Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Functions and Equations: y KX K y X K y KX K y X
Functions and Equations: y KX K y X K y KX K y X
Uploaded by
volcanius0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views1 pageThe document discusses key concepts relating to functions and equations including:
1. Directly and inversely proportional relationships defined using equations of the form y=kx and y=k/x.
2. The quadratic formula for solving quadratic equations of the form ax2+bx+c=0.
3. Properties of the parabola including vertex and concavity related to the sign of a.
4. Algebraic properties like the zero-product property, difference of squares, and expanding perfect square trinomials.
Original Description:
formulas
Original Title
formulas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key concepts relating to functions and equations including:
1. Directly and inversely proportional relationships defined using equations of the form y=kx and y=k/x.
2. The quadratic formula for solving quadratic equations of the form ax2+bx+c=0.
3. Properties of the parabola including vertex and concavity related to the sign of a.
4. Algebraic properties like the zero-product property, difference of squares, and expanding perfect square trinomials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views1 pageFunctions and Equations: y KX K y X K y KX K y X
Functions and Equations: y KX K y X K y KX K y X
Uploaded by
volcaniusThe document discusses key concepts relating to functions and equations including:
1. Directly and inversely proportional relationships defined using equations of the form y=kx and y=k/x.
2. The quadratic formula for solving quadratic equations of the form ax2+bx+c=0.
3. Properties of the parabola including vertex and concavity related to the sign of a.
4. Algebraic properties like the zero-product property, difference of squares, and expanding perfect square trinomials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
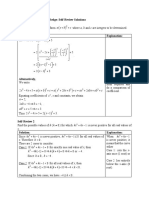
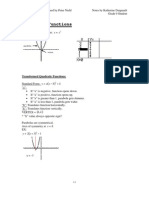
Functions and Equations
Directly Proportional y=kxy=kx k=yxk=y
x
kk: Constant of Proportionality
Inversely y=kxy=kx k=yxk=y
Proportional x
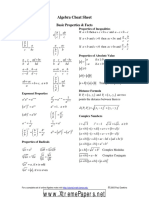
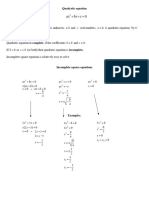
Quadratic formula x=−b±b2−4ac−−−−−−−√2ax=-b±b2-4ac2a
Concave up: a>0a>0
Concavity
ax2+bx+c=0ax2+bx+c=0 Concave down: a<0a<0
Discriminant Δ=b2−4acΔ=b2-4ac
Vertex of the parabola V(−b2a,−Δ4a)V(-b2a,-Δ4a)
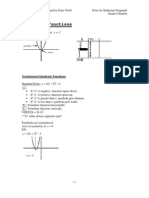
Concave up: a>0a>0
Concavity
y=a(x−h)2+ky=a(x-h)2+k Concave down: a<0a<0
Vertex of the parabola V(h,k)V(h,k)
Zero-product A×B=0⇔A=0∨B=0A×B=0⇔A=0∨B
ex : (x+2)×(x−1)=0⇔(x+2)×(x-1)=0⇔
x+2=0∨x−1=0⇔x=−2∨x=1x+2=0∨x-1=0⇔x=-
property =0
2∨x=1
Difference of two (a−b)(a+b)=a2−b2(a-b)(a+b)=a2-b2 ex : (x−2)(x+2)=x2−22=x2−4(x-2)(x+2)=x2-22=x2-4
squares
Perfect square ex : (2x+3)2=(2x)2+2⋅2x⋅3+32=(2x+3)2=(2x)2+2⋅2x⋅
(a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2(a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2 3+32=
trinomial 4x2+12x+94x2+12x+9
Binomial theorem (x+y)n=∑k=0n nCk xn−k yk
You might also like
- Algebra - Quantitative Aptitude For CAT EBOOKDocument6 pagesAlgebra - Quantitative Aptitude For CAT EBOOKaditya_kumar_me80% (5)
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat SheetSophieSzhangNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 3) Quadratic FunctionDocument17 pages(Chapter 3) Quadratic Functiondenixng100% (3)
- Note of Functions and EquationsDocument2 pagesNote of Functions and Equationsvignesh VMIXNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Lecture NotesDocument75 pagesQuadratic Equation Lecture NotesExtra WorkNo ratings yet
- Year 11 MathsDocument19 pagesYear 11 MathsSyed HasanNo ratings yet
- Middle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This ClassDocument9 pagesMiddle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This Class01. ZUENo ratings yet
- 1 - 22 - MA1200 Lec 4 Quadratic LectureDocument18 pages1 - 22 - MA1200 Lec 4 Quadratic LectureThomas KhaingMyeNo ratings yet
- Quadratic-Equations Lecture NotesDocument80 pagesQuadratic-Equations Lecture NotesSHWAANNo ratings yet
- Value of XDocument1 pageValue of XWeaNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Algebra 2 Notes! (1st Semester)Document1 pageUltimate Algebra 2 Notes! (1st Semester)Addison CollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Equations Inequations Systemes 1Document11 pagesEquations Inequations Systemes 1Pape ngor DioufNo ratings yet
- Eng Math 501e - 2011 2012 Fall - Week3 - ApplicationsDocument3 pagesEng Math 501e - 2011 2012 Fall - Week3 - ApplicationscherkessNo ratings yet
- Axb C: Chapter 0 Assumed Knowledge: Self-Review Solutions Self-Review 1Document8 pagesAxb C: Chapter 0 Assumed Knowledge: Self-Review Solutions Self-Review 1aNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2.2 Continued..Document3 pagesProblem Set 2.2 Continued..Book HouseNo ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsmacgyverNo ratings yet
- Math 9-Q1-Week-6Document12 pagesMath 9-Q1-Week-6Pinky FaithNo ratings yet
- Maths Lessons 1 To 5Document49 pagesMaths Lessons 1 To 5selar7347No ratings yet
- 1.4: Quadratic Equations: Section OutlineDocument4 pages1.4: Quadratic Equations: Section OutlineAHMED ALSHAMMARINo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Quadratic FunctionDocument20 pagesLesson 8 Quadratic FunctionNicole Daphnie LisNo ratings yet
- High School FormulasDocument1 pageHigh School FormulasNadav ElmaliahNo ratings yet
- NewProgress - AMaths TB (Sol) - ch02Document2 pagesNewProgress - AMaths TB (Sol) - ch02kkakilaiNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions PDFDocument36 pagesPartial Fractions PDFlakkaraju prasanna100% (1)
- 1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic EquationDocument8 pages1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic Equationkhrr7brbpcNo ratings yet
- Matrices: Matrix: An Arrangement of Number in To Rows and Columns Is Called A "Matrix"Document10 pagesMatrices: Matrix: An Arrangement of Number in To Rows and Columns Is Called A "Matrix"Sai ShashankNo ratings yet
- I Problems 1: PrefaceDocument7 pagesI Problems 1: PrefaceShanmuga SundaramNo ratings yet
- Algebraic IdentitiesDocument57 pagesAlgebraic IdentitiesD SAI TEJANNo ratings yet
- How To Factorize The Quadratic Equation E CientlyDocument2 pagesHow To Factorize The Quadratic Equation E CientlyNikola Pacek-VetnićNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Roots of A Quadratic EquationDocument40 pagesQuadratic Equations: Roots of A Quadratic EquationAnshuman BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document39 pagesWeek 2saumy abhishekNo ratings yet
- Integration FormulasDocument7 pagesIntegration Formulasapi-3756871100% (1)
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument2 pagesQuadratic FunctionsKatie RaineNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 5.37: SolutionDocument11 pagesPROBLEM 5.37: SolutionCliford MustaineNo ratings yet
- A Quadratic Equation (Document2 pagesA Quadratic Equation (Henry PoNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FormulaDocument2 pagesQuadratic FormulafynzenNo ratings yet
- 334 Quadfuncp 2Document2 pages334 Quadfuncp 2Louis GuyNo ratings yet
- 334 Quadfuncp 1Document2 pages334 Quadfuncp 1Louis GuyNo ratings yet
- CS 543: Computer Graphics Lecture 3 (Part II) : Points, Scalars and VectorsDocument23 pagesCS 543: Computer Graphics Lecture 3 (Part II) : Points, Scalars and VectorsChi HanaNo ratings yet
- 4.HIGH School IV REAL NUMBERS-SOME IMPORTANT INEQUALITYDocument2 pages4.HIGH School IV REAL NUMBERS-SOME IMPORTANT INEQUALITYNenad JanicijevicNo ratings yet
- Ax X B B Ax Ax X X: 2ax (2 Ax+b) +B (2ax+b) B 4 AcDocument2 pagesAx X B B Ax Ax X X: 2ax (2 Ax+b) +B (2ax+b) B 4 Acyaw197No ratings yet
- Mockb1 p2 AnsDocument8 pagesMockb1 p2 Ans。No ratings yet
- Analisis Struktur Gilbert Tua N S. 1853050003Document9 pagesAnalisis Struktur Gilbert Tua N S. 1853050003gilbert novensiusNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument69 pagesQuadratic EquationsAvishkar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Revision Summary of DSE Mathematics (Compulsory Part)Document27 pagesRevision Summary of DSE Mathematics (Compulsory Part)Roy TsangNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Formula and Discriminant NOtesDocument4 pagesQuadratic Formula and Discriminant NOtesGabbriel Emmanuel Y. CabagnotNo ratings yet
- MathEPP3rd Mock6 P2 Sol EDocument7 pagesMathEPP3rd Mock6 P2 Sol EKarina LauNo ratings yet
- MA1505 1920S1 Part I Chapter 1Document19 pagesMA1505 1920S1 Part I Chapter 1Jaehun JeongNo ratings yet
- 2.2a Quadratic EquationsDocument45 pages2.2a Quadratic EquationsMario VNo ratings yet
- MATHS SA - Msa Revision Package SolutionsDocument7 pagesMATHS SA - Msa Revision Package SolutionsglenlcyNo ratings yet
- Section 9.1 1.: y Ae Be y Ae BeDocument2 pagesSection 9.1 1.: y Ae Be y Ae BeDaniel FernandesNo ratings yet
- Functions of Several VariablesDocument4 pagesFunctions of Several VariablesKonal ShahNo ratings yet
- Multvarweek 4Document4 pagesMultvarweek 4Konal ShahNo ratings yet
- Multvarweek 4Document4 pagesMultvarweek 4Konal ShahNo ratings yet
- Rules of Differentiation and IntegrationDocument10 pagesRules of Differentiation and IntegrationKitchanan KosalathipNo ratings yet
- Semis 12345Document6 pagesSemis 12345Mariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Cambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionFrom EverandCambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Aaasr 2 RDocument1 pageAaasr 2 RvolcaniusNo ratings yet
- 123 AawDocument2 pages123 AawvolcaniusNo ratings yet
- Your Membership Has Expired. Please Choose A Plan To Renew Your MembershipDocument1 pageYour Membership Has Expired. Please Choose A Plan To Renew Your MembershipvolcaniusNo ratings yet
- Plugins InfoDocument35 pagesPlugins InfovolcaniusNo ratings yet
- Your Membership Has Expired. Please Choose A Plan To Renew Your MembershipDocument3 pagesYour Membership Has Expired. Please Choose A Plan To Renew Your MembershipvolcaniusNo ratings yet
- Xtreme FaqDocument2 pagesXtreme FaqvolcaniusNo ratings yet
- The Definitive Classical Guitar Technique BuilderDocument4 pagesThe Definitive Classical Guitar Technique Buildervolcanius100% (2)
- Yamaha USB Audio DriverDocument9 pagesYamaha USB Audio DrivervolcaniusNo ratings yet
- Welcome To B4 Ii: 1. Software UpdatesDocument3 pagesWelcome To B4 Ii: 1. Software UpdatesvolcaniusNo ratings yet
- Plugins InfoDocument35 pagesPlugins InfovolcaniusNo ratings yet