Professional Documents
Culture Documents
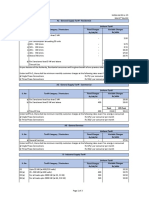
Air Conditioning:-: SL No Name of The Component/Device Specification No
Air Conditioning:-: SL No Name of The Component/Device Specification No
Uploaded by
h hazraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Conditioning:-: SL No Name of The Component/Device Specification No
Air Conditioning:-: SL No Name of The Component/Device Specification No
Uploaded by
h hazraCopyright:
Available Formats
27
-: Air Conditioning :-
Introduction :-
Most of the express or mail trains consist of multiple no of air conditioned coaches along with other general
coaches. These air conditioned coaches as it name suggests contains other special devices for the purpose of air
conditioning, which are not present in other general coaches. Besides having those special devices such as compressor,
condenser etc, the electrical system also differs from that of a general coach. The components of an air conditioned coach
are as follows :-
Components/Devices of an AC coach :-
SL Name of the Component/Device Specification No
no
1 Alternator 3 phase, 97 Volt, 25 KW, Field supply= 24 Volt 2
2 RRU/ERRU (Rectifier cum Regulator Unit) 129.5 Volt DC, 200 A 2
3 Battery 1100 AH, 2.2 V per Cell, 56 cells 1
4 Battery Charging Unit Input : 415 V 3 phase supply 1
Output : 129.5 V DC
5 Main Gear Rotary Switch, 400 A 1
6 Plant Gear Rotary Switch, 400 A 1
7 Inverter Input : 110-130 V DC 2
Output : 415 V 3 phase AC
8 Pump 0.5 H.P, 415 V 3 phase, 50 Hz 1
9 Compressor 3 phase 415 V SQIM, 10 A, p.f : 0.85 2
10 Condenser 3 phase 415 V SQIM, 1.7 A, p.f : 0.85 2
11 Blower Motor 3 phase 415 V SQIM, 2.2 A, p.f : 0.85 2
12 Liquid Receiver 2
13 Expansion Valve 2
14 Evaporator 2
Expansion principle: When a gas expands without external heat exchange it temperature falls and when it is
compressed without external heat exchange its temperature decreases.
The air-conditioning system adopted in air-conditioned coaches work on mechanical compression system
and consists of the following,
Evaporator unit consisting of cooling coil(heat exchanger), heater and motor-driven blower unit.
Thermostatic expansion valve.
Motor-driven compressor.
Air cooled condenser (with cooling fan driven by motor)
Liquid receiver and dehydrator.
Refrigerant piping for conveying the refrigerant(R-134A).
The Refrigeration Cycle: A typical refrigeration cycle in an air-conditioned coach can be represented also in a
pressure enthalpy diagram as in figure. The refrigerant gas at low pressure (represented by point C) is
compressed to point D. The compression process elevates the pressure from 37 psi(maximum 46 psi) to 150
psi(maximum 180 psi). The compression of the gas also heats up the gas to a superheat condition. The gas at the
compressor outlet is superheat and latent heat are removed at constant pressure , the refrigerant reaching the
point A at the end of this part of the cycle. The line A-B represents the expansion that takes place in the
expansion valve while the line B-C represents the refrigeration effect that is obtained in evaporator.
Apart from cooling, the air conditioning equipment is also required to provide heating when the outside
temperature varies from 400 C to 200 C .The cooling and heating will nave be necessarily automatic by means of
thermostatic controls incorporated in the unit. RDSO specification also lays down that the equipment shall admit
#Vocational TRAINING FROM 13th TO 15th JULY, 2016
#Air Conditioning.
28
fresh air at the rate of 0.35 metro cube per minute per passenger in the non-smoking area and 0.7 meter cube per
minute per passenger in the case of compartments where smoking is permitted.
Description of various components of Air -Conditioning Coach:
Alternator :- It is the main electrical source of any electrical system. It produces 3 phase alternating current and
feeds the electrical devices. In a air conditioned coach there are two such alternator of 25 KW each which
produces 97 volt A.C and can feed other electrical appliances of upto 190 A. It is situated under the coach and is
coupled with the moving axle with 12 belts. It is a brushless alternator which has its field and armature winding
both on the stator. Whenever the train therefore the axle gathers speed of 30 kmph or more, the alternator starts
generating electricity. The field winding is fed by 24 volt D.C supply from the RRU/ERRU unit. When the train
gathers enough speed as mentioned earlier, the alternator can efficiently feed the devices such as fans, lights,
motors etc.
RRU/ERRU(Rectifier cum Regulator Unit) :-
Although the modern coaches are being
manufactured with devices such as lights, fan, motors etc which operates on A.C supply, the previous generation
coaches used D.C fans, motors. Hence the generated three phase A.C is to be rectified for the operation of fans
and motors. This task is performed by the RRU unit situated under the coach. It not just only converts A.C to
D.C but also regulates the voltage level to a certain level of about 129.5 Volt. There are two RRU units each for
one alternator. It consist of power diodes and ERRU specially consist of microcontroller unit. The output of
ERRU is connected to two bus bars(+Ve and –Ve), to which other devices are connected.
Battery :- It is an auxiliary source of electric power which is mostly needed when the alternators are unable to
feed power. Such condition occurs when the train is in standstill condition. During such time, the battery can
feed power to the devices as needed. As it itself is a D.C source, it does not require any RRU unit. The battery
consists of 56 cells of 2.2 volt each connected in series with each other. It is also placed under the coach. The
capacity of a battery unit is 1100 AH which is sufficient enough to feed other electrical devices for few hours
without being charged by the alternators.
#Vocational TRAINING FROM 13th TO 15th JULY, 2016
#Air Conditioning.
29
Battery charging Unit :- It is the last source of supply. It is used only when the coach is under maintenance in
the maintenance depot. The input to the unit is 415 Volt 3 phases which is available from the maintenance
depot. The output is 129.5 volt D.C which is connected to the power bus bars. It is useful as it is uneconomical
to use battery power during maintenance. For that time being, the devices are directly fed by the external supply
using this unit.
Inverter :- This is also a fundamental unit in the
supply system of air conditioned coach as the
supply required for pumps, compressor and
condenser motors are 3 phase A.C. Though
E.M.F induced by the alternator is alternating in nature but the magnitude being 97 volt approximately, we can’t
use it directly for the above mentioned devices. Hence the inverter unit is required to convert 110-130 Volt D.C
to 415 Volt 3 phase A.C. And then those devices are connected to the output of the inverter.
Pumps :- This is needed to keep circulation of water from the water reservoir placed under the coach to the tank
placed over the bathroom section. The process is so designed that the pump continuously runs throughout the
journey. Hence it requires a continuous power supply of 3 phase 415 Volt A.C which is supplied by the inverter
as mentioned earlier. It has a Squirrel cage Induction Motor of power rating of 0.5 HP. There are two pump
units, one is kept as a stand-by unit. Both of them can be connected from any of the two inverters with the help
of a rotary switch called gear.
Evaporator unit: The evaporator unit consists of a thermostatic expansion valve, a heat exchanger, a
resistance- heating unit and a centrifugal blower driven by a motor. The function of the thermostatic expansion
valve is to allow the compressed refrigerant liquid to expand to a lower pressure corresponding to the load
demand. The expanded refrigerant passes through a heat exchanger; the heat in the air is transferred to the
refrigerant causing the cooling of the air and the evaporation of the refrigerant inside the tubes. The cooled air is
led through the ducting to the various compartments and diffused by means of air diffusers. Fresh air is drawn
through filters to eliminate dust and is mixed with the return air in the plenum on the inlet side of the evaporator.
Similarly, the return air filters so that the dust contained air in the return air is extracted. When the outside
ambient is very low and when the refrigeration is not required, the heater is switched on according to the setting
of thermostat.
Expansion valve: The primary function of the expansion value is to control the quantity of liquid refrigerant
admitted into the cooling coils of the evaporator.. The expansion valve admits more refrigerant when the air
#Vocational TRAINING FROM 13th TO 15th JULY, 2016
#Air Conditioning.
30
conditioning load is high, and reduces it to the minimum when the load is low.If the airconditioning load varies
greatly the superheat may be set between 101 O F to 150O F.
Compressor: The refrigerants vapour drawn from the evaporator is compressed by means of a multi cylinder
reciprocating compressor. The work done due to compression raises the temperature of the refrigerant vapour.
The motor used here is a 3 phase SQIM which is fed 415 volt 3 phase supply by the inverter. There are 2
compressor unit in a coach. It takes about 10 A current at nearly 0.85 P.F at long running condition.
Condenser: The condenser serves the function of extracting the heat absorbed by the refrigerant vapour in the
evaporator and the heat absorbed during the compression process. The condenser consists of a heat exchanger,
which is force-cooled by means of two or three axial flow blower fans. The refrigerant vapour is cooled at
constant pressure by means of the air blown over the finned tubes and liquefied. The refrigerant liquid leaving
the condenser is led into the liquid receiver from where it proceeds to the expansion valve on the evaporator.
The liquid receiver is a cylindrical container which contains a reserve of the refrigerant liquid. A dehydrator and
filter are also provided to ensure that the refrigerant is free from moisture and dust particles.
The motor used is also fed 415 Volt 3 phase supply by the inverter. It takes about 1.7 A current at 0.85 P.F. Like
other air conditioning devices, there are 2 condenser unit in the coach.
High Pressure cut-out: The high pressure cut-out is essentially a safety device against build up of excessive
delivery pressure and protects the compressor and piping system from damage. I t is a pressure operative switch
which switches off the compressor drive motor when the pressure exceeds a preset valve.
Low Pressure cut-out: This is also a pressure operated switch similar to the high pressure cut-out switch, but
is shuts down the compressor if the suction pressure drops down below 10 psi gauge. It protects the system
against unduly low evaporator temperatures and formation of frost on the evaporator.
Dehydrator and Filter: Water vapor or moisture will cause trouble in any refrigeration system. The moisture
may freeze and block the expansion valve orifice, and. also cause corrosion in working parts. This is best
achieved by subjecting the system of vacuum for 2 or 3 days. The dehydrator is another drying device
containing
Silica gel or other similar drying agent inserted in the refrigerant load for removing moisture from the
refrigerant while in operation. It should be provided atleast temperature when the installation is brought into
operation to remove any moisture in the piping system.
Refrigeration piping: The refrigerant piping consist of the suction line(from the evaporator outlet to the
compressor inlet) and the discharge line(from the compressor outlet to the condenser inlet), and liquid line(from
the liquid receiver to the inlet side of the expansion valve). Connections to the gauge panel from the compressor
delivery side(high pressure side), low pressure side and from the compressor crankcase, the lubricating oil
connections, are also part of the piping system, only copper pipes are used for refrigerant piping.
AC Control Panel: The control of the airconditiong system is achieved by means of Air conditioning Control
Panel.
AC Control Panel Components and their functions:
Evaporator Fan Motor Proving Relay: The prevents energisation of the compressor motor and condenser motor
or Heater till trio evaporator motor (16) comes ’ON’ and blows air into the duct through the evaporator coil.
This relay works in conjunction with a “Vone Switch” provided in trio air circuit. If the evaporator blower
motor supply fails or the motor does not run, the compressor motor and the condenser motors/Heater will get
switched ‘OFF’ by this relay.
Low Voltage Relay: This will trip to stop the compressor motor and
condenser motors/heater, and prevent them from starting by cutting off the supply to their control circuit if the
voltage of the battery is below 100 and reset when battery voltage rises to 102 V. The relay is provides with a
build-in time delay f 5 seconds, to avoid nuisance – tripping.
#Vocational TRAINING FROM 13th TO 15th JULY, 2016
#Air Conditioning.
31
Cooling Pilot Relay: Acts as an electrical link between the cooling thermostats and the control circuit of the
compressor and condenser. This is energized by electronic triggering set off by heat thermostat.
Heating Pilot Relay: Acts as an electrical link between the heating thermostats and the control circuit of heater.
This is energized by electronic triggering set off by thermostats.
Main Control Switch: This is the control switch for starting or shutting down the plant. This has got provision
to select blower only, LOW, MEDIUM and HIGH temperature setting.
Oil pressure Cut-out Switch: This protect the compressor against lubrication failure either due to lesser oil oil
pump failure or blocking of oil piping, and acts in conjuction with thermal cut-out to shut down the compressor
only if the low oil pressure persists.
Low pressure cut out: A pressure switch to protect against working of compressor with low suction pressure
due to loss of Freon gas or other reasons. This switch has been connected by means of copper piping to the
suction header of the compressor.
High pressure cut out: A pressure switch to shut down the compressor when compressor discharge pressure is
too high. The switch has been connected to the compressor discharge header by means of copper piping.
Pilot lights: These lights indicate respectively normalcy oh the mains , blower fan motor, compressor motor,
heater and normal voltage. Indications are now by LEDs.
Schematic Diagram of Electrical system of an AC Coach :-
#Vocational TRAINING FROM 13th TO 15th JULY, 2016
#Air Conditioning.
You might also like
- Line 6 Flextone 2 HD Service ManualDocument86 pagesLine 6 Flextone 2 HD Service Manualrnrmf2082No ratings yet
- Solar FanDocument37 pagesSolar Fantechcare12389% (9)
- Second Year Post Basic B.SC NursingDocument11 pagesSecond Year Post Basic B.SC NursingKailash Nagar100% (1)
- Aircraft Electrical SystemsDocument80 pagesAircraft Electrical SystemsRaghu B S67% (3)
- Electromagnetic Interference and CompatibilityDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Interference and CompatibilityYuvaraja50% (2)
- Cost Accounting 7 8 - Solution Manual Cost Accounting 7 8 - Solution ManualDocument27 pagesCost Accounting 7 8 - Solution Manual Cost Accounting 7 8 - Solution ManualMARIA100% (1)
- Train LightingDocument5 pagesTrain Lightingsanket100% (1)
- Components of Three Phase Loco.Document19 pagesComponents of Three Phase Loco.Aman ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Buet Power PlantDocument12 pagesBuet Power PlantMahmud Hasan100% (1)
- 132 KV Grid StationDocument25 pages132 KV Grid StationMarina KhanNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Static Converter For RailwayDocument20 pagesProject Report On Static Converter For RailwayScampy RamNo ratings yet
- Ncu PlantDocument18 pagesNcu PlantAmrit DasNo ratings yet
- Chashma Hydro Power Plant Internship ReportDocument10 pagesChashma Hydro Power Plant Internship ReportSaeed Anwar KhanNo ratings yet
- Grid Station OveviewDocument9 pagesGrid Station OveviewzubairNo ratings yet
- 132KV Internship ReportDocument10 pages132KV Internship ReportAbdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Power Conversion and Energy Storage: PrefaceDocument8 pagesPower Conversion and Energy Storage: PrefacehasanNo ratings yet
- Rectifier & Utilities Manual-FinalDocument136 pagesRectifier & Utilities Manual-FinalAbhinav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Application of VFD in Cycling Pumps in Thermal Power PlantDocument10 pagesApplication of VFD in Cycling Pumps in Thermal Power PlantJose Manuel FreitasNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant (Visit Report) : MR - Muhammad Sajjad HussainDocument5 pagesSteam Power Plant (Visit Report) : MR - Muhammad Sajjad HussainصصNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Automatic Control of Generating Transformer 250 Mva Cooling SystemDocument5 pagesMicrocontroller Based Automatic Control of Generating Transformer 250 Mva Cooling SystemNIRANJAN KBNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Drives in A Power Plant: SynopsisDocument22 pagesVariable Frequency Drives in A Power Plant: SynopsisReuben VargheseNo ratings yet
- Automatic Temperature Controlled FanDocument27 pagesAutomatic Temperature Controlled Fankannan100% (2)
- Power SupplyDocument3 pagesPower Supplysandyofficial.0305No ratings yet
- Sarni Power PlantDocument59 pagesSarni Power Plantdev810995No ratings yet
- 9 150427114734 Conversion Gate02Document77 pages9 150427114734 Conversion Gate02Eng-ezz AlarabNo ratings yet
- ExcitationsysDocument5 pagesExcitationsysDan GrayNo ratings yet
- American ControllersDocument16 pagesAmerican ControllersRenny PaoloneNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Grid Stations& T.LDocument51 pagesMethodology For Grid Stations& T.LiftikharNo ratings yet
- IGBT Based Auxiliary ConverterDocument28 pagesIGBT Based Auxiliary ConverterRounak Pandey89% (9)
- ExcitationRDocument4 pagesExcitationRDan GrayNo ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument4 pagesExcitationDan GrayNo ratings yet
- Stable Power Supplies in Power Station: Rectifier/ Charger Battery Rectifier/ Charger (Spare)Document6 pagesStable Power Supplies in Power Station: Rectifier/ Charger Battery Rectifier/ Charger (Spare)Santosh MondalNo ratings yet
- Alternador ReguladorDocument32 pagesAlternador ReguladorcaldasferreirasoutoNo ratings yet
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDocument9 pagesFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power System Operation and ControlDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Power System Operation and ControlAbdelrahman MuadiNo ratings yet
- Emergency Diesel Generator Set Stage-1Document14 pagesEmergency Diesel Generator Set Stage-1raghavendran raghuNo ratings yet
- Elect Aspect Coaches ICFDocument69 pagesElect Aspect Coaches ICFSaptarshi PalNo ratings yet
- Fan Speed Control Using 555 Time IcDocument33 pagesFan Speed Control Using 555 Time Icritesh chauhanNo ratings yet
- Power Supply DesignDocument8 pagesPower Supply DesigndarknessmonNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor ProtectionDocument42 pagesInduction Motor Protectionjayonline_4u91% (11)
- A Presentation On "Internship Under South Western Railway, Hubballi" byDocument26 pagesA Presentation On "Internship Under South Western Railway, Hubballi" byShruthi Mudaliar100% (1)
- 220V DC System at Thermal Power StationDocument5 pages220V DC System at Thermal Power StationArnel Pascual Laquindanum100% (1)
- 400 ElectricsDocument26 pages400 ElectricsMrAlbert2009No ratings yet
- Iiae Code:: Module 3 (Document11 pagesIiae Code:: Module 3 (PineappleJamNo ratings yet
- DBOOK wdg4Document13 pagesDBOOK wdg4RUDHRESH KUMAR SNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1.1 The Principle of WindmillDocument22 pagesChapter-1: 1.1.1 The Principle of WindmillVijay BavikattiNo ratings yet
- PWMDocument16 pagesPWMRICHIHOTS2100% (2)
- Star MazdaDocument40 pagesStar MazdastvnscottNo ratings yet
- Single PhasingDocument41 pagesSingle PhasingdiljithNo ratings yet
- 220V DC System at Thermal Power StationDocument6 pages220V DC System at Thermal Power Stationm kh100% (1)
- Basic Design RequirementDocument23 pagesBasic Design RequirementAli SialNo ratings yet
- 229 PE Innovative Practice 1Document2 pages229 PE Innovative Practice 1Sakshi BarapatreNo ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument4 pagesExcitationDan GrayNo ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument4 pagesExcitationDan GrayNo ratings yet
- Unit 02A - Elec Equip in Power StationDocument23 pagesUnit 02A - Elec Equip in Power Stationukshinde7368No ratings yet
- HVAC Instruments: Clamp-On Ammeter VoltmeterDocument8 pagesHVAC Instruments: Clamp-On Ammeter VoltmeterMuhammad Jamshaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Electric Actuator IntroductionDocument2 pagesDatasheet Electric Actuator IntroductionSenghy MaoNo ratings yet
- Katakhali ReportDocument10 pagesKatakhali ReportibrahimNo ratings yet
- 1 - AC GeneratorsDocument51 pages1 - AC Generatorsfaisl abdelgaffarNo ratings yet
- ME310grp1 Compressors - Generators (Read-Only)Document43 pagesME310grp1 Compressors - Generators (Read-Only)offiNo ratings yet
- Power Generator For MT-8BDocument60 pagesPower Generator For MT-8BTyan ScreamouscoreNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- 08 Proceduri de UrgentaDocument9 pages08 Proceduri de UrgentaSorescu Radu VasileNo ratings yet
- Autodesk BuildDocument53 pagesAutodesk BuildSturla SighvatssonNo ratings yet
- Algae Final InteractiveDocument8 pagesAlgae Final InteractivesuziethefatcatNo ratings yet
- Read More: Oneplus Bullets Wireless 2: Best In-Ear Headphones in IndiaDocument3 pagesRead More: Oneplus Bullets Wireless 2: Best In-Ear Headphones in IndiaABDULNo ratings yet
- Ultra Tech CementDocument14 pagesUltra Tech CementRaunak Doshi71% (14)
- Psychology and The Challenges of Life 13th Edition Nevid Solutions ManualDocument73 pagesPsychology and The Challenges of Life 13th Edition Nevid Solutions Manualbrianwoodsnjyoxepibt100% (14)
- Neck ExercisesDocument8 pagesNeck ExercisesAnthony Dinicolantonio100% (1)
- Average Average Set Ii Set I SampleDocument1 pageAverage Average Set Ii Set I Samplevenkateswara rao PothinaNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Chapter 3 LECTURE NOTESDocument6 pages3.0 Chapter 3 LECTURE NOTESNhư Hoàng Thụy TâmNo ratings yet
- OM-UHT Plant PDFDocument138 pagesOM-UHT Plant PDFToni0% (1)
- Evaluation of Ambient Noise Levels in Port Harcourt Metropolis, South-South, NigeriaDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Ambient Noise Levels in Port Harcourt Metropolis, South-South, NigeriaIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Msc1813ep MeduDocument2 pagesMsc1813ep MedumichaelsudjonoNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 2012Document5 pagesPractice Problems 2012Anonymous Fj3YPHNo ratings yet
- CL-1200i (1000P) &2600i&2800i - Service Manual - V1.0 - ENDocument803 pagesCL-1200i (1000P) &2600i&2800i - Service Manual - V1.0 - ENmanal al-hattaliNo ratings yet
- BASKS2Document7 pagesBASKS2NGUYEN EthanNo ratings yet
- Strilube 3125 TDSDocument2 pagesStrilube 3125 TDSchetanNo ratings yet
- Basics of HFFR ExtrusionDocument7 pagesBasics of HFFR ExtrusionYiğit IlgazNo ratings yet
- Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 1101-1103Document3 pagesChem. Commun., 2014, 50, 1101-1103RohanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Mopnth Celebration ScriptDocument4 pagesNutrition Mopnth Celebration ScriptLilian Laurel Cariquitan100% (9)
- Notified Vide SRO No. 575 Dated 22 May 2019Document3 pagesNotified Vide SRO No. 575 Dated 22 May 2019Hussain RahibNo ratings yet
- HRM IN SERVICE SECTOR AssignmentDocument6 pagesHRM IN SERVICE SECTOR AssignmentANUSREE AnilkumarNo ratings yet
- Receta PastelDocument5 pagesReceta PastelJesus BeltranNo ratings yet
- Violence Against Women in NepalDocument10 pagesViolence Against Women in NepalSunil K. DahalNo ratings yet
- Building ServicesDocument108 pagesBuilding ServicesSilvinus Clisson Pragash50% (2)
- Departments in Front Office Module 3Document40 pagesDepartments in Front Office Module 3Subhasis BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Design of A Solar Absorption Cooling System in A Greek Hospital PDFDocument8 pagesDesign of A Solar Absorption Cooling System in A Greek Hospital PDFYazid Al ShehriNo ratings yet
- Cub Cadet Parts Manual For Model 1211 SN 756300 799999Document9 pagesCub Cadet Parts Manual For Model 1211 SN 756300 799999shirley100% (56)