Professional Documents
Culture Documents
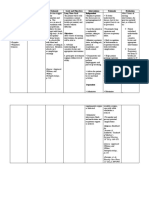
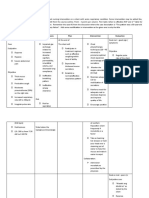
Ventilator Parameter & Its Normal Range
Ventilator Parameter & Its Normal Range
Uploaded by
Tmanoj PraveenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ventilator Parameter & Its Normal Range
Ventilator Parameter & Its Normal Range
Uploaded by
Tmanoj PraveenCopyright:
Available Formats
PHLEGM67 | home
The Creed of the Air Force Society of Cardiopulmonary Technologists | MY RESUME | Acid-Base Physiology | On Mechanical
Ventilation | The Winning Weaning Parameters | Original Articles and Views | Photo Album | Contemporary
Cardiopulmonary Topics and Practice | Death and Dying Connection | Respiratory Care Boards and Committees | The
Inspector's Corner - Regulatory Agencies | USAF Cardiopulmonary Society and AARC Affiliates | Breathe Sounds | Health
Resources | Respiratory Publications and Articles | The Wheezer Connections - Asthma Etcetera | Youth Role Modelling and
Respiratory Health Advocacy | On Becoming A Respiratory Case Manager | Whatever | Contact Me | House and Family Pixs
The Winning Weaning Parameters
Parameter Normal Range Indications Definition
for Weaning
The number of respiration per
minute. This includes all
control, IMV/SIMV and
spontaneous respiration. An
elevated respiratory rate is
the compensating mechanism
for a drop of tidal volume as a
result of increased body
exertion. This increase,
Respiratory 10-20 <30 outside the normal range, is a
Rate breaths/min breaths/min* possible indicator of the onset
of fatigue associated with the
failure of the ventilatory pump
to maintain adequate output
in the face of the imposed
workload. A low respiratory
rate may result in
hypoventilation and a
respiratory acidosis.
Delta Esophageal Pressure is
the pressure change in the
esophagus due to ventilation.
This measurement has been
reported to accurately track
changes in the pleural
pressure. During any
ventilation activity, airway
pressures maybe transmitted
across the pleural space to
Delta the esophagus. On patient
Esophageal 5-10 cmH2O <15 cmH2O initiated breaths, the true
Pressure value of Delta Esophageal
Pressure is the negative
deflection of the esophageal
pressure. On assisted breath
during mechanical support or
during controlled mechanical
ventilation, positive airway
pressure may be transmitted
across the potential space
causing a rise in esophageal
pressure above the normal
end esophageal pressure
point. Delta Esophageal
Pressure is an excellent
weaning indicator. Normal
Range for non-ventilated
patient is 2-10 cmH2O
Tidal Volume is the volume of
inhaled (VTins) or exhaled
(VTexp)gas per each breath.
This is monitored during
Tidal Volume mechanical ventilation to
7-10 ml/kg >5 ml/kg* determine if the level of
mechanical support is
adequate for the patient. It
may also be an indicator of
respiratory fatigue
Vital Capacity >15 ml/kg Yes, you should know this by
now!
Minute 5-10 <10 This one too!
Ventilation liters/minute liters/minute
Respiratory Time Fraction
(TI / TTOT) indicates endurance
and is defined as the ratio of
the inspired time to the total
time of the respiratory cycle.
This value is a ratio and there
is no unit of measure. As the
respiratory muscles fatigue,
the fraction of the breathing
cycle spent in inspiration
TI / TTOT tends to increase. When there
Respiratory .3-.4 Increase of is respiratory muscle fatigue
Time Fraction >.1* and impending respiratory
failure the ratio between
inspiratory time and total time
available for the breath may
incrementally increase to a
point in which the respiratory
pump can no longer maintain
itself and the (TI / TTOT) may
decrease dramatically.
Excessive work of breathing
is the common cause of
elevated
(TI / TTOT)
WOBp .3-.6 joules/liter <.75
joules/liter*
Pressure Time Index (PTI) is
a measure of strength and
endurance combined into one
Pressure .05-1.2 <.15* value. It combines the
Time strength measurement of
Index esophageal pressure and the
maximum inspiratory pressure
with the endurance value of
respiratory time fraction.
There are two kinds: Mean
Airway Resistance - the result
of friction in the patient
airways and endotracheal
tube throughout the entire
respiratory cycle. Expiratory
Airway Resistance is the
result of friction in the
Airway 2-5 <15 patient's airways,
Resistance cmH2O/L/sec cmH2O/L/sec endotracheal tube and
expiratory limb of the
ventilator circuit during
expiration only. Airway
resistance normally varies
inversely with lung volume
and increases in obstructive
and reactive airways disease.
It increases rapidly with
decreases in ET tube size as
a result of Poiseulle's Law.
Don't forget to subtract the
PEEP:-)
Lung 50-100 >25 If you don't know how to
Compliance ml/cm H2O ml/cm H2O calculate this parameter yet,
please drop me an e-mail and
include your school and your
instructor.
Pressure Time Product (PTP)
is an estimate of metabolic
work (oxygen consumption) of
the respiratory muscles. This
maybe used to evaluate
patient effort to overcome
both mechanical and
isometric force of respiration.
PTP decreases with the
application of optimal
pressure support (PSV) and
continuous positive airway
pressure (CPAP). PTP varies
Pressure Time 200-300 directly with total lung
Product cm resistance. This variable is an
H2O/sec/min important indicator of the
actual patient effort to breath.
Any isometric muscle
contraction by the
patient exerted to overcome
Auto PEEP or to open the
inspiratory demand system
results in no tidal volume
change and, therefore,
accomplishes little or
no measurable work. In this
case, PTP may reflect the
patient's muscular effort more
faithfully than work of
breathing. Non- intubated
patients should average
between 60-80 cm
H2O/sec/min.
Maximum Inspiratory
Pressure (MIP) is the
pressure change measured
by esophageal balloon, that
the patient can generate
when the airway is occluded
for several breaths. MIP is a
reflection of diaphragmatic
-30 cm H2O strength and may also be
Maximum low effort >-20 used to monitor respiratory
Inspiratory cm H2O* muscle endurance when
Pressure -140 cm H2O low effort serial measurements are
high effort made. MIP differs slightly
from the more commonly
used negative inspiratory
force (NIF), which is
measured at the mouth but
also reflects or measures
diaphragmatic strength.
Auto PEEP results when
insufficient expiratory time is
available between breath to
reestablish resting
equilibrium. A residual
alveolar pressure remains at
the end exhalation which is
Auto PEEP 0 <3 cm H2O undetected by the ventilators
circuitry. Causes of Auto
PEEP are: too large delivered
tidal volume, too short
expiratory time, increased
circuit impedance, low peak
inspiratory flows, high
respiratory rate, expiratory
airways obstruction or
dynamic airways collapse.
P0.1 Respiratory Drive
actually measures the neural
drive to stimulate the force of
diaphragmatic contraction. It
is defined at the airway
occlusion pressure at the first
100 msec after airway closure
prior to the patient's
P0.1 Respiratory conscious recognition of
Drive 2-4 <6 occlusion. A heightened
cmH2O cmH2O Respiratory Drive increases
work expenditure during
patient initiated ventilator
breaths and may indicate a
problem in the
cardiopulmonary system. It
plays an essential part during
machine assisted breaths in
determining the energy
expenditure of the patient. A
low value for P0.1 Respiratory
Drive may indicate when
respiratory drive is blunted.
Problems with P0.1
Respiratory Drive therefore,
are important indicators of the
ability of the patient to wean
from mechanical ventilation.
The ratio of respiratory
frequency to tidal volume is
called the Rapid, Shallow
Breathing Index (RSBI). The
RSB Index 60-90 <105* ratio has proven to be an
(RR/Vt) accurate predictor of success
when weaning patients from
mechanical ventilation
*Research indicates that these pulmonary parameters may aid qualified personnel in evaluating weaning potential. If measured values
exceed acceptable range,
successful weaning may be less likely. Ranges from these parameters are not intended as a substitute for clinical assessment.
You might also like
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics (2-Volume Set) by Robert M. Kliegman, Bonita F. Stanton, Joseph W. ST Geme III, Nina F. SchorDocument312 pagesNelson Textbook of Pediatrics (2-Volume Set) by Robert M. Kliegman, Bonita F. Stanton, Joseph W. ST Geme III, Nina F. SchorFaisal MomenNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesASSESSMENTArvin BaesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Diseases Chapter From Nelson Textbook of PediatricsDocument312 pagesRespiratory Diseases Chapter From Nelson Textbook of PediatricsMilan Andrejevic100% (1)
- Settings and Management Tip Sheet For Providers: Isp Elevated?Document1 pageSettings and Management Tip Sheet For Providers: Isp Elevated?mohamedkoriesh100% (1)
- Care of Patient On VentilatorDocument18 pagesCare of Patient On VentilatorJose Paul Rader100% (1)
- Health ResearchDocument16 pagesHealth ResearchTmanoj PraveenNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure Manual For Obstetrics and Midwifery ServicesDocument64 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Manual For Obstetrics and Midwifery ServicesTmanoj Praveen75% (4)
- The Indian Nursing CouncilDocument7 pagesThe Indian Nursing CouncilTmanoj Praveen100% (1)
- NCP Risk of AspirationDocument2 pagesNCP Risk of AspirationNura Zein100% (1)
- Form Monitoring PPI LengkapDocument30 pagesForm Monitoring PPI LengkapAgus Pudianto100% (3)
- Einc ReviewerDocument4 pagesEinc ReviewerEricson Candelaria0% (1)
- Mechanical Ventilation Settings and Basic Modes Tip Card January 2019Document4 pagesMechanical Ventilation Settings and Basic Modes Tip Card January 2019SyamalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanical VentilationDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Mechanical VentilationHussam GujjarNo ratings yet
- Mwlcems System Continuing Education Packet Mechanical VentilationDocument8 pagesMwlcems System Continuing Education Packet Mechanical VentilationSoumahoro Ibrahim JuniorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Mechanical Ventilator: HistoryDocument7 pagesChapter 2: Mechanical Ventilator: HistoryYasmin AbdelmajiedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Mechanical Ventilator: HistoryDocument7 pagesChapter 2: Mechanical Ventilator: HistoryYasmin AbdelmajiedNo ratings yet
- Ventilator LectureDocument57 pagesVentilator LecturemonishaNo ratings yet
- Ventilator Quick Guide PDFDocument2 pagesVentilator Quick Guide PDFÖzgür Barışcan KayaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation: Dr. Shivam Mohan PandeyDocument150 pagesMechanical Ventilation: Dr. Shivam Mohan PandeyshivamNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument16 pagesMechanical VentilationBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Pressure-Volume Curves of Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesPressure-Volume Curves of Respiratory SystemSiriporn PongpattarapakNo ratings yet
- Avea Ventilatorquicktips: AB CD EDocument8 pagesAvea Ventilatorquicktips: AB CD EVica BodiuNo ratings yet
- Jcinvest00338 0038Document8 pagesJcinvest00338 0038Priyadharshini KumarNo ratings yet
- Setting The VentilatorDocument3 pagesSetting The VentilatorCarlos ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Review of Patient-Ventilator DyssynchronyDocument8 pagesRapid Review of Patient-Ventilator Dyssynchronycarolina de jesusNo ratings yet
- Samsung Notes PDFDocument4 pagesSamsung Notes PDFPedro Antonio Ortega BorchardtNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument1 pageAssessmentFat NrqzNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting in Mechanical VentilatorDocument77 pagesMonitoring and Troubleshooting in Mechanical VentilatorRashma Little RobinNo ratings yet
- Lung Mechncs IDocument16 pagesLung Mechncs Iafshan.arzooNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument5 pagesMechanical Ventilationha,hr124No ratings yet
- EMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 1Document4 pagesEMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 1Emily CallerNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Mechanical VentilationDocument28 pagesPhysiology of Mechanical VentilationBaswaraj Tandur100% (1)
- High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV) تغريدDocument16 pagesHigh Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV) تغريدtaghreednurseNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument5 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionApryll Kristin Villaluna ZafeNo ratings yet
- Tidal Volume Volum Expirator/inspirator: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument9 pagesTidal Volume Volum Expirator/inspirator: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchFeier CristianNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument18 pagesMechanical Ventilationdp55gjjb2hNo ratings yet
- Texto1 S9 RespiratorioDocument6 pagesTexto1 S9 RespiratorioCAROLINA CHUMACERO BERMEONo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective BreathingDocument6 pagesNCP Ineffective BreathingCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Hopper2015 Advance Mechanical VentilationDocument7 pagesHopper2015 Advance Mechanical VentilationGuillermo MuzasNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 B Mechanical Ventilation: Managing Ventilators SettingsDocument5 pagesChapter 29 B Mechanical Ventilation: Managing Ventilators SettingsElle ReyesNo ratings yet
- (RS) Pulmonary EdemaDocument5 pages(RS) Pulmonary Edemaapi-3769252No ratings yet
- Caring For The Mechanically Ventilated PatientDocument2 pagesCaring For The Mechanically Ventilated PatientKat AlaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilator: Parameters of Mechanical VentilationDocument7 pagesMechanical Ventilator: Parameters of Mechanical Ventilationpraveen joseNo ratings yet
- Calibration Method For Ventilators and Ventilator TestersDocument74 pagesCalibration Method For Ventilators and Ventilator TestersGigin Ginanjar100% (1)
- Ventilation Dead Space Ventilation Physiology of RespirationDocument55 pagesVentilation Dead Space Ventilation Physiology of RespirationkuhutansittinurhalizaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Revised - PPTX New 2020Document72 pagesMechanical Ventilation Revised - PPTX New 2020Ahmad nazirNo ratings yet
- Datos Complementarios #3Document31 pagesDatos Complementarios #3MaaaanuelNo ratings yet
- SMART Ventilation 101 2023Document20 pagesSMART Ventilation 101 2023umar ankaNo ratings yet
- Asma Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesAsma Bahasa InggrisAstuti Dwi JayantiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanNicolne LorraineNo ratings yet
- Ventilator Omar 2016Document63 pagesVentilator Omar 2016Minutes in MEDITATIONNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation GraphicsDocument144 pagesMechanical Ventilation GraphicsSaddamNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical Ventilation (SIPHW)Document68 pagesBasics of Mechanical Ventilation (SIPHW)Sudip beraNo ratings yet
- Respiratoryfunctionandimportancetoanesthesia Final 140103050711 Phpapp02Document62 pagesRespiratoryfunctionandimportancetoanesthesia Final 140103050711 Phpapp02rijjorajooNo ratings yet
- Name: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaDocument2 pagesName: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- Ventilation-Perfusion RatioDocument34 pagesVentilation-Perfusion Rationeeba habeebNo ratings yet
- Estratégias em VentilaçãoDocument12 pagesEstratégias em VentilaçãoVeronica MorachimoNo ratings yet
- Lumb, A. 2017. Elastic Forces and Lung Volumes. Nunn's Applied Respiratory Physiology.Document17 pagesLumb, A. 2017. Elastic Forces and Lung Volumes. Nunn's Applied Respiratory Physiology.Daniel Oscar Pintos ChiesaNo ratings yet
- Cecilia, Issaiah Nicolle-Pneumothorax-NcpDocument7 pagesCecilia, Issaiah Nicolle-Pneumothorax-NcpIssaiah Nicolle Cecilia100% (1)
- CALMA, Mary Ann C. BSN - Iv-Leininger Skill: Breathe Comfortably Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesCALMA, Mary Ann C. BSN - Iv-Leininger Skill: Breathe Comfortably Nursing Care PlanMaryann CalmaNo ratings yet
- Simv/Asb Mode: Basic Settings ExplainedDocument5 pagesSimv/Asb Mode: Basic Settings ExplainedFitriyanti RosyadiNo ratings yet
- Suplemento Standardized Vocabulario V2oouewDocument16 pagesSuplemento Standardized Vocabulario V2oouewJadder InnacioNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired GasDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired GasRea LynNo ratings yet
- Dosage Calculation Workbook Fill inDocument20 pagesDosage Calculation Workbook Fill inTmanoj PraveenNo ratings yet
- ART2016631Document7 pagesART2016631Tmanoj PraveenNo ratings yet
- Nive TharDocument177 pagesNive TharTmanoj Praveen100% (1)
- Australian Ms Nursing Manual 2nd EditionDocument214 pagesAustralian Ms Nursing Manual 2nd EditionTmanoj PraveenNo ratings yet
- Complete The Crossword Puzzle Below: NameDocument2 pagesComplete The Crossword Puzzle Below: NameTmanoj PraveenNo ratings yet
- NN.11.05 Triple Lumen Central Venous Catheter Standard SetupDocument2 pagesNN.11.05 Triple Lumen Central Venous Catheter Standard SetupTmanoj PraveenNo ratings yet
- Newyork-Presbyterian: Morgan Stanley Children'S HospitalDocument41 pagesNewyork-Presbyterian: Morgan Stanley Children'S HospitalTmanoj PraveenNo ratings yet
- General Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument17 pagesGeneral Nursing Care Plan PDFTmanoj Praveen100% (1)
- While Demonstrating The New Skills To Students at The Skills LabDocument4 pagesWhile Demonstrating The New Skills To Students at The Skills LabTmanoj PraveenNo ratings yet
- Clinical Evaluation - Community Health Nursing - 1Document20 pagesClinical Evaluation - Community Health Nursing - 1Tmanoj Praveen100% (1)
- SBA MODULE Guideline For Antenatal CareDocument80 pagesSBA MODULE Guideline For Antenatal CareTmanoj Praveen33% (3)
- Virus Isolation Court Case - Docx DR FeullmichDocument2 pagesVirus Isolation Court Case - Docx DR FeullmichRaaidNo ratings yet
- Recurrent SnezzingDocument7 pagesRecurrent Snezzingrahulsinghroy17025No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledGuia Charish SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Servo-S: Data SheetDocument16 pagesVentilation Servo-S: Data SheetBreno VieiraNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome: DR Bob KlajoDocument17 pagesMeconium Aspiration Syndrome: DR Bob KlajoBob John100% (1)
- Appendix #5Document14 pagesAppendix #5Euvanie Bualan RusteNo ratings yet
- Standard Practice Guidelines Terkini FinalDocument192 pagesStandard Practice Guidelines Terkini FinalemerituspensieroNo ratings yet
- PALS Precourse Self-AssessmentDocument3 pagesPALS Precourse Self-AssessmentMarsya Julia RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular & Respiratory SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular & Respiratory SystemSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Benefit Packages (Private)Document103 pagesBenefit Packages (Private)You Are Not Wasting TIME HereNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Rouviere's Sulcus-Aspects of Incorporating This Valuable Sign For Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocument3 pages2018 - Rouviere's Sulcus-Aspects of Incorporating This Valuable Sign For Laparoscopic CholecystectomyBattousaih1No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingUtibe EdemNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Emergency Di Ruang IgdDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat Emergency Di Ruang IgdTesa Yuli DenisaNo ratings yet
- Malla de Mensajes y Contiendos de La Rde 766 OrganizacionDocument134 pagesMalla de Mensajes y Contiendos de La Rde 766 OrganizacionAisha JuárezNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1.product and Company IdentificationDocument9 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1.product and Company IdentificationMahmoofNo ratings yet
- Univar USA Inc Material Safety Data Sheet: Msds No: Version No: Order NoDocument10 pagesUnivar USA Inc Material Safety Data Sheet: Msds No: Version No: Order NoHoàng DũngNo ratings yet
- Delayed Emergence in Post Anesthesia Care Unit (Pacu) : Achmed RizalDocument15 pagesDelayed Emergence in Post Anesthesia Care Unit (Pacu) : Achmed RizalAdikurniawanNo ratings yet
- Cot 1 Vital SignsDocument22 pagesCot 1 Vital Signscristine g. magatNo ratings yet
- Care Plan Pneumonia CompressDocument18 pagesCare Plan Pneumonia CompressAahad AmeenNo ratings yet
- Case-Study-On-Pulmonary EdemaDocument100 pagesCase-Study-On-Pulmonary EdemaLouie MansaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernias (CDH)Document24 pagesCongenital Diaphragmatic Hernias (CDH)tsega tilahunNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Concept MapDocument7 pagesPediatric Concept Mapapi-508020518No ratings yet
- Wood Support-Micro Guard Product DataDocument13 pagesWood Support-Micro Guard Product DataM. Murat ErginNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - ABM - Araling Panlipunan - Applied Economics - Week 1Document11 pagesGrade 11 - ABM - Araling Panlipunan - Applied Economics - Week 1Christian LapidNo ratings yet
- Presentation April 2017Document44 pagesPresentation April 2017Ali Hossain AdnanNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale: Anjela BaidyaDocument31 pagesCor Pulmonale: Anjela BaidyaAnjela BaidyaNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms Log Form: Floor #154 BUCANDALA 2 Imus CaviteDocument5 pagesSigns and Symptoms Log Form: Floor #154 BUCANDALA 2 Imus CaviteHealth ProbeNo ratings yet