Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsPloginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal Cells
Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal Cells
Uploaded by
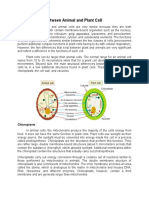
Nelson De LimaThe document describes the main organelles found in plant and animal cells. In plant cells, the nucleus controls cell fate, mitochondria provide energy, the endoplasmic reticulum helps synthesize proteins and lipids, the Golgi apparatus modifies proteins, vacuoles store water, nutrients or capture sunlight, vesicles transport proteins, lysosomes contain digestive enzymes, peroxisomes neutralize toxins, and ribosomes synthesize proteins. In animal cells, the cell membrane encloses the cytoplasm, centrioles organize microtubules in cell division, cilia and flagella aid in movement, the endoplasmic reticulum manufactures products, lysosomes digest macromolecules, mitochondria generate energy, the nucleus contains DNA, and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Revision Worksheet 2 Grade 6Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet 2 Grade 6bindu100% (1)
- Kuby Immunology Ch. 5Document14 pagesKuby Immunology Ch. 5eabazaNo ratings yet
- Plants Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell Wall PhagocyticDocument1 pagePlants Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell Wall PhagocyticHara Prasad MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsstaluciadNo ratings yet
- Biology Key TermsDocument3 pagesBiology Key TermsTia TiaNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- OrganellesDocument13 pagesOrganellesjanaNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- Pro and EuDocument15 pagesPro and EuCy BathanNo ratings yet
- ASDFASDFASDocument17 pagesASDFASDFASChristian Cyril RoldanNo ratings yet
- Cell CytoplasmDocument55 pagesCell Cytoplasmnicolaer111100% (1)
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell - LayoutDocument3 pagesPlant Cell - LayoutMahiNo ratings yet
- All About Animal CellsDocument2 pagesAll About Animal CellsJether Marc Palmerola GardoseNo ratings yet
- BiotechDocument2 pagesBiotechKristel Faye Cortez SubiaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- The Animal Cell: Eukaryotic Cells DNADocument2 pagesThe Animal Cell: Eukaryotic Cells DNAEstefanía ElizondoNo ratings yet
- 4 CellDocument17 pages4 CellNoor ul aminNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocument15 pagesParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellPaul Sotto NgujoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument51 pages2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- STM123 OutlineDocument19 pagesSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisNicole CatolicoNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document30 pagesPart 1Rion BaiganNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- By: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT: Eukaryotic CellDocument9 pagesBy: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT: Eukaryotic CellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsYukiNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKent Orriele FadriquelNo ratings yet
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellDocument7 pagesCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The CellDocument2 pagesChapter 2 The CellGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell StructureDocument3 pagesAnimal Cell StructurejwoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellLeordan SanimNo ratings yet
- Rough and Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument3 pagesRough and Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumAnna Mae DollenteNo ratings yet
- A Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The BodyDocument1 pageA Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The BodySarthepandabearNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesCell OrganellesMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Organelles.: Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOrganelles.: Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisLuzNo ratings yet
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocument9 pagesMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- 1.2. Cell Structure and Organisation PMTDocument3 pages1.2. Cell Structure and Organisation PMTJamesNo ratings yet
- فاينل انسجة نظريDocument40 pagesفاينل انسجة نظريحسن القاضيNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Genetics 101Document4 pagesGenetics 101Jhon Ric BajeNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure VocabDocument1 pageCell Structure VocabFatima ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Cell Vocabulary: NameDocument3 pagesCell Vocabulary: NameStephanie BannickNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosomes Microtubules Mitochondria Ribosomes Nucleolus NucleoporeDocument2 pagesCell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosomes Microtubules Mitochondria Ribosomes Nucleolus NucleoporedominicNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Water Aerobics Is A Type of Aerobic ExerciseDocument12 pagesWater Aerobics Is A Type of Aerobic ExercisePete MagaleNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Management SystemsDocument87 pagesFood Safety Management SystemsAshish SahuNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Crown Lengthening Surgery The BasiDocument8 pagesA Review of The Crown Lengthening Surgery The BasiPaTt Tyy RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Community Health Project TopicsDocument3 pagesCommunity Health Project Topicsthomasgrace0107No ratings yet
- Ventilation Mini ManualDocument44 pagesVentilation Mini ManualKhusnul DwinitaNo ratings yet
- Basic Nursing SkillsDocument62 pagesBasic Nursing Skillsapi-3764215100% (8)
- Antiparkinson DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast TransformationDocument14 pagesChloroplast TransformationShuddhodana MukthaNo ratings yet
- MakalahDocument34 pagesMakalahShinta RazakNo ratings yet
- Tle - He (Cookery 10) Quarter 4 - Module 5 Storing MeatDocument9 pagesTle - He (Cookery 10) Quarter 4 - Module 5 Storing MeatAdine Jeminah Limon100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocument7 pagesDaftar PustakamekkaniaNo ratings yet
- 401-Article Text-778-1-10-20190128 PDFDocument3 pages401-Article Text-778-1-10-20190128 PDFCut Nanda FitriNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderDocument6 pagesAssessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Totems of The Dead GM Guide Preview (A Setting For The Savage Worlds RPG)Document16 pagesTotems of The Dead GM Guide Preview (A Setting For The Savage Worlds RPG)Matt Kaiser100% (3)
- Standard of Nursing ServicesDocument30 pagesStandard of Nursing Servicesjvfaderon7492% (25)
- Cow's Milk Protein AllergyDocument46 pagesCow's Milk Protein AllergyChyntia PutriNo ratings yet
- Advanced Critical Reading - Columbian ExchangeDocument4 pagesAdvanced Critical Reading - Columbian ExchangeVahid UzunlarNo ratings yet
- Sommerlad-2003-Plastic and Reconstructive SurgeryDocument7 pagesSommerlad-2003-Plastic and Reconstructive SurgeryAbdul HameedNo ratings yet
- Enteral Feeding: Indications, Complications, and Nursing CareDocument6 pagesEnteral Feeding: Indications, Complications, and Nursing CareSheena CabrilesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Outcomes Intervention RationaleDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Outcomes Intervention Rationaleapi-531202141No ratings yet
- Neligan Vol 3 Chapter 03 MainDocument55 pagesNeligan Vol 3 Chapter 03 MainisabelNo ratings yet
- Correction of Intestinal Disbacteriosis in Children With Chronic Hepatitis B Associated With LambliasisDocument8 pagesCorrection of Intestinal Disbacteriosis in Children With Chronic Hepatitis B Associated With LambliasisCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Senior Project PaperDocument18 pagesSenior Project Paperapi-403904589No ratings yet
- Hegde'S Pocketguide To Treatment in Speech-Language PathologyDocument628 pagesHegde'S Pocketguide To Treatment in Speech-Language Pathologyrana binhohammedNo ratings yet
- DEEP Vein ThrombosisDocument72 pagesDEEP Vein ThrombosisLevy Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Disability Rights in IndiaDocument23 pagesDisability Rights in IndiaAnirban Saikia100% (1)
- Science9 q1 Mod1 SDOv2 1Document32 pagesScience9 q1 Mod1 SDOv2 1Amélie KatanaNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle With ECG Interpretation: Blood Pressure Heartbeat Heart RateDocument2 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle With ECG Interpretation: Blood Pressure Heartbeat Heart Ratenmahmud75No ratings yet
Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal Cells
Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal Cells
Uploaded by
Nelson De Lima0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesThe document describes the main organelles found in plant and animal cells. In plant cells, the nucleus controls cell fate, mitochondria provide energy, the endoplasmic reticulum helps synthesize proteins and lipids, the Golgi apparatus modifies proteins, vacuoles store water, nutrients or capture sunlight, vesicles transport proteins, lysosomes contain digestive enzymes, peroxisomes neutralize toxins, and ribosomes synthesize proteins. In animal cells, the cell membrane encloses the cytoplasm, centrioles organize microtubules in cell division, cilia and flagella aid in movement, the endoplasmic reticulum manufactures products, lysosomes digest macromolecules, mitochondria generate energy, the nucleus contains DNA, and
Original Description:
gagaadsf
Original Title
science 7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the main organelles found in plant and animal cells. In plant cells, the nucleus controls cell fate, mitochondria provide energy, the endoplasmic reticulum helps synthesize proteins and lipids, the Golgi apparatus modifies proteins, vacuoles store water, nutrients or capture sunlight, vesicles transport proteins, lysosomes contain digestive enzymes, peroxisomes neutralize toxins, and ribosomes synthesize proteins. In animal cells, the cell membrane encloses the cytoplasm, centrioles organize microtubules in cell division, cilia and flagella aid in movement, the endoplasmic reticulum manufactures products, lysosomes digest macromolecules, mitochondria generate energy, the nucleus contains DNA, and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesPloginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal Cells
Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal Cells
Uploaded by
Nelson De LimaThe document describes the main organelles found in plant and animal cells. In plant cells, the nucleus controls cell fate, mitochondria provide energy, the endoplasmic reticulum helps synthesize proteins and lipids, the Golgi apparatus modifies proteins, vacuoles store water, nutrients or capture sunlight, vesicles transport proteins, lysosomes contain digestive enzymes, peroxisomes neutralize toxins, and ribosomes synthesize proteins. In animal cells, the cell membrane encloses the cytoplasm, centrioles organize microtubules in cell division, cilia and flagella aid in movement, the endoplasmic reticulum manufactures products, lysosomes digest macromolecules, mitochondria generate energy, the nucleus contains DNA, and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
pLoginpartpppppp
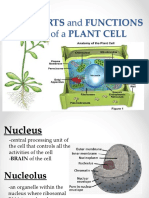
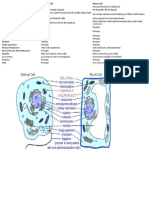
Parts of Plant cells
Nucleus: Controls the fate of the cell, tells cell if it is to be part of the muscle or skin.
Mitochondria: Powerhouse of the cell, stores energy for various cellular functions.
Endoplasmic Reticulum(ER): Helps the cell in synthesizing lipids as well as proteins and their
packaging.
Golgi Apparatus: Processes proteins generated at ER by post-translational modifications.
Vacuoles: Large and empty sacs usually filled with water in animal cells, in plant cells they may
contain nutrients and capture energy from the sun.
Vesicles: Small vacuoles that participate in carrying proteins from cell organelles or other cells.
Lysosomes: Vacuoles filled with enzymes to break the food.
Peroxisomes: Vacuoles filled with oxidizing enzymes to neutralize toxic substances.
Ribosomes: Synthesize proteins from mRNA produced by cellular genomic DNA.
Centrioles: Align chromosomes on spindle during cell-division
Cell membrane: Protection of Cellular integrity.
Microtubules: Involved in division of cellular DNA and cytoplasm.
Nucleolus: Produce ribosomes.
Villi: Increase the surface area of the cell.
Cilia: Help in transport of cellular surface
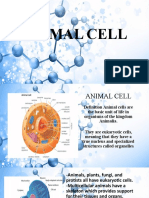
Parts of animal cells
Cell (Plasma) Membrane - thin, semi-permeable membrane that surrounds
the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosing its contents.
Centrioles - cylindrical structures that organize the assembly of microtubules during cell
division.
Cilia and flagella - specialized groupings of microtubules that protrude from some cells
and aid in cellular locomotion.
Cytoplasm - gel-like substance within the cell.
Cytoskeleton - a network of fibers throughout the cell's cytoplasm that gives the cell
support and helps to maintain its shape.
Endoplasmic Reticulum - an extensive network of membranes composed of both regions
with ribosomes (rough ER) and regions without ribosomes (smooth ER).
Golgi Complex - also called the Golgi apparatus, this structure is responsible for
manufacturing, storing and shipping certain cellular products.
Lysosomes - sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules such as nucleic acids.
Microtubules - hollow rods that function primarily to help support and shape the cell.
Mitochondria - cell components that generate energy for the cell and are the sites
of cellular respiration.
Nucleus - membrane-bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information.
Nucleolus - structure within the nucleus that helps in the synthesis of ribosomes.
Nucleopore - a tiny hole in the nuclear membrane that allows nucleic acids and
proteins to move into and out of the nucleus.
Peroxisomes - enzyme containing structures that help to detoxify alcohol, form bile acid,
and break down fats.
Ribosomes - consisting of RNA and proteins, ribosomes are responsible for protein
assembly.
You might also like
- Revision Worksheet 2 Grade 6Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet 2 Grade 6bindu100% (1)
- Kuby Immunology Ch. 5Document14 pagesKuby Immunology Ch. 5eabazaNo ratings yet
- Plants Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell Wall PhagocyticDocument1 pagePlants Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell Wall PhagocyticHara Prasad MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsstaluciadNo ratings yet
- Biology Key TermsDocument3 pagesBiology Key TermsTia TiaNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- OrganellesDocument13 pagesOrganellesjanaNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- Pro and EuDocument15 pagesPro and EuCy BathanNo ratings yet
- ASDFASDFASDocument17 pagesASDFASDFASChristian Cyril RoldanNo ratings yet
- Cell CytoplasmDocument55 pagesCell Cytoplasmnicolaer111100% (1)
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell - LayoutDocument3 pagesPlant Cell - LayoutMahiNo ratings yet
- All About Animal CellsDocument2 pagesAll About Animal CellsJether Marc Palmerola GardoseNo ratings yet
- BiotechDocument2 pagesBiotechKristel Faye Cortez SubiaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- The Animal Cell: Eukaryotic Cells DNADocument2 pagesThe Animal Cell: Eukaryotic Cells DNAEstefanía ElizondoNo ratings yet
- 4 CellDocument17 pages4 CellNoor ul aminNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocument15 pagesParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellPaul Sotto NgujoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument51 pages2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- STM123 OutlineDocument19 pagesSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisNicole CatolicoNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document30 pagesPart 1Rion BaiganNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- By: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT: Eukaryotic CellDocument9 pagesBy: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT: Eukaryotic CellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsYukiNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKent Orriele FadriquelNo ratings yet
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellDocument7 pagesCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The CellDocument2 pagesChapter 2 The CellGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell StructureDocument3 pagesAnimal Cell StructurejwoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellLeordan SanimNo ratings yet
- Rough and Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument3 pagesRough and Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumAnna Mae DollenteNo ratings yet
- A Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The BodyDocument1 pageA Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The BodySarthepandabearNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesCell OrganellesMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Organelles.: Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOrganelles.: Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisLuzNo ratings yet
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocument9 pagesMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- 1.2. Cell Structure and Organisation PMTDocument3 pages1.2. Cell Structure and Organisation PMTJamesNo ratings yet
- فاينل انسجة نظريDocument40 pagesفاينل انسجة نظريحسن القاضيNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Genetics 101Document4 pagesGenetics 101Jhon Ric BajeNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure VocabDocument1 pageCell Structure VocabFatima ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Cell Vocabulary: NameDocument3 pagesCell Vocabulary: NameStephanie BannickNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosomes Microtubules Mitochondria Ribosomes Nucleolus NucleoporeDocument2 pagesCell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosomes Microtubules Mitochondria Ribosomes Nucleolus NucleoporedominicNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Water Aerobics Is A Type of Aerobic ExerciseDocument12 pagesWater Aerobics Is A Type of Aerobic ExercisePete MagaleNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Management SystemsDocument87 pagesFood Safety Management SystemsAshish SahuNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Crown Lengthening Surgery The BasiDocument8 pagesA Review of The Crown Lengthening Surgery The BasiPaTt Tyy RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Community Health Project TopicsDocument3 pagesCommunity Health Project Topicsthomasgrace0107No ratings yet
- Ventilation Mini ManualDocument44 pagesVentilation Mini ManualKhusnul DwinitaNo ratings yet
- Basic Nursing SkillsDocument62 pagesBasic Nursing Skillsapi-3764215100% (8)
- Antiparkinson DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast TransformationDocument14 pagesChloroplast TransformationShuddhodana MukthaNo ratings yet
- MakalahDocument34 pagesMakalahShinta RazakNo ratings yet
- Tle - He (Cookery 10) Quarter 4 - Module 5 Storing MeatDocument9 pagesTle - He (Cookery 10) Quarter 4 - Module 5 Storing MeatAdine Jeminah Limon100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocument7 pagesDaftar PustakamekkaniaNo ratings yet
- 401-Article Text-778-1-10-20190128 PDFDocument3 pages401-Article Text-778-1-10-20190128 PDFCut Nanda FitriNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderDocument6 pagesAssessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Totems of The Dead GM Guide Preview (A Setting For The Savage Worlds RPG)Document16 pagesTotems of The Dead GM Guide Preview (A Setting For The Savage Worlds RPG)Matt Kaiser100% (3)
- Standard of Nursing ServicesDocument30 pagesStandard of Nursing Servicesjvfaderon7492% (25)
- Cow's Milk Protein AllergyDocument46 pagesCow's Milk Protein AllergyChyntia PutriNo ratings yet
- Advanced Critical Reading - Columbian ExchangeDocument4 pagesAdvanced Critical Reading - Columbian ExchangeVahid UzunlarNo ratings yet
- Sommerlad-2003-Plastic and Reconstructive SurgeryDocument7 pagesSommerlad-2003-Plastic and Reconstructive SurgeryAbdul HameedNo ratings yet
- Enteral Feeding: Indications, Complications, and Nursing CareDocument6 pagesEnteral Feeding: Indications, Complications, and Nursing CareSheena CabrilesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Outcomes Intervention RationaleDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Outcomes Intervention Rationaleapi-531202141No ratings yet
- Neligan Vol 3 Chapter 03 MainDocument55 pagesNeligan Vol 3 Chapter 03 MainisabelNo ratings yet
- Correction of Intestinal Disbacteriosis in Children With Chronic Hepatitis B Associated With LambliasisDocument8 pagesCorrection of Intestinal Disbacteriosis in Children With Chronic Hepatitis B Associated With LambliasisCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Senior Project PaperDocument18 pagesSenior Project Paperapi-403904589No ratings yet
- Hegde'S Pocketguide To Treatment in Speech-Language PathologyDocument628 pagesHegde'S Pocketguide To Treatment in Speech-Language Pathologyrana binhohammedNo ratings yet
- DEEP Vein ThrombosisDocument72 pagesDEEP Vein ThrombosisLevy Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Disability Rights in IndiaDocument23 pagesDisability Rights in IndiaAnirban Saikia100% (1)
- Science9 q1 Mod1 SDOv2 1Document32 pagesScience9 q1 Mod1 SDOv2 1Amélie KatanaNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle With ECG Interpretation: Blood Pressure Heartbeat Heart RateDocument2 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle With ECG Interpretation: Blood Pressure Heartbeat Heart Ratenmahmud75No ratings yet