Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Biomes PDF
1.1 Biomes PDF
Uploaded by
Duodu StevenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 1.1.2 - Features of Biomes - 24Document13 pages1.1.2 - Features of Biomes - 24Matthew PringleNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Geography Exam RevisionDocument7 pagesYear 9 Geography Exam RevisionJieshun Wang100% (2)
- Restoration and Reju. of Ponds - NITI AyogDocument156 pagesRestoration and Reju. of Ponds - NITI AyogbrahmishtanNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes - Land Biomes and Aquatic Ecosystems Filled in VersionDocument6 pagesCornell Notes - Land Biomes and Aquatic Ecosystems Filled in Versionapi-307861748No ratings yet
- Continents and Land FormsDocument76 pagesContinents and Land FormsJay100% (4)
- Week 4-5 EcosystemDocument43 pagesWeek 4-5 EcosystemKurt TongolNo ratings yet
- BIOMES AND ECOSYSTEMS - Biotic - AbioticDocument51 pagesBIOMES AND ECOSYSTEMS - Biotic - AbioticAlondra TorresNo ratings yet
- Enviro Book Chap 6Document32 pagesEnviro Book Chap 6hbuelba3No ratings yet
- Focus 1/4: Biomes/ecosystems Different From One Another? Try To Come UpDocument23 pagesFocus 1/4: Biomes/ecosystems Different From One Another? Try To Come UpCarmela BuluranNo ratings yet
- Becerra, Roann S. Activity 6Document7 pagesBecerra, Roann S. Activity 6Roann S. BecerraNo ratings yet
- Review ScienceDocument12 pagesReview Science030929No ratings yet
- Earth and LifeDocument23 pagesEarth and LifeSunsilk Na GreenNo ratings yet
- Global Ecology: Chapter OutlineDocument25 pagesGlobal Ecology: Chapter OutlinehyNo ratings yet
- Biomes Work BookletDocument25 pagesBiomes Work BookletMonica Albornoz CamachoNo ratings yet
- Biomes and Biodiversity: Biomes - Large Biological CommunitiesDocument29 pagesBiomes and Biodiversity: Biomes - Large Biological CommunitiesCasas, Jo-an Pauline A.No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Climate and BiodiversityDocument68 pagesChapter 7 Climate and BiodiversityBernard DayotNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9.2: Terrestrial and Aquatic Biomes: Chapter 9: EcologyDocument10 pagesLesson 9.2: Terrestrial and Aquatic Biomes: Chapter 9: EcologyJlo LopezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Envi SciDocument92 pagesIntroduction To Envi ScikachechiekurosakiNo ratings yet
- BIOMESDocument2 pagesBIOMESRyan Negad0% (1)
- ch06 Sec1 Revised BiomesDocument15 pagesch06 Sec1 Revised BiomesSarah BatesNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2020-21 CHY1002 TH VL2020210106371 Reference Material I 02-Nov-2020 Module 2 4Document79 pagesFALLSEM2020-21 CHY1002 TH VL2020210106371 Reference Material I 02-Nov-2020 Module 2 4Sai AravindNo ratings yet
- What Is BiodiversityDocument3 pagesWhat Is BiodiversitySheena Mae PlancoNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge: Css-PmsDocument27 pagesGeneral Knowledge: Css-PmsUnza WaqarNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Biomes - Interactive PresentationDocument70 pagesThe Concept of Biomes - Interactive PresentationjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER 5 Terrestrial and Marine Ecosystems Part 2Document3 pagesREVIEWER 5 Terrestrial and Marine Ecosystems Part 2Rechelle ArdalesNo ratings yet
- Geograohy Classnotes Lesson 4.3, 5.1 & 5.2Document3 pagesGeograohy Classnotes Lesson 4.3, 5.1 & 5.2adiva.sk09No ratings yet
- BiomesDocument65 pagesBiomesanthonyNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Biomes DevendraDocument27 pagesTerrestrial Biomes DevendradeviiserNo ratings yet
- BIOMESDocument2 pagesBIOMESAlexa LanoriasNo ratings yet
- Components of EcosytemDocument20 pagesComponents of EcosytemRosselle May JumayaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 7 & 8Document67 pagesLecture Notes 7 & 8Marvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesEnvironmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1yvonnesmithpfidmgwzek100% (32)
- Lecture 5 and 6Document27 pagesLecture 5 and 6Iam RohitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tropical Forests Lecture 2Document50 pagesIntroduction To Tropical Forests Lecture 2YENNITA JAMES BF21110144No ratings yet
- Biomes: Ecotone, May Be Wide or NarrowDocument5 pagesBiomes: Ecotone, May Be Wide or NarrowQuerecia IsidroNo ratings yet
- Climate and BiodiversityDocument51 pagesClimate and Biodiversityperlito guibaoNo ratings yet
- BiomeDocument6 pagesBiomeJohnatan HernándezNo ratings yet
- JOHNDocument4 pagesJOHNFasiko AsmaroNo ratings yet
- Biomes NotesDocument4 pagesBiomes Notessataga4241No ratings yet
- 2 Paper 1 The Living WorldDocument2 pages2 Paper 1 The Living WorldSerena ChughNo ratings yet
- BiosphereDocument24 pagesBiosphereWasim badamiNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial BiomeDocument6 pagesTerrestrial BiomeSereneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Ecosystem TypesDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Ecosystem TypesJaffy Bustamante100% (1)
- Biosphere: Group 4Document61 pagesBiosphere: Group 4Juliana Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadDocument11 pagesLiving in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadTina Morgan100% (19)
- KO The Living WorldDocument2 pagesKO The Living WorldGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Yan Han Shao - 9.8 Work Period BiomesDocument7 pagesYan Han Shao - 9.8 Work Period Biomesyan han shaoNo ratings yet
- Poster A4Document1 pagePoster A4zacktudorukNo ratings yet
- LU1 PhysicalenvironmentDocument14 pagesLU1 Physicalenvironmentjohn rey fabilloNo ratings yet
- RIKADocument9 pagesRIKANicko LaboniteNo ratings yet
- Benifits of BiodiversityDocument14 pagesBenifits of BiodiversitylamaNo ratings yet
- What Are Biomes?Document2 pagesWhat Are Biomes?Nishaleeny Nainar AyyavoNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument16 pagesEcosystemAdrelynx JoviNo ratings yet
- 25 BOT 101 Ecology Lecture 2Document37 pages25 BOT 101 Ecology Lecture 2samuelogunsola005No ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Biome Concept in Ecology: BIOL 4120: Principles of EcologyDocument72 pagesLecture 5: Biome Concept in Ecology: BIOL 4120: Principles of EcologyClarkNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadBrett Bunch100% (20)
- Environment.05.Terrestrial EcosystemDocument25 pagesEnvironment.05.Terrestrial Ecosystemvcvikram14No ratings yet
- Interactive World Biomes Map PowerpointDocument7 pagesInteractive World Biomes Map PowerpointТатьяна КучеренкоNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 PDFDocument17 pagesUnit 7 PDFashishNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument15 pagesBiomesSupasiri JarusombutiNo ratings yet
- Ekologi Pertemuan 1 2020Document57 pagesEkologi Pertemuan 1 2020TiaraDiahNo ratings yet
- Low-Water Garden: How To Beat The Drought And Grow a Thriving Garden Using Low-Water TechniquesFrom EverandLow-Water Garden: How To Beat The Drought And Grow a Thriving Garden Using Low-Water TechniquesNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 365 November 20, 2017: Sample Channel Ratio (SCR)Document21 pagesBCHEM 365 November 20, 2017: Sample Channel Ratio (SCR)Duodu StevenNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 264 Jan. 28, 2016: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyDocument29 pagesBCHEM 264 Jan. 28, 2016: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 264 Mar. 05, 2015 Radioisotope Techniques The Nature of Radioactivity Atomic StructureDocument16 pagesBCHEM 264 Mar. 05, 2015 Radioisotope Techniques The Nature of Radioactivity Atomic StructureDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 365 October 28, 2019Document47 pagesBCHEM 365 October 28, 2019Duodu StevenNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 264 Jan. 22, 2015: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyDocument43 pagesBCHEM 264 Jan. 22, 2015: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of The Immune System: I. Humoral (Antibody-Mediated) ImmunityDocument9 pagesDual Nature of The Immune System: I. Humoral (Antibody-Mediated) ImmunityDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions On Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions On Monoclonal AntibodiesDuodu Steven100% (1)
- Succession Quiz AnswersDocument2 pagesSuccession Quiz AnswersDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Study of How The Body Limits Invasion by Non-Self and Recognises and Eliminates Altered SelfDocument28 pagesImmunology: Study of How The Body Limits Invasion by Non-Self and Recognises and Eliminates Altered SelfDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument83 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Digestive SystemDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Ecological SuccessionDocument16 pagesEcological SuccessionDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Barbarian - Path of ThunderstormsDocument1 pageBarbarian - Path of ThunderstormsAlejandro Moriña de MoraNo ratings yet
- Human Ecological Adaptations: Tarun GoyalDocument25 pagesHuman Ecological Adaptations: Tarun GoyalSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- 5-Sediment Traps and BasinsDocument16 pages5-Sediment Traps and BasinsAnonymous d6vkxJNo ratings yet
- EnglandDocument2 pagesEnglandDariya MinNo ratings yet
- Forest ClassificationDocument13 pagesForest Classificationm a zargarNo ratings yet
- Geologic Processes On Earth's SurfaceDocument25 pagesGeologic Processes On Earth's SurfaceLian AenNo ratings yet
- (English) Dear Future Generations - Sorry (2024) (DownSub - Com)Document3 pages(English) Dear Future Generations - Sorry (2024) (DownSub - Com)Malek 19No ratings yet
- Upsc Geography NotesDocument3 pagesUpsc Geography NotesparthirajamechNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Report of Construction of HL RCC Bridge at MANGALPUR TO FARSHANI GHIRAENI OVER HARHA RIVERDocument9 pagesHydrology Report of Construction of HL RCC Bridge at MANGALPUR TO FARSHANI GHIRAENI OVER HARHA RIVERV P GUPTANo ratings yet
- DECEMBER 9th Natural DisastersDocument1 pageDECEMBER 9th Natural DisasterscudaNo ratings yet
- Competence 8Document8 pagesCompetence 8Mabel Albares100% (1)
- Air Wells, Dew Ponds and Fog Fences - Methods To Condense Atmospheric HumidityDocument42 pagesAir Wells, Dew Ponds and Fog Fences - Methods To Condense Atmospheric HumidityJason BetzNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2090997718300099 Main - CompressedDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S2090997718300099 Main - CompressedAsep IrawanNo ratings yet
- Dewpoint and Vapor Pressure Deficit EquationsDocument2 pagesDewpoint and Vapor Pressure Deficit EquationssureshNo ratings yet
- Alemu DiribssaDocument104 pagesAlemu Diribssakedir100% (1)
- GEO 110 NotesDocument9 pagesGEO 110 NotesaliNo ratings yet
- Steart BookletDocument20 pagesSteart BookletWessex ArchaeologyNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text About Global WarmingDocument4 pagesExplanation Text About Global WarmingFajar Prasetya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 14 Feb 2022 PDFDocument5 pagesAdobe Scan 14 Feb 2022 PDFmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Shangai Houton ParkDocument15 pagesShangai Houton ParkHari HaranNo ratings yet
- Lagos (Nigeria) Ooding and in Uence of Urban PlanningDocument14 pagesLagos (Nigeria) Ooding and in Uence of Urban PlanningOjolowo OlamideNo ratings yet
- FloodsDocument14 pagesFloodsImogen AdamsNo ratings yet
- Green Infrastructure Retrofit As An Alternative To Conventional Stormwater ManagementDocument32 pagesGreen Infrastructure Retrofit As An Alternative To Conventional Stormwater ManagementPranav MishraNo ratings yet
- CZMP Fisheries Min 1Document291 pagesCZMP Fisheries Min 1tamilNo ratings yet
- The Changing Face of The Ethiopian Rift Lakes and Their EnvironsDocument18 pagesThe Changing Face of The Ethiopian Rift Lakes and Their EnvironsTariku GemedaNo ratings yet
- Wetland Conservation and LawDocument15 pagesWetland Conservation and LawHimangshu Sonowal0% (1)
- Geochemistry of Limestones Deposited in Various Plate Tectonic SettingsDocument22 pagesGeochemistry of Limestones Deposited in Various Plate Tectonic SettingsAlberto Ra VitalaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Social Issues and The Environment From Unsustainable To Sustainable DevelopmentDocument37 pagesUnit-Iv Social Issues and The Environment From Unsustainable To Sustainable DevelopmentarumugamNo ratings yet
1.1 Biomes PDF
1.1 Biomes PDF
Uploaded by
Duodu StevenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1 Biomes PDF
1.1 Biomes PDF
Uploaded by
Duodu StevenCopyright:
Available Formats
Section
Name Date
Biomes
1.1
Summary
Textbook pages 8–33
Before You Read
A biome includes large regions that have similar living and non-living components.
Tundra and desert are two examples of biomes. What other biomes can you name?
◆
What is a biome?
✏ Make Flash Cards The biosphere is the thin layer of air, land, and water on or
For each biome, write a near Earth’s surface where living things exist. A biome is the
question on one side of the largest division of the biosphere. Biomes are characterized by
flash card. Write the answer their biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components.
on the other side. Quiz your-
self until you can answer all What are Earth’s biomes like?
the questions.
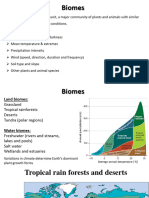
Earth has eight terrestrial (land-based) biomes.
Biome Main characteristics
tundra ■ located in the upper northern hemisphere; very cold and dry
■ due to permanently frozen soil, plants are short and there are few trees
boreal forest ■ found in the far north; below freezing half the year
■ mainly coniferous (cone-bearing) trees
temperate deciduous ■ located in temperate regions, mostly eastern North America, eastern Asia, and western
forest Europe
■ trees lose their leaves in winter
■ large seasonal changes with four distinct seasons
temperate rainforest ■ found along coastlines where ocean winds drop large amounts of moisture
■ cool and very wet, allowing trees (mainly evergreens) to grow very tall
grassland ■ occurs in temperate and tropical regions
■ covered with grasses that have deep roots, which are well adapted for drought
tropical rainforest ■ found in a wide band around the equator
■ wet and warm year-round, allowing for the growth of a dense canopy of tall trees
desert ■ occur in temperate and tropical regions; days are hot and nights are cold
■ rainfall is minimal and plants and animals are adapted to reduce water loss
permanent ice ■ includes the polar land masses and large polar ice caps
■ the few animals that live here are well insulated against the extreme cold
2 MHR • Section 1.1 Biomes © 2008 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited
002_013_BCSci10_U1CH01_098461.in2 2 Pdf 2nd 6/30/08 5:58:14 PM
Section
Name Date
1.1
Summary
continued
●
How do abiotic factors influence the characteristics
and distribution of biomes? ✔ Reading Check
What are the two main
Identical biomes are found in different parts of the world. abiotic factors that
These biomes all have similar plants and animals (biotic influence the character-
factors) because they have similar temperatures and istics and distribution of
precipitation patterns (abiotic factors). Temperature and biomes?
precipitation are the main abiotic factors that influence the
characteristics and distribution of biomes. The following
factors influence temperature and precipitation:
◆ latitude
◆ elevation
◆ wind
◆ ocean currents ● ✔
What are climatographs? Climatograph
Fort Nelson, British Columbia, 59ºN
Average Precipitation (mm)
Climate is the average pattern of weather conditions that 180 25
Average Temperature (ºC)
160 15
occur in a region over a period of years. Temperature and 140
precipitation are two important factors that determine climate. 120 5
100
A climatograph is a graph of climate data for a specific –5
80
region. A climatograph gives average temperature and 60 –15
40
average total precipitation for each month. 20
–25
0 –35
J F M A MJ J A S O N D
How are organisms adapted to the specific Month
conditions of their biome?
Adaptations are characteristics that enable organisms to
better survive and reproduce. Organisms are specially adapted
for survival in the specific environmental conditions of their
●
biome. There are three types of adaptations:
◆ structural adaptations: physical parts or features of an
✔ Reading Check
organism that enable it to survive and reproduce. List the three main types
of adaptations displayed by
◆ physiological adaptations: a chemical or physical event
organisms.
that takes place in the body of an organism to support its
ability to survive and reproduce
◆ behavioural adaptations: things that an organism
does (ways that it behaves) that enable it to survive and
reproduce. ● ✔
© 2008 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Section 1.1 Biomes • MHR 3
002_013_BCSci10_U1CH01_098461.in3 3 Pdf 2nd 6/30/08 5:58:16 PM
Cloze
Name Date Activity
Section 1.1
Use with textbook pages 8–28.
Biomes and ecosystems
Vocabulary
abiotic latitude
adaptations ocean currents
behavioural physiological
biome precipitation
biotic structural
climatograph temperature
elevation terrestrial
Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. Use each term only once.
1. components are the living organisms in an environment, such
as plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria.
2. components are the non-living parts of an environment, such
as sunlight, soil, moisture, and temperature.
3. A includes large regions that have similar biotic components
and abiotic components.
4. A biome is land-based.
5. and are two important abiotic factors
that influence the characteristics of biomes and the distribution of biomes on Earth.
6. is the distance measured in degrees north or south from the
equator.
7. is the height of a land mass above sea level.
8. are another abiotic factor that affects temperature and
precipitation and therefore influences the characteristics of biomes.
9. A is a graph of climate data for a specific region and is
generated from data usually obtained over 30 years from local weather observation
stations.
10. are characteristics that enable organisms to better survive and
reproduce.
11. A adaptation is a physical feature of an organism’s body
having a specific function that contributes to the survival of the organism. A
adaptation is a physical or chemical event that occurs within
the body of an organism that enables survival. A adaptation
refers to what an organism does to survive in the unique conditions of
its environment.
4 MHR • Section 1.1 Biomes © 2008 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited
002_013_BCSci10_U1CH01_098461.in4 4 Pdf 2nd 6/30/08 5:58:17 PM
Applying
Name Date Knowledge
Section 1.1
Use with textbook pages 20–28.
Various biomes
Complete the following table, describing the general locations and two to three
main physical features of the eight terrestrial biomes.
Biome Location(s) Physical features
tundra
boreal forest
temperate deciduous
forest
temperate rainforest
grassland (temperate and tropical)
tropical rainforest
desert (hot and cold) hot desert:
cold desert:
permanent ice (polar ice)
© 2008 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Section 1.1 Biomes • MHR 5
002_013_BCSci10_U1CH01_098461.in5 5 Pdf 2nd 6/30/08 5:58:19 PM
Interpreting
Name Date Illustrations
Section 1.1
Use with textbook pages 16–28.
Climatographs
Which world biomes are represented by the data in the following climatographs?
A B
Average Precipitation (mm)
Average Precipitation (mm)
180 25 Average Temperature (ºC) 180 25
Average Temperature (ºC)
160 160
15 15
140 140
120 5 120 5
100 –5 100 –5
80 80
60 –15 60 –15
40 –25 40 –25
20 20
0 –35 0 –35
J F M A MJ J A S O N D J F M A MJ J A S O N D
Month Month
Biome: Biome:
C D
Average Precipitation (mm)
600 25 180 25
Average Temperature (ºC)
Average Precipitation (mm)
15 160
Average Temperature (ºC)
500 15
5 140
400
120 5
300 –5
100
200 –15 ⫺5
80
100 –25 60 ⫺15
0 –35 40
J F M A MJ J A S O N D ⫺25
20
Month
0 ⫺35
J F MA MJ J A S O N D
Month
Biome: Biome:
E F
180 35 300 35
Average Precipitation (mm)
Average Precipitation (mm)
Average Temperature (ºC)
160
Average Temperature (ºC)
25 250 25
140
120 15 200 15
100 5
5 150
80
60 –5 100 –5
40 50 –15
–15
20
0 –25 0 –25
J F MA MJ J A S O N D J F MA MJ J A S O N D
Month Month
Biome: Biome:
6 MHR • Section 1.1 Biomes © 2008 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited
002_013_BCSci10_U1CH01_098461.in6 6 Pdf 2nd 6/30/08 5:58:21 PM
Assessment
Name Date
Section 1.1
Use with textbook pages 8–28. 8. Which of the following is an abiotic
component of an environment?
Biomes A. algae
B. sunlight
Match each Term on the left with the best
Descriptor on the right. Each Descriptor may only C. fungi
be used once. D. plants
Term Descriptor
9. Which of the following is a biotic
1. abiotic A. the distance measured component of an ecosystem?
2. adaptations in degrees north or
3. biome south from the equator
A. moisture
4. biotic B. characteristics that B. sand
5. climate enable organisms to
C. bacteria
6. latitude better survive and
reproduce D. temperature
C. relating to non-living
parts of an environ- 10. Which of the following is a characteristic
ment, such as sunlight, of the boreal forest biome?
soil, moisture, and A. below freezing half the year
temperature
D. relating to the living B. long, hot summers
organisms, such as C. polar land masses
plants, animals, fungi,
and bacteria D. lots of precipitation
E. the largest division of 11. Which world biome is represented by a
the biosphere climatograph that illustrates an average
F. the average conditions precipitation of 300 cm in the month of
of the atmosphere in a January?
large region over
30 years A. grassland
Circle the letter of the best answer. B. tropical rainforest
C. permanent ice
7. A biome is best represented by a:
D. temperate deciduous forest
A. river
12. Which world biome is represented by a
B. city climatograph that illustrates an average
C. latitude temperature of –25ºC in the month of July?
D. desert A. boreal forest
B. tropical rainforest
C. permanent ice
D. tundra
© 2008 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Section 1.1 Biomes • MHR 7
002_013_BCSci10_U1CH01_098461.in7 7 Pdf 2nd 6/30/08 5:58:23 PM
You might also like
- 1.1.2 - Features of Biomes - 24Document13 pages1.1.2 - Features of Biomes - 24Matthew PringleNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Geography Exam RevisionDocument7 pagesYear 9 Geography Exam RevisionJieshun Wang100% (2)
- Restoration and Reju. of Ponds - NITI AyogDocument156 pagesRestoration and Reju. of Ponds - NITI AyogbrahmishtanNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes - Land Biomes and Aquatic Ecosystems Filled in VersionDocument6 pagesCornell Notes - Land Biomes and Aquatic Ecosystems Filled in Versionapi-307861748No ratings yet
- Continents and Land FormsDocument76 pagesContinents and Land FormsJay100% (4)
- Week 4-5 EcosystemDocument43 pagesWeek 4-5 EcosystemKurt TongolNo ratings yet
- BIOMES AND ECOSYSTEMS - Biotic - AbioticDocument51 pagesBIOMES AND ECOSYSTEMS - Biotic - AbioticAlondra TorresNo ratings yet
- Enviro Book Chap 6Document32 pagesEnviro Book Chap 6hbuelba3No ratings yet
- Focus 1/4: Biomes/ecosystems Different From One Another? Try To Come UpDocument23 pagesFocus 1/4: Biomes/ecosystems Different From One Another? Try To Come UpCarmela BuluranNo ratings yet
- Becerra, Roann S. Activity 6Document7 pagesBecerra, Roann S. Activity 6Roann S. BecerraNo ratings yet
- Review ScienceDocument12 pagesReview Science030929No ratings yet
- Earth and LifeDocument23 pagesEarth and LifeSunsilk Na GreenNo ratings yet
- Global Ecology: Chapter OutlineDocument25 pagesGlobal Ecology: Chapter OutlinehyNo ratings yet
- Biomes Work BookletDocument25 pagesBiomes Work BookletMonica Albornoz CamachoNo ratings yet
- Biomes and Biodiversity: Biomes - Large Biological CommunitiesDocument29 pagesBiomes and Biodiversity: Biomes - Large Biological CommunitiesCasas, Jo-an Pauline A.No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Climate and BiodiversityDocument68 pagesChapter 7 Climate and BiodiversityBernard DayotNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9.2: Terrestrial and Aquatic Biomes: Chapter 9: EcologyDocument10 pagesLesson 9.2: Terrestrial and Aquatic Biomes: Chapter 9: EcologyJlo LopezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Envi SciDocument92 pagesIntroduction To Envi ScikachechiekurosakiNo ratings yet
- BIOMESDocument2 pagesBIOMESRyan Negad0% (1)
- ch06 Sec1 Revised BiomesDocument15 pagesch06 Sec1 Revised BiomesSarah BatesNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2020-21 CHY1002 TH VL2020210106371 Reference Material I 02-Nov-2020 Module 2 4Document79 pagesFALLSEM2020-21 CHY1002 TH VL2020210106371 Reference Material I 02-Nov-2020 Module 2 4Sai AravindNo ratings yet
- What Is BiodiversityDocument3 pagesWhat Is BiodiversitySheena Mae PlancoNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge: Css-PmsDocument27 pagesGeneral Knowledge: Css-PmsUnza WaqarNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Biomes - Interactive PresentationDocument70 pagesThe Concept of Biomes - Interactive PresentationjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER 5 Terrestrial and Marine Ecosystems Part 2Document3 pagesREVIEWER 5 Terrestrial and Marine Ecosystems Part 2Rechelle ArdalesNo ratings yet
- Geograohy Classnotes Lesson 4.3, 5.1 & 5.2Document3 pagesGeograohy Classnotes Lesson 4.3, 5.1 & 5.2adiva.sk09No ratings yet
- BiomesDocument65 pagesBiomesanthonyNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Biomes DevendraDocument27 pagesTerrestrial Biomes DevendradeviiserNo ratings yet
- BIOMESDocument2 pagesBIOMESAlexa LanoriasNo ratings yet
- Components of EcosytemDocument20 pagesComponents of EcosytemRosselle May JumayaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 7 & 8Document67 pagesLecture Notes 7 & 8Marvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesEnvironmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1yvonnesmithpfidmgwzek100% (32)
- Lecture 5 and 6Document27 pagesLecture 5 and 6Iam RohitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tropical Forests Lecture 2Document50 pagesIntroduction To Tropical Forests Lecture 2YENNITA JAMES BF21110144No ratings yet
- Biomes: Ecotone, May Be Wide or NarrowDocument5 pagesBiomes: Ecotone, May Be Wide or NarrowQuerecia IsidroNo ratings yet
- Climate and BiodiversityDocument51 pagesClimate and Biodiversityperlito guibaoNo ratings yet
- BiomeDocument6 pagesBiomeJohnatan HernándezNo ratings yet
- JOHNDocument4 pagesJOHNFasiko AsmaroNo ratings yet
- Biomes NotesDocument4 pagesBiomes Notessataga4241No ratings yet
- 2 Paper 1 The Living WorldDocument2 pages2 Paper 1 The Living WorldSerena ChughNo ratings yet
- BiosphereDocument24 pagesBiosphereWasim badamiNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial BiomeDocument6 pagesTerrestrial BiomeSereneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Ecosystem TypesDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Ecosystem TypesJaffy Bustamante100% (1)
- Biosphere: Group 4Document61 pagesBiosphere: Group 4Juliana Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadDocument11 pagesLiving in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadTina Morgan100% (19)
- KO The Living WorldDocument2 pagesKO The Living WorldGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Yan Han Shao - 9.8 Work Period BiomesDocument7 pagesYan Han Shao - 9.8 Work Period Biomesyan han shaoNo ratings yet
- Poster A4Document1 pagePoster A4zacktudorukNo ratings yet
- LU1 PhysicalenvironmentDocument14 pagesLU1 Physicalenvironmentjohn rey fabilloNo ratings yet
- RIKADocument9 pagesRIKANicko LaboniteNo ratings yet
- Benifits of BiodiversityDocument14 pagesBenifits of BiodiversitylamaNo ratings yet
- What Are Biomes?Document2 pagesWhat Are Biomes?Nishaleeny Nainar AyyavoNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument16 pagesEcosystemAdrelynx JoviNo ratings yet
- 25 BOT 101 Ecology Lecture 2Document37 pages25 BOT 101 Ecology Lecture 2samuelogunsola005No ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Biome Concept in Ecology: BIOL 4120: Principles of EcologyDocument72 pagesLecture 5: Biome Concept in Ecology: BIOL 4120: Principles of EcologyClarkNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadBrett Bunch100% (20)
- Environment.05.Terrestrial EcosystemDocument25 pagesEnvironment.05.Terrestrial Ecosystemvcvikram14No ratings yet
- Interactive World Biomes Map PowerpointDocument7 pagesInteractive World Biomes Map PowerpointТатьяна КучеренкоNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 PDFDocument17 pagesUnit 7 PDFashishNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument15 pagesBiomesSupasiri JarusombutiNo ratings yet
- Ekologi Pertemuan 1 2020Document57 pagesEkologi Pertemuan 1 2020TiaraDiahNo ratings yet
- Low-Water Garden: How To Beat The Drought And Grow a Thriving Garden Using Low-Water TechniquesFrom EverandLow-Water Garden: How To Beat The Drought And Grow a Thriving Garden Using Low-Water TechniquesNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 365 November 20, 2017: Sample Channel Ratio (SCR)Document21 pagesBCHEM 365 November 20, 2017: Sample Channel Ratio (SCR)Duodu StevenNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 264 Jan. 28, 2016: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyDocument29 pagesBCHEM 264 Jan. 28, 2016: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 264 Mar. 05, 2015 Radioisotope Techniques The Nature of Radioactivity Atomic StructureDocument16 pagesBCHEM 264 Mar. 05, 2015 Radioisotope Techniques The Nature of Radioactivity Atomic StructureDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 365 October 28, 2019Document47 pagesBCHEM 365 October 28, 2019Duodu StevenNo ratings yet
- BCHEM 264 Jan. 22, 2015: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyDocument43 pagesBCHEM 264 Jan. 22, 2015: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of The Immune System: I. Humoral (Antibody-Mediated) ImmunityDocument9 pagesDual Nature of The Immune System: I. Humoral (Antibody-Mediated) ImmunityDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions On Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions On Monoclonal AntibodiesDuodu Steven100% (1)
- Succession Quiz AnswersDocument2 pagesSuccession Quiz AnswersDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Study of How The Body Limits Invasion by Non-Self and Recognises and Eliminates Altered SelfDocument28 pagesImmunology: Study of How The Body Limits Invasion by Non-Self and Recognises and Eliminates Altered SelfDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument83 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Digestive SystemDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Ecological SuccessionDocument16 pagesEcological SuccessionDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Barbarian - Path of ThunderstormsDocument1 pageBarbarian - Path of ThunderstormsAlejandro Moriña de MoraNo ratings yet
- Human Ecological Adaptations: Tarun GoyalDocument25 pagesHuman Ecological Adaptations: Tarun GoyalSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- 5-Sediment Traps and BasinsDocument16 pages5-Sediment Traps and BasinsAnonymous d6vkxJNo ratings yet
- EnglandDocument2 pagesEnglandDariya MinNo ratings yet
- Forest ClassificationDocument13 pagesForest Classificationm a zargarNo ratings yet
- Geologic Processes On Earth's SurfaceDocument25 pagesGeologic Processes On Earth's SurfaceLian AenNo ratings yet
- (English) Dear Future Generations - Sorry (2024) (DownSub - Com)Document3 pages(English) Dear Future Generations - Sorry (2024) (DownSub - Com)Malek 19No ratings yet
- Upsc Geography NotesDocument3 pagesUpsc Geography NotesparthirajamechNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Report of Construction of HL RCC Bridge at MANGALPUR TO FARSHANI GHIRAENI OVER HARHA RIVERDocument9 pagesHydrology Report of Construction of HL RCC Bridge at MANGALPUR TO FARSHANI GHIRAENI OVER HARHA RIVERV P GUPTANo ratings yet
- DECEMBER 9th Natural DisastersDocument1 pageDECEMBER 9th Natural DisasterscudaNo ratings yet
- Competence 8Document8 pagesCompetence 8Mabel Albares100% (1)
- Air Wells, Dew Ponds and Fog Fences - Methods To Condense Atmospheric HumidityDocument42 pagesAir Wells, Dew Ponds and Fog Fences - Methods To Condense Atmospheric HumidityJason BetzNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2090997718300099 Main - CompressedDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S2090997718300099 Main - CompressedAsep IrawanNo ratings yet
- Dewpoint and Vapor Pressure Deficit EquationsDocument2 pagesDewpoint and Vapor Pressure Deficit EquationssureshNo ratings yet
- Alemu DiribssaDocument104 pagesAlemu Diribssakedir100% (1)
- GEO 110 NotesDocument9 pagesGEO 110 NotesaliNo ratings yet
- Steart BookletDocument20 pagesSteart BookletWessex ArchaeologyNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text About Global WarmingDocument4 pagesExplanation Text About Global WarmingFajar Prasetya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 14 Feb 2022 PDFDocument5 pagesAdobe Scan 14 Feb 2022 PDFmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Shangai Houton ParkDocument15 pagesShangai Houton ParkHari HaranNo ratings yet
- Lagos (Nigeria) Ooding and in Uence of Urban PlanningDocument14 pagesLagos (Nigeria) Ooding and in Uence of Urban PlanningOjolowo OlamideNo ratings yet
- FloodsDocument14 pagesFloodsImogen AdamsNo ratings yet
- Green Infrastructure Retrofit As An Alternative To Conventional Stormwater ManagementDocument32 pagesGreen Infrastructure Retrofit As An Alternative To Conventional Stormwater ManagementPranav MishraNo ratings yet
- CZMP Fisheries Min 1Document291 pagesCZMP Fisheries Min 1tamilNo ratings yet
- The Changing Face of The Ethiopian Rift Lakes and Their EnvironsDocument18 pagesThe Changing Face of The Ethiopian Rift Lakes and Their EnvironsTariku GemedaNo ratings yet
- Wetland Conservation and LawDocument15 pagesWetland Conservation and LawHimangshu Sonowal0% (1)
- Geochemistry of Limestones Deposited in Various Plate Tectonic SettingsDocument22 pagesGeochemistry of Limestones Deposited in Various Plate Tectonic SettingsAlberto Ra VitalaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Social Issues and The Environment From Unsustainable To Sustainable DevelopmentDocument37 pagesUnit-Iv Social Issues and The Environment From Unsustainable To Sustainable DevelopmentarumugamNo ratings yet