Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thesis Pa
Thesis Pa
Uploaded by
Joshua OliverOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thesis Pa
Thesis Pa
Uploaded by
Joshua OliverCopyright:
Available Formats
Clerigo, Joshua Oliver P.
ME-5105
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF COIL SPRING IN VEHICLES USING FINITE ELEMENTS
METHOD
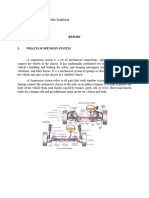
Suspension system is the most important component in automobile that is responsible
for smoothing out the ride and keeping the car in control. Specifically, it maximizes the
friction between the tires and the road to provide steering stability and good handling,
and also provides comfort for passengers to limit the impact of particular road conditions
to the car, but also to the passengers riding inside. The suspension system consists
of many parts like axles, shock absorber, springs, ball joints and arm rods.
The spring is flexible part of the system and it can be defined as the elastic body, which
deforms when it subjected to load and returns to its original shape when the load
diminishes. Commercial automobiles have coil spring in the front and leaf spring
in the rear. Coil spring is manufactured from the particular wire, which is treated
with heat to produce the desired shape. The ability of spring to withstand the load
depends on its shape, the total diameter of spring and the diameter of the wire. The
failure of the spring may occur because of the poor properties of materials of spring in
addition to high cyclic fatigue.
The simulation of spring is will be carried out by using Solid works 2018 with specific
dimensions and analysis it with finite element analyzer ANSYS 14. Five materials will be
selected to simulate. The deformation, strain, stress and shear stress will be obtained
numerically under various values of load.
This study aims to determine the best material for coil spring.
Arga, Paul Christian A.
ME-5105
Design and Analysis of Magnetic Breaking System
Magnetic braking works because of induced currents and Lenz's law. If you attach a
metal plate to the end of a pendulum and let it swing, its speed will greatly decrease
when it passes between the poles of a magnet.
When the plate enters the magnetic field, an electric field is induced in metal and
circulating eddy currents are generated. These currents act to oppose the change in flux
through the plate, in accordance with Lenz's Law.
The currents in turn heat the plate, thereby reducing its kinetic energy. The practical
uses for magnetic braking are numerous and commonly found in industry today. This
phenomenon can be used to damp unwanted nutations in satellites, to eliminate
vibrations in spacecrafts, and to separate nonmagnetic metals from solid waste.
The subject of magnetic braking is rarely discussed in introductory physics texts. To
calculate the magnetic drag force on a moving metal object is generally difficult and
implies solving Maxwell's equations in time-dependent situation.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Sample ProblemDocument23 pagesSample ProblemJoshua Oliver67% (9)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Sample ProblemDocument19 pagesSample ProblemJoshua Oliver100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Volkswagen Polo-Mk4 Workshop Manual (Polo Mk4)Document1,579 pagesVolkswagen Polo-Mk4 Workshop Manual (Polo Mk4)Adrian Schembri100% (1)
- 2009 Ranger RZR 170 Service ManualDocument187 pages2009 Ranger RZR 170 Service ManualBrian CookNo ratings yet
- 2014-15 Ranger RZR-1000 XP XP4 Service ManualDocument539 pages2014-15 Ranger RZR-1000 XP XP4 Service ManualBrian Cook100% (1)
- Steam Power Plants EnglishDocument1 pageSteam Power Plants EnglishJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Midterms Fluid MechDocument42 pagesMidterms Fluid MechJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Self Evaluation FI 2 2019 2020 1Document2 pagesSelf Evaluation FI 2 2019 2020 1Joshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Advantage: Disadvantage:: Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydro StationsDocument3 pagesAdvantage: Disadvantage:: Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydro StationsJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- ECE For Schoology 5b840106d4169Document4 pagesECE For Schoology 5b840106d4169Joshua OliverNo ratings yet
- How To Test CapacitorDocument4 pagesHow To Test CapacitorJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Sec Endorsements September2016 PDFDocument357 pagesSec Endorsements September2016 PDFJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Saf Trailer Air Suspensions: Selection GuideDocument24 pagesSaf Trailer Air Suspensions: Selection GuideCitlally juarezNo ratings yet
- 1520-Article Text-5847-1-10-20120207Document8 pages1520-Article Text-5847-1-10-20120207Junaid YusfzaiNo ratings yet
- Air Lift Axle 001Document28 pagesAir Lift Axle 001J.T. NoneyaNo ratings yet
- LandroverDocument29 pagesLandroverOnur KulaNo ratings yet
- SDLG - LG918 Brochure Single PagesDocument4 pagesSDLG - LG918 Brochure Single Pagesjonathan tbgNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Elements of Machine Design Micro Project' With YouDocument10 pagesI Am Sharing 'Elements of Machine Design Micro Project' With YouUttareshwar Mohalkar100% (1)
- Tempo Ultra Isotronic - Edp - enDocument31 pagesTempo Ultra Isotronic - Edp - enPeter ErženNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: Limited Edition Lykan, 7 Units WorldwideDocument1 pageTechnical Data: Limited Edition Lykan, 7 Units WorldwideAllen HardingNo ratings yet
- Sae Vehicle Dynamics Technology Collection Papers ListeDocument84 pagesSae Vehicle Dynamics Technology Collection Papers ListearstjunkNo ratings yet
- Tata 1109 G LPT BrochureDocument2 pagesTata 1109 G LPT BrochureVishal Karad100% (1)
- AlforoDocument42 pagesAlforoKRISTIAN REY ALFORO (YanYan)No ratings yet
- Assignment 4 SuspensionDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 SuspensionAdam LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Y. B. Patil Polytechnic Akurdi, Pune: - Introduction To AutomobilesDocument15 pagesY. B. Patil Polytechnic Akurdi, Pune: - Introduction To AutomobilesNilesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Intern SummerDocument25 pagesIntern SummerPrakash GNo ratings yet
- C-3271 InstDocument21 pagesC-3271 InstRSS RSSNo ratings yet
- Eh1100 3Document7 pagesEh1100 3Alfonso BerRamNo ratings yet
- bc900xl Brush Chipper Spec Sheet Updated Sep 2021Document2 pagesbc900xl Brush Chipper Spec Sheet Updated Sep 2021SavindaNo ratings yet
- 4X2 10 - 12cubic Dumper TruckDocument1 page4X2 10 - 12cubic Dumper TruckTnek OnairdaNo ratings yet
- Whiteline Tuning Guide - WEB-DOWNLOADDocument27 pagesWhiteline Tuning Guide - WEB-DOWNLOADshuttleworthandsonsNo ratings yet
- Aprilia Tuono 1000 Wiring Diagram 2005 OnwardsDocument120 pagesAprilia Tuono 1000 Wiring Diagram 2005 Onwardsmylitter5391No ratings yet
- Raize BrochureDocument11 pagesRaize BrochuremohithkotianNo ratings yet
- AFV Modeller - 2015 09-10Document68 pagesAFV Modeller - 2015 09-10Marino Cordetti100% (1)
- MP180E24W: Technical DescriptionsDocument14 pagesMP180E24W: Technical DescriptionsBroCactusNo ratings yet
- HCR1200EDII E1109 F3 - JVDocument8 pagesHCR1200EDII E1109 F3 - JVJorge Velarde LatorreNo ratings yet
- The Truck Trailer Suspension Axles Failure AnalysiDocument8 pagesThe Truck Trailer Suspension Axles Failure AnalysiEnqua QuaNo ratings yet
- Limitations To Suspension Performance in A Two-Degree-Of-Freedom Car Active SuspensionDocument4 pagesLimitations To Suspension Performance in A Two-Degree-Of-Freedom Car Active SuspensionÉdgar StaveNo ratings yet
- Ashok Leyland 4220 BrochureDocument2 pagesAshok Leyland 4220 BrochureAmit AcharyaNo ratings yet