Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Being First
Being First
Uploaded by
Henny Setyawan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesBeing First
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBeing First
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesBeing First
Being First
Uploaded by
Henny SetyawanBeing First
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 3
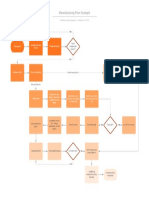
Info Sheet: Seven Drivers of Change
Info Sheet
Seven Drivers of Change
Introduction
There are seven different catalysts or drivers of organizational change. All seven drivers must be addressed
to accurately scope your change effort and plan its rollout strategy. The relationship between the drivers is
depicted in the model below, followed by their definitions.
Notice that the first four types of drivers are quite familiar to most executives, while the last three are relatively
new areas of attention. Not surprisingly, we consistently find that the problems most organizations have with
their change efforts come from inadequate attention to these less tangible drivers (culture, leader and
employee behavior, and leader and employee mindset). This is especially true with transformational change,
0 be sure to pay special attention to these drivers! They are essential to your Case for Change, especially in
determining the accurate type and scope of your change.
Definitions of the Seven Drivers of Change
Environmental Forces—the dynamics of the larger context within which organizations and people operate
These forces include
* Social
* Business and economic
* Political
(©2018 Being Fist ne BeingFistcom Page 1 ofS
Info Sheet:
Aces Ores of Change
*
‘even Drivers of Change
IRST
+ Governmental
+ Technological
+ Demographic
+ Legal
+ Natural environment
Marketplace Requirements for Success—The aggregate set of customer requirements that determine what it
takes for a business to succeed in its marketplace. This includes not only the actual product or service needs,
but also requirements like speed of delivery, customization capability, level of quality, need for innovation,
level of customer service, etc. Changes in Marketplace requirements often are the result of changes in
environmental forces.
Business Imperatives—Business imperatives outline what the company must do strategically to be successful,
given its marketplace requirements. This can require systematic rethinking and change to the company's
mission, strategy, goals, products and services, pricing or branding. Strategic Plans typically address
business imperatives,
Organizational Imperatives—Organizational imperatives specify what must change in the organization's
structure, systems, processes, technology, resources, skill base, or staffing to successfully realize its strategic
business imperatives,
Cultural Imperatives—Cultural imperatives denote how the norms—or collective way—of being, working, and
relating in the company must change to support and drive the organization's new strategy, design, and
operations.
Leader and Employee Behavior—Collective behavior creates and expresses an organization's culture
Behavior speaks to more than just overt actions; it describes the style, tone, or character that permeates what
people do. Leaders and employees must choose to behave differently to recreate the organization's culture.
Leader and Employee Mindset—Mindset encompasses the worldview, assumptions, beliefs or mental models
that cause people to behave in ways that can drive a sustained change in behavior and culture. Becoming
aware that we each have a mindset, and that it directly affects our feelings, decisions, actions, and results, is
often the critical first step in building individual and organizational capacity to change. A shift of mindset is
often required for organizational leaders to recognize changes in the environmental forces and marketplace
requirements and thereby be able to determine the best new strategic business direction, structure, or
operation for the organization. Mindset change in employees is often required for them to understand the
rationale for the changes being asked of them
Every organization undergoing major change has its own story about why it must change. This story can be
very clearly told using the Drivers of Change model. The typical organizational change story, told using the
Drivers of Change model, goes like this: changes in the environment create new requirements for success in
the marketplace as customers demand new services or products. Meeting these new marketplace and
customer requirements demands the formation of new business strategies, that in turn require certain
changes in the organization's structure, systems, processes, or technology to be successfully implemented. In
transformational change, the scope of these organizational changes are often so significant that they also
require the culture to change for the new strategy and organizational design to operate smoothly and
produce its outcomes. Culture change demands change in leader and employee behavior, which further
requires leaders and employees to shift their mindsets, often about meeting customer needs, their business
model, how work gets done, or even how they work with each other
Each of the drivers is a critical factor required for your organization's change to succeed: if mindset doesn't
change, the behavior can't change. If behavior doesn't change, culture won'., and therefore, major changes
in the organization won't succeed, and the business strategy will fail. Ultimately, all the components must
change to produce the results required to meet the new marketplace requirements,
Once you have identified your organization's particular drivers, you will be able to describe to your entire
employee body your organization's story of change required. This should be done in employee-friendly terms.
(©2018 Being Fist ne BeingFistcom Page of
Tesh 18.2Acess Ores of Change
Info Sheet: Seven Drivers of Change *
out Drivers of Change story helps you to clarify the rationale and build motivation for making the change
happen
(© 2018 Being Fist, ne BeingFistcom Pages of
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Manufacturing Flow ExampleDocument1 pageManufacturing Flow ExampleHenny SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Kotter's 8 Step Model of Change: 1. Creating An Urgency: This Can Be Done in The Following WaysDocument2 pagesKotter's 8 Step Model of Change: 1. Creating An Urgency: This Can Be Done in The Following WaysHenny Setyawan0% (1)
- ISYS8033 Services Oriented Enterprise: Course Credit Theory: 4 Course Credit PracticumDocument11 pagesISYS8033 Services Oriented Enterprise: Course Credit Theory: 4 Course Credit PracticumHenny SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Verb EnglishDocument2 pagesVerb EnglishHenny SetyawanNo ratings yet