Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra: E Lements of Power System Analysis
Algebra: E Lements of Power System Analysis
Uploaded by
aladin AboyaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Graded Quiz - CourseraDocument5 pagesGraded Quiz - CourseraAri de enNo ratings yet
- AE PHD SummaryDocument3 pagesAE PHD SummaryNumkang KangNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument47 pagesNetwork TopologySujeet Kumar100% (1)
- 11 SVDDocument47 pages11 SVDhenry chaccaNo ratings yet
- 0 Short Review of Some Mathematics, Nomenclature and NotationDocument14 pages0 Short Review of Some Mathematics, Nomenclature and NotationWong Zam MingYinNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis: Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesPower System Analysis: Lecture NotesalfredzNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis VTU NotesDocument47 pagesNetwork Analysis VTU NotesSagar S Poojary50% (2)
- 18248-Article Text-50721-1-10-20210318Document31 pages18248-Article Text-50721-1-10-20210318Priya SaputraNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra & Ordinary Differential Equations MATH-121: Lecture # 20Document8 pagesLinear Algebra & Ordinary Differential Equations MATH-121: Lecture # 20Syeda Fatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- CH 1 MatricesDocument24 pagesCH 1 MatricesSidharth AnchaliaNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Transformer Modeling Using Symmetrical ComponentsDocument7 pagesThree-Phase Transformer Modeling Using Symmetrical ComponentsHarry Miranda MedranoNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - Part II: Projection, Eigendecomposition, SVDDocument20 pagesLinear Algebra - Part II: Projection, Eigendecomposition, SVDjohn biancoNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra Cheat SheetMiriam Quan100% (1)
- Linear Graph Modeling: State Equation FormulationDocument38 pagesLinear Graph Modeling: State Equation Formulation古卜升No ratings yet
- Unit2 KCVDocument47 pagesUnit2 KCVsanoopmkNo ratings yet
- PSA. Part 2Document22 pagesPSA. Part 2SachinNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Vector AlgebraDocument16 pagesVectors and Vector Algebrapetrified pixelNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis - ECE - 3rd Sem - VTU - Unit 2 - Network Topology - Ramisuniverse, RamisuniverseDocument20 pagesNetwork Analysis - ECE - 3rd Sem - VTU - Unit 2 - Network Topology - Ramisuniverse, Ramisuniverseramisuniverse71% (7)
- Electric Circuits and FieldsDocument14 pagesElectric Circuits and FieldsManjunath N KammarNo ratings yet
- Caff Cfs 313: of IsDocument15 pagesCaff Cfs 313: of IsRaymondNo ratings yet
- Notes 8 - Bus Admittance MatrixDocument16 pagesNotes 8 - Bus Admittance MatrixCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Immitance InverterDocument4 pagesImmitance Inverteramitgh88No ratings yet
- Lect 4 - Rank - Echelon Form - 16B1NMA533 - 4Document20 pagesLect 4 - Rank - Echelon Form - 16B1NMA533 - 49921103067No ratings yet
- Mce371 13Document19 pagesMce371 13Abul HasnatNo ratings yet
- 2.7.3 Example: 2.2 Matrix AlgebraDocument8 pages2.7.3 Example: 2.2 Matrix Algebrafredy8704No ratings yet
- Node and Mesh Analysis by InspectionDocument5 pagesNode and Mesh Analysis by InspectionRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Homework 1: E1 241 - Dynamics of Linear Systems (Aug 2021) Due Date: Sept 08, 2021 Maximum Marks: 140Document2 pagesHomework 1: E1 241 - Dynamics of Linear Systems (Aug 2021) Due Date: Sept 08, 2021 Maximum Marks: 140Anand GuptaNo ratings yet
- LiteratureDocument19 pagesLiteraturepankaj kumar sumanNo ratings yet
- PenroseDocument7 pagesPenroseAngelika ErhardtNo ratings yet
- Irjet V2i2115 PDFDocument6 pagesIrjet V2i2115 PDFManicharanNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument28 pagesLinear ProgrammingRaka SubiNo ratings yet
- CS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #9: The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Low-Rank Matrix ApproximationsDocument10 pagesCS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #9: The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Low-Rank Matrix Approximationsenjamamul hoqNo ratings yet
- A2 Fundamental TheoryDocument14 pagesA2 Fundamental TheoryKelly TorresNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 (Vectors and Tensors)Document18 pagesLecture2 (Vectors and Tensors)entesar kareemNo ratings yet
- Linear Independence: Wei-Ta ChuDocument39 pagesLinear Independence: Wei-Ta Chunizad dardNo ratings yet
- PCE 6237 Advanced Power System Analysis: Lecture One: Section ThreeDocument26 pagesPCE 6237 Advanced Power System Analysis: Lecture One: Section ThreeBedasa ToleraNo ratings yet
- Construction of Combinatorial PyramidsDocument10 pagesConstruction of Combinatorial PyramidsMyda RafaelNo ratings yet
- For A Given Vector in 2D Space, Stretching It by A Value of 2 Is CalledDocument23 pagesFor A Given Vector in 2D Space, Stretching It by A Value of 2 Is CalledIgorJales100% (1)
- Electrical Networks and Lie TheoryDocument14 pagesElectrical Networks and Lie TheoryvzraNo ratings yet
- Matrices: Elementary Matrix TheoryDocument17 pagesMatrices: Elementary Matrix Theorybhen422No ratings yet
- 40 2. Systems of Linear EquationsDocument1 page40 2. Systems of Linear Equationsdhivikarthi6No ratings yet
- Symmetry 2Document17 pagesSymmetry 2fitriana dewi kurniawatiNo ratings yet
- 19 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Ordinary Differential Equations, and ControlDocument12 pages19 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Ordinary Differential Equations, and ControljackkelthorNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalues of GraphsDocument29 pagesEigenvalues of GraphsDenise ParksNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Kashif KhanDocument17 pagesAssignment 2 Kashif Khanengineerkashif97No ratings yet
- Stability Analysis For VAR SystemsDocument12 pagesStability Analysis For VAR SystemscosminNo ratings yet
- 2.3 ALGEBRA-Simultaneous EquationsDocument11 pages2.3 ALGEBRA-Simultaneous EquationsAmana IBNo ratings yet
- Primitive Network and Graph Theory PDFDocument12 pagesPrimitive Network and Graph Theory PDFDhavalVoraNo ratings yet
- Eigenvector and Eigenvalue ProjectDocument10 pagesEigenvector and Eigenvalue ProjectIzzy ConceptsNo ratings yet
- The Einstein Summation Notation (Barr)Document25 pagesThe Einstein Summation Notation (Barr)frege6534No ratings yet
- TY - ECE - SEM6 - Notes - Unit I (2) - CS - AAHDocument8 pagesTY - ECE - SEM6 - Notes - Unit I (2) - CS - AAHAgha HusainNo ratings yet
- Matrix Appendix (Katsuhiko Ogata) System Dynamics (4th Edition)Document15 pagesMatrix Appendix (Katsuhiko Ogata) System Dynamics (4th Edition)TracerLifeNo ratings yet
- Texto de Algebra Lineal U de Harvard PDFDocument47 pagesTexto de Algebra Lineal U de Harvard PDFJohn J Gomes EsquivelNo ratings yet
- A Course Manual On Engineering ElectromaDocument107 pagesA Course Manual On Engineering ElectromaIbaad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Power System Parameters and EquationsDocument29 pagesPower System Parameters and EquationsCatrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- L04 Maths FoundationsDocument30 pagesL04 Maths FoundationsJuwii ChanNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Linear Algebra FunctionsDocument15 pagesMATLAB Linear Algebra FunctionsAhmed HwaidiNo ratings yet
- Yu Kuzmina 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1847 012031Document6 pagesYu Kuzmina 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1847 012031louis donyNo ratings yet
- Sparse ArrayDocument2 pagesSparse ArrayzulkoNo ratings yet
- MR 6 2017 Solutions 1Document28 pagesMR 6 2017 Solutions 1StephenNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Matrix Computations: Second EditionDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Matrix Computations: Second EditionmohsinamanNo ratings yet
- 4 LinearlEquationsDocument15 pages4 LinearlEquationsSachin DhimanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Enginering Mathematics For Chemical EnginDocument8 pagesAdvanced Enginering Mathematics For Chemical EnginFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- DFT-Discrete Fourier TransformDocument9 pagesDFT-Discrete Fourier TransformErsin ErolNo ratings yet
- DeterminantDocument10 pagesDeterminantRadhey Shyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Roger A. Horn, Charles R. Johnson - Topics in Matrix Analysis-Cambridge University Press (2008)Document615 pagesRoger A. Horn, Charles R. Johnson - Topics in Matrix Analysis-Cambridge University Press (2008)June KangNo ratings yet
- Ebook Advanced Linear and Matrix Algebra 1St Edition Nathaniel Johnston Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Advanced Linear and Matrix Algebra 1St Edition Nathaniel Johnston Online PDF All Chapternancy.collins448100% (10)
- A1201132722 63869 8 2023 K21MDCA2QSetAllocationDocument12 pagesA1201132722 63869 8 2023 K21MDCA2QSetAllocationHanu VadlamudiNo ratings yet
- Matrix MultiplicationDocument13 pagesMatrix Multiplicationrida.me99No ratings yet
- 331 Notes MatrixDocument15 pages331 Notes MatrixSharifullah ShamimNo ratings yet
- Math 208 Exercise PackDocument112 pagesMath 208 Exercise PackChiOfGreeNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Linear EquationsDocument5 pagesModule 3: Linear EquationsAbedaNo ratings yet
- Quick Maths Revisiontwenty20Document40 pagesQuick Maths Revisiontwenty20nithinganesh174No ratings yet
- Gallopoulos - Parallelism in Matrix ComputationsDocument505 pagesGallopoulos - Parallelism in Matrix ComputationsThermionNo ratings yet
- IGNOU - Lecture Notes - Linear AlgebraDocument29 pagesIGNOU - Lecture Notes - Linear Algebraruchi21julyNo ratings yet
- IFEM AppP PDFDocument7 pagesIFEM AppP PDFPippo MiriNo ratings yet
- Matrix - An IntroductionDocument10 pagesMatrix - An IntroductionMajid AbNo ratings yet
- State Transition MatrixDocument26 pagesState Transition MatrixmemotetoNo ratings yet
- Fionaw Linear Algebra Math 232Document4 pagesFionaw Linear Algebra Math 232Kimondo KingNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - Solved Assignments - Fall 2005 SemesterDocument28 pagesLinear Algebra - Solved Assignments - Fall 2005 SemesterMuhammad Umair100% (1)
- Matrix Multiplication ParallelDocument5 pagesMatrix Multiplication ParallelAirNo ratings yet
- ES272 ch4bDocument18 pagesES272 ch4btarafe5509No ratings yet
- Exercises AlgebraDocument22 pagesExercises AlgebraTien KimNo ratings yet
- The FFT Via Matrix Factorizations: A Key To Designing High Performance ImplementationsDocument42 pagesThe FFT Via Matrix Factorizations: A Key To Designing High Performance Implementationsdangtung.dttNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes MatricesDocument90 pagesLecture Notes MatricesRR886No ratings yet
- Ex4Data - Mat: 221 Matlab Assignment 4Document3 pagesEx4Data - Mat: 221 Matlab Assignment 4Austin KonNo ratings yet
- The Open Leontief Input-Output ModelDocument3 pagesThe Open Leontief Input-Output ModelNhi HoàngNo ratings yet
Algebra: E Lements of Power System Analysis
Algebra: E Lements of Power System Analysis
Uploaded by
aladin AboyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra: E Lements of Power System Analysis
Algebra: E Lements of Power System Analysis
Uploaded by
aladin AboyaCopyright:
Available Formats
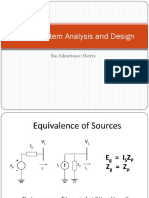
174 ELEMENTS OF POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS
DE ELIMINATION BY MATRIX ALGEBRA
7.4 NO
t enter or leave the
may be eliminated by matrix manipulation of the standard node ell
Nodes
owever, only those nodes at which current does no
tions. H
e eliminated.
network can b
dard node equations in matrix notation are expressed as
The stan (7.21)
I == )(bus Y
d V are column matrices and yl,„, is a symmetrical square matrix, N
where I an ,
trices must be so arranged that elements associated with nodes to be
column ma
e in the lower rows of the matrices. Elements of the square admit, trices are
eliminated ar The co lumn ma
partitioned
re located correspondingly.
tance matrix a re separated from
ments associated with nodes to be eliminated a
so that the ele
ents. The admittance matrix is partitioned so that oethleemr eeniets.
the other elem
eliminated are separated from
Identified only wi th nodes to be cording to these
and vertical lines. When partitioned ac
ments by horizontal
rules, Eq. (7.21) becomes
Li 1VvAd
(7.22)
[LT
currents entering the nodes to be
where Ix is the submatrix composed of the
des. Of
eliminated and Vx is the submatrix composed of the voltages of these no
course, every element in Ix is zero, for the nodes could not be eliminated other-
wise. The self- and mutual admittances composing K are those identified only
with nodes to be retained. M is composed of the self- and mutual admittances
identified only with nodes to be eliminated. It is a square matrix whose order is
equal to the number of nodes to be eliminated. L and its transpose LT are
ed
composed of only those mutual admittances common to a node to be retain and
to one to be eliminated.
Performing the multiplication indicated in Eq. (7.22) gives
IA KVA + LVx (7.23)
and
lx = LTVA + MVx (7.24)
74)
Since all elements of lx are zero, subtracting LTVA from both sides of Eq, (7 —
and multiplying both sides by the inverse of M (denoted by IN/1- 1) yields
4
—111-1LTVA Vx (7.2
5)
This expression for Vx substituted in Eq. (7.23) gives
IA = KV
A — LM-1LTVA (7.26)
which is a node equation having the admittance matrix
Ybus
LM- 11.7
(7.2'1
You might also like
- Graded Quiz - CourseraDocument5 pagesGraded Quiz - CourseraAri de enNo ratings yet
- AE PHD SummaryDocument3 pagesAE PHD SummaryNumkang KangNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument47 pagesNetwork TopologySujeet Kumar100% (1)
- 11 SVDDocument47 pages11 SVDhenry chaccaNo ratings yet
- 0 Short Review of Some Mathematics, Nomenclature and NotationDocument14 pages0 Short Review of Some Mathematics, Nomenclature and NotationWong Zam MingYinNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis: Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesPower System Analysis: Lecture NotesalfredzNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis VTU NotesDocument47 pagesNetwork Analysis VTU NotesSagar S Poojary50% (2)
- 18248-Article Text-50721-1-10-20210318Document31 pages18248-Article Text-50721-1-10-20210318Priya SaputraNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra & Ordinary Differential Equations MATH-121: Lecture # 20Document8 pagesLinear Algebra & Ordinary Differential Equations MATH-121: Lecture # 20Syeda Fatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- CH 1 MatricesDocument24 pagesCH 1 MatricesSidharth AnchaliaNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Transformer Modeling Using Symmetrical ComponentsDocument7 pagesThree-Phase Transformer Modeling Using Symmetrical ComponentsHarry Miranda MedranoNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - Part II: Projection, Eigendecomposition, SVDDocument20 pagesLinear Algebra - Part II: Projection, Eigendecomposition, SVDjohn biancoNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra Cheat SheetMiriam Quan100% (1)
- Linear Graph Modeling: State Equation FormulationDocument38 pagesLinear Graph Modeling: State Equation Formulation古卜升No ratings yet
- Unit2 KCVDocument47 pagesUnit2 KCVsanoopmkNo ratings yet
- PSA. Part 2Document22 pagesPSA. Part 2SachinNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Vector AlgebraDocument16 pagesVectors and Vector Algebrapetrified pixelNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis - ECE - 3rd Sem - VTU - Unit 2 - Network Topology - Ramisuniverse, RamisuniverseDocument20 pagesNetwork Analysis - ECE - 3rd Sem - VTU - Unit 2 - Network Topology - Ramisuniverse, Ramisuniverseramisuniverse71% (7)
- Electric Circuits and FieldsDocument14 pagesElectric Circuits and FieldsManjunath N KammarNo ratings yet
- Caff Cfs 313: of IsDocument15 pagesCaff Cfs 313: of IsRaymondNo ratings yet
- Notes 8 - Bus Admittance MatrixDocument16 pagesNotes 8 - Bus Admittance MatrixCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Immitance InverterDocument4 pagesImmitance Inverteramitgh88No ratings yet
- Lect 4 - Rank - Echelon Form - 16B1NMA533 - 4Document20 pagesLect 4 - Rank - Echelon Form - 16B1NMA533 - 49921103067No ratings yet
- Mce371 13Document19 pagesMce371 13Abul HasnatNo ratings yet
- 2.7.3 Example: 2.2 Matrix AlgebraDocument8 pages2.7.3 Example: 2.2 Matrix Algebrafredy8704No ratings yet
- Node and Mesh Analysis by InspectionDocument5 pagesNode and Mesh Analysis by InspectionRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Homework 1: E1 241 - Dynamics of Linear Systems (Aug 2021) Due Date: Sept 08, 2021 Maximum Marks: 140Document2 pagesHomework 1: E1 241 - Dynamics of Linear Systems (Aug 2021) Due Date: Sept 08, 2021 Maximum Marks: 140Anand GuptaNo ratings yet
- LiteratureDocument19 pagesLiteraturepankaj kumar sumanNo ratings yet
- PenroseDocument7 pagesPenroseAngelika ErhardtNo ratings yet
- Irjet V2i2115 PDFDocument6 pagesIrjet V2i2115 PDFManicharanNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument28 pagesLinear ProgrammingRaka SubiNo ratings yet
- CS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #9: The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Low-Rank Matrix ApproximationsDocument10 pagesCS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #9: The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Low-Rank Matrix Approximationsenjamamul hoqNo ratings yet
- A2 Fundamental TheoryDocument14 pagesA2 Fundamental TheoryKelly TorresNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 (Vectors and Tensors)Document18 pagesLecture2 (Vectors and Tensors)entesar kareemNo ratings yet
- Linear Independence: Wei-Ta ChuDocument39 pagesLinear Independence: Wei-Ta Chunizad dardNo ratings yet
- PCE 6237 Advanced Power System Analysis: Lecture One: Section ThreeDocument26 pagesPCE 6237 Advanced Power System Analysis: Lecture One: Section ThreeBedasa ToleraNo ratings yet
- Construction of Combinatorial PyramidsDocument10 pagesConstruction of Combinatorial PyramidsMyda RafaelNo ratings yet
- For A Given Vector in 2D Space, Stretching It by A Value of 2 Is CalledDocument23 pagesFor A Given Vector in 2D Space, Stretching It by A Value of 2 Is CalledIgorJales100% (1)
- Electrical Networks and Lie TheoryDocument14 pagesElectrical Networks and Lie TheoryvzraNo ratings yet
- Matrices: Elementary Matrix TheoryDocument17 pagesMatrices: Elementary Matrix Theorybhen422No ratings yet
- 40 2. Systems of Linear EquationsDocument1 page40 2. Systems of Linear Equationsdhivikarthi6No ratings yet
- Symmetry 2Document17 pagesSymmetry 2fitriana dewi kurniawatiNo ratings yet
- 19 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Ordinary Differential Equations, and ControlDocument12 pages19 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Ordinary Differential Equations, and ControljackkelthorNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalues of GraphsDocument29 pagesEigenvalues of GraphsDenise ParksNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Kashif KhanDocument17 pagesAssignment 2 Kashif Khanengineerkashif97No ratings yet
- Stability Analysis For VAR SystemsDocument12 pagesStability Analysis For VAR SystemscosminNo ratings yet
- 2.3 ALGEBRA-Simultaneous EquationsDocument11 pages2.3 ALGEBRA-Simultaneous EquationsAmana IBNo ratings yet
- Primitive Network and Graph Theory PDFDocument12 pagesPrimitive Network and Graph Theory PDFDhavalVoraNo ratings yet
- Eigenvector and Eigenvalue ProjectDocument10 pagesEigenvector and Eigenvalue ProjectIzzy ConceptsNo ratings yet
- The Einstein Summation Notation (Barr)Document25 pagesThe Einstein Summation Notation (Barr)frege6534No ratings yet
- TY - ECE - SEM6 - Notes - Unit I (2) - CS - AAHDocument8 pagesTY - ECE - SEM6 - Notes - Unit I (2) - CS - AAHAgha HusainNo ratings yet
- Matrix Appendix (Katsuhiko Ogata) System Dynamics (4th Edition)Document15 pagesMatrix Appendix (Katsuhiko Ogata) System Dynamics (4th Edition)TracerLifeNo ratings yet
- Texto de Algebra Lineal U de Harvard PDFDocument47 pagesTexto de Algebra Lineal U de Harvard PDFJohn J Gomes EsquivelNo ratings yet
- A Course Manual On Engineering ElectromaDocument107 pagesA Course Manual On Engineering ElectromaIbaad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Power System Parameters and EquationsDocument29 pagesPower System Parameters and EquationsCatrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- L04 Maths FoundationsDocument30 pagesL04 Maths FoundationsJuwii ChanNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Linear Algebra FunctionsDocument15 pagesMATLAB Linear Algebra FunctionsAhmed HwaidiNo ratings yet
- Yu Kuzmina 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1847 012031Document6 pagesYu Kuzmina 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1847 012031louis donyNo ratings yet
- Sparse ArrayDocument2 pagesSparse ArrayzulkoNo ratings yet
- MR 6 2017 Solutions 1Document28 pagesMR 6 2017 Solutions 1StephenNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Matrix Computations: Second EditionDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Matrix Computations: Second EditionmohsinamanNo ratings yet
- 4 LinearlEquationsDocument15 pages4 LinearlEquationsSachin DhimanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Enginering Mathematics For Chemical EnginDocument8 pagesAdvanced Enginering Mathematics For Chemical EnginFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- DFT-Discrete Fourier TransformDocument9 pagesDFT-Discrete Fourier TransformErsin ErolNo ratings yet
- DeterminantDocument10 pagesDeterminantRadhey Shyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Roger A. Horn, Charles R. Johnson - Topics in Matrix Analysis-Cambridge University Press (2008)Document615 pagesRoger A. Horn, Charles R. Johnson - Topics in Matrix Analysis-Cambridge University Press (2008)June KangNo ratings yet
- Ebook Advanced Linear and Matrix Algebra 1St Edition Nathaniel Johnston Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Advanced Linear and Matrix Algebra 1St Edition Nathaniel Johnston Online PDF All Chapternancy.collins448100% (10)
- A1201132722 63869 8 2023 K21MDCA2QSetAllocationDocument12 pagesA1201132722 63869 8 2023 K21MDCA2QSetAllocationHanu VadlamudiNo ratings yet
- Matrix MultiplicationDocument13 pagesMatrix Multiplicationrida.me99No ratings yet
- 331 Notes MatrixDocument15 pages331 Notes MatrixSharifullah ShamimNo ratings yet
- Math 208 Exercise PackDocument112 pagesMath 208 Exercise PackChiOfGreeNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Linear EquationsDocument5 pagesModule 3: Linear EquationsAbedaNo ratings yet
- Quick Maths Revisiontwenty20Document40 pagesQuick Maths Revisiontwenty20nithinganesh174No ratings yet
- Gallopoulos - Parallelism in Matrix ComputationsDocument505 pagesGallopoulos - Parallelism in Matrix ComputationsThermionNo ratings yet
- IGNOU - Lecture Notes - Linear AlgebraDocument29 pagesIGNOU - Lecture Notes - Linear Algebraruchi21julyNo ratings yet
- IFEM AppP PDFDocument7 pagesIFEM AppP PDFPippo MiriNo ratings yet
- Matrix - An IntroductionDocument10 pagesMatrix - An IntroductionMajid AbNo ratings yet
- State Transition MatrixDocument26 pagesState Transition MatrixmemotetoNo ratings yet
- Fionaw Linear Algebra Math 232Document4 pagesFionaw Linear Algebra Math 232Kimondo KingNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - Solved Assignments - Fall 2005 SemesterDocument28 pagesLinear Algebra - Solved Assignments - Fall 2005 SemesterMuhammad Umair100% (1)
- Matrix Multiplication ParallelDocument5 pagesMatrix Multiplication ParallelAirNo ratings yet
- ES272 ch4bDocument18 pagesES272 ch4btarafe5509No ratings yet
- Exercises AlgebraDocument22 pagesExercises AlgebraTien KimNo ratings yet
- The FFT Via Matrix Factorizations: A Key To Designing High Performance ImplementationsDocument42 pagesThe FFT Via Matrix Factorizations: A Key To Designing High Performance Implementationsdangtung.dttNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes MatricesDocument90 pagesLecture Notes MatricesRR886No ratings yet
- Ex4Data - Mat: 221 Matlab Assignment 4Document3 pagesEx4Data - Mat: 221 Matlab Assignment 4Austin KonNo ratings yet
- The Open Leontief Input-Output ModelDocument3 pagesThe Open Leontief Input-Output ModelNhi HoàngNo ratings yet