Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reyes, Ronald Allan L. BSLM 2B
Reyes, Ronald Allan L. BSLM 2B
Uploaded by
Haydee Felicen100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
396 views4 pagesGM crops have been developed to increase yields, resist pests and herbicides, and improve nutrition. However, they also present some risks. The top three GM crops discussed are corn, soybeans, and cotton. Corn is mostly used for animal feed and ingredients like high fructose corn syrup. Soybeans provide protein but have been linked to fertility and health issues. Bt cotton reduces pesticide use but is expensive and ineffective against some pests. Overall, GM crops offer benefits like increased supplies and reduced costs or pesticide use, but also raise concerns about unknown health impacts, gene transfer, and effects on small farmers.
Original Description:
fff
Original Title
ff
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGM crops have been developed to increase yields, resist pests and herbicides, and improve nutrition. However, they also present some risks. The top three GM crops discussed are corn, soybeans, and cotton. Corn is mostly used for animal feed and ingredients like high fructose corn syrup. Soybeans provide protein but have been linked to fertility and health issues. Bt cotton reduces pesticide use but is expensive and ineffective against some pests. Overall, GM crops offer benefits like increased supplies and reduced costs or pesticide use, but also raise concerns about unknown health impacts, gene transfer, and effects on small farmers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
396 views4 pagesReyes, Ronald Allan L. BSLM 2B
Reyes, Ronald Allan L. BSLM 2B
Uploaded by
Haydee FelicenGM crops have been developed to increase yields, resist pests and herbicides, and improve nutrition. However, they also present some risks. The top three GM crops discussed are corn, soybeans, and cotton. Corn is mostly used for animal feed and ingredients like high fructose corn syrup. Soybeans provide protein but have been linked to fertility and health issues. Bt cotton reduces pesticide use but is expensive and ineffective against some pests. Overall, GM crops offer benefits like increased supplies and reduced costs or pesticide use, but also raise concerns about unknown health impacts, gene transfer, and effects on small farmers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Reyes, Ronald Allan L.
BSLM 2B
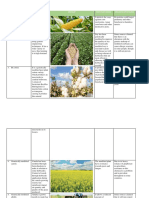
GMO CROPS/ LIVE STOCKS DESCRIPTION IMAGE ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
1. CORN This crop is used to produce many Is that it has a higher level Is that changes to the
different ingredients used in of hardiness. structure of the plant occur
processed foods and drinks, It can be resilient in difficult in a way that would not
including high-fructose corn syrup growing conditions, such necessarily occur through
and corn starch. But the bulk of the as drought, or be able to natural development.
GM corn grown around the world is withstand an infestation of Scientists have been able
used to feed livestock. weeds or pests to still to infuse animal DNA,
produce a good yield. pesticides, herbicides, and
That allows croplands to other items into the plant
become more consistent in structure and that offers the
what they can produce. potential of future health
concerns.
It could be a contributing
factor to antibiotic-
resistance.
2. SOYBEANS The second largest U.S. crop after More Supply of Protein. Fertility Issues and Infant
corn, GM soy is used primarily in Lower Costs. Mortality.
animal feed and in soybean oil— Many Uses. Changes in the Liver.
which is widely used for processed Allergenic.
foods and in restaurant chains. In
fact, soybean oil accounts for 61%
of Americans' vegetable-oil
consumption. It's also often used to
make an emulsifier called soy
lecithin, which is present in a lot of
processed foods, including dark
chocolate bars and candy.
3. COTTON Much of GM cotton is turned into Bt cotton can substantially High cost of Bt cotton seeds
cottonseed oil, which is used for reduce the number of as compared to non Bt
frying in restaurants and in pesticide sprayings, which cotton seeds.
packaged foods like potato chips, reduces worker and Effectiveness up to 120
oily spreads like margarine, even environmental exposure to days, after that the toxin
things like cans of smoked oysters. chemical insecticides and producing efficiency of the
Some parts of the plant are also reduces energy use. Bt gene drastically
used in animal feed, and what's left reduces.Ineffective against
over can be used to create food sucking pests like jassids,
fillers such as cellulose. aphids, whitefly etc.
4. POTATOES A new kid on the block, the Less pesticide better for Harmful health risks
very recently approved GM crop is farmers health Cause health problems for
resistant to bruising and may Reduces soil erosion animal eating the product
produce less of a cancer-causing Better quality potatoes Gene transfer may occur
chemical, called acrylamide, when between organisms
exposed to high heat. It has not yet
seen adoption in the food supply,
but is expected to be.
5. PAPAYA Bred to withstand ringspot virus, Crop resistance Unknown health hazards
which can destroy papaya plants, Increased security for Pollen of the GM strains
these genetically engineered papaya members may fertilize neighboring
'Rainbow Papayas' were first New variant of the papaya organic strains of the
commercially produced in the late crop papaya plant therefore
1990s. Much of the yield is grown rendering them non-organic
in Hawaii.
6. SQUASH Zucchini and yellow summer Keeps squash healthy Can cause allergic
squash have been commercially Improves colour, reactions and the mutagen
available in the U.S. since the mid- appearance, texture, is to blame.
to late-'90s, though GM squash quality and flavor. No economic value
accounts for just 25,000 acres of Strong concentration of High nutrional uptake.
farmland, by some estimates. vitamins like Bb,
manganese and
Potassium.
7. CANOLA GM canola is used to make oil for Potential reductions of The accelerated evolutions
cooking, as well as margarine. It's chemical fertilizers and of resistant pest population
also used to produce emulsifiers pesticide The majority of seeds sales
that are used in packaged foods. GM crops require less for the worlds major crops
By some estimates, 90% of canola energy investment in are controlled by a few seed
grown in the U.S. and Canada is farming, thereby reducing companies.
GM. the carbon footprint. Patent protected GM seeds
Higher crop yields could have created financial and
offset greenhouse gas social challenges for many
emissions at skills similar farmers
to win and solar energy
8. ALFALFA In a controversial decision in 2011, Seed giant Monsanto Organic farmers and
the FDA approved the commercial developed an alfalfa seed consumers argue that the
use of GM alfalfa that contains a that’s resistant to the genetically modified plant
gene making it resistant to weedkiller Roundup, which will cross-pollinate with the
herbicide. The crop is used mainly means alfalfa farmers can non-genetically modified
as hay for cattle. use the chemical on the counterpart, effectively
plant, which saves time, "contaminating" the organic
labor and money on crop.
weeding. Only about 1 percent of the
The genetically-modified country's total alfalfa crop is
alfalfa seed also allows organic, the risk is high that
farmers to grow more there will be cross-
plants per acre, which pollination.
helps keep food prices low the organic alfalfa contains
even a trace of genetically-
modified material, it can’t
be labeled as organic
9. APPLES Another newly approved crop, this stay fresh for much longer the ability to choose the
apple from a Canadian biotech than an ordinary apple gene to manipulate they are
company does not brown even would. unaware of the proper
after it's been sliced. It recently The modified apple will not placement of the gene into
received FDA approval. The brown or rot nearly as the DNA.
agency said it is safe to eat, which quickly as a regular apple incapable of determining
means they may appear on would. the long term affects of
supermarket shelves. bagged apples will no genetically modified food
longer need to be washed cannot be sure if these
in antioxidants which will changes are healthy for the
help to restore their natural human body.
taste.
10. SUGARBEETS More than half the granulated tolerance to crops could cause a sugar
sugar in the United States comes adaptation to climate and shortage
from GM sugar beets, which have location factors disappointing crop yields
been in production since 2008. spend less money and doubt over the
Though their use was temporarily producing more foods environment benefits of
halted due to safety reduce tillings
concerns, production resumed in Creates BT resistance
2011. bugs.
You might also like
- AML Gold - Precious Metal Sector Case StudiesDocument5 pagesAML Gold - Precious Metal Sector Case Studiesjabir pkNo ratings yet
- IO AB Utrient Cycles: BjectivesDocument7 pagesIO AB Utrient Cycles: BjectivesSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- 1319 Case StudyDocument7 pages1319 Case StudyElizabeth SamudioNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Data Management) - Math 101Document8 pagesModule 4 (Data Management) - Math 101Flory CabaseNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Pesticide Use QuestionnaireDocument13 pagesVietnam Pesticide Use QuestionnaireSharmadevan SundrasegaranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Science: Body of KnowledgeDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Management Science: Body of KnowledgeRetarded Edits100% (1)
- The Land Transportation OfficeDocument4 pagesThe Land Transportation OfficeMaùreen AbegailNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Impact of Rice Farming in ArgaoDocument14 pagesChallenges and Impact of Rice Farming in ArgaoTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes: Lesson 9: Biodiversity and The Healthy SocietyDocument3 pagesLearning Outcomes: Lesson 9: Biodiversity and The Healthy SocietyDianne Jane LirayNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - Conceptualize A GMODocument2 pagesExercise 1 - Conceptualize A GMOKO JI AN DO (Fries)No ratings yet
- PoemDocument13 pagesPoemedy zairani bin zakariaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper FinalDocument20 pagesResearch Paper FinalJucelle_Kae_Pa_23630% (1)
- What Are Genetically Modified Organisms (Gmos) What Are Genetically Modified Organisms (Gmos)Document17 pagesWhat Are Genetically Modified Organisms (Gmos) What Are Genetically Modified Organisms (Gmos)Minhaj HaiderNo ratings yet
- Art Junnel Domingo - Module 1 Lesson4Document2 pagesArt Junnel Domingo - Module 1 Lesson4Tom RaplizaNo ratings yet
- Information Age Assignment SALARDADocument2 pagesInformation Age Assignment SALARDADoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4-Johari Window ButlerDocument3 pagesAssignment 4-Johari Window ButlerKuume JakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Elasticity and Its ApplicationDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Elasticity and Its ApplicationValcorza Karen100% (1)
- Exercise 1: Bring Forth or Challenge ForthDocument2 pagesExercise 1: Bring Forth or Challenge ForthLlewellyn Aspa100% (1)
- Research Chapter 4 GuideDocument4 pagesResearch Chapter 4 GuideEunice Hernandez100% (1)
- Exercise 2 Magnification-1Document5 pagesExercise 2 Magnification-1Jerjer King0% (1)
- Effectiveness of Snake Plant and Aloe Vera Extract in Healing WoundsDocument11 pagesEffectiveness of Snake Plant and Aloe Vera Extract in Healing WoundsArchille Laraga JosephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Vera Carpentero LamisNo ratings yet
- BSADocument2 pagesBSALyca Mae CubangbangNo ratings yet
- Subedi Et Al., 2020: Freynman Method For Online ClassDocument4 pagesSubedi Et Al., 2020: Freynman Method For Online ClassSHARRAH MAE A. CABINONo ratings yet
- STS Module 13+finalDocument59 pagesSTS Module 13+finalDesiree GalletoNo ratings yet
- Waste Management MandaueDocument56 pagesWaste Management MandaueEnp Gus Agosto100% (3)
- INTRODUCTION To Vegetable FarmingDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION To Vegetable Farmingjim schaultzNo ratings yet
- GMOs in FoodDocument4 pagesGMOs in FoodJean Zyrin AndaNo ratings yet
- GECMAT Assignment #3Document7 pagesGECMAT Assignment #3Sunny EggheadNo ratings yet
- Matrix Primals 2018 2Document2 pagesMatrix Primals 2018 2LordoftheStrings Knnth100% (2)
- SLM No. 2 Gec 104 Week 3Document37 pagesSLM No. 2 Gec 104 Week 3pluto bautistaNo ratings yet
- Backyard Gardening Using Recycled MaterialsDocument4 pagesBackyard Gardening Using Recycled MaterialsPamela Joyce RiambonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - MathDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - MathSming123No ratings yet
- ALLANDocument8 pagesALLANExequiel Obaldo LamatonNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument8 pagesNarrative ReportJamaica Razzel SibayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 123 Research PaperDocument19 pagesChapter 123 Research PaperAarjhay Cunanan AdaNo ratings yet
- GL Obal I Zat I On Lesson2:TheglobaleconomyDocument2 pagesGL Obal I Zat I On Lesson2:TheglobaleconomyKristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument16 pagesBusiness Planareolajoshua13No ratings yet
- Importance of Waste Management Main PointsDocument3 pagesImportance of Waste Management Main PointsEric Linguh50% (4)
- BEGGARSDocument10 pagesBEGGARSAliyah Marie RemoNo ratings yet
- Computer in Our Daily LifeDocument5 pagesComputer in Our Daily LifeEmily Despabiladeras DulpinaNo ratings yet
- Capstone Research (Gr. 4)Document35 pagesCapstone Research (Gr. 4)ShyenNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Healthy Society (Gmo)Document5 pagesBiodiversity and Healthy Society (Gmo)yhcaesthetic proNo ratings yet
- Answers Ge 10 Module 1Document8 pagesAnswers Ge 10 Module 1isagani abrilNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Activities of Leonard Ray R. MendozaDocument2 pagesModule 2 Activities of Leonard Ray R. MendozaLeonardray MendozaNo ratings yet
- MODULAR COPY ONLY GTE Module 7Document5 pagesMODULAR COPY ONLY GTE Module 7Kizha marie TacdaNo ratings yet
- Talahib NFPC Comparative StudyDocument6 pagesTalahib NFPC Comparative StudykirstennoelleignacioNo ratings yet
- Thesis Intro RRL FinalDocument11 pagesThesis Intro RRL FinalMarvin PameNo ratings yet
- Final Tree AnalysisDocument11 pagesFinal Tree AnalysisLionel Denis0% (1)
- SURVEY QUESTIONS FMA 2022 - Katryn AnisDocument7 pagesSURVEY QUESTIONS FMA 2022 - Katryn AnisRhica Macasaya MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 RRLDocument8 pagesChapter 2 RRLZisaNo ratings yet
- GEC 201 Lesson 1 - What Is GlobalizationDocument6 pagesGEC 201 Lesson 1 - What Is GlobalizationReygie Fabriga0% (1)
- Work Sheet-7 Newtons 3laws Work SheetDocument11 pagesWork Sheet-7 Newtons 3laws Work SheetAndy MontesNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of GMOsDocument1 pageAdvantages and Disadvantages of GMOsSandra Arenas HerreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Gene Therapy - ModifiedDocument27 pagesChapter 11 Gene Therapy - ModifiedPRINCESS JEAN DELOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Southern Luzon State UniversityDocument4 pagesSouthern Luzon State Universityshadow friendNo ratings yet
- Experimental DesignDocument6 pagesExperimental DesignVann MantawidNo ratings yet
- The Feasibility of Jackfruit Peeling As Binder To Whiteware Plastic Mass (Revised Chapter 1,2,3)Document26 pagesThe Feasibility of Jackfruit Peeling As Binder To Whiteware Plastic Mass (Revised Chapter 1,2,3)Joshua PicartNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Various Functional Area PlansDocument4 pagesParts of The Various Functional Area PlansPym SaclausoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument2 pagesConceptual FrameworkKristyn GeraldezNo ratings yet
- BCHE 111 Chemistry For Engineers - Written Report - 083019Document3 pagesBCHE 111 Chemistry For Engineers - Written Report - 083019Magus Angelico Yap100% (1)
- Climate Change Seminar ReflectionDocument2 pagesClimate Change Seminar Reflectionapi-339880069No ratings yet
- GM Crops/Livestocks Description Image Advantages DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesGM Crops/Livestocks Description Image Advantages DisadvantagesCarlo Lopez CantadaNo ratings yet
- Triple Alliance Dual Alliance Triple Entente Central Powers AlliesDocument2 pagesTriple Alliance Dual Alliance Triple Entente Central Powers AlliesHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Affidavit-Sis JonaDocument1 pageAffidavit-Sis JonaHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Alaminos City, Pangasinan Philippines: Hundred IslandsDocument2 pagesAlaminos City, Pangasinan Philippines: Hundred IslandsHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- San Beda College Alabang Religious Education Department: Wounded FamiliesDocument13 pagesSan Beda College Alabang Religious Education Department: Wounded FamiliesHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument27 pagesCommunication ModelsHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Haydee F ASSIGN 1 TLEDocument1 pageHaydee F ASSIGN 1 TLEHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Patron Saints of San Beda College of AlabangDocument2 pagesLesson 1: Patron Saints of San Beda College of AlabangHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- ENG ACT. Haydee Felicen 9 - ROSEWOODDocument1 pageENG ACT. Haydee Felicen 9 - ROSEWOODHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- To Whom It May Concern:: February 5, 2019Document3 pagesTo Whom It May Concern:: February 5, 2019Haydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Yvonne Felicen 08 March 2019 Bslm-1A Mr. Christopher Rey R. BajamondeDocument1 pageYvonne Felicen 08 March 2019 Bslm-1A Mr. Christopher Rey R. BajamondeHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Southernside Montessori School Mini Task Third Quarter TLE Grade 8Document1 pageSouthernside Montessori School Mini Task Third Quarter TLE Grade 8Haydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- The Concept of TimeDocument2 pagesThe Concept of TimeHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Southernside Montessori School: Camella Homes 4 Poblacion, Muntinlupa CityDocument1 pageSouthernside Montessori School: Camella Homes 4 Poblacion, Muntinlupa CityHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Grade8 Ass2Document1 pageGrade8 Ass2Haydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 EnglishDocument2 pagesNotes 2 EnglishHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Assign 1 Values-savings-DepositDocument1 pageAssign 1 Values-savings-DepositHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper: The Ascent of Money: A Financial HistoryDocument2 pagesReflection Paper: The Ascent of Money: A Financial HistoryHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Camella Homes 4, Poblacion, Muntinlupa City: Southernside Montessori SchoolDocument2 pagesCamella Homes 4, Poblacion, Muntinlupa City: Southernside Montessori SchoolHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Front of The Classroom: Virtually AllDocument2 pagesFront of The Classroom: Virtually AllHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 ACROSTICDocument1 pageAssign 2 ACROSTICHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 History of RoboticsDocument4 pagesNotes 1 History of RoboticsHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- I Love My FamilyDocument1 pageI Love My FamilyHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Acitvity - Human Bingo GameDocument1 pageAcitvity - Human Bingo GameHaydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- What Is Robotics?Document1 pageWhat Is Robotics?Haydee FelicenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AccountingDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Accountingmoon loverNo ratings yet
- The Death of Inflation Roger BootleDocument5 pagesThe Death of Inflation Roger BootleFrederico SoteroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HIVDocument10 pagesDrug Study HIVAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Johnrey For Demo DLPDocument8 pagesJohnrey For Demo DLPmelany r. malvarosaNo ratings yet
- Toyo Tire Canada Inc.: All Season For Crossover VehiclesDocument2 pagesToyo Tire Canada Inc.: All Season For Crossover Vehicles1977julNo ratings yet
- Role of Idea Development in Effective Essay WritingDocument98 pagesRole of Idea Development in Effective Essay WritingGânőőķ WäřņäNo ratings yet
- WB 3078 TW 0117779Document2 pagesWB 3078 TW 0117779saheb aliNo ratings yet
- Rebates Form: ASA Philippines Foundation IncDocument6 pagesRebates Form: ASA Philippines Foundation IncRichard Boy Terte FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Barud Ahmed Mohamed @Document10 pagesBarud Ahmed Mohamed @Abdirazaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Puntel Metafísica Um TradicionalDocument22 pagesPuntel Metafísica Um TradicionalAlexandroNo ratings yet
- May 232013Document1 pageMay 232013cody_chatman8477No ratings yet
- Situational Leadership in EducationDocument22 pagesSituational Leadership in EducationRoss Thorburn100% (1)
- Graphic Era Hill University, Dehradun: Presentation & Format of The ProjectDocument5 pagesGraphic Era Hill University, Dehradun: Presentation & Format of The ProjectAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- SACABAYA 2024 Sports Rules & Forms (Football)Document4 pagesSACABAYA 2024 Sports Rules & Forms (Football)Travis DavisNo ratings yet
- Zeffere Ketema Paym FinalDocument186 pagesZeffere Ketema Paym FinalEphremHailuNo ratings yet
- Polaris Outlaw 90 - Sportsman 90 Owners ManualDocument200 pagesPolaris Outlaw 90 - Sportsman 90 Owners Manualrafa_r0No ratings yet
- Customer Case Study SodexoDocument12 pagesCustomer Case Study SodexoRick LowNo ratings yet
- Coliseum ReadingDocument2 pagesColiseum Readingrosember lopezNo ratings yet
- The Effects of New Technology On Parents Child Relationship in Dina, JhelumDocument4 pagesThe Effects of New Technology On Parents Child Relationship in Dina, JhelumThe Explorer IslamabadNo ratings yet
- Cfid ListDocument43 pagesCfid ListJimuel Guanzon ArtiendaNo ratings yet
- CLP Talk 04 - Repentance and Faith PDFDocument5 pagesCLP Talk 04 - Repentance and Faith PDFJason YosoresNo ratings yet
- Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthDocument4 pagesSworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net Worthjohn welsonNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument25 pagesBusiness PlanJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Australian Sharemarket: TablesDocument21 pagesAustralian Sharemarket: TablesallegreNo ratings yet
- Ito 2015Document8 pagesIto 2015laurabarbosamedNo ratings yet
- Translation and Language Teaching - Malmkjaer, K.Document5 pagesTranslation and Language Teaching - Malmkjaer, K.Igara OliveiraNo ratings yet
- NeijiaDocument5 pagesNeijiaCarlos Estrada MarzoNo ratings yet