur as well and can cause the • Difficulty breathing
development of blisters and sometimes fever, chills, • Nausea or vomiting
and weakness. In these instances, the individual • Muscle spasms
should always be referred to a physician for further • Rapid heartbeat
evaluation. • Swelling of the lips and throat
• Confusion
• Loss of consciousness
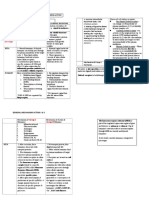
NON- Preventing sunburn /suntan: Before getting bite or sting
PRESCRI 1. Tips (Watch the clock and Wear the right
PTION clothes such as sun-protective cloth) 1. Insect repellent
MEDICA 2. Protective agents to keep the skin while outside Not designed to eliminate pests makes
TIONS in the sun (sunscreen that protects against both people less attractive to the pest.
(OTC) UVA and UVB rays.
Sunscreen should have a sun protection factor Common active ingredients in registered
(SPF) of at least 30 skin-applied insect repellents:
And Catnip Oil – from plant Nepeta Cataria
Applying sunscreen: sp.
Apply sunscreen about 30 minutes Citronella Oil - from the leaves and
TREATM before going outside. stems of different species of
ENT Use sunscreen even on overcast days Cymbopogon (lemongrass)
because UV rays can penetrate clouds. DEET - Chemical name: N,N-diethyl-
Reapply sunscreen every two hours -- meta toluamide
or more often if sweating heavily or Picaridin - a synthetic compound first
swimming. made in the 1980s. It was made to
resemble the natural compound
Sunburn/suntan piperine, which is found in the group of
relief: plants that are used to produce black
To treat the burn on two fronts relieving pepper
reddened, inflamed skin while easing pain.
OTC sunscreen: After getting bite or sting
1. Products typically include a
combination of two to six of these 2. The majority of bites and stings can be
active ingredients: oxybenzone, treated at home, especially if the
avobenzone, octisalate, octocrylene, reaction is mild.
homosalate and octinoxate. Remove the stinger if it is lodged
2. Mineral sunscreens use zinc oxide in the skin
and/or titanium dioxide. Then, wash the affected area
Next, apply an ice pack to reduce
pain and swelling.
3. In addition to these, may treat the
patients with:
Topical anti-itch agents
TREATMENT
Commonly used products contain:
•1% hydrocortisone – for pruritis
Minor to moderate sunburn - initially treated with •Mint oil - counterirritant
the use of cool •Menthol - counterirritant
cloths or compresses to affected areas; taking cool •Camphor – counterirritant
showers or baths; Counterirritant is a substance which creates
For treatments: irritation or mild inflammation in one
(1) Applying topical agents - aloe vera, various skin location with the goal of lessening
protectants, or topical hydrocortisone to the affected discomfort and/or inflammation.
areas. *Topical hydrocortisone should never be
applied to an area of open blisters. Oral pain relievers – NSAIDs
(2) Oral OTC analgesics may be appropriate for (Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Diclofenac)
some individuals. and OTC analgesics (Paracetamol /
(3) Systemic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs acetaminophen)
(NSAIDS) has been shown to decrease
inflammation caused by exposure to UV rays. Anti-histamines – to reduce
TOPICAL AGENTS: itchiness systemically.
• Apply soothing lotions that contain aloe vera to
sunburned areas. Antihistamine use to treat various
• Topical steroids (such as 1% hydrocortisone symptoms caused by histamine.
cream) can help with sunburn pain and swelling. • Long-acting antihistamines provide
Not recommended for children below 2 years old, symptom
unless prescribed by doctors. relief for up to 8-12 hours, while shorter
NON-PRESCRIPTION MEDICATIONS acting agents last for up to 4 hours but
To help treat fever or pain in sunburn; begin
• Paracetamol / Acetaminophen working faster
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(NSAIDs): Oral Antihistamines
Ibuprofen tablet 1st generation antihistamines:
Naproxen tablet
Diclofenac Tablet H1-antagonists / H1-blockers block the
• Aspirin (also a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory action of histamine at the H1-receptor,
drug) helping relieve allergic reactions.
Cause drowsiness in most people
(penetrate BBB)
eg:
Chlorpheniramine
Diphenhydramine
Brompheniramine
Carbinoxamine
Dexchlorpheniramine
Doxylamine
2nd generation antihistamines:
H1-antagonists / H1-blockers
Newer drugs - much more selective
for peripheral H1-receptors as
opposed to the central nervous
system H1 receptors and cholinergic
receptors. This selectivity
significantly reduces the occurrence
of adverse drug reactions, such as
sedation (calmness) do not
penetrate BBB
Less likely to cause drowsiness
eg:
Ketotifen
Terfenadine
Cetirizine
Loratadine
Goal of 1. Adequate pain relief
treatment 2. Healing
3. Overall skin protection to minimize skin
irritation and prevent further complications such
as infections.
4. Selection of treatment depends on the severity
of the sunburn.
You might also like
- CPS Dependent Information FormDocument2 pagesCPS Dependent Information Formtristero312No ratings yet
- 1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionDocument30 pages1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- The Dangers of Excessive Sun TanningDocument2 pagesThe Dangers of Excessive Sun TanningdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- C. High Risk ToddlerDocument7 pagesC. High Risk ToddlerjimwelluismNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument20 pagesBurnsrazAn swNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Education Session - Skin ConditionsDocument43 pages2.0 Education Session - Skin ConditionsCampboss CBSNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Management of Sunburn: Roshni PR, Remya Reghu, Meenu Vijayan and Parvati KrishnanDocument4 pagesEvaluation and Management of Sunburn: Roshni PR, Remya Reghu, Meenu Vijayan and Parvati KrishnanMasri RaisNo ratings yet
- What Causes Sunburn?: Consequences of SunburnsDocument2 pagesWhat Causes Sunburn?: Consequences of SunburnsadmassuNo ratings yet
- Biophys14tav 14Document32 pagesBiophys14tav 14gizex2013No ratings yet
- Irritant Contact DermatitisDocument5 pagesIrritant Contact DermatitisJohn P M SinagaNo ratings yet
- RingwormDocument7 pagesRingwormSAMSON, MAXZENE ANICKANo ratings yet
- Changes in The Integumentary System of Older Adults 1Document48 pagesChanges in The Integumentary System of Older Adults 1Winter SpringNo ratings yet
- MelanomaDocument1 pageMelanomaapi-518183280No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledJEANETTE ESCARONo ratings yet
- Skin ConditionsDocument43 pagesSkin ConditionspdladvaNo ratings yet
- ToddlersDocument85 pagesToddlersMICHELLE MONTEBONNo ratings yet
- EczemaDocument13 pagesEczemaCollective123No ratings yet
- BurnDocument10 pagesBurnMS AntikaNo ratings yet
- Himalaya Sunscreen LotionDocument78 pagesHimalaya Sunscreen Lotionshantanusen100% (1)
- Derma Quiz 3 NotesDocument11 pagesDerma Quiz 3 NotesJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer Prevention at Work An Employee Sun Safety ProgramDocument33 pagesSkin Cancer Prevention at Work An Employee Sun Safety ProgramLicca ArgallonNo ratings yet
- Thera Merged 09-02-21Document104 pagesThera Merged 09-02-21Thea RayNo ratings yet
- Uv Presentaion 2019Document43 pagesUv Presentaion 2019Mustafa MabroukNo ratings yet
- Burns ReportDocument9 pagesBurns ReportLia-Jy SanoanNo ratings yet
- 02 BurnsDocument22 pages02 BurnsTahir ZamanNo ratings yet
- Case Study IGDocument2 pagesCase Study IGCheha PaikNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Ch.11Document7 pagesStudy Guide Ch.11Draquillany ShieldsNo ratings yet
- Seborrhoeic Dermatitis in Adults Dec 22 1Document3 pagesSeborrhoeic Dermatitis in Adults Dec 22 1defowar249No ratings yet
- P.E First Aid Treatment For Burns (ISABEDRA)Document13 pagesP.E First Aid Treatment For Burns (ISABEDRA)Reycard IsabedraNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document10 pagesPresentation 2Ieva PetrylaiteNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument1 pageScabiesMarco Antonio KoffNo ratings yet
- Burns 3Document31 pagesBurns 3Reann LeeNo ratings yet
- Ringworm 11 594kDocument2 pagesRingworm 11 594kFufu LufuNo ratings yet
- How To Treat A BurnDocument12 pagesHow To Treat A Burnhany winihastutiNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY-FUNCTION-Acabo Ano BaliliDocument36 pagesINTEGUMENTARY-FUNCTION-Acabo Ano Balilicoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Changes Associated With Ageing Integumentary SystemDocument24 pagesChanges Associated With Ageing Integumentary Systemedward osae-oppongNo ratings yet
- Skin Reaction in RadiotherapyDocument3 pagesSkin Reaction in RadiotherapyAhmad DiabNo ratings yet
- Effective Skin Care For WomenDocument7 pagesEffective Skin Care For WomenFeirniadoll100% (1)
- BurnsDocument9 pagesBurnsVincentus BinNo ratings yet
- Skin AbnormalitiesDocument5 pagesSkin AbnormalitiesRegimae BartolomeNo ratings yet
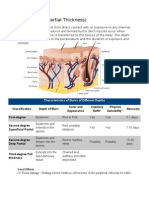
- Burns (Deep Partial Thickness) : Characteristics of Burns of Different DepthsDocument8 pagesBurns (Deep Partial Thickness) : Characteristics of Burns of Different DepthsHencynt SoriaNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Speech (Outline) - ENGKU AISYAH NUHA PDFDocument5 pagesPersuasive Speech (Outline) - ENGKU AISYAH NUHA PDFengkuNo ratings yet
- Eczema, Group 3Document19 pagesEczema, Group 3Kuto Yvonne CheronoNo ratings yet
- GENOVE, ERICKA IS-Module2Document11 pagesGENOVE, ERICKA IS-Module2Ericka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis Clinical Case Presentation OutlineDocument6 pagesDermatitis Clinical Case Presentation OutlineSamson, Arielle Cate D.No ratings yet
- Atopic DermaDocument12 pagesAtopic DermaMohamed ElmardiNo ratings yet
- P.E 4 W. 3 Lesson2Document3 pagesP.E 4 W. 3 Lesson2Vanessa Mae AguilarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Skin and Parasitic DiseasesDocument14 pagesNursing Management of Skin and Parasitic Diseasesyer tagalajNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 AnatomyDocument24 pagesChapter - 14 AnatomyAltea PasiaNo ratings yet
- Scabies: Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesScabies: Signs and SymptomsIbrahim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2Document15 pagesUntitled 2api-327697210No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Wound Care - With CommentsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan On Wound Care - With CommentsJoyJoy Tabada CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Sports Med BrochureDocument1 pageSports Med Brochureapi-434212093No ratings yet
- Burn First Aid: Dr. Nawal Alghareeb Done By: - Mashael AlsaediDocument7 pagesBurn First Aid: Dr. Nawal Alghareeb Done By: - Mashael AlsaedikymoNo ratings yet
- Common Skin Problem During AdolescenceDocument12 pagesCommon Skin Problem During AdolescenceKristela Mae ColomaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3Document2 pagesLaboratory 3Reizel Grace PaladaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument22 pagesIntegumentary SystemEunice Angela FulguerasNo ratings yet
- 世界顶级英文杂志特刊珍藏版vol16Your Health Now - 皮肤Document21 pages世界顶级英文杂志特刊珍藏版vol16Your Health Now - 皮肤newstarchj3No ratings yet
- PPP-BURNS 118slDocument30 pagesPPP-BURNS 118slCath BrilNo ratings yet
- Scabies Information Leaflet 2018Document2 pagesScabies Information Leaflet 2018zonk lateNo ratings yet
- From Vampire to Victory: My 24-Year Battle and Breakthrough with EczemaFrom EverandFrom Vampire to Victory: My 24-Year Battle and Breakthrough with EczemaNo ratings yet
- List of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Document2 pagesList of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- Common Cold and InfluenzaDocument5 pagesCommon Cold and InfluenzaJaz MnNo ratings yet
- The Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesDocument5 pagesThe Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Injury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisDocument5 pagesInjury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisJaz MnNo ratings yet
- General Mechanism of Action1Document2 pagesGeneral Mechanism of Action1Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- Skin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure InfectionDocument2 pagesSkin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure InfectionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Function of Pituitary HormonesDocument1 pageFunction of Pituitary HormonesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Exercise - Occupations PDFDocument2 pagesVocabulary Exercise - Occupations PDFYaiza Almengló Ortega100% (1)
- 1st Indonesia Prosthodontic Society Meeting & IPROSI Congress XIDocument27 pages1st Indonesia Prosthodontic Society Meeting & IPROSI Congress XITalitha UlimaNo ratings yet
- Osha 29 CFR 1926.1400Document13 pagesOsha 29 CFR 1926.1400Aly MurrietaNo ratings yet
- Stress BustingDocument24 pagesStress BustingMarianne ChristieNo ratings yet
- Generalized Body Pain and Weakness: 1. Encourage The PatientDocument4 pagesGeneralized Body Pain and Weakness: 1. Encourage The PatientVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- Where in The World Is Dantian - Flowing ZenDocument10 pagesWhere in The World Is Dantian - Flowing ZenAfzal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Soal USM STAN 2014 - Kunci Jawaban-1Document6 pagesSoal USM STAN 2014 - Kunci Jawaban-1mochshenNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: by Mayo Clinic StaffDocument9 pagesDysphagia: by Mayo Clinic StaffRoseNo ratings yet
- Immunology in Transplantation - Basics For BeginnersDocument6 pagesImmunology in Transplantation - Basics For BeginnersTuan Thanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Priorities For 2019-21: Newfoundland and Labrador Teachers' AssociationDocument11 pagesPriorities For 2019-21: Newfoundland and Labrador Teachers' Associationwsgf khiiNo ratings yet
- 6 1 Journal DisminoreDocument16 pages6 1 Journal DisminoreDenny DarmawanNo ratings yet
- S.S or AffidavitDocument9 pagesS.S or AffidavitAngelieNo ratings yet
- Cultivation Method Slides-1Document9 pagesCultivation Method Slides-1Azam TavarehNo ratings yet
- Emdp Etm Workbook A4 PrintDocument56 pagesEmdp Etm Workbook A4 PrintivanNo ratings yet
- Oxyblock DDocument13 pagesOxyblock DВиталий ВойкуNo ratings yet
- الباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فوراDocument163 pagesالباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فورانادين مطر0% (1)
- Vims-Vas Final SeptDocument115 pagesVims-Vas Final SeptR Lamb D LeonNo ratings yet
- Vascular Access in Neonates and Children: Daniele G. Biasucci Nicola Massimo Disma Mauro PittirutiDocument405 pagesVascular Access in Neonates and Children: Daniele G. Biasucci Nicola Massimo Disma Mauro PittirutiErick HernandezNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Interpreting With Heart and Mind: An Intermediate Textbook For Medical InterpretingDocument38 pagesHealthcare Interpreting With Heart and Mind: An Intermediate Textbook For Medical Interpretingjorge marin50% (2)
- Potential MKTDocument67 pagesPotential MKTReevesNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Design Calculation - North - Molino - PH1 - 5jun2017Document5 pagesPlumbing Design Calculation - North - Molino - PH1 - 5jun2017Jazent Anthony RamosNo ratings yet
- William 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 397 012006Document17 pagesWilliam 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 397 012006mrccahmedNo ratings yet
- GuiaZonaExplosivaUSA EUROPA PDFDocument1 pageGuiaZonaExplosivaUSA EUROPA PDFRafaelNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications in Bachelor of Physical Education/Grade 9 (Multiple Choice Test)Document1 pageTable of Specifications in Bachelor of Physical Education/Grade 9 (Multiple Choice Test)Gilbert Bulado0% (1)
- Risk Assessment of Landfill Disposal Sites State of The Art 2008 Waste ManagementDocument13 pagesRisk Assessment of Landfill Disposal Sites State of The Art 2008 Waste ManagementgkarlatirNo ratings yet
- CHN 1 - Community AssessmentDocument24 pagesCHN 1 - Community AssessmentKristel AnneNo ratings yet
- Facial Massage: Peggy MclemoreDocument21 pagesFacial Massage: Peggy MclemoreAmimul EhsanNo ratings yet
- Waste Sector GHG Protocol - Version 5 - October 2013 - 1Document79 pagesWaste Sector GHG Protocol - Version 5 - October 2013 - 1ibrahim syedNo ratings yet
- Training Redefined 90 Workouts Dr. Joel SeedmanDocument248 pagesTraining Redefined 90 Workouts Dr. Joel Seedmanradarm2018555No ratings yet