Professional Documents
Culture Documents
.K Uh, I
.K Uh, I
Uploaded by
Rahul AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hesi Psych Study GuideDocument16 pagesHesi Psych Study GuideR100% (17)
- Paediatrics Cardiology MCQDocument9 pagesPaediatrics Cardiology MCQJOYANTA ROY100% (2)
- PCOS Diet: The Complete Guide to Fight PCOS, Prevent Diabetes, Lose Weight and Increase FertilityFrom EverandPCOS Diet: The Complete Guide to Fight PCOS, Prevent Diabetes, Lose Weight and Increase FertilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- PCOS No More - Take Control of PCOS Symptoms & Treatments - A Holistic System of Lifestyle Changes, Diet, & Exercises to Beat Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Naturally & Permanently. PCOS Recipes Included.From EverandPCOS No More - Take Control of PCOS Symptoms & Treatments - A Holistic System of Lifestyle Changes, Diet, & Exercises to Beat Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Naturally & Permanently. PCOS Recipes Included.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Document10 pagesPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Juliet Amondi100% (2)
- Farm Management - Robotic Farm Management - LelyDocument70 pagesFarm Management - Robotic Farm Management - LelyHo Duc ThamNo ratings yet
- "Cure Tooth Decay" - Photographic Proof!Document12 pages"Cure Tooth Decay" - Photographic Proof!Chef Jem100% (1)
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome 2Document22 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome 2Michelle Panlilio0% (1)
- Dark Green Vintage Minimalist Aesthetic Newspaper Fashion Marketing Ad Instagram StoryDocument4 pagesDark Green Vintage Minimalist Aesthetic Newspaper Fashion Marketing Ad Instagram StoryJana Emery SumagangNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentDocument19 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentGrace Ann Rodriguez SanDiegoNo ratings yet
- PCOS Booklet Final Low Quality Aster IVFDocument8 pagesPCOS Booklet Final Low Quality Aster IVFasterivfNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)Document8 pagesAssignment: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)tehseenullahNo ratings yet
- 2019521625048 - Rittik Paul PCOSDocument5 pages2019521625048 - Rittik Paul PCOSpaulrittik2000No ratings yet
- Pi Pcos Update-2022 230717 221503Document7 pagesPi Pcos Update-2022 230717 221503PeterNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - Johns Hopkins MedicineDocument5 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - Johns Hopkins MedicineWINDA NURHASANAHNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument5 pagesPolycystic Ovary SyndromeAle W.S.No ratings yet
- Pcos ReportDocument49 pagesPcos ReportSneha kohliNo ratings yet
- PCOSDocument3 pagesPCOSpravallikakvNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : Made by Hamza Shawal 60Document29 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : Made by Hamza Shawal 60Muhammad HamadNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : February 2020Document5 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : February 2020Lia MeivianeNo ratings yet
- PcosDocument6 pagesPcosDana MradNo ratings yet
- PcosDocument9 pagesPcosMonomay HalderNo ratings yet
- Polycystric Ovary Syndrome FilesDocument7 pagesPolycystric Ovary Syndrome FilesElla Jean B. LunzagaNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Disorder AwarenessDocument6 pagesHormonal Disorder AwarenessRasell Fhaye A. RazonNo ratings yet
- PCOS Ebook v1.18Document22 pagesPCOS Ebook v1.18க100% (2)
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : by Aleandro Dizon Bn4ADocument12 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : by Aleandro Dizon Bn4AAleandro DizonNo ratings yet
- How To Get Pregnant With PcosDocument20 pagesHow To Get Pregnant With PcosConfused parentNo ratings yet
- Polycystic-Ovarian-Disease pptDocument15 pagesPolycystic-Ovarian-Disease pptjhapankaj5234No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Under Supervision ofDocument7 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome: Under Supervision ofHend HamedNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)Document6 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)saleemut3No ratings yet
- What Causes Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument8 pagesWhat Causes Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Clinical Picture of pcosWPS OfficeDocument11 pagesClinical Picture of pcosWPS OfficeEsraa SalemNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Johns Hopkins MedicineDocument1 pagePolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Johns Hopkins MedicinehercimacielNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Vidhya-4Document16 pagesBiology Project Vidhya-4suriya251004No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument2 pagesPolycystic Ovary SyndromeLalee BelarminoNo ratings yet
- Pcos - Clinical Case DiscussionDocument4 pagesPcos - Clinical Case Discussionreham macadatoNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document5 pagesLec 3mudassir qazalbashNo ratings yet
- Kenneth NegsDocument2 pagesKenneth NegsGwen Stefani DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- Acog Pcos PDFDocument3 pagesAcog Pcos PDFJoanne BlancoNo ratings yet
- Enlarged Polycystic OvariesDocument4 pagesEnlarged Polycystic OvariesKaly RieNo ratings yet
- What Causes Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) ?: Infertility Menstrual IrregularitiesDocument8 pagesWhat Causes Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) ?: Infertility Menstrual IrregularitiesdnllkzaNo ratings yet
- PCODDocument16 pagesPCODfitfemme12126No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome PCOSDocument15 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome PCOSdrug123addict25No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument17 pagesPolycystic Ovary SyndromeramsaybajjuNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (Pcos) : Name: Adelita Dwi Aprilia Name Atom: EndocrinologyDocument2 pagesPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (Pcos) : Name: Adelita Dwi Aprilia Name Atom: EndocrinologyAdelita Dwi ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Hyperandrogenism: Arrest Occurs When The Granulosa Cells of The Ovaries Normally Begin To ProduceDocument7 pagesHyperandrogenism: Arrest Occurs When The Granulosa Cells of The Ovaries Normally Begin To ProduceNathan JeffreyNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Factsheet: Key PointsDocument3 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Factsheet: Key PointsrhaineNo ratings yet
- B. ProlactinomaDocument3 pagesB. ProlactinomaSheena CullaNo ratings yet
- Pcod Natural TreatmentDocument4 pagesPcod Natural Treatmenttusharphale100% (1)
- Introduction PCOSDocument14 pagesIntroduction PCOSalex.avenko1030No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)Document8 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)Danijela GagovicNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document15 pagesDocument 5SamNo ratings yet
- Research EssayDocument3 pagesResearch Essayapi-510714949No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Understanding Ovaries and OvulationDocument5 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome: Understanding Ovaries and OvulationBhavik ShahNo ratings yet
- How To Reverse Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument24 pagesHow To Reverse Polycystic Ovary SyndromeJudi Ann MagsacayNo ratings yet
- Final Research Essay PcosDocument13 pagesFinal Research Essay Pcosapi-510714949No ratings yet
- And Getting Pregnant: A Beginner'S Guide and Patient Stories of HopeDocument23 pagesAnd Getting Pregnant: A Beginner'S Guide and Patient Stories of HopehaurakhansaNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - Reproductive and Metabolic Aspects - Sundhed - DKDocument8 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - Reproductive and Metabolic Aspects - Sundhed - DKPavel BerlinschiNo ratings yet
- Do I Have PCOS? Understanding the Cause and Reversing Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)From EverandDo I Have PCOS? Understanding the Cause and Reversing Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)No ratings yet
- How to Beat PCOS Naturally & Regain a Healthy & Fertile Life Now ( A Simple Guide on PCOS Diet & Exercises to Conquer PCOS Permanently Today)From EverandHow to Beat PCOS Naturally & Regain a Healthy & Fertile Life Now ( A Simple Guide on PCOS Diet & Exercises to Conquer PCOS Permanently Today)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Pcod and Pcos DriistiDocument2 pagesPcod and Pcos DriistiKirti MathurNo ratings yet
- Power Over Pcos EbookDocument160 pagesPower Over Pcos EbookIra Ayu Lestari100% (2)
- Name Class Section Subject: Sohon Sen XI B BiologyDocument36 pagesName Class Section Subject: Sohon Sen XI B BiologySohon SenNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument8 pagesPolycystic Ovary SyndromeTahir BilalNo ratings yet
- Finding Answers: Handsmart: Breaking Down Barriers Forged by FireDocument6 pagesFinding Answers: Handsmart: Breaking Down Barriers Forged by FireRoger Goodledy100% (1)
- Research Article Response of Black Nightshade To Different Cropping Systems and The Effect On Physiological Parameters and Mineral CompositionDocument11 pagesResearch Article Response of Black Nightshade To Different Cropping Systems and The Effect On Physiological Parameters and Mineral CompositionfooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For GDMDocument7 pagesDrug Study For GDMFuture RNNo ratings yet
- AmgenDocument22 pagesAmgenleonard1655012No ratings yet
- Asthma PudDocument7 pagesAsthma PudChristine TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region III Schools Division Office of Pampanga San Pedro, San Simon, PampangaDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region III Schools Division Office of Pampanga San Pedro, San Simon, PampangaMia NuguidNo ratings yet
- IVIG RateDocument2 pagesIVIG RatelydiasusantiNo ratings yet
- Klinefelter SyndromeDocument3 pagesKlinefelter SyndromeAnonymous stZJzmPNo ratings yet
- A Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDocument3 pagesA Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument65 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisSiti AminahNo ratings yet
- Organic Manures - 17.12.12Document59 pagesOrganic Manures - 17.12.12Ananda Preethi100% (1)
- Hubungan Temuan MRI Dengan Klinis Nyeri Pasien Herniasi Nukleus Pulposus LumbalDocument13 pagesHubungan Temuan MRI Dengan Klinis Nyeri Pasien Herniasi Nukleus Pulposus LumbalHendrawanDianAgungWicaksanaNo ratings yet
- Biogenic Amines by HPLCDocument7 pagesBiogenic Amines by HPLCNeidys SanchezNo ratings yet
- PsychosisSelfCareJune22 V2DDocument115 pagesPsychosisSelfCareJune22 V2DLindseyRae Parker100% (1)
- The Bourne Identity-Psychological DiddordersDocument23 pagesThe Bourne Identity-Psychological DiddordersSahil NaikNo ratings yet
- 08 DN 005 BA Int OkDocument64 pages08 DN 005 BA Int OkvbogachevNo ratings yet
- NCP-risk For BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP-risk For BleedingAce Dioso Tubasco100% (2)
- (Download PDF) A Specter Haunting Europe The Myth of Judeo Bolshevism Paul Hanebrink Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) A Specter Haunting Europe The Myth of Judeo Bolshevism Paul Hanebrink Online Ebook All Chapter PDFray.groce871100% (15)
- Rs. Akademis Jaury Jusuf Putera: Data Kamar Inap PasienDocument3 pagesRs. Akademis Jaury Jusuf Putera: Data Kamar Inap PasienNs Ilham ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Reportorial 2Document36 pagesReportorial 2Alistair Jude C. BacaocoNo ratings yet
- Project Soaprise ScriptDocument2 pagesProject Soaprise ScriptGarima DixitNo ratings yet
- MSDS Clorox High Efficiency Bleach Cleaner 0607Document1 pageMSDS Clorox High Efficiency Bleach Cleaner 0607Henry Rutledge100% (1)
- 5 6312240703955009631Document28 pages5 6312240703955009631udit satijaNo ratings yet
- Acsnano 1c05272Document11 pagesAcsnano 1c05272tbnwdkc2dxNo ratings yet
- Mandagni Is The Root Cause For All Diseases According To Ayurvedic & Allopathic ViewsDocument8 pagesMandagni Is The Root Cause For All Diseases According To Ayurvedic & Allopathic ViewsmasdfgNo ratings yet
.K Uh, I
.K Uh, I
Uploaded by
Rahul AgarwalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
.K Uh, I
.K Uh, I
Uploaded by
Rahul AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
.
2019
INTRODUCTION
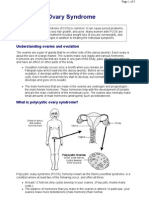
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome/ Polycystic Ovarian Disorder
(PCOS/PCOD) is a relatively common hormonal disorder that causes a
number of different symptoms in women of reproductive age.
Common to all women with PCOS is an irregularity in the menstrual cycle
and the presence of excess male hormones (androgens).
The condition was named because of the finding of enlarged ovaries
containing multiple small cysts (polycystic ovaries).
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 1
. 2019
Some common Facts about PCOS/PCOD
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that affects a woman’s
hormone levels.
Women with PCOS produce higher-than-normal amounts of male hormones.
This hormone imbalance causes them to skip menstrual periods and makes it
harder for them to get pregnant.
PCOS also causes hair growth on the face and body, and baldness. And it can
contribute to long-term health problems like diabetes and heart disease.
Birth control pills and diabetes drugs can help fix the hormone imbalance and
improve symptoms.
PCOS is a problem with hormones that affects women during their
childbearing years (ages 15 to 44). Between 2.2 and 26.7 percent of women
in this age group have PCOS.
Many women have PCOS but don’t know it. In one study, up to 70 percent of
women with PCOS hadn’t been diagnosed.
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 2
. 2019
SYMPTOMS
Disruptions in the menstrual cycle that typically begin around the onset
of puberty.
An increase in the production of androgens (male hormones) by the
ovaries in PCOS may lead to excess hair growth in areas suggesting a
male pattern, known as hirsutism.
Excess androgens can lead to acne and male pattern balding.
Due to absence or reduction in ovulation, progesterone level reduces
which leads in growth stimulation of the endometrium which causes
dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Insulin resistance
Weight gain and obesity
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 3
. 2019
CAUSES
Currently, there is no known cause of PCOS. However, there are associations
with excess insulin, low-grade inflammation, and genetics.
Risk factors
PCOS is thought to have a genetic component. People who have a mother or
sister with PCOS are more likely to develop PCOS than someone whose
relatives do not have the condition. This family link is the main risk factor.
Sugar is the body's primary source of energy, and it is regulated in the body
by insulin, which is secreted by the pancreas. A person with insulin resistance
is unable to use insulin efficiently. This causes the pancreas to go into
overdrive secreting additional insulin to meet the body's glucose needs.
Excess insulin is thought to affect a woman's ability to ovulate because of its
effect on androgen production. Research has shown that women with PCOS
have low-grade inflammation that stimulates polycystic ovaries to produce
androgens.
Associated health risks
There are several health risks associated with PCOS.
These include:
type 2 diabetes
infertility
high cholesterol
elevated lipids
sleep apnea
liver disease
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 4
. 2019
abnormal uterine bleeding
high blood pressure
obesity possibly leading to issues with low self-esteem and depression
metabolic syndrome
nonalcoholic fatty liver (steatohepatitis)
depression and anxiety
Also, there is an increased risk of endometrial cancer, gestational diabetes,
pregnancy-induced high blood pressure, heart attacks, and miscarriage.
HOW PCOS/PCOD AFFECTS YOUR BODY
Having higher-than-normal androgen levels can affect your fertility and other
aspects of your health.
Infertility
To get pregnant, you have to ovulate. Women who don’t ovulate regularly
don’t release as many eggs to be fertilized. PCOS is one of the leading causes
of infertility in women.
Metabolic syndrome
Up to 80 percent of women with PCOS are overweight or obese. Both obesity
and PCOS increase your risk for high blood sugar, high blood pressure, low
HDL (“good”) cholesterol, and high LDL (“bad”) cholesterol.
Together, these factors are called metabolic syndrome, and they increase the
risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
Sleep apnea
This condition causes repeated pauses in breathing during the night, which
interrupt sleep.
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 5
. 2019
Sleep apnea is more common in women who are overweight — especially if
they also have PCOS. The risk for sleep apnea is 5 to 10 times higher in
obese women with PCOS than in those without PCOS.
Endometrial cancer
During ovulation, the uterine lining sheds. If you don’t ovulate every month,
the lining can build up.
A thickened uterine lining can increase your risk for endometrial cancer.
Depression
Both hormonal changes and symptoms like unwanted hair growth can
negatively affect your emotions. Many with PCOS end up
experiencing depression and anxiety.
WHEN TO SEEK HELP
It is appropriate to seek the advice of your health care practitioner if you have
irregular or absent menstrual periods, abnormal or excessive hair growth,
difficulty in getting pregnant, or any of the other troubling symptoms of
PCOS.
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 6
. 2019
DIAGNOSIS
A gynaecologist maybe able to diagnose PCOS on the basis of:
Medical history: To get detailed information about menstrual periods and
weight changesPresence of at least two of the following symptoms is
indicative of PCOS:
Irregular periods
Signs of high levels of androgens
– Hirsutism
– Acne
– Thinning of scalp hair
Higher blood levels of androgens
Polycystic ovaries
Physical examination
A pelvic exam can look for any problems with your ovaries or other parts of
your reproductive tract. During this test, your doctor inserts gloved finger
into your vagina and checks for any growths in your ovaries or uterus.
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 7
. 2019
Tests
Blood tests check for higher-than-normal levels of male hormones.
You might also have blood tests to check your cholesterol, insulin, and
triglyceride levels to evaluate your risk for related conditions like heart
disease and diabetes.
Imaging: Ultrasound can be safely used to demonstrate the presence of
cysts in the ovaries. Ultrasound uses sound waves to generate an image
of the ovaries.
Additional tests
Screening for depression and anxiety
Screening for obstructive sleep apnoea
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 8
. 2019
TREATMENTS
There is no cure for PCOS, but treatment aims to manage the symptoms that
affect an individual.
This will depend on whether the individual wants to become pregnant and
aims to reduce the risk of secondary medical conditions, such as heart disease
and diabetes.
There are several recommended treatment options, including:
Birth control pills: These can help regulate hormones and menstruation.
Diabetes medications: These help manage diabetes, if necessary.
Fertility medications: If pregnancy is desired, these include the use of
clomiphene (Clomid), a combination of clomiphene and metformin, or
injectable gonadotropins, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and
luteinizing hormone (LH) medications. In certain situations, letrozole
(Femara) may be recommended.
Fertility treatments: These include in-vitro fertilization (IVF) or
inseminations.
Excessive hair growth may be reduced with the drug spironolactone
(Aldactone) or eflornithine (Vaniqa). Finasteride (Propecia) may also be
recommended, but it should not be handled by women who may become
pregnant.
Other possible options to manage hair growth is laser hair removal,
electrolysis, hormonal treatments, or vitamin and mineral use.
Surgery
Surgical options include:
Ovarian drilling: Tiny holes made in the ovaries can reduce the levels of
androgens being produced.
Oophorectomy: Surgery removes one or both ovaries.
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 9
. 2019
Hysterectomy: This involves removal of all or part of the uterus.
Cyst aspiration: Fluid is removed from the cyst.
What lifestyle modifications could be beneficial for
women with PCOS?
Some lifestyle modifications that can help in reducing the effects of PCOS
include
Maintenance of a healthy weight: Weight loss can lower insulin and
androgen levels and may restore ovulation.
Diet management and limitation in consumption of carbohydrates:
High-carbohydrate and low-fat diets may increase insulin levels.
Exercise regularly: Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels and control
body weight.
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 10
. 2019
PRESCRIPTION
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 11
. 2019
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 12
. 2019
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 13
. 2019
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 14
. 2019
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 15
. 2019
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 16
. 2019
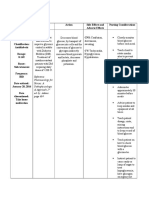
SOME COMMON DRUGS USED IN THE TREATMENT OF
PCOS/PCOD
BRAND NAME GENERIC NAME COMPANY NAME
Metformin Metformin Zanza health care
hydrochloride
Seasonique Ethinyl estradiol Teva Pharmacueticals
Desolon-30 Desogestrel Dewcare
Blisovi Fe 1.5/30 Ethinyl estradiol / Lupin
norethindrone
Aviane Ethinyl estradiol/ Barr laboratories, Inc.
levonorgestrel
Levora Ethinyl estradiol/ Watson Pharma
levonorgestrel
Nobal spas Drotaverine HCL & Mankind
Nimesulide
Ovusitol D Vitamin D Italfarmaco
MyoNext Inositol,Melatonin & Cadila
folic acid
Furocyst Chemical Resources
Estrostep Norethindrone acetate- Allergan
ethinyl estradiol
Orthotri-cyslen Norgestimate-ethinyl Janssen
estradiol
Yasmin Drospirenone-ethinyl Bayer
estradiol
Fortamet Metformin Watson
Aldactone spironolactone Pfizer
Clomid Clomiphene citrate Aventis
Letrozole Letrozole Cipla
Provera progesterone Pfizer
Menopur menotropins Ferring
Bravelle urofollitripin Ferring
Victoza Liraglutide Novo nordisk
Propecia Finasteride Merick sharp & dohme
Melmet Metformin Micro labs
hydrochloride
Dox T Doxycycline hyclate Dr. Reddy's lab
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 17
. 2019
Zantac Renetidine
Taxim Cefixime Alkem
Sarfixim-AZ Cefixime Sarcoma Remedies
Meftel spas Mefenamic acid and Blue Cross
Dicyclomine HCL
Pantoin-40 Pentoprazol Ajans life science
Desthali Vidhyapeeth Page 18
You might also like
- Hesi Psych Study GuideDocument16 pagesHesi Psych Study GuideR100% (17)
- Paediatrics Cardiology MCQDocument9 pagesPaediatrics Cardiology MCQJOYANTA ROY100% (2)
- PCOS Diet: The Complete Guide to Fight PCOS, Prevent Diabetes, Lose Weight and Increase FertilityFrom EverandPCOS Diet: The Complete Guide to Fight PCOS, Prevent Diabetes, Lose Weight and Increase FertilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- PCOS No More - Take Control of PCOS Symptoms & Treatments - A Holistic System of Lifestyle Changes, Diet, & Exercises to Beat Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Naturally & Permanently. PCOS Recipes Included.From EverandPCOS No More - Take Control of PCOS Symptoms & Treatments - A Holistic System of Lifestyle Changes, Diet, & Exercises to Beat Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Naturally & Permanently. PCOS Recipes Included.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Document10 pagesPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Juliet Amondi100% (2)
- Farm Management - Robotic Farm Management - LelyDocument70 pagesFarm Management - Robotic Farm Management - LelyHo Duc ThamNo ratings yet
- "Cure Tooth Decay" - Photographic Proof!Document12 pages"Cure Tooth Decay" - Photographic Proof!Chef Jem100% (1)
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome 2Document22 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome 2Michelle Panlilio0% (1)
- Dark Green Vintage Minimalist Aesthetic Newspaper Fashion Marketing Ad Instagram StoryDocument4 pagesDark Green Vintage Minimalist Aesthetic Newspaper Fashion Marketing Ad Instagram StoryJana Emery SumagangNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentDocument19 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentGrace Ann Rodriguez SanDiegoNo ratings yet
- PCOS Booklet Final Low Quality Aster IVFDocument8 pagesPCOS Booklet Final Low Quality Aster IVFasterivfNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)Document8 pagesAssignment: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)tehseenullahNo ratings yet
- 2019521625048 - Rittik Paul PCOSDocument5 pages2019521625048 - Rittik Paul PCOSpaulrittik2000No ratings yet
- Pi Pcos Update-2022 230717 221503Document7 pagesPi Pcos Update-2022 230717 221503PeterNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - Johns Hopkins MedicineDocument5 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - Johns Hopkins MedicineWINDA NURHASANAHNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument5 pagesPolycystic Ovary SyndromeAle W.S.No ratings yet
- Pcos ReportDocument49 pagesPcos ReportSneha kohliNo ratings yet
- PCOSDocument3 pagesPCOSpravallikakvNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : Made by Hamza Shawal 60Document29 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : Made by Hamza Shawal 60Muhammad HamadNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : February 2020Document5 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : February 2020Lia MeivianeNo ratings yet
- PcosDocument6 pagesPcosDana MradNo ratings yet
- PcosDocument9 pagesPcosMonomay HalderNo ratings yet
- Polycystric Ovary Syndrome FilesDocument7 pagesPolycystric Ovary Syndrome FilesElla Jean B. LunzagaNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Disorder AwarenessDocument6 pagesHormonal Disorder AwarenessRasell Fhaye A. RazonNo ratings yet
- PCOS Ebook v1.18Document22 pagesPCOS Ebook v1.18க100% (2)
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : by Aleandro Dizon Bn4ADocument12 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) : by Aleandro Dizon Bn4AAleandro DizonNo ratings yet
- How To Get Pregnant With PcosDocument20 pagesHow To Get Pregnant With PcosConfused parentNo ratings yet
- Polycystic-Ovarian-Disease pptDocument15 pagesPolycystic-Ovarian-Disease pptjhapankaj5234No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Under Supervision ofDocument7 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome: Under Supervision ofHend HamedNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)Document6 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)saleemut3No ratings yet
- What Causes Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument8 pagesWhat Causes Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Clinical Picture of pcosWPS OfficeDocument11 pagesClinical Picture of pcosWPS OfficeEsraa SalemNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Johns Hopkins MedicineDocument1 pagePolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Johns Hopkins MedicinehercimacielNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Vidhya-4Document16 pagesBiology Project Vidhya-4suriya251004No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument2 pagesPolycystic Ovary SyndromeLalee BelarminoNo ratings yet
- Pcos - Clinical Case DiscussionDocument4 pagesPcos - Clinical Case Discussionreham macadatoNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document5 pagesLec 3mudassir qazalbashNo ratings yet
- Kenneth NegsDocument2 pagesKenneth NegsGwen Stefani DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- Acog Pcos PDFDocument3 pagesAcog Pcos PDFJoanne BlancoNo ratings yet
- Enlarged Polycystic OvariesDocument4 pagesEnlarged Polycystic OvariesKaly RieNo ratings yet
- What Causes Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) ?: Infertility Menstrual IrregularitiesDocument8 pagesWhat Causes Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) ?: Infertility Menstrual IrregularitiesdnllkzaNo ratings yet
- PCODDocument16 pagesPCODfitfemme12126No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome PCOSDocument15 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome PCOSdrug123addict25No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument17 pagesPolycystic Ovary SyndromeramsaybajjuNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (Pcos) : Name: Adelita Dwi Aprilia Name Atom: EndocrinologyDocument2 pagesPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (Pcos) : Name: Adelita Dwi Aprilia Name Atom: EndocrinologyAdelita Dwi ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Hyperandrogenism: Arrest Occurs When The Granulosa Cells of The Ovaries Normally Begin To ProduceDocument7 pagesHyperandrogenism: Arrest Occurs When The Granulosa Cells of The Ovaries Normally Begin To ProduceNathan JeffreyNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Factsheet: Key PointsDocument3 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Factsheet: Key PointsrhaineNo ratings yet
- B. ProlactinomaDocument3 pagesB. ProlactinomaSheena CullaNo ratings yet
- Pcod Natural TreatmentDocument4 pagesPcod Natural Treatmenttusharphale100% (1)
- Introduction PCOSDocument14 pagesIntroduction PCOSalex.avenko1030No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)Document8 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)Danijela GagovicNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document15 pagesDocument 5SamNo ratings yet
- Research EssayDocument3 pagesResearch Essayapi-510714949No ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Understanding Ovaries and OvulationDocument5 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome: Understanding Ovaries and OvulationBhavik ShahNo ratings yet
- How To Reverse Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument24 pagesHow To Reverse Polycystic Ovary SyndromeJudi Ann MagsacayNo ratings yet
- Final Research Essay PcosDocument13 pagesFinal Research Essay Pcosapi-510714949No ratings yet
- And Getting Pregnant: A Beginner'S Guide and Patient Stories of HopeDocument23 pagesAnd Getting Pregnant: A Beginner'S Guide and Patient Stories of HopehaurakhansaNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - Reproductive and Metabolic Aspects - Sundhed - DKDocument8 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) - Reproductive and Metabolic Aspects - Sundhed - DKPavel BerlinschiNo ratings yet
- Do I Have PCOS? Understanding the Cause and Reversing Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)From EverandDo I Have PCOS? Understanding the Cause and Reversing Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)No ratings yet
- How to Beat PCOS Naturally & Regain a Healthy & Fertile Life Now ( A Simple Guide on PCOS Diet & Exercises to Conquer PCOS Permanently Today)From EverandHow to Beat PCOS Naturally & Regain a Healthy & Fertile Life Now ( A Simple Guide on PCOS Diet & Exercises to Conquer PCOS Permanently Today)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Pcod and Pcos DriistiDocument2 pagesPcod and Pcos DriistiKirti MathurNo ratings yet
- Power Over Pcos EbookDocument160 pagesPower Over Pcos EbookIra Ayu Lestari100% (2)
- Name Class Section Subject: Sohon Sen XI B BiologyDocument36 pagesName Class Section Subject: Sohon Sen XI B BiologySohon SenNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument8 pagesPolycystic Ovary SyndromeTahir BilalNo ratings yet
- Finding Answers: Handsmart: Breaking Down Barriers Forged by FireDocument6 pagesFinding Answers: Handsmart: Breaking Down Barriers Forged by FireRoger Goodledy100% (1)
- Research Article Response of Black Nightshade To Different Cropping Systems and The Effect On Physiological Parameters and Mineral CompositionDocument11 pagesResearch Article Response of Black Nightshade To Different Cropping Systems and The Effect On Physiological Parameters and Mineral CompositionfooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For GDMDocument7 pagesDrug Study For GDMFuture RNNo ratings yet
- AmgenDocument22 pagesAmgenleonard1655012No ratings yet
- Asthma PudDocument7 pagesAsthma PudChristine TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region III Schools Division Office of Pampanga San Pedro, San Simon, PampangaDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region III Schools Division Office of Pampanga San Pedro, San Simon, PampangaMia NuguidNo ratings yet
- IVIG RateDocument2 pagesIVIG RatelydiasusantiNo ratings yet
- Klinefelter SyndromeDocument3 pagesKlinefelter SyndromeAnonymous stZJzmPNo ratings yet
- A Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDocument3 pagesA Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument65 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisSiti AminahNo ratings yet
- Organic Manures - 17.12.12Document59 pagesOrganic Manures - 17.12.12Ananda Preethi100% (1)
- Hubungan Temuan MRI Dengan Klinis Nyeri Pasien Herniasi Nukleus Pulposus LumbalDocument13 pagesHubungan Temuan MRI Dengan Klinis Nyeri Pasien Herniasi Nukleus Pulposus LumbalHendrawanDianAgungWicaksanaNo ratings yet
- Biogenic Amines by HPLCDocument7 pagesBiogenic Amines by HPLCNeidys SanchezNo ratings yet
- PsychosisSelfCareJune22 V2DDocument115 pagesPsychosisSelfCareJune22 V2DLindseyRae Parker100% (1)
- The Bourne Identity-Psychological DiddordersDocument23 pagesThe Bourne Identity-Psychological DiddordersSahil NaikNo ratings yet
- 08 DN 005 BA Int OkDocument64 pages08 DN 005 BA Int OkvbogachevNo ratings yet
- NCP-risk For BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP-risk For BleedingAce Dioso Tubasco100% (2)
- (Download PDF) A Specter Haunting Europe The Myth of Judeo Bolshevism Paul Hanebrink Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) A Specter Haunting Europe The Myth of Judeo Bolshevism Paul Hanebrink Online Ebook All Chapter PDFray.groce871100% (15)
- Rs. Akademis Jaury Jusuf Putera: Data Kamar Inap PasienDocument3 pagesRs. Akademis Jaury Jusuf Putera: Data Kamar Inap PasienNs Ilham ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Reportorial 2Document36 pagesReportorial 2Alistair Jude C. BacaocoNo ratings yet
- Project Soaprise ScriptDocument2 pagesProject Soaprise ScriptGarima DixitNo ratings yet
- MSDS Clorox High Efficiency Bleach Cleaner 0607Document1 pageMSDS Clorox High Efficiency Bleach Cleaner 0607Henry Rutledge100% (1)
- 5 6312240703955009631Document28 pages5 6312240703955009631udit satijaNo ratings yet
- Acsnano 1c05272Document11 pagesAcsnano 1c05272tbnwdkc2dxNo ratings yet
- Mandagni Is The Root Cause For All Diseases According To Ayurvedic & Allopathic ViewsDocument8 pagesMandagni Is The Root Cause For All Diseases According To Ayurvedic & Allopathic ViewsmasdfgNo ratings yet