Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adaptive Design On Crank and Slotted Lever Mechanism
Adaptive Design On Crank and Slotted Lever Mechanism
Uploaded by
pranav razdanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adaptive Design On Crank and Slotted Lever Mechanism
Adaptive Design On Crank and Slotted Lever Mechanism
Uploaded by
pranav razdanCopyright:
Available Formats
ADBU-Journal of Engineering Technology
Adaptive design on crank and slotted lever mechanism
Arup JyotiChutia,
Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tezpur University
Napaam - 784028, Assam. India.
aruprhino@gmail.com
Abstract:One of the famous mechanisms for quick return motion to obtain reciprocating
motion is crank and slotted lever mechanism. In this paper an adaptive design on this
mechanism is briefly discussed. Certain changes have been made to the crank and the slotted
lever mechanism to incorporate the class 1 lever instead of class 3 lever used in the mechanism.
Moreover a possible approach for obtaining more than one reciprocating motion simultaneously
from the same mechanism is discussed.
Keywords: Link, mechanism, lever, slotted bar.
1.Introduction In this mechanism, the slider 1 reciprocates in
oscillating slotted lever 4 and link 2 rotates whole
link 3 is fixed. Another link 5 (PR) connects the
A quick return mechanism is a mechanism that converts rotary
end of the link 4 to ram. The latter carries the
motion into reciprocating motion at different rate for its two cutting tool which reciprocates perpendicular to the
strokes i.e. working & idle stroke. Since the time taken for fixed link3.
return stroke is less than its working stroke, it is called as quick
return mechanism. It is widely use in machine tool such as The ram and hence the cutting tool reverses its
shaping machines, power-driven saws etc. In this mechanism direction when the link 2 is perpendicular to link 4.
class 3 lever is used which is basically a distance multiplier. The cutting stroke takes place during angle β
whereas return stroke i.e. Idle stroke takes place
The main purpose of this paper is to use class- 1 lever in the during angle α which is equal to 360-β.
mechanism instead of class- 3 levers and to discuss few other Thus
possible arrangements in the design so obtained.
1.1Crank and slotted lever mechanism:
The lever mechanism
A lever is one of the simplest mechanical devices.
A lever consists of a beam or rod. It is pivoted to a
part called the fulcrum. In crank and slotted lever
mechanism “class 3- lever” i.e. the effort is placed
between the load and the fulcrum is used.
Fig2. The lever mechanism
Fig1. Crank and slotted lever mechanism
Both first and second class levers are usually force
multiplier whereas third one is the distance multiplier.
AJET, ISSN: 2348-7305, Volume 4(1), 2016 215-1
ADBU-Journal of Engineering Technology
2. Description of the modified mechanism
In this modified mechanism the slider (link 1), crank (link 2)
and fixed support (link 3) all are similar to earlier design
except the slotted bar (link 4). Here slotted bar is supported
by a hinge joint at the fulcrum (A) as shown in the figure.
The extended part of the slotted bar on the other side of
fulcrum from the crank and the slider is connected to link
5(PR) which transmits the motion from link 4 to the ram.
Fig4: Angular relationship diagram
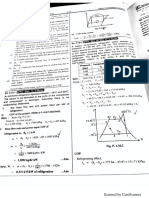
2.2Forces and angular relationship
Let ϴ1 = inclination of the slotted bar with the vertical
γ = inclination of the crank with the vertical
From ΔOBC,OBC=BCO
=ϴ2 (since, OC=OB= crank length, r)
Also, γ = 2ϴ2 (from triangle’s law)
Now from ΔCBE, B=90 (angle in a semicircle)
CB=CEcosϴ2
And CD=CBcosϴ2
=CEcos2ϴ2
Now, tanϴ1= , BD=CDtanϴ2
=
Fig3: Modified mechanism = =
ϴ1=tan-1( )
2.1Length of stroke and time ratio
Let OAB1=Inclination of the slotted bar with the
vertical=90-α/2 Let F1= effort applied
OAB1=P2AM(opposite angles) Now, length of F2= force developed at the junction of link 4 and5 L 1= effort
stroke=R1R2=P1P2=2P2M length from the fulcrum
=2AP2Sin(90-α/2) L2= distance of the developed force F2 from the fulcrum
By applying moment equation at the fulcrum, A We have,
𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑢𝑡𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑠𝑡𝑟𝑜𝑘𝑒 𝛽 F1L1=F2L2
Time Ratio= 𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑒𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛 𝑠𝑡𝑟𝑜𝑘𝑒
=𝛼
AJET, ISSN: 2348-7305, Volume 4(1), 2016 215-2
ADBU-Journal of Engineering Technology
Moreover, automatic class 1 lever is possible which might be
F2= applied to construct automatic scissor.
From Fig applying sine law to ΔABO, = In the modified mechanism, if two slotted levers are included
inclined to each other at different angle then two motions would be
obtained from the same mechanism simultaneously.
F2= Fig: Two slotted bar inclined to each other using in the same
mechanism to obtain two reciprocating motion simultaneously.
3.Comparison with the slotted lever mechanism
Basic difference lies in the arrangement of slotted bar in between
the two mechanisms. Developed force F2 is always less than the
effort F1 in the crank and slotted lever mechanism whereas F2
may increase or decrease in the modified design as
preconstruction.
3.1. Special design of the slotted bar
In the modified mechanism, if we design the slotted bar in such
a way that the junction of link 4 and 5(PR) can be made at
various position as shown in the fig. then the design will be able
to cope up with variation of developed force F2 with the stroke
length (P1P2) within certain limit.
Fig6. Two slotted bar
5.Discussion
In this paper, configuration of a modified design for the quick
return mechanism is briefly introduced. This modified mechanism
is a good alternative. When specially modified slotted bar is used,
this mechanism gives the flexibility of variation of developed force
Fig5: Special design of the slotted bar showing various position F2 with the stroke length within certain limit. Using of class-1 lever
of the junction between link 4 and link5 (PR). in the mechanism is helpful to leverage the effort (F1). Moreover
proper construction would give the freedom for more than one
motion simultaneously from the same mechanism which would
increase productivity rate.
4.Other possible arrangement
AJET, ISSN: 2348-7305, Volume 4(1), 2016 215-3
ADBU-Journal of Engineering Technology
Acknowledgment
I express my sincere gratitude to all the professors,
friends and my dear brothers & sisters of our university
for theirs inspiring words and to my dear parents for their
constant and instant support
References
[1] Wen-Hsiang Hsieh and Chia-Heng Tsai, ―A Study
On A Novel Quick Return Mechanism‖, Vol. No. 08-
CSME-13, E.I.C. Accession 3051, September 2009.
[2] Matt Campbell Stephen S. Nestinger, Department of
Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering, University
of California Davis, CA 95616,―ComputerAided
Design and Analysis Of the Whitworth Quick Return
Mechanism‖.
[3] Dr. Harry H. Cheng, ―Computer-Aided Mechanism
Design‖ in journal of Mechanical Engineering
Science, volume 220, March 14, 2004
[4] Ron P. Podhorodeski, Scott B. Nokleby and Jonathan
D. Wittchen, ―Quick-return mechanism design and
analysis‖, Robotics and Mechanisms Laboratory,
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of
Victoria, PO Box 3055, Victoria, British Columbia,
Canada
Author detail
Arup JyotiChutia, currently a student of 6th semester of
B.Tech in Mechanical Engineering in Tezpur University,
India. He has completed his H.S school from JNV
Tinsukia, Assam.
AJET, ISSN: 2348-7305, Volume 4(1), 2016 215-4
You might also like
- Very Advanced Maternal Age, TOG-2021Document10 pagesVery Advanced Maternal Age, TOG-2021saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- Modelado Rotary Pendulum Workbook InstructorDocument60 pagesModelado Rotary Pendulum Workbook Instructorsolid34100% (1)
- PHY133 Angular MomentumDocument6 pagesPHY133 Angular MomentumAngel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Can Crusher MechanismDocument23 pagesCan Crusher Mechanismsaqlain05No ratings yet
- Woytowich R.calculation of Prope - dec.1979.JSRDocument7 pagesWoytowich R.calculation of Prope - dec.1979.JSRJohn KokarakisNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE VIIDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in TLE VIIJose Nilo Pastorall70% (10)
- Kasatha 5eDocument1 pageKasatha 5eBryce St. LouisNo ratings yet
- Kinematics-Of-Machinery 2 Mark QuestionsDocument33 pagesKinematics-Of-Machinery 2 Mark QuestionsNishanth ShannmugamNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machines (Me1252) UNIT-1 Simple Mechanism. Two MarksDocument32 pagesKinematics of Machines (Me1252) UNIT-1 Simple Mechanism. Two MarksRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Kinematics OF Machinery: Adithya Institute of TechnologyDocument34 pagesKinematics OF Machinery: Adithya Institute of TechnologybalajimetturNo ratings yet
- TOM Lab ManualDocument47 pagesTOM Lab Manualsrihari raoNo ratings yet
- Application of Intelligent Controller in A Ball and Beam Control SystemDocument16 pagesApplication of Intelligent Controller in A Ball and Beam Control SystemjerrythaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines (314205) : Design, Fabrication and Analysis of Dual Can CrusherDocument10 pagesMechanics of Machines (314205) : Design, Fabrication and Analysis of Dual Can Crushersaqlain05No ratings yet
- Lab5a Fa10Document4 pagesLab5a Fa10alexlenevez_12130% (1)
- Me 6401 Kom - Uti Ans KeyDocument11 pagesMe 6401 Kom - Uti Ans Keylogeshboy007100% (1)
- Classification of CamsDocument18 pagesClassification of CamsabasNo ratings yet
- Two Speed Epicycle Gear TrainsDocument7 pagesTwo Speed Epicycle Gear Trainsxmtqnkn8vjNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MechanismsDocument82 pagesKinematics of MechanismsviahulNo ratings yet
- Quick Return MechanismDocument5 pagesQuick Return MechanismAarya ParadkarNo ratings yet
- Ch09 SSM 070904Document26 pagesCh09 SSM 070904VinhTranNo ratings yet
- Quick Return MechanismsDocument2 pagesQuick Return MechanismsAbhinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery (AU 402) : Types of Kinematic Chain With Four Lower PairsDocument11 pagesKinematics of Machinery (AU 402) : Types of Kinematic Chain With Four Lower PairsJanardhanaNo ratings yet
- Use of Connectors in ABAQUS/Explicit To Simulate Dynamic Motion Along A Curved PathDocument15 pagesUse of Connectors in ABAQUS/Explicit To Simulate Dynamic Motion Along A Curved PathTina LoweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gear Trains.Document11 pagesChapter 2 Gear Trains.sbusisoNo ratings yet
- Shear and Moment DiagramDocument10 pagesShear and Moment Diagramkim adrian bangayanNo ratings yet
- SKshah Unit 1 Part 2Document18 pagesSKshah Unit 1 Part 2Neelesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Research On Kinematics of 3-Dof Connecting Rod ManDocument10 pagesResearch On Kinematics of 3-Dof Connecting Rod Manpad abtNo ratings yet
- Mechanism 1Document82 pagesMechanism 1papulimech100% (3)
- Report of Mechanics of Machines 1Document12 pagesReport of Mechanics of Machines 1muhammaduzairNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual MEC229: Theory of Machines LaboratoryDocument51 pagesLaboratory Manual MEC229: Theory of Machines Laboratoryhemanth singhNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Control of A Furuta Rotary Inverted PendulumDocument27 pagesNonlinear Control of A Furuta Rotary Inverted PendulumdiemtrieuNo ratings yet
- Inversion of The MechanismDocument5 pagesInversion of The MechanismRanjit Rajendran100% (1)
- 2 DOF Ball Balancer - Workbook (Instructor)Document32 pages2 DOF Ball Balancer - Workbook (Instructor)Raaj LavaNo ratings yet
- 2 DOF Ball Balancer - Workbook (Instructor) PDFDocument32 pages2 DOF Ball Balancer - Workbook (Instructor) PDFRaaj LavaNo ratings yet
- Shaft PulleyDocument12 pagesShaft PulleykeirthNo ratings yet
- DOM-I-Force Analysis PDFDocument26 pagesDOM-I-Force Analysis PDFNaveenKrishNo ratings yet
- physicsHL IADocument15 pagesphysicsHL IAAziz Samet ZorluNo ratings yet
- Static Mechanical System Section1: Stress, Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument17 pagesStatic Mechanical System Section1: Stress, Shear Force and Bending MomentHadhi Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Shear and Moment Diagram - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesShear and Moment Diagram - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPrabhat MishraNo ratings yet
- SRV02-Series Ball & Beam: Student HandoutDocument13 pagesSRV02-Series Ball & Beam: Student HandoutKeli KeyNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2011Document5 pagesZhang 2011Sajad Sadeghi MoghadamNo ratings yet
- Trajectory - Tracking - of - A - Pneumatically - Driven - PDocument6 pagesTrajectory - Tracking - of - A - Pneumatically - Driven - PQuyết Nguyễn CôngNo ratings yet
- Solved Questions MTM PDFDocument12 pagesSolved Questions MTM PDFRajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- 01 Engine Force AnalysisDocument27 pages01 Engine Force AnalysisSunny DesharNo ratings yet
- Robotics: Kinematics, Dynamics and Motion Control Module - 5 VITDocument60 pagesRobotics: Kinematics, Dynamics and Motion Control Module - 5 VITHarisankar R N R 21BRS1524No ratings yet
- 10ROTATIONAL Equilibrium and Non-Equilibrium (P211) Rev2.2Document7 pages10ROTATIONAL Equilibrium and Non-Equilibrium (P211) Rev2.2Shriya SaiNo ratings yet
- Shear and Moment Diagram - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesShear and Moment Diagram - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediazidaaanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Practical File: Prof. R. A. KhanDocument33 pagesTheory of Machines Practical File: Prof. R. A. KhanBarbie JooNo ratings yet
- A Slider-Crank Experiment To Determine The Action of Static ForcesDocument10 pagesA Slider-Crank Experiment To Determine The Action of Static ForcesRazali Yusoff100% (1)
- Nonlinear Analysis and Control of A Reaction-Wheel-Based 3-D Inverted PendulumDocument12 pagesNonlinear Analysis and Control of A Reaction-Wheel-Based 3-D Inverted PendulumVictor PassosNo ratings yet
- Crank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Document9 pagesCrank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Vipin YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab3a 2019Document10 pagesLab3a 2019Olivia PowerNo ratings yet
- Tme 11303 CHP1Document26 pagesTme 11303 CHP1Tuisyen Al FatehNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document11 pagesClass 3Manjula sNo ratings yet
- Pendulo Doble MotorDocument10 pagesPendulo Doble Motorjuan alarconNo ratings yet
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlFrom EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Complex Systems: Application to Aeronautical DynamicsFrom EverandModeling of Complex Systems: Application to Aeronautical DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Openfaom Turbo Compressible Turbulent SolverDocument20 pagesOpenfaom Turbo Compressible Turbulent Solverpranav razdanNo ratings yet
- Star CD UserDocument406 pagesStar CD Userpranav razdanNo ratings yet
- Ding 2014Document4 pagesDing 2014pranav razdanNo ratings yet
- 08521629Document5 pages08521629pranav razdanNo ratings yet
- VCC NumericalDocument13 pagesVCC Numericalpranav razdanNo ratings yet
- Notes On RacDocument25 pagesNotes On Racpranav razdanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Assessment of Intelligence in Clinical PsychologyDocument1 pageImportance of Assessment of Intelligence in Clinical PsychologyKimberly AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Workbook For Developmental Communications 1 UNIT 6Document14 pagesWorkbook For Developmental Communications 1 UNIT 6soldadodeslealNo ratings yet
- Tve 8 Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument11 pagesTve 8 Shielded Metal Arc WeldingJOHN ALFRED MANANGGITNo ratings yet
- Steamshovel Press Issue 04Document60 pagesSteamshovel Press Issue 04liondog1No ratings yet
- Ip Talks Presentation - Keaune ReevesDocument2 pagesIp Talks Presentation - Keaune Reeveskarina talledoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge of Cervical Cancer and Acceptance of HPVDocument6 pagesKnowledge of Cervical Cancer and Acceptance of HPVALIF FITRI BIN MOHD JASMINo ratings yet
- Viber For Business - Advertising Solutions-2Document24 pagesViber For Business - Advertising Solutions-2htetarkar022023No ratings yet
- Angela SolikovaDocument10 pagesAngela SolikovaGirisha PathakNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Lessons From The Bhagavad GitaDocument13 pagesEntrepreneurial Lessons From The Bhagavad GitaMahima FamousNo ratings yet
- Form 1.3 Summary of Current CompetenciesDocument3 pagesForm 1.3 Summary of Current CompetenciesJinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal PlantsDocument36 pagesMedicinal PlantsGuardian AngelsNo ratings yet
- Persons With Disabilities: Key PointsDocument8 pagesPersons With Disabilities: Key PointsShane ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Bowthorpe News May 2017Document36 pagesBowthorpe News May 2017Anonymous AySEIwycNo ratings yet
- Sony Bravia CatalogueDocument25 pagesSony Bravia CataloguerealindiapropertyNo ratings yet
- Services Provided by Merchant BanksDocument4 pagesServices Provided by Merchant BanksParul PrasadNo ratings yet
- LoB Player Guide Pyram KingDocument15 pagesLoB Player Guide Pyram KingRonaldo SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Brigada Solicitation and InvitationDocument3 pagesBrigada Solicitation and Invitationguendolyn templadoNo ratings yet
- ASD PEDS Administration GuidelinesDocument5 pagesASD PEDS Administration GuidelinesInes Arias PazNo ratings yet
- Size & Estimation of DWDocument12 pagesSize & Estimation of DWGiuseppe GiuseppeNo ratings yet
- 01 Boothe V Director of PatentsDocument3 pages01 Boothe V Director of PatentsPio Guieb AguilarNo ratings yet
- Notice: Agency Information Collection Activities Proposals, Submissions, and ApprovalsDocument2 pagesNotice: Agency Information Collection Activities Proposals, Submissions, and ApprovalsJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Schwarze Schlichte Salesfolder enDocument6 pagesSchwarze Schlichte Salesfolder en姚晓卫No ratings yet
- Laporan Minggu 1 & 2 B.Inggris Nur Kholis-29-2AI1Document6 pagesLaporan Minggu 1 & 2 B.Inggris Nur Kholis-29-2AI1Kawek KagoelNo ratings yet
- Light Sport Aircraft: Standard Terminology ForDocument6 pagesLight Sport Aircraft: Standard Terminology ForAhmad Zubair RasulyNo ratings yet
- Dungeoncraft Wild Beyond The Witchlight v1.1Document9 pagesDungeoncraft Wild Beyond The Witchlight v1.1RalphNo ratings yet
- Pediatric OrthopaedicDocument66 pagesPediatric OrthopaedicDhito RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Kakhisong Church A2-ModelDocument1 pageKakhisong Church A2-ModelanzaniNo ratings yet