Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 viewsDistinguishing Arterial, Diabetic, & Vascular Ulcers
Distinguishing Arterial, Diabetic, & Vascular Ulcers
Uploaded by
Ryan Eko Purnomo SiddikThis document distinguishes between arterial, diabetic, and venous ulcers by comparing their predisposing factors, anatomical locations, wound characteristics, and patient assessments. Arterial ulcers are associated with peripheral vascular disease and affect areas with less soft tissue coverage like the toes and feet. They have even wound margins, necrosis, and severe pain. Diabetic ulcers occur on pressure points of the feet and are often deep with granular tissue. Venous ulcers are irregular in shape and located below the knee, with signs of swelling and dilated veins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Lower ExtremityDocument1 pageLower ExtremityKamilya AmirovaNo ratings yet
- Wounds & Ulcers: Dr. Ranjeet PatilDocument40 pagesWounds & Ulcers: Dr. Ranjeet PatilPatrico Rillah SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Endocrine Disorder - Common Short - 240317 - 180114Document57 pagesIntroduction To Endocrine Disorder - Common Short - 240317 - 180114Durrah Abd GafarNo ratings yet
- Common Skin TumorsDocument6 pagesCommon Skin TumorskateverdadNo ratings yet
- Examination of Lumps and BumpsDocument47 pagesExamination of Lumps and Bumpszoya shaikhNo ratings yet
- Nodules: - Chalazion - Acute HordeolaDocument20 pagesNodules: - Chalazion - Acute HordeolaShari' Si WahyuNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination, DR - Maria-1Document77 pagesPhysical Examination, DR - Maria-1Nafay WorldNo ratings yet
- Scrotal Swellings: Dr. A. D. IkobhoDocument65 pagesScrotal Swellings: Dr. A. D. IkobhoPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument3 pagesPhysical AssessmentahrhicxNo ratings yet
- 19 Salivary GlandsDocument14 pages19 Salivary GlandsIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The BreastDocument14 pagesAssessment of The BreastArlyn MendenillaNo ratings yet
- Type of The Wound-JCF 4thDocument25 pagesType of The Wound-JCF 4thTaufik HidayantoNo ratings yet
- Leprosy: Anustha Vishnoi BPT 4 YrDocument33 pagesLeprosy: Anustha Vishnoi BPT 4 YrAnustha VishnoiNo ratings yet
- CM3 - Cu18 Assessment of Female Genitalia and RectumDocument8 pagesCM3 - Cu18 Assessment of Female Genitalia and RectumKyla ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Superficial Soft Tissue SwellingDocument41 pagesSuperficial Soft Tissue SwellingIgwe SolomonNo ratings yet
- Cm3+ +Cu17+Assessment+of+Male+Genitalia+and+RectumDocument9 pagesCm3+ +Cu17+Assessment+of+Male+Genitalia+and+Rectumnicole erminoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain For Medical Finals (Based On Newcastle University Learning Outcomes)Document60 pagesAbdominal Pain For Medical Finals (Based On Newcastle University Learning Outcomes)RedTabsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Lower Extremity Venous Ulceration - DR Caitriona Canning PDFDocument40 pagesLecture 2 - Lower Extremity Venous Ulceration - DR Caitriona Canning PDFAlexander EnnesNo ratings yet
- Paediatric RashesDocument15 pagesPaediatric RashesAaron Nameer Abrar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Psoriasis Clinical FeaturesDocument37 pagesPsoriasis Clinical FeaturesVartika RatanNo ratings yet
- Integumentry Dermatitis Bacterial Impetigo Cellulitis Abscess DefDocument17 pagesIntegumentry Dermatitis Bacterial Impetigo Cellulitis Abscess DefMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- Integumentry PDFDocument17 pagesIntegumentry PDFMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- Neuro General Neuro: Proptosis/ Exophthalmos ChemosisDocument4 pagesNeuro General Neuro: Proptosis/ Exophthalmos ChemosisShakina FareedNo ratings yet
- Oral Lesion ListDocument10 pagesOral Lesion Listabsjob1No ratings yet
- Derm LOsDocument37 pagesDerm LOskatherine nunnNo ratings yet
- Hair Skin Nail AssessmentDocument6 pagesHair Skin Nail AssessmentJJNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis and AbscessDocument10 pagesCellulitis and Abscessbasel alogilyNo ratings yet
- GangreneDocument44 pagesGangreneAkshat SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Transplantation of Skin: Grafts and Flaps: John Marquis Converse, Joseph Mccarthy, Raymond Braurer, Donald BallantyneDocument40 pagesTransplantation of Skin: Grafts and Flaps: John Marquis Converse, Joseph Mccarthy, Raymond Braurer, Donald BallantyneMuhammad Avicenna Abdul SyukurNo ratings yet
- Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Addis Ababa University SOMDocument64 pagesDivision of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Addis Ababa University SOMYil MosNo ratings yet
- CPWSC - Triangle - Wound Assesment A4 - 5-Pages - INTERACTIVEDocument5 pagesCPWSC - Triangle - Wound Assesment A4 - 5-Pages - INTERACTIVEdwiNo ratings yet
- Patho PracticalsDocument27 pagesPatho Practicalsroyce charlieNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Database Form Gynecology Database FormDocument3 pagesGynecology Database Form Gynecology Database FormNeil Victor Ongco PajugotNo ratings yet
- CPWSC - Triangle - Wound Assesment TN.J PRESSURE ULCERDocument5 pagesCPWSC - Triangle - Wound Assesment TN.J PRESSURE ULCERNicen SuherlinNo ratings yet
- Slides Collection 2012-2019Document11 pagesSlides Collection 2012-2019amanabbNo ratings yet
- Joint PainDocument11 pagesJoint PainSandarekha PereraNo ratings yet
- Vascular Diseases: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonDocument57 pagesVascular Diseases: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonVincent SerNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin InfectionsDocument9 pagesBacterial Skin InfectionskateverdadNo ratings yet
- Must KnowDocument2 pagesMust KnowLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- A Patient With Dilated Leg Veins: Aaesha JavedDocument67 pagesA Patient With Dilated Leg Veins: Aaesha JavedzaminazzNo ratings yet
- LRR DERMATDocument190 pagesLRR DERMATpdivyashreerajNo ratings yet
- Small BowelDocument4 pagesSmall Bowelsarguss14100% (1)
- Physical Examination Related NutritionDocument40 pagesPhysical Examination Related NutritionYohan SamudraNo ratings yet
- UcellosisDocument4 pagesUcellosisyandraNo ratings yet
- Varicose Veins: Short History Positioning of The PatientDocument2 pagesVaricose Veins: Short History Positioning of The PatientAshan BopitiyaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Diagnosis of Blistering Diseases: Pathologists PerspectiveDocument18 pagesApproach To The Diagnosis of Blistering Diseases: Pathologists PerspectivePaulino GarciaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing TipsDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Nursing TipsMarem RiegoNo ratings yet
- Sinus and FistulaDocument3 pagesSinus and FistulaAndrew BonusNo ratings yet
- LeprosyDocument22 pagesLeprosyvisweswar030406No ratings yet
- Approach To Systemic Vasculitis - Print VersionDocument32 pagesApproach To Systemic Vasculitis - Print Versionnamhom.md44No ratings yet
- Listeriosis - O&G SeminarDocument17 pagesListeriosis - O&G SeminarFaris Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Ulcers Diabetic Foot UlcersDocument38 pagesNeuropathic Ulcers Diabetic Foot UlcersFatima AliNo ratings yet
- Cpe Common Diagnoses 6-4-2021Document9 pagesCpe Common Diagnoses 6-4-2021Shubham HarishNo ratings yet
- High Yield Topics by DR Stephen Mwenya ImedDocument7 pagesHigh Yield Topics by DR Stephen Mwenya ImedStephen Angel100% (1)
- Varicose VeinsDocument27 pagesVaricose Veinsusmanshah7795No ratings yet
- Ug SpottersDocument274 pagesUg SpottersAnjana UNo ratings yet
- 26 Non-Odontogenic CystsDocument7 pages26 Non-Odontogenic CystsShreesh MishraNo ratings yet
- 6 Skin Hair and NailsDocument5 pages6 Skin Hair and Nailsthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Drajat Leg UlcerDocument28 pagesDrajat Leg Ulcerdila2706No ratings yet
- Edema Assessment - PhysiopediaDocument3 pagesEdema Assessment - PhysiopediaJovie Anne Cabangal100% (1)
- SeizuresDocument1 pageSeizuresRock GoodNo ratings yet
- Pedia 102 Quiz 2 SemifinalsDocument11 pagesPedia 102 Quiz 2 Semifinalsquidditch07No ratings yet
- 3Document4 pages3Heeta PanchasaraNo ratings yet
- Internal Diseases Propedeutics. Part II. Diagnostics of Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument100 pagesInternal Diseases Propedeutics. Part II. Diagnostics of Cardiovascular DiseasesХассан ЯасирNo ratings yet
- 2014 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Rheumatic DiseaseDocument13 pages2014 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Rheumatic DiseaseKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- DM Type II Case StudyDocument28 pagesDM Type II Case StudyRichard Sy67% (3)
- Radiodermatitis India TransDocument14 pagesRadiodermatitis India TransNaufal Fadhil Mufid LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism and Pregnancy Vol.2Document9 pagesHypothyroidism and Pregnancy Vol.2RakhiNo ratings yet
- Gerser, 2005Document10 pagesGerser, 2005Elisabet GobelliNo ratings yet
- Spinal Injury: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniDocument47 pagesSpinal Injury: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- ACVIM Consensus Statement On The Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument28 pagesACVIM Consensus Statement On The Diagnosis and TreatmentBê LagoNo ratings yet
- Blood Urea Blood Creatinine Creatinine Clearance Uric Acid: Laboratory TrainingDocument44 pagesBlood Urea Blood Creatinine Creatinine Clearance Uric Acid: Laboratory Trainingعلي عبيد العتابيNo ratings yet
- Fournier's Gangrene: Literature Review and Clinical CasesDocument8 pagesFournier's Gangrene: Literature Review and Clinical CasesDaniel RusieNo ratings yet
- 3rd YrMedical Surgical NursingDocument24 pages3rd YrMedical Surgical Nursingpunam todkarNo ratings yet
- тест офтал.Document24 pagesтест офтал.inspire.consultancy00No ratings yet
- Curcuma y MetforminaDocument8 pagesCurcuma y MetforminaJorge Luis Plasencia CubaNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Uric AcidDocument31 pagesPresentation - Uric AcidTc Khoon100% (1)
- NEJMoa2312323 1Document10 pagesNEJMoa2312323 1lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Tata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALDocument27 pagesTata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALNikko Khairul DafaNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument8 pagesFungis138140No ratings yet
- Case of Obstructive JaundiceDocument23 pagesCase of Obstructive JaundiceAjay Agrawal100% (1)
- Environmental Mercury and Its Toxic Effects: ReviewDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Mercury and Its Toxic Effects: ReviewZusely Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Augmentin DdsDocument12 pagesAugmentin DdsQureshi imtiyazNo ratings yet
- Clinical Profile and Evaluation of Serum Prolactin Level in Cirrhosis of Liver With Special Reference To Child Pugh ScoreDocument6 pagesClinical Profile and Evaluation of Serum Prolactin Level in Cirrhosis of Liver With Special Reference To Child Pugh ScoreIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 1 - Ruth Withey - 1335 1355 1Document24 pages1 - Ruth Withey - 1335 1355 1Dr. Zaheer AliNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - CholelithiasisDocument35 pagesCase Presentation - Cholelithiasisarief2704900% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsSidiq AboobakerNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell MorphologyDocument51 pagesBlood Cell MorphologyYojan Leo Irakurri PuenteNo ratings yet
- Reviewer MuscularDocument17 pagesReviewer MuscularKatrina Ericah A. MoañaNo ratings yet
Distinguishing Arterial, Diabetic, & Vascular Ulcers
Distinguishing Arterial, Diabetic, & Vascular Ulcers
Uploaded by
Ryan Eko Purnomo Siddik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageThis document distinguishes between arterial, diabetic, and venous ulcers by comparing their predisposing factors, anatomical locations, wound characteristics, and patient assessments. Arterial ulcers are associated with peripheral vascular disease and affect areas with less soft tissue coverage like the toes and feet. They have even wound margins, necrosis, and severe pain. Diabetic ulcers occur on pressure points of the feet and are often deep with granular tissue. Venous ulcers are irregular in shape and located below the knee, with signs of swelling and dilated veins.
Original Description:
Metode modern dressing
Original Title
Asesment Venus Ulcer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document distinguishes between arterial, diabetic, and venous ulcers by comparing their predisposing factors, anatomical locations, wound characteristics, and patient assessments. Arterial ulcers are associated with peripheral vascular disease and affect areas with less soft tissue coverage like the toes and feet. They have even wound margins, necrosis, and severe pain. Diabetic ulcers occur on pressure points of the feet and are often deep with granular tissue. Venous ulcers are irregular in shape and located below the knee, with signs of swelling and dilated veins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageDistinguishing Arterial, Diabetic, & Vascular Ulcers
Distinguishing Arterial, Diabetic, & Vascular Ulcers
Uploaded by
Ryan Eko Purnomo SiddikThis document distinguishes between arterial, diabetic, and venous ulcers by comparing their predisposing factors, anatomical locations, wound characteristics, and patient assessments. Arterial ulcers are associated with peripheral vascular disease and affect areas with less soft tissue coverage like the toes and feet. They have even wound margins, necrosis, and severe pain. Diabetic ulcers occur on pressure points of the feet and are often deep with granular tissue. Venous ulcers are irregular in shape and located below the knee, with signs of swelling and dilated veins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
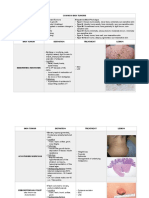
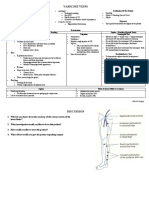
Distinguishing
www.woundconsultant.com
Arterial, Diabetic, & Vascular Ulcers
Arterial Ulcers Diabetic Ulcers Venous Ulcers
Predisposing Factors
• Peripheral vascular • Diabetic patient with • Valve incompetence
disease (PVD) peripheral neuropathy in perforating veins
• Diabetes mellitus • History of deep vein
• Advanced Age thrombophlebitis and
thrombosis
• Previous history of
ulcers
• Obesity
• Advanced age
Anatomic Location
• Between toes or tips • On plantar aspect of • On medial lower led
of toes foot and ankle
• Over phalangeal • Over metatarsal • On malleolar area
heads heads
• Around lateral • Under heel
malleolus
• At sites subjected to
trauma or rubbing of
footwear
Wound Characteristics
• Even wound margins • Even wound margins • Irregular wound
• Gangrene or necrosis • Deep wound bed margins
• Deep, pale wound • Cellulitis or underlying • Superficial wound
bed osteomyelitis • Ruddy, granular
• Blanched or purpuric • Granular tissue tissue
periwound tissue present unless PVD is • Usually no pain
• Severe pain present • Frequently moderate
• Cellulitis • Low to moderate to heavy exudate
• Minimal exudate drainage
Patient Assessment
• Thin, shinny, dry skin • Diminished or absent • Firm edema
• Hair loss on ankle & sensation in foot • Dilated superficial
foot • Foot deformities veins
• Thickened toenails • Palpable pulses • Dry, thin skin
• Pallor on elevation • Warm foot • Evidence of healed
and dependent rubor • Subcutaneous fat ulcers
• Cyanosis atrophy • Periwound and leg
• Decreased hyperpigmintation
temperature • Possible dermatitis
• Absent or diminished
pulses
You might also like
- Lower ExtremityDocument1 pageLower ExtremityKamilya AmirovaNo ratings yet
- Wounds & Ulcers: Dr. Ranjeet PatilDocument40 pagesWounds & Ulcers: Dr. Ranjeet PatilPatrico Rillah SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Endocrine Disorder - Common Short - 240317 - 180114Document57 pagesIntroduction To Endocrine Disorder - Common Short - 240317 - 180114Durrah Abd GafarNo ratings yet
- Common Skin TumorsDocument6 pagesCommon Skin TumorskateverdadNo ratings yet
- Examination of Lumps and BumpsDocument47 pagesExamination of Lumps and Bumpszoya shaikhNo ratings yet
- Nodules: - Chalazion - Acute HordeolaDocument20 pagesNodules: - Chalazion - Acute HordeolaShari' Si WahyuNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination, DR - Maria-1Document77 pagesPhysical Examination, DR - Maria-1Nafay WorldNo ratings yet
- Scrotal Swellings: Dr. A. D. IkobhoDocument65 pagesScrotal Swellings: Dr. A. D. IkobhoPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument3 pagesPhysical AssessmentahrhicxNo ratings yet
- 19 Salivary GlandsDocument14 pages19 Salivary GlandsIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The BreastDocument14 pagesAssessment of The BreastArlyn MendenillaNo ratings yet
- Type of The Wound-JCF 4thDocument25 pagesType of The Wound-JCF 4thTaufik HidayantoNo ratings yet
- Leprosy: Anustha Vishnoi BPT 4 YrDocument33 pagesLeprosy: Anustha Vishnoi BPT 4 YrAnustha VishnoiNo ratings yet
- CM3 - Cu18 Assessment of Female Genitalia and RectumDocument8 pagesCM3 - Cu18 Assessment of Female Genitalia and RectumKyla ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Superficial Soft Tissue SwellingDocument41 pagesSuperficial Soft Tissue SwellingIgwe SolomonNo ratings yet
- Cm3+ +Cu17+Assessment+of+Male+Genitalia+and+RectumDocument9 pagesCm3+ +Cu17+Assessment+of+Male+Genitalia+and+Rectumnicole erminoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain For Medical Finals (Based On Newcastle University Learning Outcomes)Document60 pagesAbdominal Pain For Medical Finals (Based On Newcastle University Learning Outcomes)RedTabsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Lower Extremity Venous Ulceration - DR Caitriona Canning PDFDocument40 pagesLecture 2 - Lower Extremity Venous Ulceration - DR Caitriona Canning PDFAlexander EnnesNo ratings yet
- Paediatric RashesDocument15 pagesPaediatric RashesAaron Nameer Abrar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Psoriasis Clinical FeaturesDocument37 pagesPsoriasis Clinical FeaturesVartika RatanNo ratings yet
- Integumentry Dermatitis Bacterial Impetigo Cellulitis Abscess DefDocument17 pagesIntegumentry Dermatitis Bacterial Impetigo Cellulitis Abscess DefMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- Integumentry PDFDocument17 pagesIntegumentry PDFMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- Neuro General Neuro: Proptosis/ Exophthalmos ChemosisDocument4 pagesNeuro General Neuro: Proptosis/ Exophthalmos ChemosisShakina FareedNo ratings yet
- Oral Lesion ListDocument10 pagesOral Lesion Listabsjob1No ratings yet
- Derm LOsDocument37 pagesDerm LOskatherine nunnNo ratings yet
- Hair Skin Nail AssessmentDocument6 pagesHair Skin Nail AssessmentJJNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis and AbscessDocument10 pagesCellulitis and Abscessbasel alogilyNo ratings yet
- GangreneDocument44 pagesGangreneAkshat SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Transplantation of Skin: Grafts and Flaps: John Marquis Converse, Joseph Mccarthy, Raymond Braurer, Donald BallantyneDocument40 pagesTransplantation of Skin: Grafts and Flaps: John Marquis Converse, Joseph Mccarthy, Raymond Braurer, Donald BallantyneMuhammad Avicenna Abdul SyukurNo ratings yet
- Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Addis Ababa University SOMDocument64 pagesDivision of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Addis Ababa University SOMYil MosNo ratings yet
- CPWSC - Triangle - Wound Assesment A4 - 5-Pages - INTERACTIVEDocument5 pagesCPWSC - Triangle - Wound Assesment A4 - 5-Pages - INTERACTIVEdwiNo ratings yet
- Patho PracticalsDocument27 pagesPatho Practicalsroyce charlieNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Database Form Gynecology Database FormDocument3 pagesGynecology Database Form Gynecology Database FormNeil Victor Ongco PajugotNo ratings yet
- CPWSC - Triangle - Wound Assesment TN.J PRESSURE ULCERDocument5 pagesCPWSC - Triangle - Wound Assesment TN.J PRESSURE ULCERNicen SuherlinNo ratings yet
- Slides Collection 2012-2019Document11 pagesSlides Collection 2012-2019amanabbNo ratings yet
- Joint PainDocument11 pagesJoint PainSandarekha PereraNo ratings yet
- Vascular Diseases: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonDocument57 pagesVascular Diseases: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonVincent SerNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin InfectionsDocument9 pagesBacterial Skin InfectionskateverdadNo ratings yet
- Must KnowDocument2 pagesMust KnowLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- A Patient With Dilated Leg Veins: Aaesha JavedDocument67 pagesA Patient With Dilated Leg Veins: Aaesha JavedzaminazzNo ratings yet
- LRR DERMATDocument190 pagesLRR DERMATpdivyashreerajNo ratings yet
- Small BowelDocument4 pagesSmall Bowelsarguss14100% (1)
- Physical Examination Related NutritionDocument40 pagesPhysical Examination Related NutritionYohan SamudraNo ratings yet
- UcellosisDocument4 pagesUcellosisyandraNo ratings yet
- Varicose Veins: Short History Positioning of The PatientDocument2 pagesVaricose Veins: Short History Positioning of The PatientAshan BopitiyaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Diagnosis of Blistering Diseases: Pathologists PerspectiveDocument18 pagesApproach To The Diagnosis of Blistering Diseases: Pathologists PerspectivePaulino GarciaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing TipsDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Nursing TipsMarem RiegoNo ratings yet
- Sinus and FistulaDocument3 pagesSinus and FistulaAndrew BonusNo ratings yet
- LeprosyDocument22 pagesLeprosyvisweswar030406No ratings yet
- Approach To Systemic Vasculitis - Print VersionDocument32 pagesApproach To Systemic Vasculitis - Print Versionnamhom.md44No ratings yet
- Listeriosis - O&G SeminarDocument17 pagesListeriosis - O&G SeminarFaris Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Ulcers Diabetic Foot UlcersDocument38 pagesNeuropathic Ulcers Diabetic Foot UlcersFatima AliNo ratings yet
- Cpe Common Diagnoses 6-4-2021Document9 pagesCpe Common Diagnoses 6-4-2021Shubham HarishNo ratings yet
- High Yield Topics by DR Stephen Mwenya ImedDocument7 pagesHigh Yield Topics by DR Stephen Mwenya ImedStephen Angel100% (1)
- Varicose VeinsDocument27 pagesVaricose Veinsusmanshah7795No ratings yet
- Ug SpottersDocument274 pagesUg SpottersAnjana UNo ratings yet
- 26 Non-Odontogenic CystsDocument7 pages26 Non-Odontogenic CystsShreesh MishraNo ratings yet
- 6 Skin Hair and NailsDocument5 pages6 Skin Hair and Nailsthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Drajat Leg UlcerDocument28 pagesDrajat Leg Ulcerdila2706No ratings yet
- Edema Assessment - PhysiopediaDocument3 pagesEdema Assessment - PhysiopediaJovie Anne Cabangal100% (1)
- SeizuresDocument1 pageSeizuresRock GoodNo ratings yet
- Pedia 102 Quiz 2 SemifinalsDocument11 pagesPedia 102 Quiz 2 Semifinalsquidditch07No ratings yet
- 3Document4 pages3Heeta PanchasaraNo ratings yet
- Internal Diseases Propedeutics. Part II. Diagnostics of Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument100 pagesInternal Diseases Propedeutics. Part II. Diagnostics of Cardiovascular DiseasesХассан ЯасирNo ratings yet
- 2014 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Rheumatic DiseaseDocument13 pages2014 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Rheumatic DiseaseKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- DM Type II Case StudyDocument28 pagesDM Type II Case StudyRichard Sy67% (3)
- Radiodermatitis India TransDocument14 pagesRadiodermatitis India TransNaufal Fadhil Mufid LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism and Pregnancy Vol.2Document9 pagesHypothyroidism and Pregnancy Vol.2RakhiNo ratings yet
- Gerser, 2005Document10 pagesGerser, 2005Elisabet GobelliNo ratings yet
- Spinal Injury: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniDocument47 pagesSpinal Injury: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- ACVIM Consensus Statement On The Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument28 pagesACVIM Consensus Statement On The Diagnosis and TreatmentBê LagoNo ratings yet
- Blood Urea Blood Creatinine Creatinine Clearance Uric Acid: Laboratory TrainingDocument44 pagesBlood Urea Blood Creatinine Creatinine Clearance Uric Acid: Laboratory Trainingعلي عبيد العتابيNo ratings yet
- Fournier's Gangrene: Literature Review and Clinical CasesDocument8 pagesFournier's Gangrene: Literature Review and Clinical CasesDaniel RusieNo ratings yet
- 3rd YrMedical Surgical NursingDocument24 pages3rd YrMedical Surgical Nursingpunam todkarNo ratings yet
- тест офтал.Document24 pagesтест офтал.inspire.consultancy00No ratings yet
- Curcuma y MetforminaDocument8 pagesCurcuma y MetforminaJorge Luis Plasencia CubaNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Uric AcidDocument31 pagesPresentation - Uric AcidTc Khoon100% (1)
- NEJMoa2312323 1Document10 pagesNEJMoa2312323 1lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Tata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALDocument27 pagesTata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALNikko Khairul DafaNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument8 pagesFungis138140No ratings yet
- Case of Obstructive JaundiceDocument23 pagesCase of Obstructive JaundiceAjay Agrawal100% (1)
- Environmental Mercury and Its Toxic Effects: ReviewDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Mercury and Its Toxic Effects: ReviewZusely Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Augmentin DdsDocument12 pagesAugmentin DdsQureshi imtiyazNo ratings yet
- Clinical Profile and Evaluation of Serum Prolactin Level in Cirrhosis of Liver With Special Reference To Child Pugh ScoreDocument6 pagesClinical Profile and Evaluation of Serum Prolactin Level in Cirrhosis of Liver With Special Reference To Child Pugh ScoreIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 1 - Ruth Withey - 1335 1355 1Document24 pages1 - Ruth Withey - 1335 1355 1Dr. Zaheer AliNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - CholelithiasisDocument35 pagesCase Presentation - Cholelithiasisarief2704900% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsSidiq AboobakerNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell MorphologyDocument51 pagesBlood Cell MorphologyYojan Leo Irakurri PuenteNo ratings yet
- Reviewer MuscularDocument17 pagesReviewer MuscularKatrina Ericah A. MoañaNo ratings yet