Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth Science Unpacked (1) 1st Quarter
Earth Science Unpacked (1) 1st Quarter
Uploaded by
Genalyn Cirpo TayoneCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- DLL - ELS - WEEK - 1 - 1 - UNIQUENESS OF PLANET EARTH - S1112ES Ia e 3Document3 pagesDLL - ELS - WEEK - 1 - 1 - UNIQUENESS OF PLANET EARTH - S1112ES Ia e 3Ryan Duque100% (2)
- DLL Earth Science - Week 5Document4 pagesDLL Earth Science - Week 5X-handi Fallarna100% (1)
- Final DLPDocument3 pagesFinal DLPԱբրենիկա ՖերլինNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Earth and Life ScienceHarold Pascua Tuya100% (2)
- PEAC CIDAM Template 2019 Earth ScienceDocument10 pagesPEAC CIDAM Template 2019 Earth ScienceJaruay Celeridad100% (1)
- 8279 13632 1 SM PDFDocument12 pages8279 13632 1 SM PDFFarhan RazyNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science I. ObjectivesJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Prelim - Phy Scie11Document3 pagesPrelim - Phy Scie11JaenicaPaulineCristobalNo ratings yet
- Esls DLL 07-0408Document6 pagesEsls DLL 07-0408Genesis NgNo ratings yet
- DLL Earth and Life Science7-18Document4 pagesDLL Earth and Life Science7-18Jonas Miranda CabusbusanNo ratings yet
- TOS - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE - MIDTERM EXAM EditedDocument3 pagesTOS - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE - MIDTERM EXAM EditedLeah Marfe Sapid Gentallan100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical SciencemheldsDocument17 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Physical Sciencemheldsjocel manalangNo ratings yet
- DLL Science Week 2Document11 pagesDLL Science Week 2JR EretnacNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science TOSDocument16 pagesEarth Life Science TOSMarY grace lorcaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Summative Test ELSDocument5 pages2021 Summative Test ELSKristian Jay NantaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide in Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesTeaching Guide in Physical ScienceCamille Hontalba LptNo ratings yet
- LC 39Document3 pagesLC 39JT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Els 1 6 4 19Document2 pagesEls 1 6 4 19Mark Kevin Villareal100% (2)
- SHS Core Earth Science CGDocument6 pagesSHS Core Earth Science CGJake Arman PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document7 pagesWeek 5Michelle Ramirez Co-GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLL Earth and Life Week 1Document3 pagesDLL Earth and Life Week 1Queency Panaglima PadidaNo ratings yet
- Mpaihs Grade 11 Reshel Resplandor Science (SHS) Earth and Life Science First Quarter 1Document5 pagesMpaihs Grade 11 Reshel Resplandor Science (SHS) Earth and Life Science First Quarter 1Resplandor Tristeza ReshelNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Test: Earth & Life ScienceDocument10 pagesFirst Quarterly Test: Earth & Life Scienceglaiza abucayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Earth and Life ScienceDocument4 pagesAssessment Earth and Life ScienceMitz Villaruz-FernandezNo ratings yet
- Prenza National High School Marilao, Bulacan: A Lesson Guide in Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesPrenza National High School Marilao, Bulacan: A Lesson Guide in Earth ScienceallanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Final ExamDocument3 pagesPhysical Science Final ExamLope FelisildaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 12 - How The Elements Found in The Universe Were Formed-2Document6 pagesPhysical Science 12 - How The Elements Found in The Universe Were Formed-2Levigilda Carbos100% (1)
- S11.12LT IIa 4Document35 pagesS11.12LT IIa 4augeneiiNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Summative Test in Earth and LifeDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Summative Test in Earth and LifeJarven SaguinNo ratings yet
- New DLL SHS - Earth & Life Science July 1-5, 2019-2020Document2 pagesNew DLL SHS - Earth & Life Science July 1-5, 2019-2020BeeWin50% (2)
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMaria Liza Lastima abrinica0% (1)
- Physical Science Lesson 1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Lesson 1Mary Ann TolibaoNo ratings yet
- ELS Performance Task 3Document2 pagesELS Performance Task 3Kristine Claire LaureteNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info New DLL Physical Science PRDocument27 pagesToaz - Info New DLL Physical Science PRBrynard GarbosaNo ratings yet
- DLP Racel AsuncionDocument3 pagesDLP Racel Asuncionshermaine genistonNo ratings yet
- Exam Earth and Life 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesExam Earth and Life 2nd QuarterCathy BeeNo ratings yet
- Earth Science DLL Week 6Document2 pagesEarth Science DLL Week 6Maribel Lescano100% (1)
- Lesson Plan On Deformation of CrustDocument3 pagesLesson Plan On Deformation of CrustCHANo ratings yet
- TOS Earth & Life Science 2019-2020Document8 pagesTOS Earth & Life Science 2019-2020Celso Tambis Jr.100% (1)
- G11 - Earth and Life Science - SUMMATIVE EXAM With ANSWERSDocument4 pagesG11 - Earth and Life Science - SUMMATIVE EXAM With ANSWERSPaul Patrick Guanzon100% (2)
- Physical Science Summative Test q1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Summative Test q1Josh JuanesNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Week 4 DLLDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Week 4 DLLReyes CzarinaNo ratings yet
- S11ES If 14Document6 pagesS11ES If 14allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- S11ES Ic D 8Document3 pagesS11ES Ic D 8allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Wk1Document29 pagesEarth and Life Science Wk1Kenneth ManozonNo ratings yet
- 1Q - Exam - Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pages1Q - Exam - Earth and Life ScienceAlexis John Hisula VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Tos - Final - Exam Earth and Life Science 1Document2 pagesTos - Final - Exam Earth and Life Science 1Rudula Amper100% (1)
- Senior High LP - BioenergeticsDocument2 pagesSenior High LP - Bioenergeticsking devesfruto100% (2)
- St. Paul School General Natividad, INC Misereor Village, Balaring, General M. Natividad, 3125 Nueva Ecija S.Y 2017-2018Document5 pagesSt. Paul School General Natividad, INC Misereor Village, Balaring, General M. Natividad, 3125 Nueva Ecija S.Y 2017-2018Edralyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- Daily - Lesson - Log - in - Earth sCIENCE 2020Document4 pagesDaily - Lesson - Log - in - Earth sCIENCE 2020Zllehb BhelayzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Earth and Life Science: Exogenic ProcessesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Earth and Life Science: Exogenic ProcessesNuevalyn Quijano FernandoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMaricar Cesista NicartNo ratings yet
- Evidence For and Explain The Formation of The Light Elements in The Big Bang TheoryDocument7 pagesEvidence For and Explain The Formation of The Light Elements in The Big Bang TheoryJohn Nerlo DequiñaNo ratings yet
- Senior High LP - Energy FlowDocument3 pagesSenior High LP - Energy Flowking devesfrutoNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument7 pagesDLPIan ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cot 1-JeanDocument5 pagesCot 1-Jeanrosie tapayanNo ratings yet
- First Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterDocument11 pagesFirst Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterElvie CalinisanNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: GRADE 1 To 12Document5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: GRADE 1 To 12Arlynn Arcaño IslaNo ratings yet
- Earth and LifeDocument8 pagesEarth and LifeLeslie Lara DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMeldie Ann B. LeopoldoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science MELCsDocument4 pagesEarth and Life Science MELCsValiant TiaciNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Webquest Lab SheetDocument4 pagesRock Cycle Webquest Lab Sheetapi-268569185No ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Q1-11 WEEK 7&8Document5 pages4th Summative Test Q1-11 WEEK 7&8Lalaine De Guzman CanoNo ratings yet
- Le Roux 2005. Bay Sedimentation As Controlled by Regional Crust Behavior, Local Tectonics and Eustatic Sea Level Changes Coquimbo Formation (MIocene-Pliocene), Bay of Tongoy, Central Chile PDFDocument21 pagesLe Roux 2005. Bay Sedimentation As Controlled by Regional Crust Behavior, Local Tectonics and Eustatic Sea Level Changes Coquimbo Formation (MIocene-Pliocene), Bay of Tongoy, Central Chile PDFLuis MolinaNo ratings yet
- Science Week 10Document6 pagesScience Week 10Sheheer The Ice Cream100% (1)
- Peta in Earth SciDocument6 pagesPeta in Earth Sciariel sanchezNo ratings yet
- In Memoriam: Geologia CroaticaDocument14 pagesIn Memoriam: Geologia Croaticaado_bajricNo ratings yet
- Tugas TPPI - Baihaqi A. KhatimDocument3 pagesTugas TPPI - Baihaqi A. KhatimBAIHAQI A KHATIM KHATIMNo ratings yet
- 8.20 Ha. Quartz and Feldspar Mine of United Mineral Corporation, Hakeempet (V), MDK Dist. - Rejection of ECDocument2 pages8.20 Ha. Quartz and Feldspar Mine of United Mineral Corporation, Hakeempet (V), MDK Dist. - Rejection of ECprasanna 4uNo ratings yet
- Puposal For Consolidation Grouting in TunnelDocument22 pagesPuposal For Consolidation Grouting in TunneljunaidNo ratings yet
- Mylonites: IndexDocument46 pagesMylonites: IndexMiguel AcoNo ratings yet
- Ratoi Et Al.Document1 pageRatoi Et Al.Simalcsik AngelaNo ratings yet
- Tectonostratigraphic Framework and Depositional History Pattern of The Cretaceous SuccessionsDocument27 pagesTectonostratigraphic Framework and Depositional History Pattern of The Cretaceous Successionsomaradilgeo12No ratings yet
- Bernaolaetal SEG2019 CarhuacayanDocument4 pagesBernaolaetal SEG2019 CarhuacayanVictor ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Dill, (2015) - Pegmatites y AplitesDocument145 pagesDill, (2015) - Pegmatites y AplitesDiego Ardila100% (1)
- Modul 8 - Metamorphic RocksDocument52 pagesModul 8 - Metamorphic RocksEldeNo ratings yet
- Soil Science ReviewerDocument2 pagesSoil Science ReviewerDeejee Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Geology of Rajasthan PDFDocument140 pagesGeology of Rajasthan PDFGirijesh Pandey100% (1)
- Cornejo, P. Et Al. (1997)Document35 pagesCornejo, P. Et Al. (1997)WilliamsRafaelMataRimacNo ratings yet
- Geocronología Del Magmatismo Mesozoico-Cenozoico en El Centro de Chile, Lat. 31 ° - 36 ° S - Drake Et Al 1982Document11 pagesGeocronología Del Magmatismo Mesozoico-Cenozoico en El Centro de Chile, Lat. 31 ° - 36 ° S - Drake Et Al 1982Marcela diaz riveraNo ratings yet
- Applied Geology Lab ManualDocument22 pagesApplied Geology Lab ManualkoloshrabeaaNo ratings yet
- Kurdistan GeologyDocument174 pagesKurdistan Geologygeorgesoden100% (1)
- Pb-Zn-Cu Mineralization in The Filfila Massif, Northeastern AlgeriaDocument4 pagesPb-Zn-Cu Mineralization in The Filfila Massif, Northeastern AlgeriaEddir BelmNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.5: Modeling: Sedimentary Rock FormationDocument42 pagesLesson 1.5: Modeling: Sedimentary Rock FormationVanessa NapierNo ratings yet
- Qi 2006Document18 pagesQi 2006Mbarouk Shaame MbaroukNo ratings yet
- Classification of Igneous RocksDocument5 pagesClassification of Igneous RocksMa Bernadette VielleNo ratings yet
- Small-Scale Spatial and Temporal Variations in Mid-Ocean Ridge Crest Magmatic ProcessesDocument6 pagesSmall-Scale Spatial and Temporal Variations in Mid-Ocean Ridge Crest Magmatic Processespiyush guptaNo ratings yet
- Curso Skarn Meinert1Document69 pagesCurso Skarn Meinert1César VargasNo ratings yet
- Minerals of IndianaDocument74 pagesMinerals of IndianaMuhammad ZakriyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrothermal Breccia Texture PDFDocument36 pagesHydrothermal Breccia Texture PDFAnggit Tri Atmaja100% (1)
Earth Science Unpacked (1) 1st Quarter
Earth Science Unpacked (1) 1st Quarter
Uploaded by
Genalyn Cirpo TayoneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth Science Unpacked (1) 1st Quarter
Earth Science Unpacked (1) 1st Quarter
Uploaded by
Genalyn Cirpo TayoneCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region XI
Division of Compostela Valley
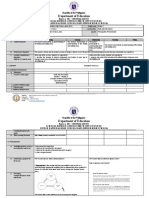
EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE K TO 12 CURRICULUM GUIDE / BUDGET OF WORK
Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4
FIRST
EARTH SCIENCE
QUARTER
I. ORIGIN AND STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
I.A. UNIVERSE AND SOLAR SYSTEM
1. State the different hypothesis explaining the origin of the Universe. (S11/12ES-Ia-e1)
2. Describe the different hypotheses explaining the origin of the Solar System.(S11/12ES-Ia-e2)
Learning 3. Explain the current advancements/information on the solar system.( S11/12ES-Ia-e3)
Competencies 4. Recognized the uniqueness of Earth, being the only planet in the solar system with
properties necessary to support life. (S11/12ES-Ia-e4)
- Describe the structure - Explain the Big Bang
- Identify the large scale - Recognize the
and composition of the Theory and evidences
and small scale difference in the
Universe. supporting the theory.
properties of the Solar physical and chemical
- State the different - Explain the red-shift
System. properties between the
hypothesis that and how it is used as
- Discuss the different Earth and its
preceded the Big Bang proof of an expanding
hypotheses explaining neighboring planets.
Week 1
Theory of the universe. the origin of the solar - Identify the factors
Origin of the Universe. system. that allow a planet to
- State most recent support life.
advancements/
information on the solar
system.
Suggested Video Viewing: ASTRONOMY Multimedia Program w/ embedded Pre and Post Assessment
Activities
Pre-Test Concept Mastery Check Concept Mastery Check
Assessment on Origin of the on Origin of the Solar
Universe System
I.B. EARTH AND EARTH SYSTEMS
5. Explain that the Earth consists of four subsystems, across whose boundaries matter and energy
flow. (S11/12ES-Ia-e5)
Learning 6. Show the contributions of personalities on the understanding of the Earth systems. (S11/12ES-Ia-
Competencies e6)
7. Identify the layers of the Earth (crust, mantle, core). (S11/12ES-Ia-e7)
8. Differentiate the layers of the Earth. (S11/12ES-Ia-e8)
- Define the concept of - Identify the layers of 1st Summative
a system. the Earth (crust, Test/Post Test
- Recognize the Earth mantle, core)
as a system composed - Differentiate the
of subsystems. layers of the Earth
- Discuss the
Week 2
interaction of Earth
Sub system
- Discuss the historical
development of the
concept of Earth
System.
Suggested
Activities
Review on the Concepts
Assessment
of Chapter 1
II. EARTH MATERIALS AND PROCESSES
II.A. MINERALS AND ROCKS
Learning 1. Identify common rock-forming minerals using their physical and chemical properties. S11/12ES-
Competencies Ia-9)
- Demonstrate
understanding about
Week 2
physical and chemical
properties of mineral.
Suggested
Activities
Pre-Test on Minerals-
Assessment
Endogenic Processes
II.A. & B MINERALS AND ROCKS
1. Identify common rock-forming minerals using their physical and chemical properties. (S11/12ES-
Learning
Ia-9)
Competencies
2. Classify rocks into igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. (S11/12ES-Ib-10)
- Identify certain minerals using specific tests.
- Explain how cooling influences the crystal size
- Identify some common rock-forming minerals of minerals
Week 3
- Identify the different types of igneous rocks
(Intrusive & Extrusive)
Suggested Group Activity: Determining Mineral properties Group Activity: Classifying a rock
Activities
Assessment
II.A. MINERALS AND ROCKS
Learning 1. Classify rocks into igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. (S11/12ES-Ib-10)
Competencies
- Identify the different types of metamorphic
-Discuss the processes that change sediments rocks.
into sedimentary rock
- Discuss the rock cycle.
Week 4 - Identify the different types of Sedimentary
Rocks
Suggested Group Activity: Classifying a rock
Activities
Concept Mastery Check/Review
Assessment
II.B. ENDOGENIC PROCESSES
3. Describe where the Earth’s internal heat comes from. (S11/12ES-Ib-14
4. Describe how magma is formed (magmatism). (S11/12ES-Ic-15)
Learning 5. Describe what happens after magma is formed (plutonism and volcanism). (S11/12ES-Ic-16)
Competencies 6. Compare and contrast the formation of the different types of igneous rocks. (S11/12ES-Ic-17)
7. Describe the changes in mineral components and texture of rocks due to changes in pressure and
temperature (metamorphism). (S11/12ES-Ic-18)
- Identify the sources of - Describe the - Differentiate contact
Earth's internal heat. formation of plutonic and regional
- Identify the different and volcanic rocks. metamorphism.
types of magma and its - Identify common 2nd Summative
Week 5
composition. examples of Test/Post Test
- Explain the different metamorphic rocks.
ways to generate
magma.
Suggested
Activities
Assessment
II.C. EXOGENIC PROCESSES
8. Describe how rocks undergo weathering. (S11/12ES-Ib-11)
9. Explain how the products of weathering are carried away by erosion and deposited elsewhere.
Learning
(S11/12ES-Ib-12)
Competencies
10. Make a report on how rocks and soil move downslope to the direct action of gravity. (S11/12ES-
Ib-13)
- ldentify the controls of - describe the different - Identify the different - Identify the controls of
weathering. processes of erosion deposition sites. mass wasting.
- Identify and and its mobile agents. - Differentiate the types
Week 6
differentiate the types - discuss loading of mass wasting.
of weathering and its capacity and
causes. competency of a river.
Suggested
Activities
Pre Test- Exogenic-
Assessment Deformation of the
Crust
II.D. DEFORMATION OF THE CRUST
11. Describe how rocks behave under different types of stress such as compression, pulling apart,
and shearing. (S11/12ES-Ic-19)
12. Explain how the continents drift. (S11/12ES-Id-20)
Learning
13. Cite evidence that support continental drift. (S11/12ES-Id-21)
Competencies
14. Explain how the movement of plates leads to the formation of folds and faults. (S11/12ES-Id-22)
15. Explain how the seafloor spreads. (S11/12ES-Id-23)
16. Describe the structure and evolution of ocean basins. (S11/12ES-Id-24)
- identify the different - Trace the history of - Explain the
types of stress and its continental drift and its mechanism of seafloor
deformation and supporting evidences. spreading.
3rd Summative
Week 7 products. - Describe how plates - Identify the structure
Test/Post Test
move and identify the and parts of an ocean
types of folds and basin.
faults.
Deformation Paper Spread
Suggested (using Wooden Box; (Using Chairs and
Activities Sand & Flour) Paper to demonstrate
Seafloor Spreading)
Assessment Concept Mastery Check
II.E. HISTORY OF THE EARTH
17. Describe how layers of rocks (stratified rocks) are formed. (S11/12ES-Ie-25)
18. Describe the different methods (relative and absolute dating) of determining the age of stratified
rocks. (S11/12ES-Ie-26)
Learning 19. Explain how relative and absolute dating were used to determine the subdivisions of geologic
Competencies time. (S11/12ES-Ie-27)
20. Describe how marker fossils (also known as guide fossils) are used to define and identify
subdivisions of the geologic time scale. (S11/12ES-Ie-28)
21. Describe how the Earth's history can be interpreted from the geologic time scale.(S11/12ES-Ie-29)
- Identify the - Determine the process - Identify the different - Describe Earth's
fundamental principles of absolute dating. types of marker fossils history form the
Week 8 of stratigraphy. -Differentiate the in the time intervals of geologic time scale and
- Determine the process relative dating from the geologic time scale. its important events.
of relative dating. absolute dating.
Suggested Individual/Group:
Activities Picture I
Assessment
III. NATURAL HAZARDS, MITIGATION AND ADAPTATION
III.A. GEOLOGIC PROCESSES AND HAZARDS
1. Describe the various hazards that may happen in the event of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions,
and landslides. (S11/12ES-If-30)
2. Using hazard maps, identify areas prone to hazards brought about by earthquakes, volcanic
Learning eruptions, and landslides (S11/12ES-If-31)
Competencies 3. Give practical ways of coping with geological hazards caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions,
and landslides. (S11/12ES-If-32)
4. Identify human activities that speed up or trigger landslides (S11/12ES-If-33)
5. Suggest ways to help lessen the occurrence of landslides in your community. (S11/12ES-Ig-34)
- Identify the different hazards caused by
earthquake ,Volcanic, & Landslide.
- Identify areas prone to earthquake, Volcanic, &
Landslide hazards
.- Determine what to do before, during and after
Week 9 an earthquake. Volcanic eruption and landslide
- Identify the human activities that can cause
landslide.
- Suggests mitigation measures to avoid or
reduce landslide occurrence.
Suggested Conduct a survey to assess the possible geologic
Activities hazards that your community may experience.
Assessment
III.B. HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL PHENOMENA AND HAZARDS
6. Describe the various hazards that may happen in the wake of tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods,
or ipo-ipo.( S11/12ES-Ig-35)
Learning 7. Using hazard maps, identify areas prone to hazards brought about by tropical cyclones, monsoons,
Competencies floods, or ipo-ipo. (S11/12ES-Ig-36)
8. Give practical ways of coping with hydrometeorological hazards caused by tropical cyclones,
monsoons, floods, or ipo-ipo. (S11/12ES-Ih-37)
- Identify the different hazards caused by tropical
cyclones, monsoons, floods, or ipo-ipo.
.
- Identify areas prone to tropical cyclones,
Week 9 monsoons, floods, or ipo-ipo.
- Determine what to do before, during and after a
tropical cyclone, monsoons, floods, or ipo-ipo.
Conduct a survey or design a study to assess the
Suggested
possible hydrometeorological hazards that your
Activities
community may experience
Assessment
III.C. MARINE AND COASTAL PROCESSES AND THEIR EFFECTS
9. Describe how coastal processes result in coastal erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion.
(S11/12ES-Ih-38)
Learning 10. Identify areas in your community prone to coastal erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion.
Competencies (S11/12ES-Ii-39)
11. Give practical ways of coping with coastal erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion.
(S11/12ES-Ii-40)
12. Cite ways to prevent or mitigate the impact of land development, waste disposal, and construction
of structures on control coastal processes. (S11/12ES-Ii-41)
- Identify the causes of - Identify areas in the - Identify mitigation
coastal erosion, province prone to measures to reduce the
submersion and salt coastal erosion, impact of land
water intrusion. submersion and salt development, water
water intrusion. disposal and
r . construction of
Week 10 Quarterly Exam
- Identify mitigation structures on coastal
measures to reduce areas.
coastal erosion,
submersion and salt
water intrusion.
Presentation &
Suggested
Submission of
Activities
Performance Tasks
Concept Mastery Check
Assessment
Prepared by:
Jennifer C. Baloca
Teacher II- SHS Compostela National High School
Rex Bryan B. Ranalan
Teacher II- SHS Pantukan National High School
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region XI
Division of Compostela Valley
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE
1ST Quarter Examination
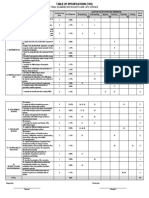
TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS
Number DOMAINS Total
Content Standard Hours Percentage of Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creating
Items
Universe & Solar I- 1 I- 4 I- 3, 5 I- 2 5
3 8 5
System
Earth & Earth I- 8 I-9 I- 7 I- 6, 10, 7
5 13 7 II- 8 11
Systems
Minerals and Rocks I- 15 I- 18 I-14,16,17 I – 12,13 IV- 1-2 12
8 20 12
II- 3,4,5,6,7
Exogenic Processes 4 10 6 I- 22,24 I- 19, 21 I- 23 I- 20 5
Endogenic Processes 5 13 7 I- 25, IV- 3-5 I-26,27 4
Deformation of the I- 32 I-36 I-34 2
3 8 5
Crust
History of the Earth 3 8 5 I- 33 I-30,31 I-29 I – 28,35 5
Geologic Processes III- 1-5 5
3 8 5
and Hazards
Hydrometeorological I- 40 I- 37, 38, 4
39
Phenomena and 3 8 4
Hazards
Marine and Coastal 3 8 4 II- 1, 2, 9, 10 3
Processes and their
Effects
TOTAL 40 100 60 4 18 4 15 12 7 60
Prepared by:
Jennifer C. Baloca
Teacher II- SHS Compostela National High School
Rex Bryan B. Ranalan
Teacher II- SHS Pantukan National High School
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region XI
Division of Compostela Valley
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE
1ST Quarter Examination
Answer key
Test I Test II
Test III
1. A 21. A 1. True Lahar Pyroclastic Flow
2. B 22. D 2. True Water Saturated
3. C 23. D 3. Inorganic Volcanic Hazard Occur on Active
4. B 24. C 4. Graphite Mixture of Solid Volcano
and liquid Rapid Movement
5. C 25. C 5. True Gas, ash & lava
6. C 26. D 6. High Pressure Occur on both fragments
7. D 27. A 7. Compaction active and inactive
volcano Hot
8. B 28. A 8. Lithosphere
9. D 29. D 9. True Pyroclastic
10. B 30. B 10. True Material
11. A 31. D
12. C 32. C
13. C 33. C
14. D 34. C
Test IV (Answers may vary)
15. A 35. C
Sample answers
16. D 36. C 1. Igneous Rock Texture will depend on where it was cooled and solidified. Coarse grained textures
17.D 37. B are formed below the ground meanwhile the fine grain textures are formed above the ground.
18. D 38. A
19. A 39. A 2. Compressional stress dominates the subduction zones since it is a convergent zone. Foliated
20. C 40. D metamorphic rocks are formed in this zone due to compressional stress.
You might also like
- DLL - ELS - WEEK - 1 - 1 - UNIQUENESS OF PLANET EARTH - S1112ES Ia e 3Document3 pagesDLL - ELS - WEEK - 1 - 1 - UNIQUENESS OF PLANET EARTH - S1112ES Ia e 3Ryan Duque100% (2)
- DLL Earth Science - Week 5Document4 pagesDLL Earth Science - Week 5X-handi Fallarna100% (1)
- Final DLPDocument3 pagesFinal DLPԱբրենիկա ՖերլինNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Earth and Life ScienceHarold Pascua Tuya100% (2)
- PEAC CIDAM Template 2019 Earth ScienceDocument10 pagesPEAC CIDAM Template 2019 Earth ScienceJaruay Celeridad100% (1)
- 8279 13632 1 SM PDFDocument12 pages8279 13632 1 SM PDFFarhan RazyNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science I. ObjectivesJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Prelim - Phy Scie11Document3 pagesPrelim - Phy Scie11JaenicaPaulineCristobalNo ratings yet
- Esls DLL 07-0408Document6 pagesEsls DLL 07-0408Genesis NgNo ratings yet
- DLL Earth and Life Science7-18Document4 pagesDLL Earth and Life Science7-18Jonas Miranda CabusbusanNo ratings yet
- TOS - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE - MIDTERM EXAM EditedDocument3 pagesTOS - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE - MIDTERM EXAM EditedLeah Marfe Sapid Gentallan100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical SciencemheldsDocument17 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Physical Sciencemheldsjocel manalangNo ratings yet
- DLL Science Week 2Document11 pagesDLL Science Week 2JR EretnacNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science TOSDocument16 pagesEarth Life Science TOSMarY grace lorcaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Summative Test ELSDocument5 pages2021 Summative Test ELSKristian Jay NantaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide in Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesTeaching Guide in Physical ScienceCamille Hontalba LptNo ratings yet
- LC 39Document3 pagesLC 39JT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Els 1 6 4 19Document2 pagesEls 1 6 4 19Mark Kevin Villareal100% (2)
- SHS Core Earth Science CGDocument6 pagesSHS Core Earth Science CGJake Arman PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document7 pagesWeek 5Michelle Ramirez Co-GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLL Earth and Life Week 1Document3 pagesDLL Earth and Life Week 1Queency Panaglima PadidaNo ratings yet
- Mpaihs Grade 11 Reshel Resplandor Science (SHS) Earth and Life Science First Quarter 1Document5 pagesMpaihs Grade 11 Reshel Resplandor Science (SHS) Earth and Life Science First Quarter 1Resplandor Tristeza ReshelNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Test: Earth & Life ScienceDocument10 pagesFirst Quarterly Test: Earth & Life Scienceglaiza abucayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Earth and Life ScienceDocument4 pagesAssessment Earth and Life ScienceMitz Villaruz-FernandezNo ratings yet
- Prenza National High School Marilao, Bulacan: A Lesson Guide in Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesPrenza National High School Marilao, Bulacan: A Lesson Guide in Earth ScienceallanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Final ExamDocument3 pagesPhysical Science Final ExamLope FelisildaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 12 - How The Elements Found in The Universe Were Formed-2Document6 pagesPhysical Science 12 - How The Elements Found in The Universe Were Formed-2Levigilda Carbos100% (1)
- S11.12LT IIa 4Document35 pagesS11.12LT IIa 4augeneiiNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Summative Test in Earth and LifeDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Summative Test in Earth and LifeJarven SaguinNo ratings yet
- New DLL SHS - Earth & Life Science July 1-5, 2019-2020Document2 pagesNew DLL SHS - Earth & Life Science July 1-5, 2019-2020BeeWin50% (2)
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMaria Liza Lastima abrinica0% (1)
- Physical Science Lesson 1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Lesson 1Mary Ann TolibaoNo ratings yet
- ELS Performance Task 3Document2 pagesELS Performance Task 3Kristine Claire LaureteNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info New DLL Physical Science PRDocument27 pagesToaz - Info New DLL Physical Science PRBrynard GarbosaNo ratings yet
- DLP Racel AsuncionDocument3 pagesDLP Racel Asuncionshermaine genistonNo ratings yet
- Exam Earth and Life 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesExam Earth and Life 2nd QuarterCathy BeeNo ratings yet
- Earth Science DLL Week 6Document2 pagesEarth Science DLL Week 6Maribel Lescano100% (1)
- Lesson Plan On Deformation of CrustDocument3 pagesLesson Plan On Deformation of CrustCHANo ratings yet
- TOS Earth & Life Science 2019-2020Document8 pagesTOS Earth & Life Science 2019-2020Celso Tambis Jr.100% (1)
- G11 - Earth and Life Science - SUMMATIVE EXAM With ANSWERSDocument4 pagesG11 - Earth and Life Science - SUMMATIVE EXAM With ANSWERSPaul Patrick Guanzon100% (2)
- Physical Science Summative Test q1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Summative Test q1Josh JuanesNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Week 4 DLLDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Week 4 DLLReyes CzarinaNo ratings yet
- S11ES If 14Document6 pagesS11ES If 14allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- S11ES Ic D 8Document3 pagesS11ES Ic D 8allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Wk1Document29 pagesEarth and Life Science Wk1Kenneth ManozonNo ratings yet
- 1Q - Exam - Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pages1Q - Exam - Earth and Life ScienceAlexis John Hisula VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Tos - Final - Exam Earth and Life Science 1Document2 pagesTos - Final - Exam Earth and Life Science 1Rudula Amper100% (1)
- Senior High LP - BioenergeticsDocument2 pagesSenior High LP - Bioenergeticsking devesfruto100% (2)
- St. Paul School General Natividad, INC Misereor Village, Balaring, General M. Natividad, 3125 Nueva Ecija S.Y 2017-2018Document5 pagesSt. Paul School General Natividad, INC Misereor Village, Balaring, General M. Natividad, 3125 Nueva Ecija S.Y 2017-2018Edralyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- Daily - Lesson - Log - in - Earth sCIENCE 2020Document4 pagesDaily - Lesson - Log - in - Earth sCIENCE 2020Zllehb BhelayzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Earth and Life Science: Exogenic ProcessesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Earth and Life Science: Exogenic ProcessesNuevalyn Quijano FernandoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMaricar Cesista NicartNo ratings yet
- Evidence For and Explain The Formation of The Light Elements in The Big Bang TheoryDocument7 pagesEvidence For and Explain The Formation of The Light Elements in The Big Bang TheoryJohn Nerlo DequiñaNo ratings yet
- Senior High LP - Energy FlowDocument3 pagesSenior High LP - Energy Flowking devesfrutoNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument7 pagesDLPIan ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cot 1-JeanDocument5 pagesCot 1-Jeanrosie tapayanNo ratings yet
- First Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterDocument11 pagesFirst Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterElvie CalinisanNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: GRADE 1 To 12Document5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: GRADE 1 To 12Arlynn Arcaño IslaNo ratings yet
- Earth and LifeDocument8 pagesEarth and LifeLeslie Lara DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMeldie Ann B. LeopoldoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science MELCsDocument4 pagesEarth and Life Science MELCsValiant TiaciNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Webquest Lab SheetDocument4 pagesRock Cycle Webquest Lab Sheetapi-268569185No ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Q1-11 WEEK 7&8Document5 pages4th Summative Test Q1-11 WEEK 7&8Lalaine De Guzman CanoNo ratings yet
- Le Roux 2005. Bay Sedimentation As Controlled by Regional Crust Behavior, Local Tectonics and Eustatic Sea Level Changes Coquimbo Formation (MIocene-Pliocene), Bay of Tongoy, Central Chile PDFDocument21 pagesLe Roux 2005. Bay Sedimentation As Controlled by Regional Crust Behavior, Local Tectonics and Eustatic Sea Level Changes Coquimbo Formation (MIocene-Pliocene), Bay of Tongoy, Central Chile PDFLuis MolinaNo ratings yet
- Science Week 10Document6 pagesScience Week 10Sheheer The Ice Cream100% (1)
- Peta in Earth SciDocument6 pagesPeta in Earth Sciariel sanchezNo ratings yet
- In Memoriam: Geologia CroaticaDocument14 pagesIn Memoriam: Geologia Croaticaado_bajricNo ratings yet
- Tugas TPPI - Baihaqi A. KhatimDocument3 pagesTugas TPPI - Baihaqi A. KhatimBAIHAQI A KHATIM KHATIMNo ratings yet
- 8.20 Ha. Quartz and Feldspar Mine of United Mineral Corporation, Hakeempet (V), MDK Dist. - Rejection of ECDocument2 pages8.20 Ha. Quartz and Feldspar Mine of United Mineral Corporation, Hakeempet (V), MDK Dist. - Rejection of ECprasanna 4uNo ratings yet
- Puposal For Consolidation Grouting in TunnelDocument22 pagesPuposal For Consolidation Grouting in TunneljunaidNo ratings yet
- Mylonites: IndexDocument46 pagesMylonites: IndexMiguel AcoNo ratings yet
- Ratoi Et Al.Document1 pageRatoi Et Al.Simalcsik AngelaNo ratings yet
- Tectonostratigraphic Framework and Depositional History Pattern of The Cretaceous SuccessionsDocument27 pagesTectonostratigraphic Framework and Depositional History Pattern of The Cretaceous Successionsomaradilgeo12No ratings yet
- Bernaolaetal SEG2019 CarhuacayanDocument4 pagesBernaolaetal SEG2019 CarhuacayanVictor ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Dill, (2015) - Pegmatites y AplitesDocument145 pagesDill, (2015) - Pegmatites y AplitesDiego Ardila100% (1)
- Modul 8 - Metamorphic RocksDocument52 pagesModul 8 - Metamorphic RocksEldeNo ratings yet
- Soil Science ReviewerDocument2 pagesSoil Science ReviewerDeejee Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Geology of Rajasthan PDFDocument140 pagesGeology of Rajasthan PDFGirijesh Pandey100% (1)
- Cornejo, P. Et Al. (1997)Document35 pagesCornejo, P. Et Al. (1997)WilliamsRafaelMataRimacNo ratings yet
- Geocronología Del Magmatismo Mesozoico-Cenozoico en El Centro de Chile, Lat. 31 ° - 36 ° S - Drake Et Al 1982Document11 pagesGeocronología Del Magmatismo Mesozoico-Cenozoico en El Centro de Chile, Lat. 31 ° - 36 ° S - Drake Et Al 1982Marcela diaz riveraNo ratings yet
- Applied Geology Lab ManualDocument22 pagesApplied Geology Lab ManualkoloshrabeaaNo ratings yet
- Kurdistan GeologyDocument174 pagesKurdistan Geologygeorgesoden100% (1)
- Pb-Zn-Cu Mineralization in The Filfila Massif, Northeastern AlgeriaDocument4 pagesPb-Zn-Cu Mineralization in The Filfila Massif, Northeastern AlgeriaEddir BelmNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.5: Modeling: Sedimentary Rock FormationDocument42 pagesLesson 1.5: Modeling: Sedimentary Rock FormationVanessa NapierNo ratings yet
- Qi 2006Document18 pagesQi 2006Mbarouk Shaame MbaroukNo ratings yet
- Classification of Igneous RocksDocument5 pagesClassification of Igneous RocksMa Bernadette VielleNo ratings yet
- Small-Scale Spatial and Temporal Variations in Mid-Ocean Ridge Crest Magmatic ProcessesDocument6 pagesSmall-Scale Spatial and Temporal Variations in Mid-Ocean Ridge Crest Magmatic Processespiyush guptaNo ratings yet
- Curso Skarn Meinert1Document69 pagesCurso Skarn Meinert1César VargasNo ratings yet
- Minerals of IndianaDocument74 pagesMinerals of IndianaMuhammad ZakriyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrothermal Breccia Texture PDFDocument36 pagesHydrothermal Breccia Texture PDFAnggit Tri Atmaja100% (1)